Cup-and-Ring Stones: Grid Reference – NN 5320 3584

Also Known as:
- Duncroisk 1 (Morris 1981)
- Duncroisk 4 (Canmore)
- Keeper’s Cottage
Getting Here
From the north side of Killin, take the minor road next to the Bridge of Lochay Hotel at Killin, past the hydroelectric station, through the wooded section until the fields open out again. The first gorgeous old house you come to is on the right-hand side of the road. Stop here! (I could really do with living here misself – tis a truly superb place!) You can ask the lady at the house where the carvings are and she’s very happy to point them out – they’re on the rocky crag near the bottom-end of the field on the other side of the road.
Archaeology & History
What a brilliant setting and clump of carvings we have here! As you get to the rocky hillock in the field, you see that there are numerous rocks visible along the ridge, a number of which have carvings on them – some with just cups, but most possess a number of cup-and-rings. It’s an excellent spot! Depending on the time of year when you come here will determine whether or not you get a better look at the carvings or not. I’d recommended April and May as the best time, as the vegetation is at its lowest then. Visiting the site near the end of summer doesn’t give you as good a view — but even then, if you like your rock art, you’ll still love it! The rocks here are mainly quartzite schist, with a number of the surfaces being almost pure quartz. Intriguingly, none of the pure quartz sections appear to have been carved on.
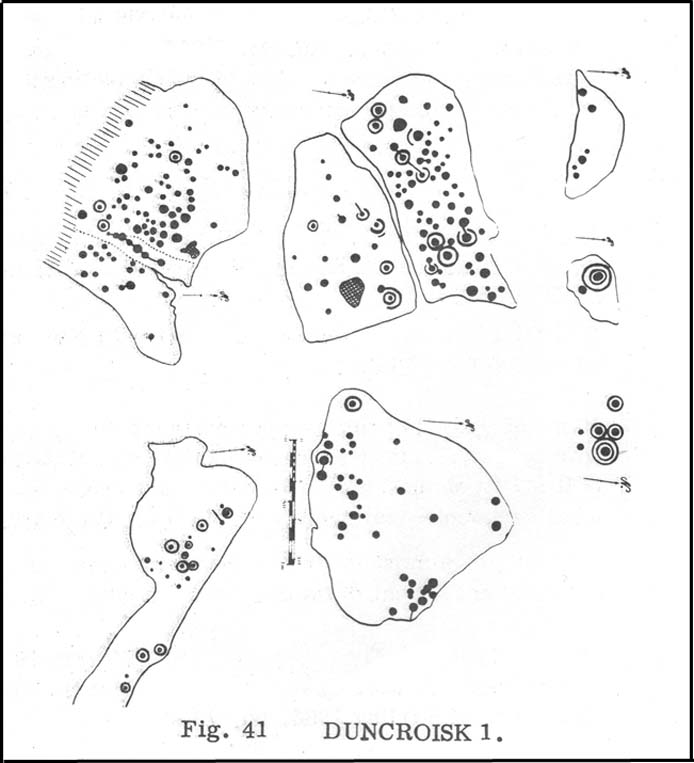
The carvings here were first mentioned in an article by D. Haggart (1895), who described them as “a very remarkable set of incised rock sculptures…discovered lately in this neighbourhood by Mr John McNaughton.” And remarkable they are indeed! In Ronald Morris’ (1981) survey of this site — which he labelled Duncroisk 1 — he counted eight separate rock surfaces that had been carved, marking them as carvings a-h, but there are at least eleven of them here; and in all honesty, if we could strip the surface of the hill of its vegetation, we’d probably find a few more hidden away!
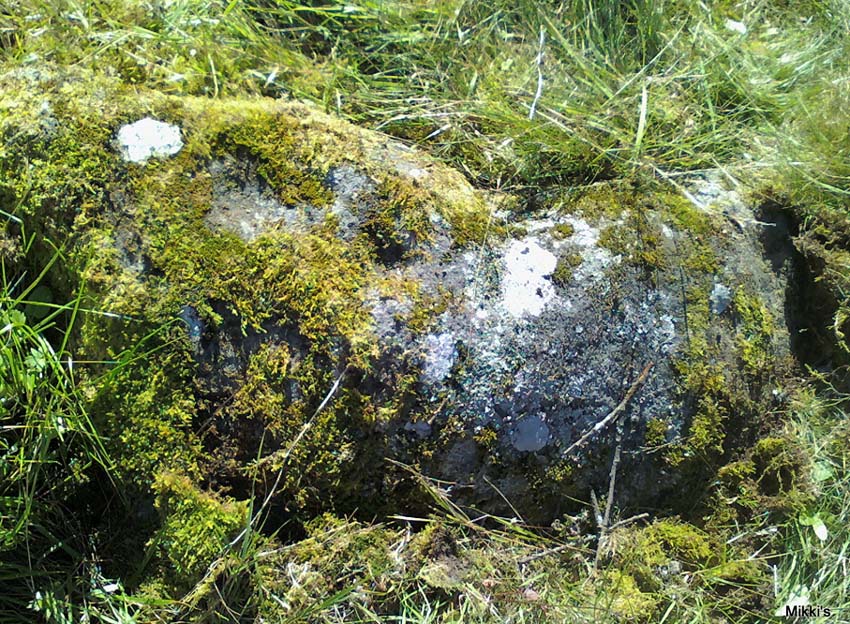

As you’ve walked across the field from the road, past the first unrecorded cup-marked stone near the start of the rocky rise, we reach Mr Morris’s ‘stone A’ near the easternmost end of the ridge, which is just a small slab of stone with “at least 6 cup-marks” on its surface. It’s easily missed in poor light, so watch out. However, if you reach ‘stone b’ (described below), just walk back ten steps and you’ll see it.
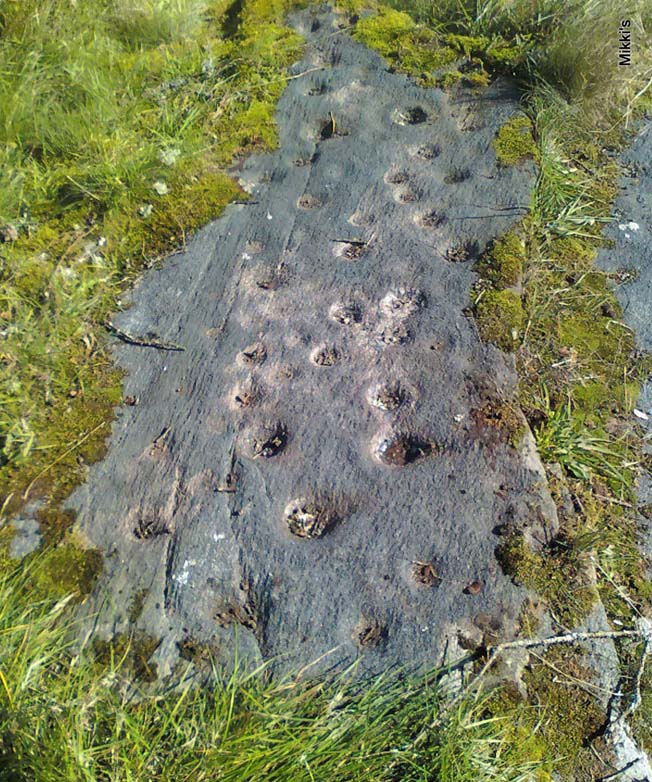

Ten yards west is ‘Stone B’, seemingly split into two sections, whereupon we find “a cup-and-two-rings and at least 12 cups-and-one-ring, up to 19cm in diameter – some rings gapped, others not, some with and some without a radial groove from the cup, and some with a “runner” or cup in a ring. There are also at least 58 cups” on this section of rock. ‘Stone C’ can also be missed, this time due to its size and the fact that the larger cup-marked surfaces are ahead of you. But assuming you don’t miss it, this carving consists of “a well-preserved cup-and-two-complete-rings 25cm in diameter, and a cup.”
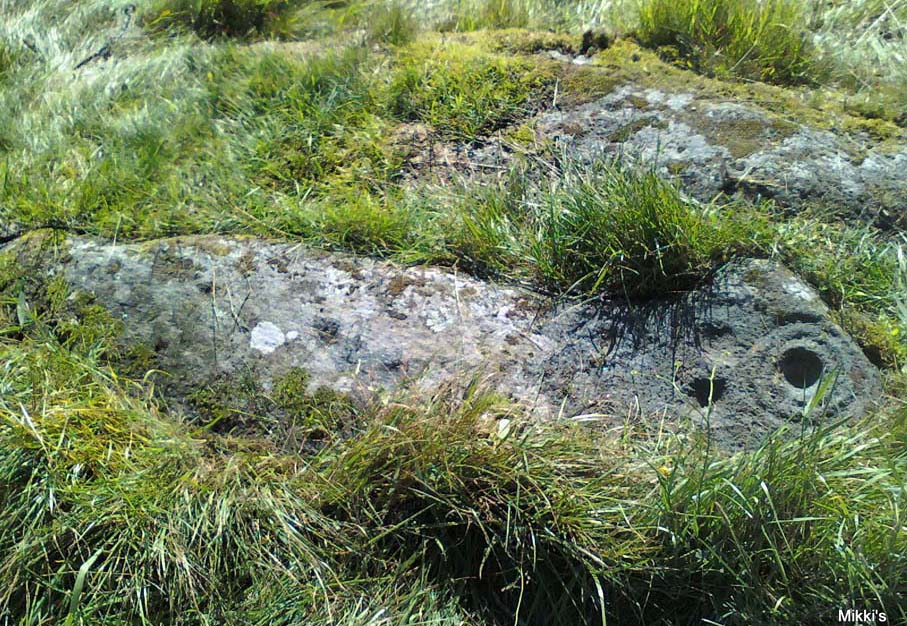

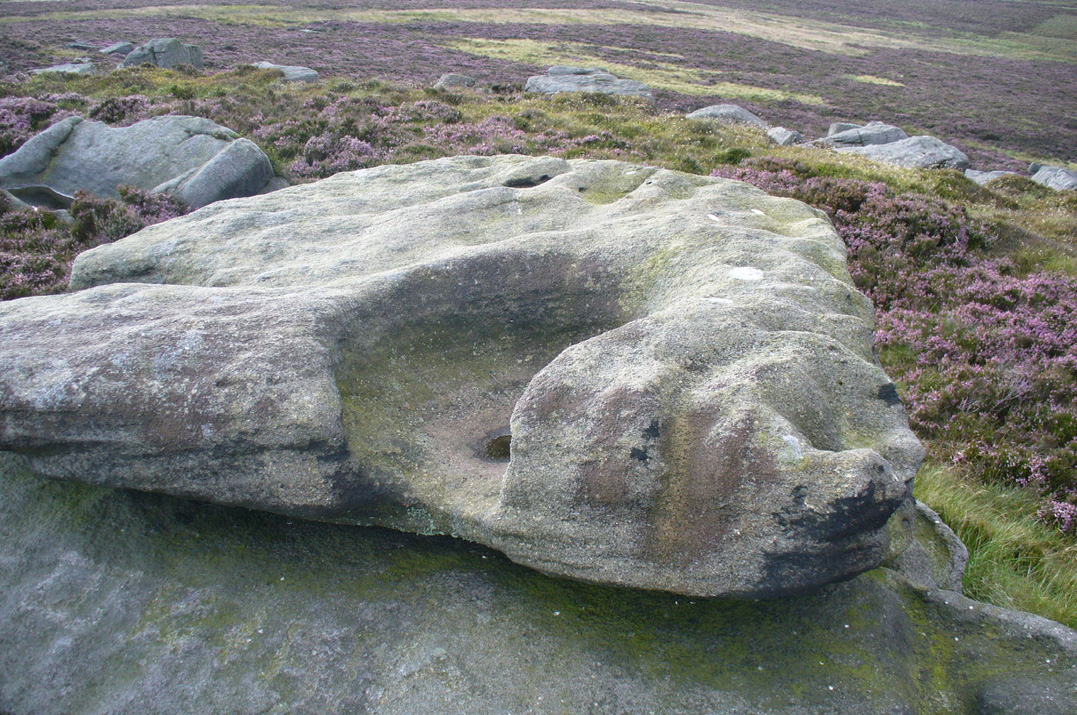
‘Stone D’ is just next to ‘stone C’, but with rather more ornate designs etched upon it. This is one of the more archetypal petroglyph designs that are found in the photo-guides and textbooks. Morris (1981) told that it consisted “of a cup-and-two-complete-rings and 2 cups-and-one-complete-ring up to 20cm in diameter, also a cup-and-one-complete-ring and 2 cups.” The photo here shows it pretty clearly.
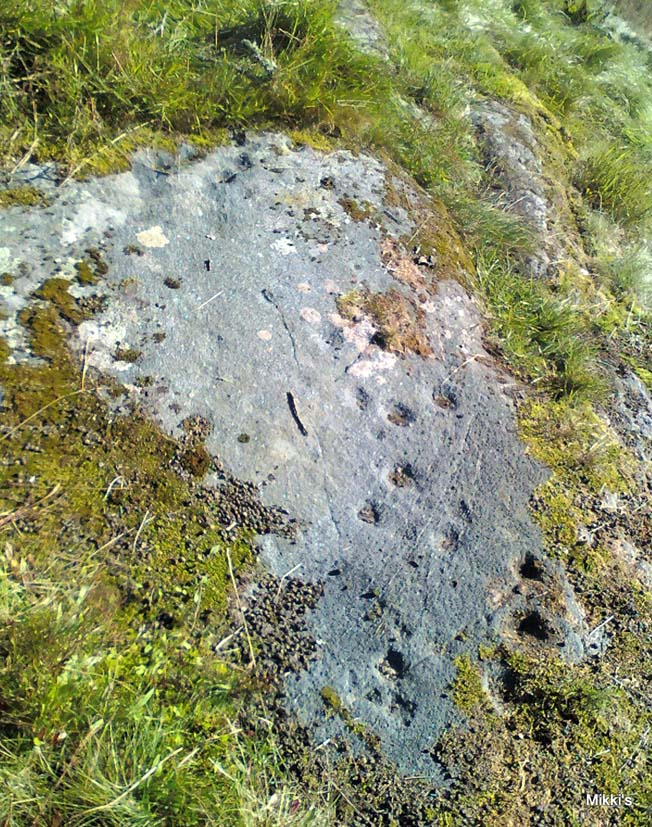
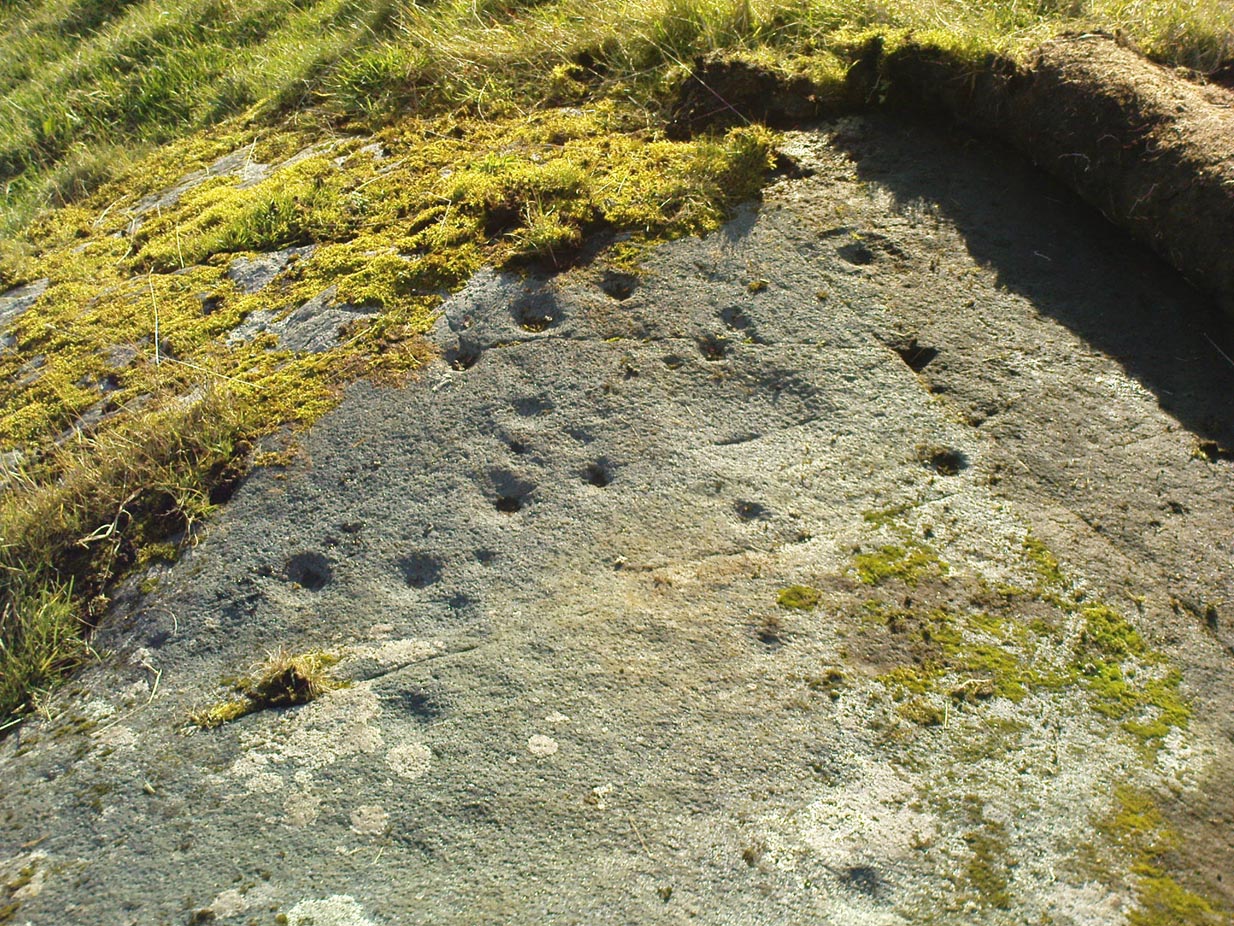


‘Stone E’ is the next one along, just a foot or two away and Mr Morris (1981) told that the carving consists of “2 cups-and-one-ring up to 13cm in diameters, 1 complete, the others gapped, joined by groove to a cup, and at least 33 cups (C.G. Cash counted 42 in 1911).” Most of the carved elements on this rock are around the edges of the stone. A very large faded circular depression, man-made, is also visible on this section of the petroglyph (above left), suggestive of lunar symbolism.
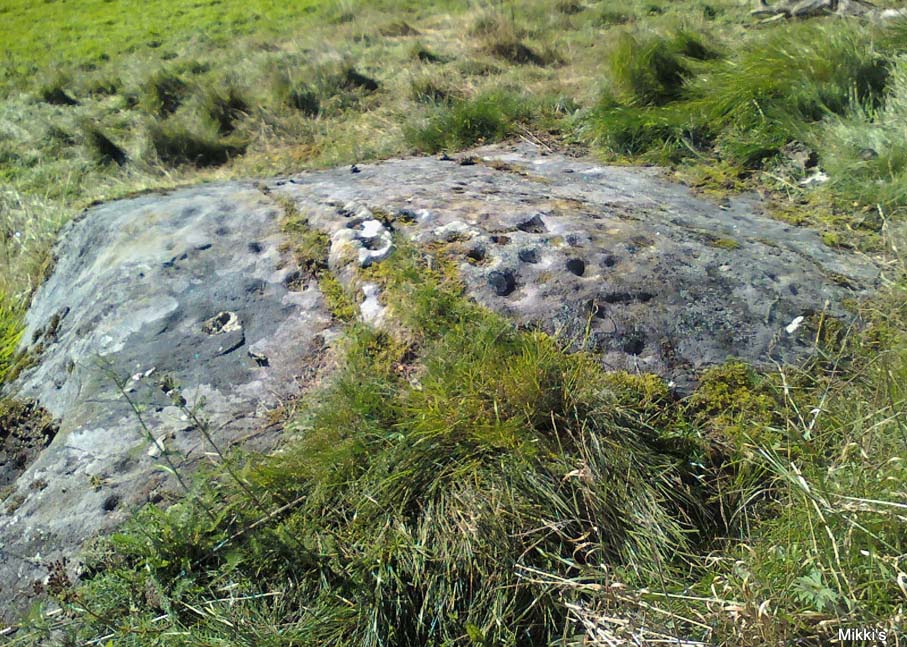

‘Stone F’ is less than 10 yards further west and has the greatest number of cup-markings of the entire group here, as Morris described: “3 cups-and-one-complete-ring up to 9cm in diameter, and at least 80 cups, a few of which are widely scattered over a big area sloping steeply further south, beyond the attached diagram.” It’s perhaps the most notable of the carved rocks along the ridge here — not by virtue of its design, more its geological physique than anything else.
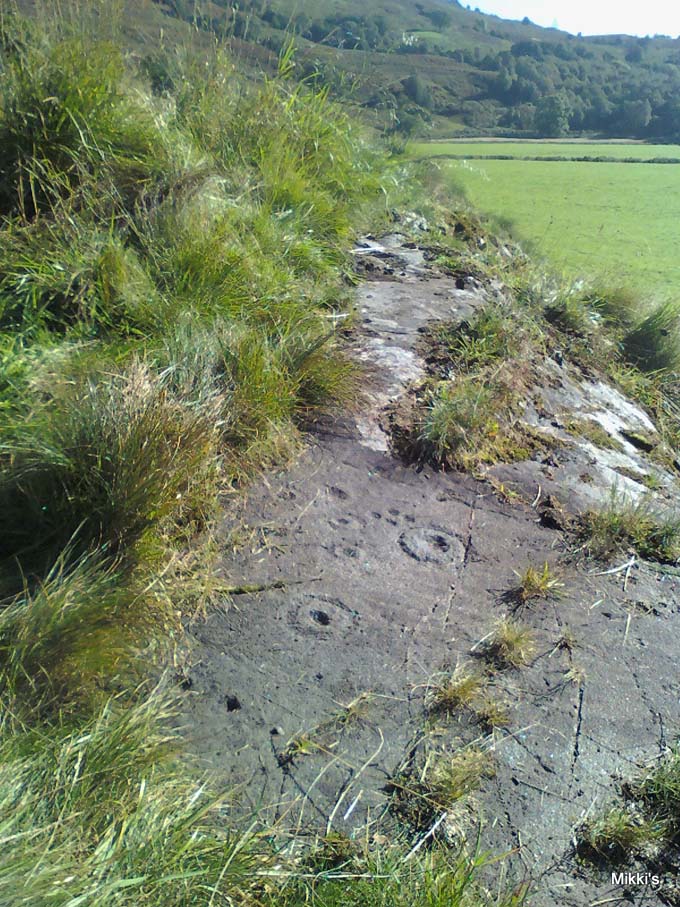

‘Stone G’ is next along and has a curious look about it, suggestive of more modern times. At first sight it doesn’t seem to have quite the magnitude that Morris’ description affords it, but on closer inspection by rolling some of the covering turf back away from the rock, you can see what he meant. This stone has “10 cups-and-one-complete-ring, up to 10cm diameter…and also 15 cups.” One of the cup-and-rings on this section was found by Morris to have been “the smallest so far recorded by the author in Scotland.”
Then we reach ‘stone H’ at the eastern end of the carved ridge, consisting of simply 3 cup-markings. One of them has a faint arc pecked around it. Further along the rock, a complete cup-and-ring is visible close to the edge.
This entire line of petroglyphs is a fine place in a fine setting, perfect for meditative practices! Other carvings can be found close by: Duncroisk 3 is a coupla hundred yards east across the field just over the fence by the riverside; and Duncroisk 2 is on the other side of the fence down towards the River Lochay on the same side of the adjacent burn less than 100 yards away (though this is trickier to reach). Other prehistoric sites can be found not too far away…
Folklore
Local people tell of having seen curious lights flitting along the edges of the field, river Lochay and roadside close to the carved rocks hereby.

References:
- Cash, C.G., “Archaeological Gleanings from Killin,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, volume 46, 1911-12.
- Cormack, E.A., “Cross-Markings and Cup-Markings at Duncroisk, Glen Lochay,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 84, 1952.
- Gillies, William A., In Famed Breadalbane, Munro Press: Perth 1938.
- Haggart, D., “Notice of the Discovery of Cup-and-Ring Sculpturings at Duncrosk, near the Falls of Lochay, in Glenlochay,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, volume 29, 1894-95.
- Morris, Ronald W.B., The Prehistoric Rock Art of Southern Scotland, BAR 86: Oxford 1981.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian