Chambered Cairn: OS Grid Reference – NC 72245 56745
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 6276
- Long Skelpick
- Skelpick Burn
Getting Here

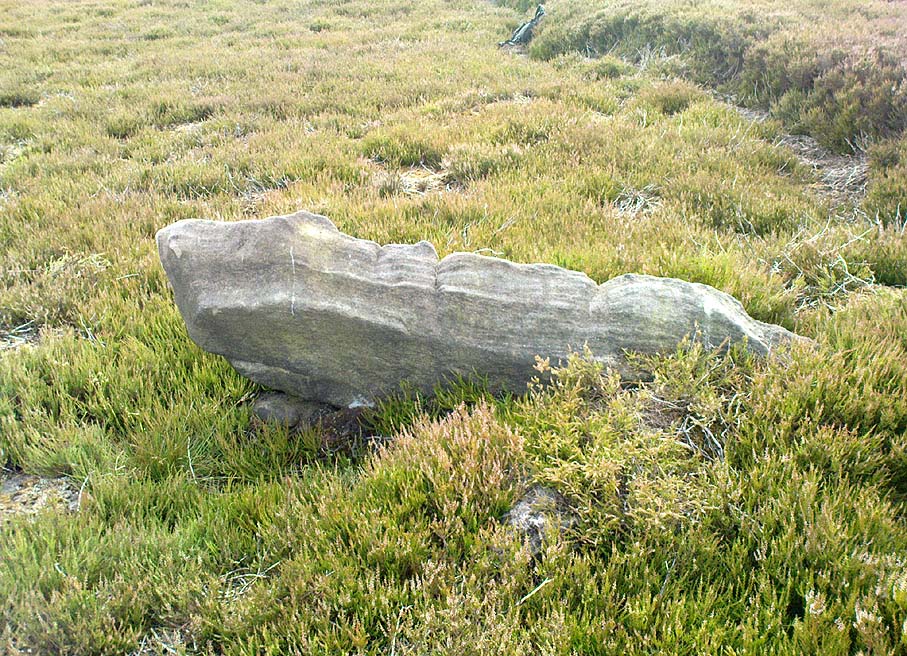
The huge cairn, looking east
From the delightful village of Bettyhill, take the A836 road west. A mile out, just as the tiny road bridge crosses the sea-river, take the tiny road on your left. Go past the roadside lochan until you reach the first Skelpick house several miles down. Walk across the fields on your left (east) until you reach the wobbly wooden tidgy-widgy-bridgey that crosses the Skelpick Burn. Across on the other side – you can’t miss it!
Archaeology & History

The overgrown northern face
As you wander down the poetic geoscapes of Strathnaver, meandering back and forth along the tributaries and Her tiny primal forest remains, on the edges of Her marshes, rivulets and rocky moorlands, tomb after tomb raise themselves to the eyes and feet of the wanderer. They’re everywhere it seems! But this one, above all others, hits the eyesight with an unexpected magnitude. This is a giant–one helluva giant!–and typical of the structure and status of many of the immense prehistoric chambered tombs in this remote northern region of our entrancing heathen isles.
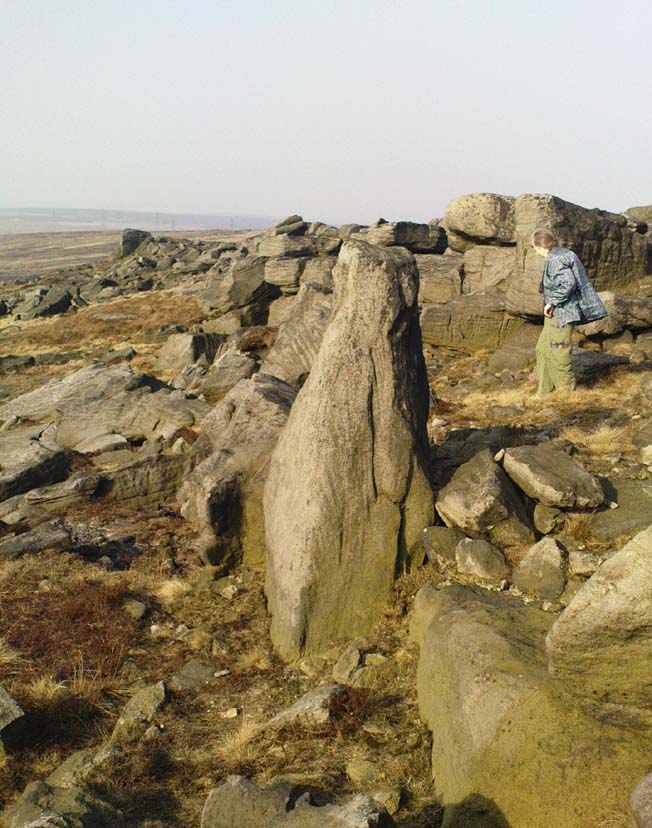
Rising out of the moorland heather to a height of sixteen feet in parts, tens of thousands of rocks make up this elongated artificial ridge, running like a spine NNW-SSE down the direction of the glen, pointing to the lowest dip in the distant southern horizon several miles away. And although overgrown when we visited the site, at each extremity the elongated cairn has curious stretches of stones projecting out of its sides, like a pair of horns at each end. Weird!

The long cairn, heading south

The giant cairn, heading north
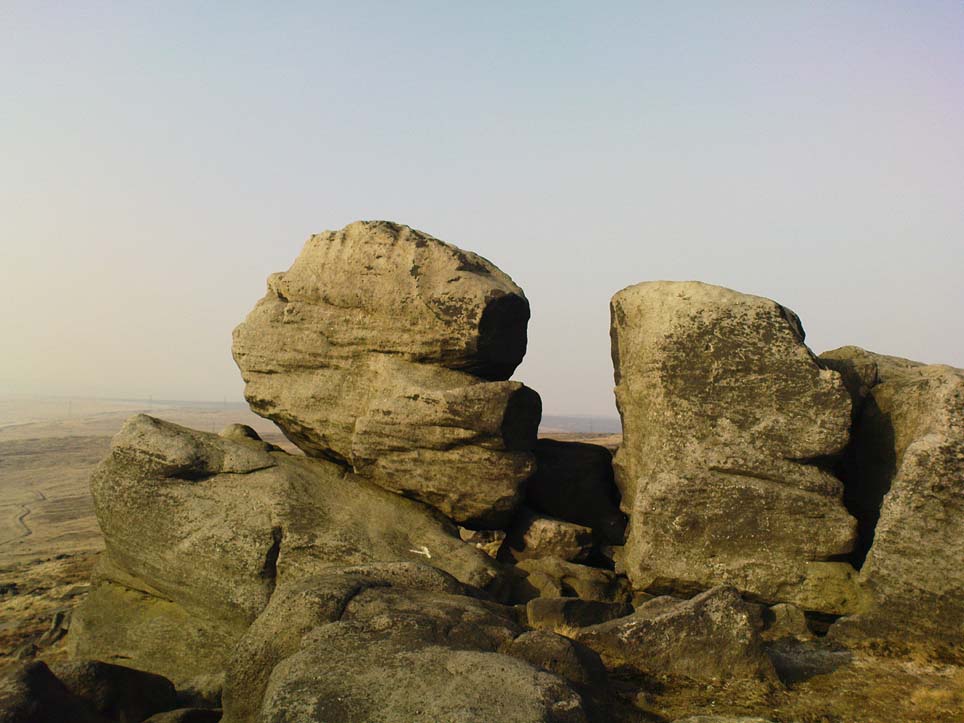
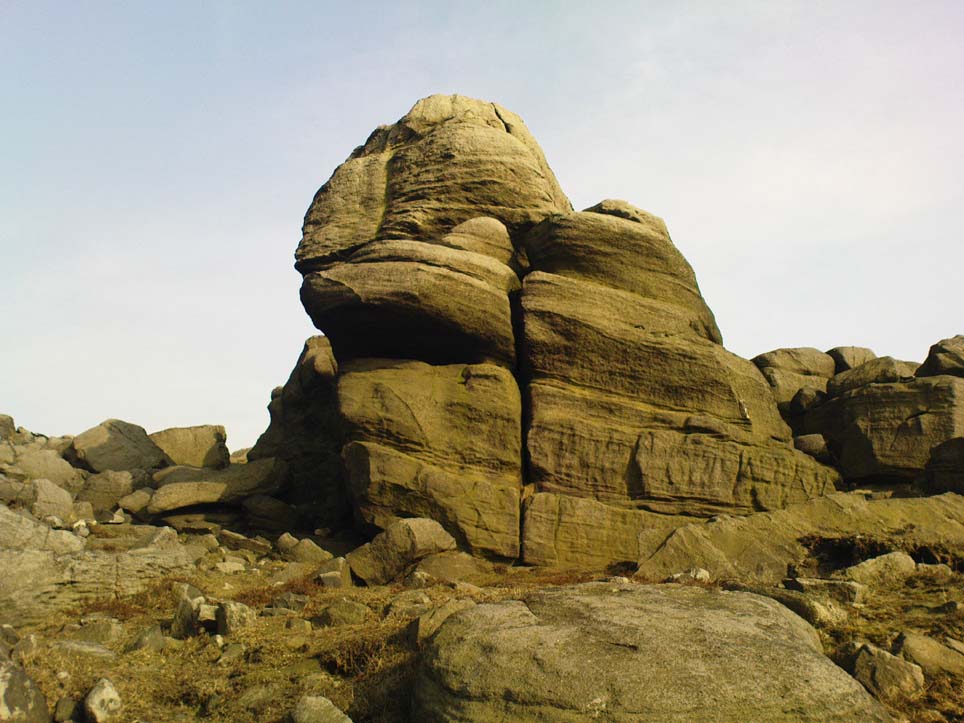
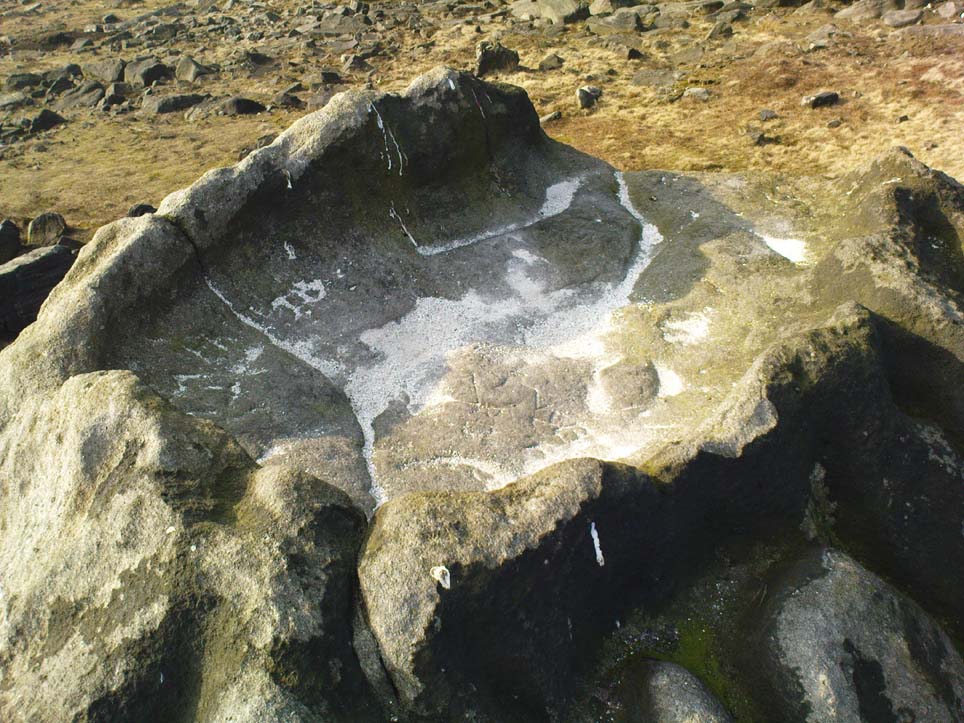
Once you get on top of the cairn, its northern end is the most impressive section. Wider than the rest of the monument, this is where, some ten feet below the top of the rock-pile, a large internal opening was covered over, hiding an impressive chamber (two birch trees mark the spot). This is in incredibly good condition when you remember that you are looking at something that was built in the neolithic period some 6000 years ago!

Spider guards chamber of bones

Little Lara at the entrance
On my first visit, I sat inside the shelter of the chamber for around an hour, either inside the main ‘tomb’ section, or beneath a huge intact covering stone 12 feet outside the entrance (hiding from both rain and midges) that stretches from one side of the cairn to the other; noting, on its underside, two cup-marks: one is definitely crustacean in nature, whilst the other may be man-made (though we cannot discount it too having a crustacean origin). But we can safely say that this long stone was dragged some considerable distance from the coast to its present position and positioned into this giant cairn. This covering stone rests precariously on a collection of many small well-placed rocks, themselves held up on two rigid solid standing stones, deeply embedded god-knows-how-deep in the solid Earth. They stand about 3 feet high in their present position above the ground.

Central stone in chamber

Gordon gives idea of its size
The well-preserved ‘tomb’ section at the northern end of the cairn was opened sometime in the middle of the 19th century by James Horsburgh (1870)—although its description as a ‘tomb’ could be questionable here, as no funerary remains have ever been found inside it. Horsburgh described the site as a,
“long cairn, 80 or 90 yards in length, which I opened and came upon a polygonal-shaped chamber, 11 feet in diameter, the sides consisting of large stones 6 feet high, one of them 7 feet by 4 and 1½ feet thick, placed at a distance from each other of 3 or 4 feet, the intervals being built up with long square stones. The roof had been formed with very large flags overlaying each other. The chamber had been opened from the top and the whole inside was filled with stones and rubbish, so that I only cleared it out. Before I commenced operations, however, there was no appearance of it having been meddled with, and I dug it by chance where the cairn appeared to be highest. Nothing whatever was found in it.”
This lack of funerary remains may simply be due to the collapse of stones destroying any evidences at the time Horsburgh dug into the cairn—or it may have had other functions instead. Shortly after Horburgh’s analysis, John Stuart (1870) came to visit the site in his grand tour of the megaliths of the region, telling that,
“on the waterside is a long cairn with a chamber at its north end, of about 12 feet across, formed of six slabs, with the space between them carefully filled up with masonry. Some of the slabs are of great size. A passage leading to another chamber is blocked up. The walls of the chamber begin to converge at a height of 6 feet, and were probably covered by flags.”

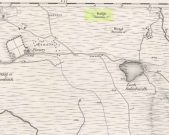
Stuart’s 1874 ground plan

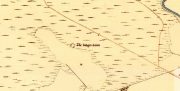
Long Skelpick on 1878 map
Highlighted on the first Ordnance Survey map in 1878, it was Mr Stuart (1874) who gave us our earliest ground-plan of Long Skelpick, as illustrated here. But since then the site has been described by a number of antiquarians and archaeologists. However, the most detailed account is given in the legendary Audrey Henshall’s (1995) updated site profile. I make no apologies for reproducing her lengthy account of this cairn almost in its entirety, as it is an astonishing megalithic monument. She wrote:
“…The cairn is 72m long overall, including the horns which define a forecourt at each end… The cairn is about 20m wide across the chamber, narrowing to 14m wide at a little south of centre, and expanding slightly to about 16m wide at the south end. At the north end the forecourt is difficult to define, though the ends of the horn are clear. Between them there is loose rubble which rises steeply to merge with the cairn material covering the passage, and which northwards merges into the downward slope of the ground. The passage entrance is hidden beneath this stony material; presumably there is deliberate blocking immediately in front of the entrance…but this has been covered by cairn material removed from the chamber area when it was investigated. The forecourt is about 13.5m wide by about 7m deep. The chamber is exposed in a deep hollow in the cairn, but south of it the cairn remains to a height of 3.4m (measured from the chamber floor), and from here to near the south end it continues as a ridge of bare irregular stones. Except for a few superficial hollows, it appears to be undisturbed, neither robbed nor substantially distorted, and it retains the steep pitch of its long sides. The cairn gradually diminishes in height southwards to about 2.8m high at about 12m north of the south forecourt. At this point there is a transverse hollow across the cairn 2.7m wide and about 0.7m deep, which may be an original feature (though in this area a relatively recent deep hollow has been made into the cairn from the east side reaching almost to the median line). The cairn has clearly been robbed from the south end to within 1.7m of the transverse hollow, presumably to build the square enclosure just to the south. The southeast horn is clear and the southwest horn can just be traced though it has probably been truncated. Between them, the edge of the forecourt is rather vague except for two laid slabs near the centre which appears to be part of an edging wall-face. The south forecourt has been about 10m wide and probably about 3.5m deep. The west edge of the cairn is clear though overgrown with heather, except for 20m at the north end where it is overlaid with bare stones evidently thrown down when the chamber was opened, and north of this the cairn merges into the natural slope. All along the east side the cairn merges with the slope of the ridge and has deep heather growing almost to the crest, so that the cairn edge is difficult to trace.
“The axis of the passage and chamber is nearly NNW to SSE, skew by about 13° by the axis of the cairn. The entrance can only be seen from the roofed passage. A pair of transverse stones set 0.56m apart forms the portal at the outer end of the passage. They are over 0.7m and 0.4m long, 0.25m and 0.18m thick, and 0.7m and 0.65m high. The original blocking, a neat stack of six horizontal slabs reaching to within 0.2m of the roof, is in place between them, with the south edges of the stones flush with the south faces of the portal stones. To the north of the slabs there can just be seen loose stones, smaller than those of the cairn material.
“The passage os 1.8m long and 1.15m wide at the outer end increasing to 1.3m wide at the inner end. A slab forms most of each wall. The slabs are 1.36m and 1.31m long by 0.5m and 0.45m high with two or three courses of walling above them, though this is displaced inwards and in a precarious state. Walling fills the short gaps at the ends of the stones, though missing from the NE corner. At the inner end of the passage a pair of portal stones forms the entry into the ante-chamber. They are 0.94m and 0.78m long by 0.26m and 0.44m thick, and 0.86m and 0.77m high, set 0.8m apart. At the outer end of the passage a lintel rests on the east portal stone and passes a little above the west portal stone, and the north edge of the lintel projects a little north of their outer faces. The lintel is 0.8m wide by 0.3m thick, 0.7m above the floor, tilted slightly down to the south. The next tow lintels rise in inverted steps, each overlapping the upper surface of that to the north with the third lintel 1m above floor level. The fourth lintel is missing and a gap of 0.5m is spanned by rubble; it is likely that a substantial stone at the top of each side wall is an end portion of this lintel, the centre part of which has broken away. The innermost lintel is lower, 0.86m above the floor, resting directly on the east portal stone and on a corbel stone over the shorter west portal stone at the chamber entrance. The lintel is over 2m long, 0.65m wide and 0.75m thick in the centre, and the face to the chamber is triangular.
“The chamber walls are constructed of spaced orthostats linked by panels of walling. All the orthostats are intact. The walling is of quite large quarried rectangular slabs, in general 0.07m to 0.02m thick, and where well-preserved can be seen to have been carefully built. At a height of about 0.7m the walling changes to courses of large corbel stones, often 0.23m to 0.4m thick, up to 0.9m wide, and 1m or so long. They are laid with their long axes running back into the cairn and their inner ends generally slightly oversailing; their appearance is rougher and heavier than the walling below. There is a considerable amount of displaced stone on the chamber floor, but all vertical measurements are taken from approximately floor level.
“The ante-chamber is about 2.5m long by 2.5m wide at the south end. The east wall consists of an orthostat 1.3m long by 0.36m thick, and 1.1m high, with a horizontal upper surface. The spaces between it and the outer and inner east portal stones of the chamber are filled with walling about 1.15m high, and above this and the orthostat are two courses of corbel stones giving a total height of 1.7m with a considerable overhang, at the southeast corner as much as 0.5m though possibly there has been some displacement. Only a short length at the south end of the west wall is visible. An orthostat set close to the west outer portal stone was visible in the 19th century…but this is hidden by rubble.
“The entrance between the ante-chamber and main chamber has been spacious, 1.06m wide and probably about 1.4m high. The portal stones are 0.85m and over 1.06m long, 0.42m and 0.25m to 0.4m wide, and 1.1m and 0.9m high, and their upper edges slope down into the cairn. The lintel above them is somewhat displaced with its wider face tilted down from south to north. Its east end rests on a corbel stone supported by displaced walling to the southeast of the portal stone, and its west end rests on displaced walling on the shoulder of the west portal stone and on the panel of walling to the southwest. The lintel is about 3m long by 1m wide and 0.35m thick.
“The main chamber is 3.5m long by about 3.25m wide. There are five orthostats in the wall. That on the axis has a horizontal upper surface and the others are rounded and rather irregular in shape. From the northeast, clockwise, they are 0.7m, 0.77m and 0.84m (at maximum 1.14m), over 1.3m and 0.86m long and, as far as can be seen, they vary from 0.1m to 0.4m thick. They are all of similar height, between 1 and 1.22m; the tallest is the northwest orthostat. Most of the linking walling remains. Between the east portal stone and the east orthostat only the upper courses are visible; between the east and southeast orthostats there are six neat courses of walling and above them three courses of corbel stones oversailing by 0.3m at a height of 1.7m (though the lowest courses of walling at the north end have been pulled away and the upper part of the wall is in danger of collapse). The walling between the southeast and the south orthostats has fallen away, but was intact in 1955… Between the south and southwest orthostats walling remains almost level with their tops and butts against the face of the latter, the south end of which is hidden. The last two panels of walling on the west side of the chamber survive to half the height of the adjacent orthostats.
“Part of the chamber was evidently visible in 1800 (Cardonnel …) and subsequently it must have been filled in. Horsburgh investigated the main chamber in 1866… His descriptions and measurements are fairly accurate except that he gave the height of the orthostats as 6ft and one as 7ft (1.8m and 2.1m); this seems to be an exaggeration as the present floor level, also extending down the passage, appears to be at approximately at the original level. He estimated that the roof height of the main chamber had been 10ft (3m)…

Old lichen upon the cairn-stones

Of mosses and lichens hereon…
Much of the length of the cairn is very overgrown in a living repertoire of medicinal mosses and lichens which, of themselves, are centuries old in places. Their profusion is a great indicator, not only of the cleanliness of the air betrayed in the cities of homo-profanus, but also a telling sign that visitors to this distant realm are few and far between. Tis a beautiful site in a spectacular ancient arena…
…to be continued…
Folklore
There is great superstition amongst some locals even today that this immense cairn should not be tampered with and it is said to be haunted.
References:
- Gourley, Robert, Sutherland: An Archaeological Guide, Birlinn: Edinburgh 1996.
- Henshall, Audrey S., The Chambered Tombs of Scotland – volume 1, Edinburgh University Press 1963.
- Henshall, Audrey S., “The Distant Past,” in The Sutherland Book (edited by Donald Omand), Northern Times: Golspie 1991.
- Henshall, Audrey S., The Chambered Cairns of Sutherland, Edinburgh University Press 1995.
- Horsburgh, James, “Notes of Cromlechs, Duns, Hut-circles, Chambered Cairns and other Remains, in the County of Sutherland“, in Proceedings Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 7, 1870.
- Lelong, Olivia C., “Writing People into the Landscape: Approaches to the Archaeology of Badenoch and Strathnaver,” University of Glasgow 2002.
- Mackie, Euan W., Scotland: An Archaeological Guide, Faber: London 1975.
- o’ Reilly, Kevin & Crockford, Ashley, What to See Around Bettyhill, privately printed 2009.
- Royal Commission on Ancient & Historical Monuments, Scotland, Second report and inventory of monuments and constructions in the county of Sutherland. HMSO: Edinburgh 1911.
- Stuart, John, “Report to the Committee of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, Appointed to Arrange for the Application of a Fund Left by the Late Mr A. Henry Rhind, for Excavating Early Remains,” in Proceedings Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 7, 1870.
- Stuart, John, “Notice of Excavations in Cairns in Strathnaver, Sutherlandshire,” in Proceedings Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 10, 1874.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to the beautiful Aisha Domleo for not only getting me up here, but also for the use of photos in this site profile.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian