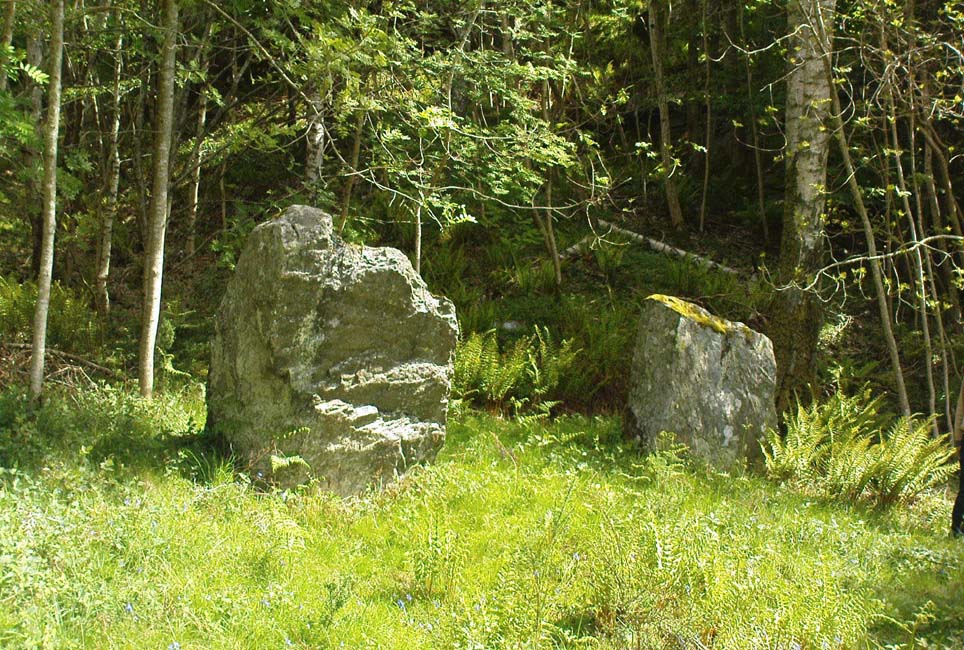
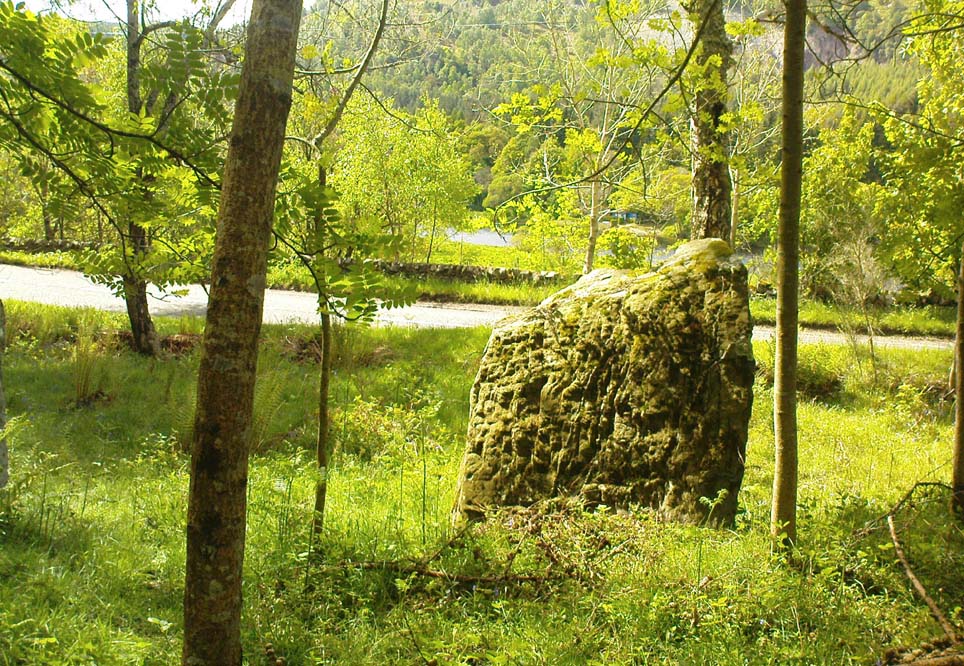
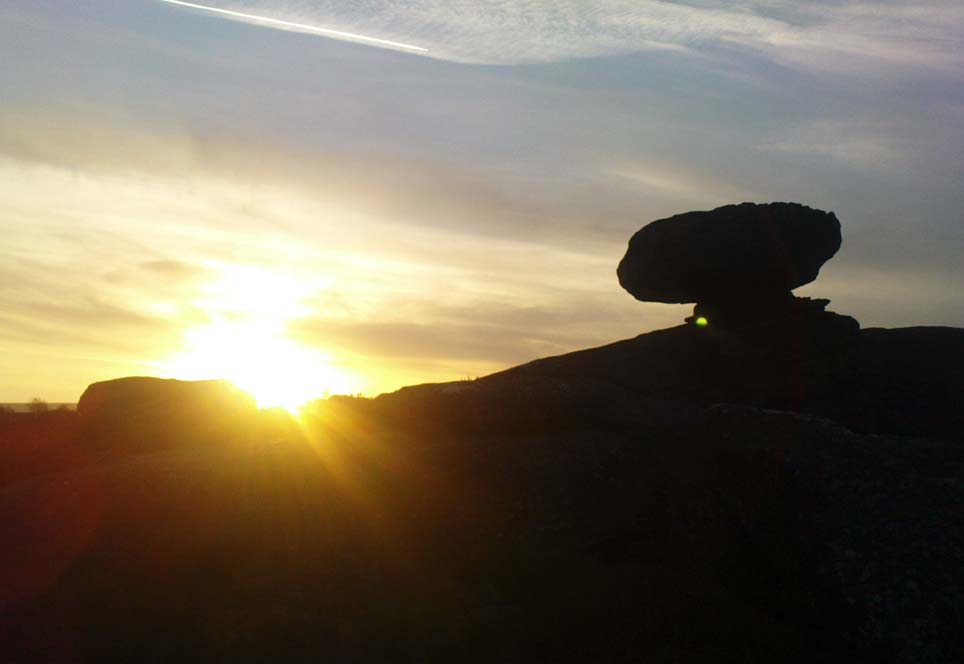
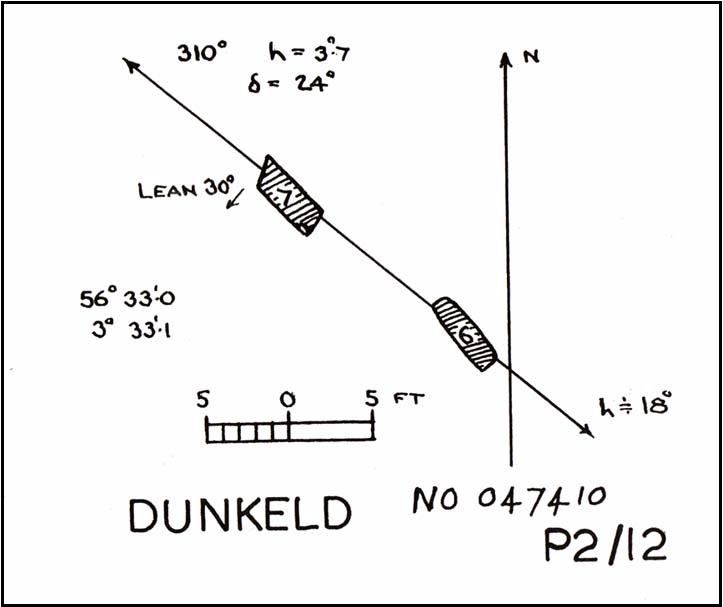
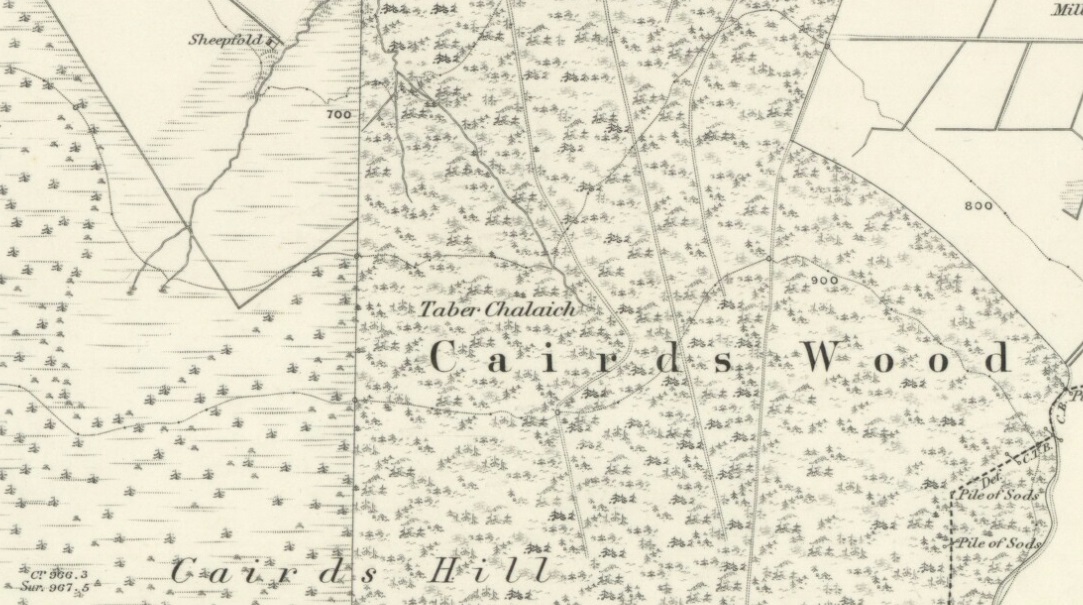
Legendary Rocks: OS Grid Reference – NS 816 970
Also Known as:
- Carla Craig
- Carlin Craig
- Witches’ Craig
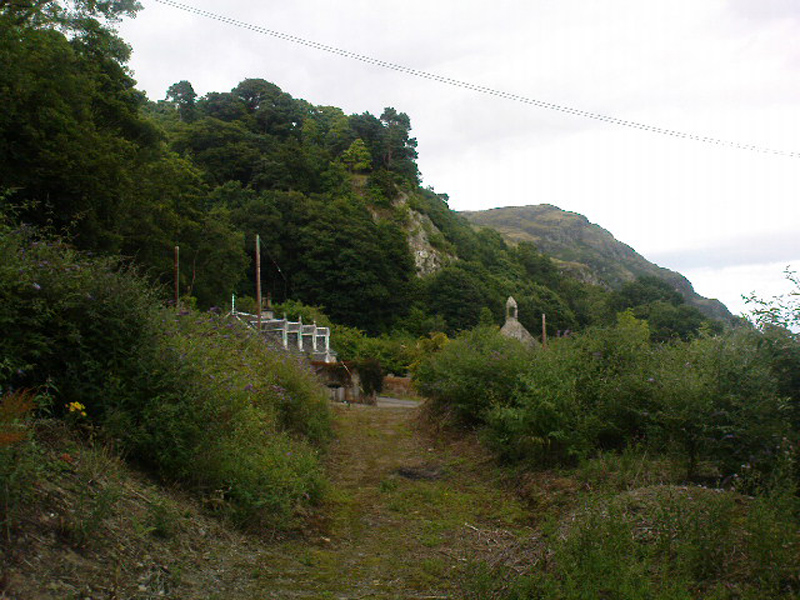

If you’re coming from Blairlogie, a half-mile west of the village, take the B998 road to the university, but turn right up the first road that runs uphill into the trees. But if you’re coming from Stirling or Bridge of Allan, keep your eyes peeled for the barely visible B998 at the crossroads and go up the hill, and along, for a good mile, below the Uni, past the factory, then up the small road on your left. Up this road go past the church another 100 yards and you’ll see the derelict ruins of Logie Kirk on your right. Right above the ruin you’ll see the tree-lined cliff immediately behind. This is the Carlie Craig!
Folklore

The tree-covered Carlie Crags above the old ruined church and graveyard of Logie Kirk immediately below (thought to have been built in 1684) has long been associated with legends of old witches. Deriving its name from ‘carlin’, a witch or old woman (cailleach), the Crags were traditionally the place of heathen rites (authentic ones, not your plastic pagan types). In David Morris’ (1935) essay on the local township, he told the common story that “an elder in Logie Kirk was of the opinion that the Carla’ Craig…was haunted.” At the end of the 19th century, Morris remembered a local lady known as ‘Ailie’, who was said by many old folk to be the traditional “witch of Logie.”
“Sickly children were brought to her for her blessing. Occasionally people came from as far as Stirling on this errand. Her method of giving the blessing was to blow her breath on the child, and this was supposed to ward off evil. It was also said that anyone buried in Logie Kirkyard on the first day of May, Hallowe’en, or other days of that kind, without her blessing, would not rest in his grave…”
Another legend told that,
“around 1720 witches were believed to rendezvous with the Evil One (i.e. the devil) who would appear in the form of a large black dog.”
A lengthier account of the belief in witchcraft and animistic pre-christian rites above the crags was told by Charles Rogers (1853):
“About the second decade of last century, there lived in the parish of Logie several ill-favoured old women, to whom the reputation of witchcraft was confidently attached. They were believed to hold nocturnal dialogues and midnight revels with the Evil One, and Carlie Crag was regarded as one of their places of rendezvous. Satan, though he was believed to appear to them in various forms, was understood, in his interviews with the dreaded sisterhood, to appear most frequently in the aspect of a large shaggy dog, in which form it was alleged he had repeatedly been seen by the minister. An elder of the kirk had been returning of an evening from a shooting excursion among the hills, with a trusty musket, which he had picked up some years before on the field of Sheriffmuir, and discovering on the top of Carlie an animal realizing the description of the Satanic mastiff, resolved to try upon it the effects of a shot. He knelt down cautiously near the foot of the crag, and after ejaculating a short prayer, and slipping into his musket a silver coin, fired with trembling heart but steady aim. His victim, evidently shot dead, tumbled to the base, and the delighted and astonished elder lost no time in personally communicating to the minister the success of his wonderful adventure. Though not a little superstitious, the minister was somewhat sceptical as to the mysterious dog being really dead. He however agreed to accompany his elder next morning to the foot of the crag to inspect the carcase; but on reaching the spot, they found the remains of no shaggy dog or evil genius, but the lifeless form of the beautiful pet goat of a poor and aged woman, a much respected parishioner. The minister and elder both shed tears. The wicked dog still lived, the innocent goat had perished. The elder however took credit to himself for his good intentions and valorous intrepidity ; and the minister deemed it proper to improve the subject in his pulpit prelections on the following Sabbath. Discoursing on the subject of resistance to the Devil, he remarked, that the Evil One might assume numerous shapes and forms; that he went about as a roaring lion was declared in the Word, but he might take to himself various other aspects. He might even appear as a black colley dog.” But whatever form he may assume,” added the minister, ” he cannot be overcome or destroyed by powder and shot. There is a gun, however, that will shoot him, and it is this — it is the Bible. Shoot him then, every one of you, with this gun, and he shall be shot.”
Whether the vicar’s biblical superstitions were adopted by local people—who were so much more used to the living animism of landscape and natural cycles—is questionable. The crag is a fine site for ritual magick and its associative devil-lore probably derives from Pictish shamanistic practices, remains of which are evident across the Scottish hillls and northern England, where they survived for some considerable time…
References:
- Morris, David, B., “Causewayhead a Hundred Years Ago”, in Transactions of the Stirling Natural History and Archaeological Society, 1935.
- Roger, Charles, A Week at Bridge of Allan, Adam & Charles Black: Edinburgh 1853.
- Watson, Angus, The Ochils – Placenames, History, Tradition, Perth & Kinross District Libraries 1995.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian