‘Standing Stone’: OS Grid Reference – SS 8896 3355
Getting Here
You can’t really miss this. Take the road south from Winsford, up the steep hill onto the moors and before you reach the crossroads, look up across the slope on your left where you’ll see a small building on its own. Go there!
Archaeology & History
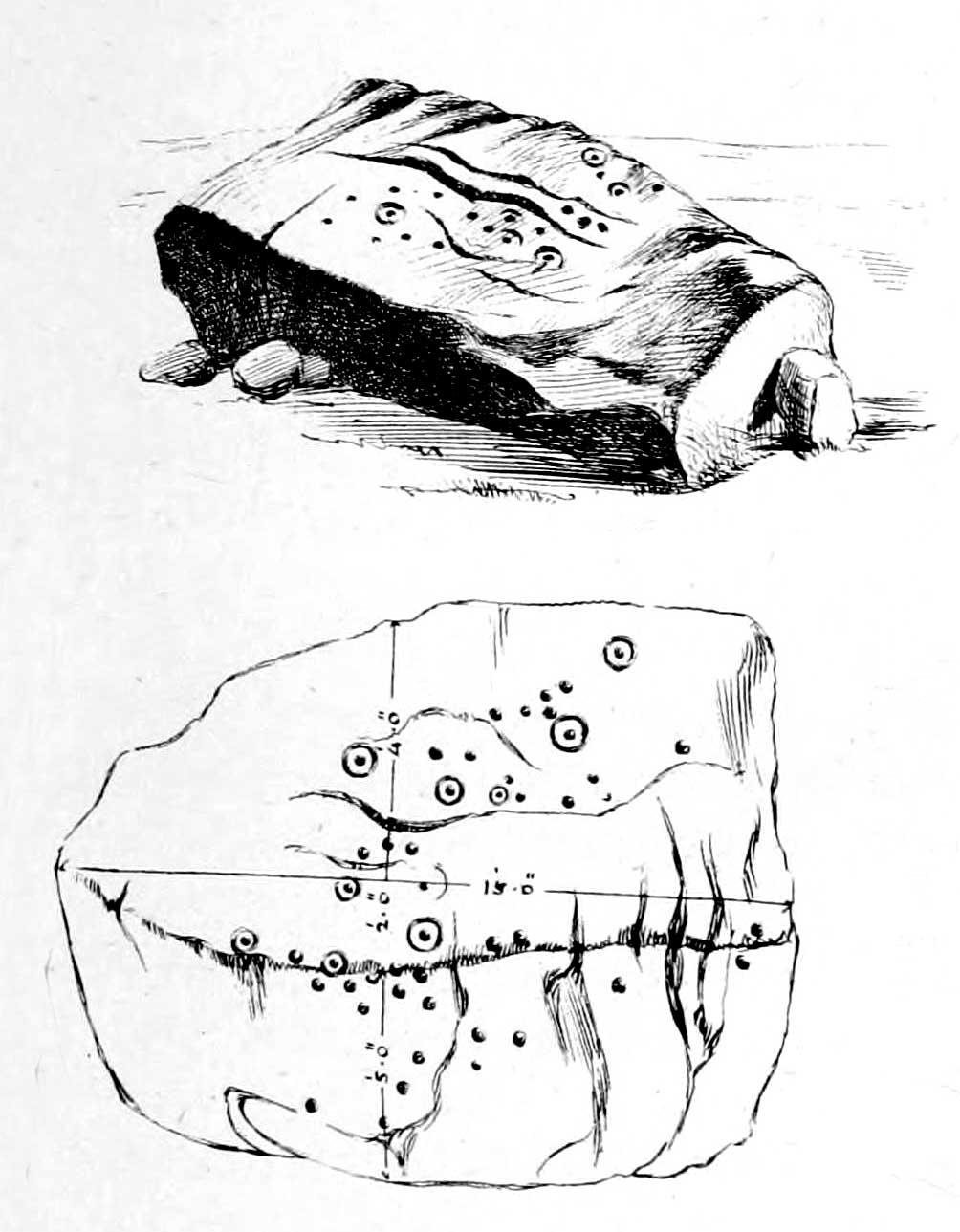
A curious upright monolith more than five feet long (though some of this is embedded in the ground) with the words ‘CARAACI NEPVS’ carved on one side, is strangely closetted in a silly ‘house’ of its own on the moortops! But the origins and history of the stone are contentious. Some proclaim it as prehistoric, others Romano-British, and others as being from the Dark Ages. In the 1960s and ’70s, archaeological tradition had its origins in the Romano-British period, and certainly the carved lettering on the sides of the stone seem to indicate a Roman provenance; but as the great Exmoor historian S.H. Burton (1974) told,
“It is possible that the stone was erected hundreds of years before it was inscribed, and the existence of an ancient trackway alongside, leading to the Barle, strengthens this possibility. But, like most things about the Caratacus Stone, this is guesswork.”
We know it stood here in the 13th century as it was described in perambulation records of 1219 and 1279 AD; but it’s more than likely to be a monolith erected in the Dark Ages. Grinsell (1970) however is a little more cautious, telling:
“The likelihood of the person in whose memeory this stone was raised claiming kinship with the Caratacus who was the arch-enemy of Rome, c. AD 45-50, has on more than one occasion been questioned. It is, however, too tempting to be abandoned by the present writer.”
The carving on the stone was deciphered by the legendary Prof. John Rhys at the end of the 1800s, telling it to have been Carataci Nepos, the Kinsman of Caratacus (and variants thereof), who held out against the Romans in south Wales until AD 50. The old Celtic writer, R.A.S. Macalister, thought the stone to have been dedicated to a local christian hero, St. Carantoc, but this notion has been generally dismissed.
Folklore
The old stone is said to be a site where buried treasure exists — though none has ever been found. There is also an old tradition that “ghostly horses and waggons rumble towards the stone at midnight” — but this as likely relates to its proximity with the old crossroads a short distance away.
References:
- Burton, S.H., Exmoor, Hale: London 1974.
- Grinsell, L.V., The Archaeology of Exmoor, David & Charles: Newton Abbot 1970.
- Page, John Lloyd Warden, An Exploration of Exmoor and the Hill Country of West Somerset, Seeley 1890.
- Vowles, Alfred, History of the Caratacus Stone, privately printed 1939.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian