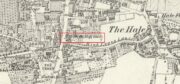
Holy Well (destroyed): OS Grid reference – TQ 3337 8245
Archaeology & History
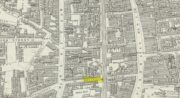
First described at the beginning of the 12th century as “fons qui dicitur Haliwelle“, these sacred waters were thereafter described in a variety of documents before eventually, in 1382, giving its name to the road on which it was found. When the topographer John Stow (1603) described the well—along with those of St. Clement’s and Clerken Well—it was once “sweet, wholesome, and clear” and “frequented by scholars and youths of the city in the summer evenings.” However, in his day it was already in decline, as he told that the “Holy well is much decayed and spoiled, with filthiness purposely laid there, for the heightening of the ground for garden plots.”
The history of the site was mentioned in John Noorthouck’s (1773) survey, where he told us:
“In the parish are two prebends, and part of a third, belonging to St Paul’s cathedral, in the city of London: The first dominated by Eald-Street, or Old Street, received that appellation from the Saxons being part of the Roman military way: the second, which had been a separate village for many years, by the name of Hochestone, vulgarly Hoxton, likewise itself to be of a Saxon origin: the third called Haliwell, had its name from a vicinal fountain, which, for the salubrity of its water, had the epithet Holy conferred on it.
In King John’s Court, Holywell-lane, are to be found the ruins of the priory of St. John Baptist, of Benedictine nuns, founded by Robert the son of Gelranni, prependary of Haliwell, and confirmed by charter of Richard I in the year1189. It was rebuilt in the reign of Henry VII by Sir Thomas Lovell, knight of the garter; who was there buried: and the following ditty was in consequence painted in most of the windows.
“All the nuns of Holywell,
“Pray for the soul of Thomas Lovell.”
The complete demise of the well occurred in the early part of the 19th century and efforts to locate its original position have proved troublesome. Indeed, the modern Holywell Lane would seem to be little more than an approximation of its whereabouts. It was an issue explored at some length in the great A.S. Foord’s (1910) magnum opus, who wrote:
“In recent times efforts have been made to locate the well, and some of the results communicated to Notes and Queries. A Mr. R. Clark drew attention, through the medium of that publication, to an article in The Builder of September 19, 1896, which states that ”the ancient holy well should be looked for in the area between Bateman’s Row and New Inn Yard and behind the Board School in Curtain Road, that is to say, west of New Inn Street.” This is all very circumstantial, but the writer bases his statement on the survey by Peter Chassereau, taken in 1745, in which the supposed position of the well is marked by a cross and the words “Ye well from which the liberty derives its name.” It should be borne in mind however that, as pointed out by Colonel W. F. Prideaux, Chassereau did not make his survey till more than two hundred years had elapsed from the date of the dissolution of the Nunnery (1539); the position of the well could therefore have been only a matter of tradition. Another contributor to Notes and Queries (8th Series, May 22, 1897), quotes an article in the Journal of the Royal Institute of British Architects (vol. iv., 3rd series, p. 237), by Mr. E. W. Hudson, who says that the well of the priory was situate on the south side of what is known as Bateman’s Row, but was formerly (before 1799) called Cash’s Alley, near Curtain Road. This agrees substantially with Mr. Clark’s statement. Mr. Lovegrove, writing in 1904, says: “The well itself is to be found in a marble-mason’s yard in Bateman’s Row, but is covered over.” The same writer notes that of the Nunnery buildings only a piece of stone wall about 50 feet long, in a timber yard at 186, High Street, Shoreditch, is now left.”
References:
- Foord, Alfred Stanley, Springs, Streams and Spas of London: History and Association, T. Fisher Unwin: London 1910.
- Gover, J.E.B., Mawer, Allen & Stenton, F.M., The Place-Names of Middlesex, Cambridge University Press 1942.
- Lovegrove, G.H., “Holywell Priory, Shoreditch,” in Home Counties, volume 6, 1904.
- Mills, A.D., A Dictionary of London Place-Names, Oxford University Press 2001.
- Noorthouck, John, A New History of London, Including Westminster and Southwark, R. Baldwin: London 1773.
- Stow, John, A Survey of London, John Windet: London 1603.
- Sunderland, Septimus, Old London Spas, Baths and Wells, John Bale: London 1915.
- Wood, Alexander, Ecclesiastical Antiquities of London, Burns & Oates: London 1874.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian