Cross: OS Grid Reference – SD 94057 39369
Also Known as:
- Herders Common Cross
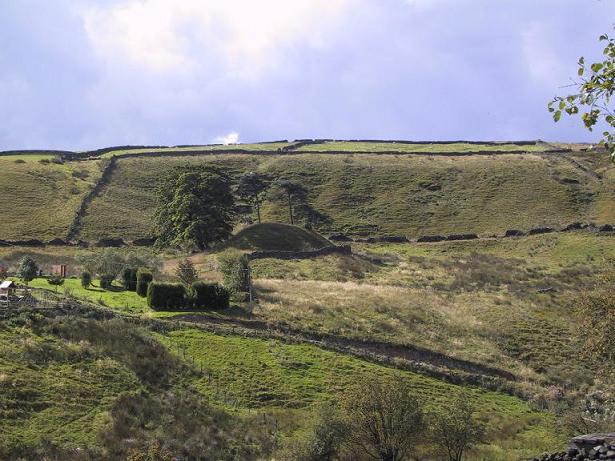
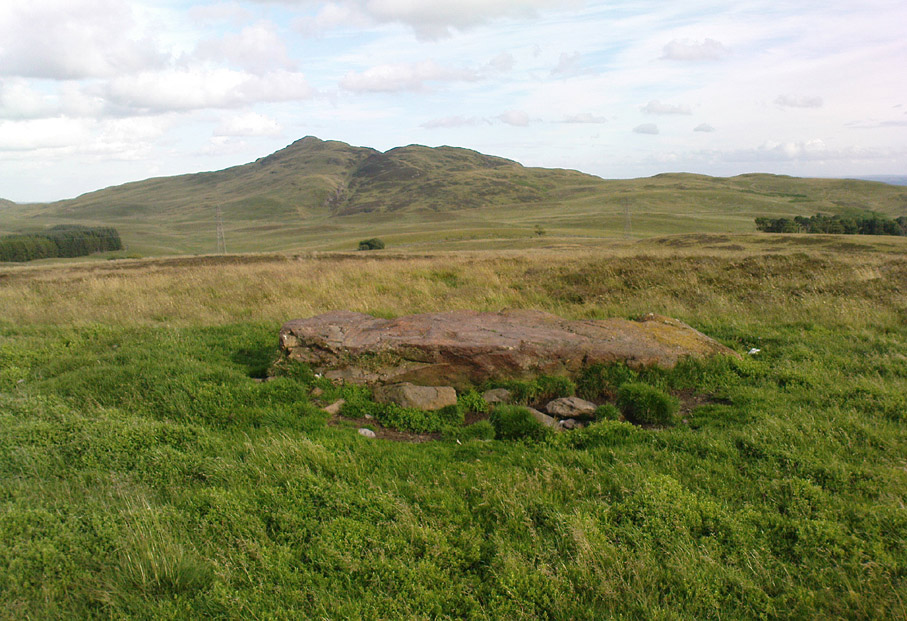
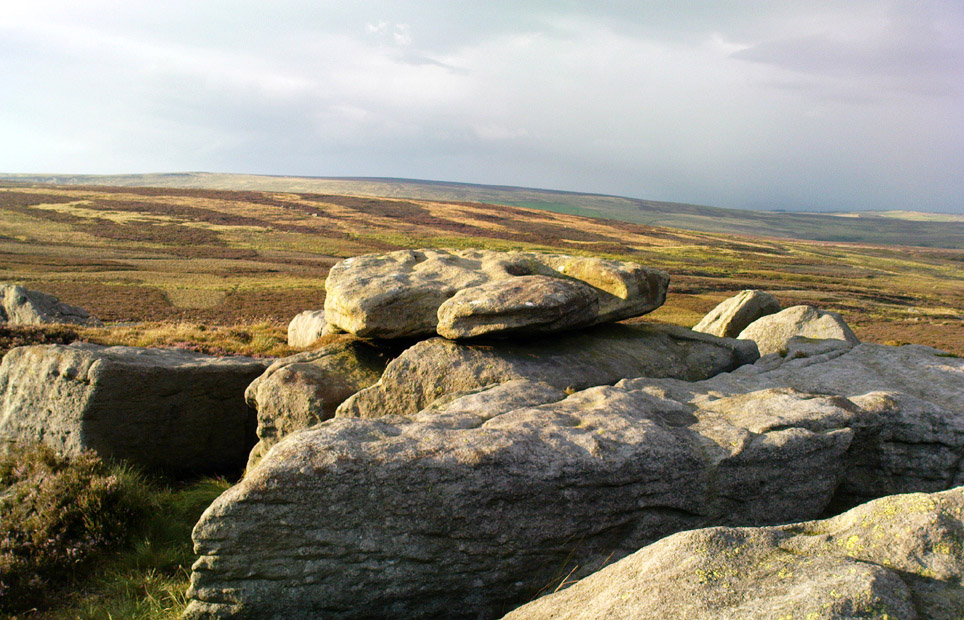
From Laneshaw Bridge, near Colne, take the long country road that goes up above Wycoller to Stanbury and Haworth over the Yorkshire-Lancashire border. A couple of miles uphill, there’s a parking spot with views across the moors. Stop here. Cross the road and walk up for about 100 yards, going thru the rickety gate on the left, and up the field (past the small disused quarry) until you see the large rock looming ahead of you, perched on its own. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
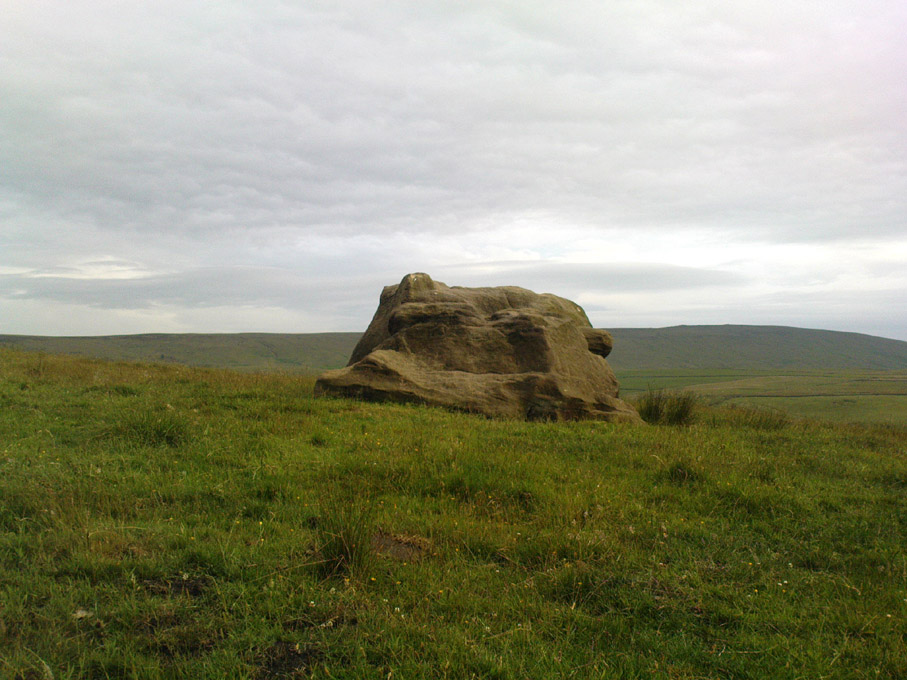

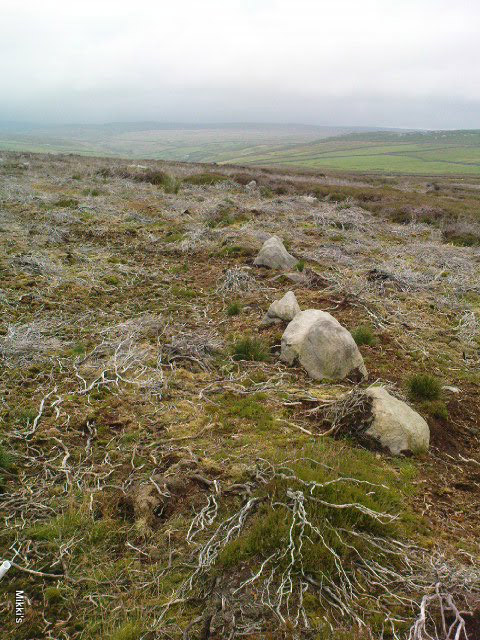
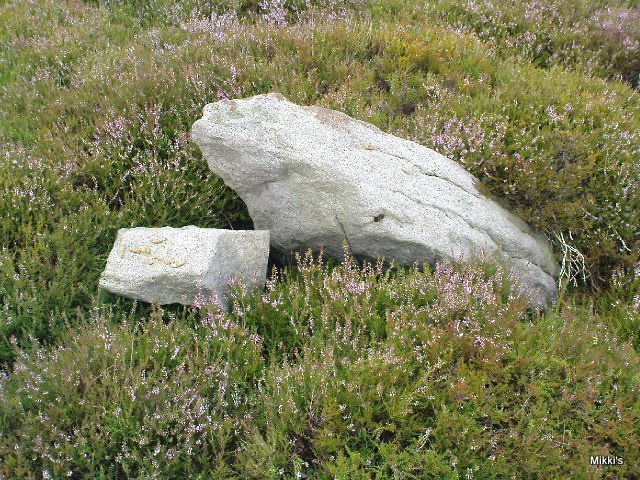
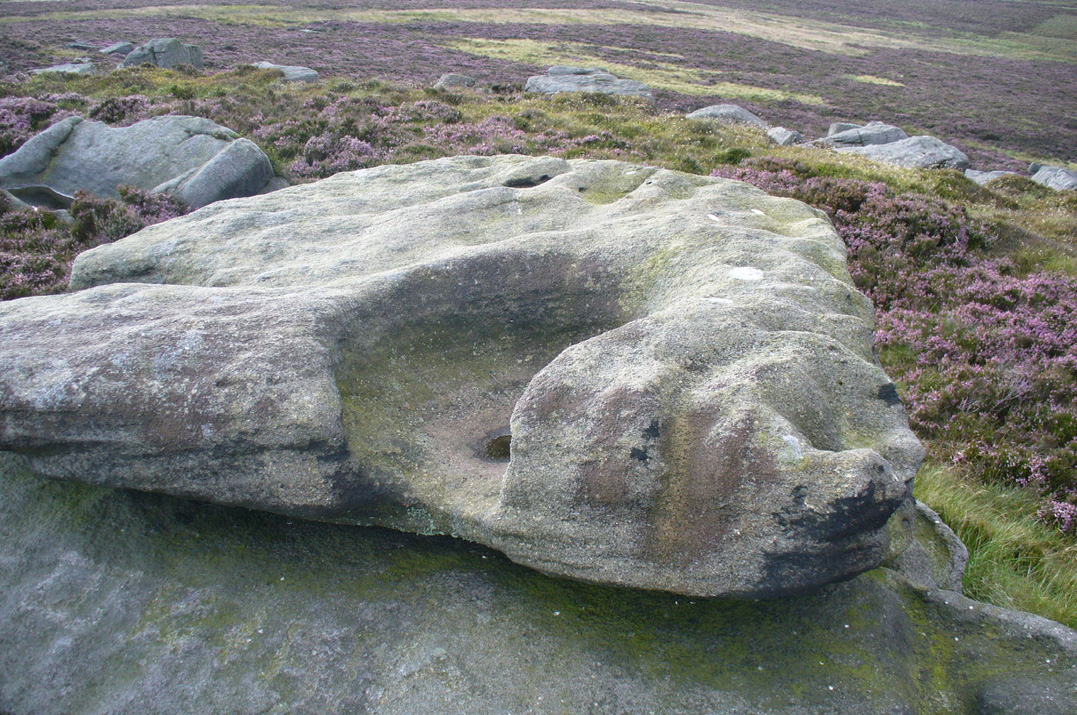
This is a really curious spot to me. A large singular boulder sat on the edge of an uninhabited moorland with no real history of heathenism, nor religious practices; yet someone at sometime in the not-too-distant past saw something here that made them cut a large square hollow into the top of this stone, in which they stuck an old cross. We came across this site a few weeks ago quite by accident, but realised that the deep hollow in the rock was an old cross base; so when I got home I checked Taylor’s (1906) magnum opus, expecting to find some info therein. But even Taylor seemed to know nothing of this place.
A week or two later, Paul Hornby pointed me in the direction of an unpublished essay by a local chap called Clifford Byrne (1974) who’d studied some of the early christian remains in the region and who wrote the following of what he named “Herders Cross”:
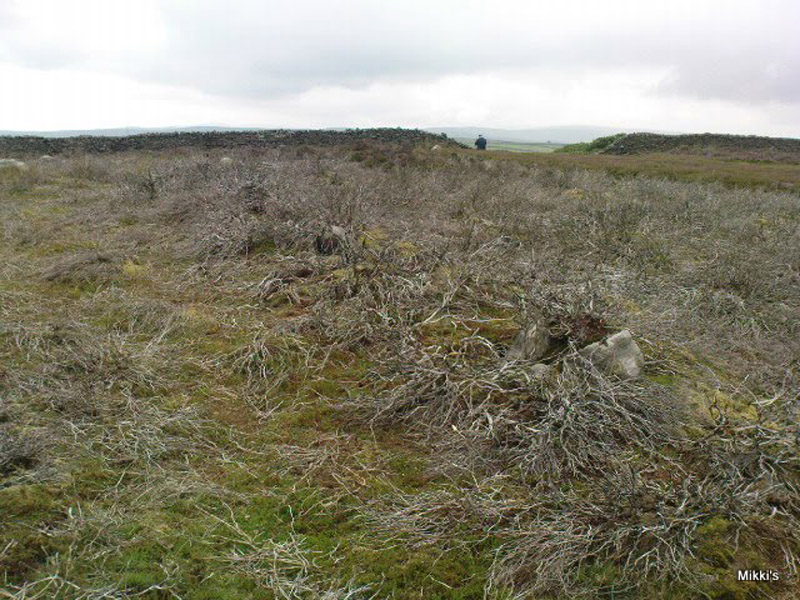
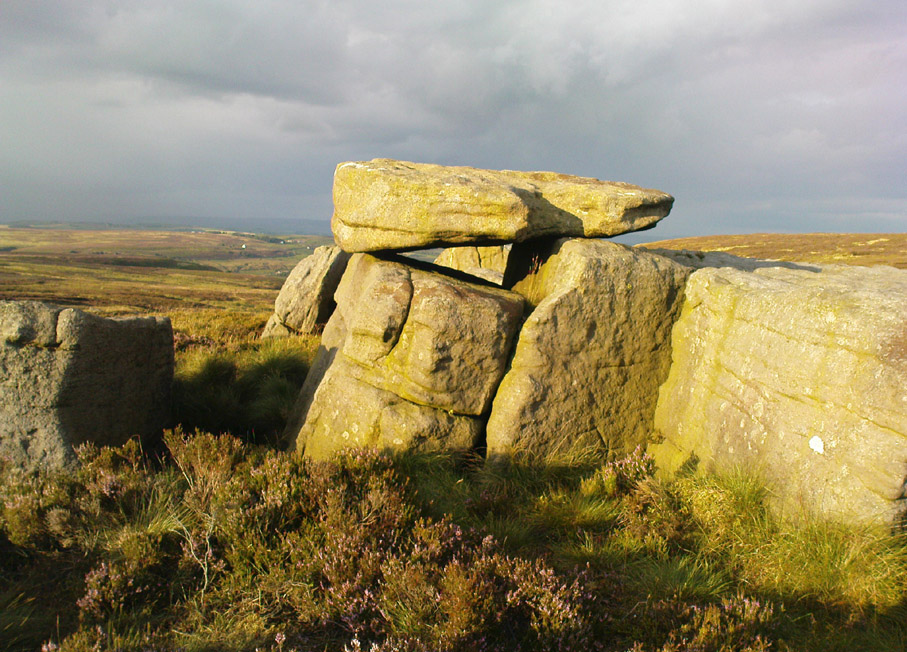
“This cross, or more properly its socket, is probably one of the least known in the area. It was shown to the writer by Mr Stanley Cookson of Trawden, who discovered the socket in passing, so to speak. On the road to Haworth from Laneshawbridge, opposite the site of Foster’s Leap rocks, on the east side of the road, is a really huge boulder on the moor top. In the south side is the cross socket, whilst on the north side of the rock can be made out a right-angled mark which implies that either the socket was being placed on that side in the first instance, or that two sockets were once envisaged…
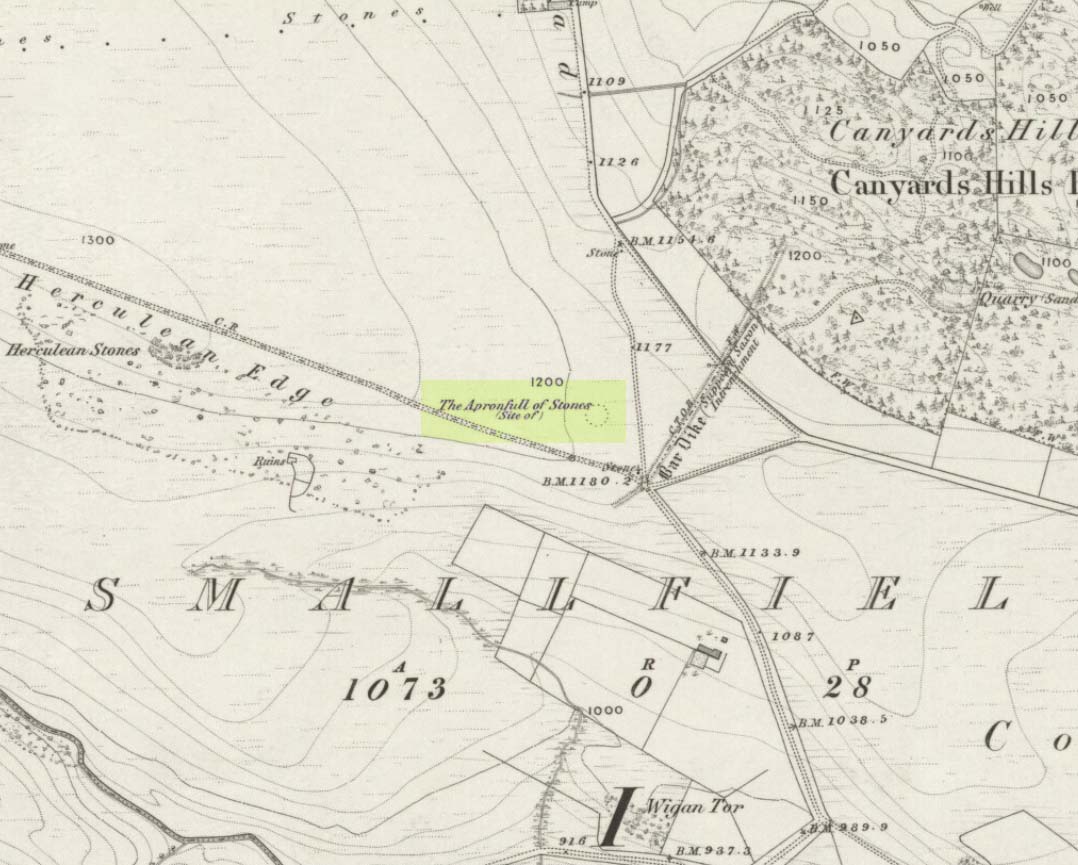
“Old maps show the rock in situ with a “shaft” protruding from the top. Some yards west a shallow pony track bypasses the site, whilst some four or five hundred yards east a very well worn and ancient road, long unused, passes in the direction of Emmot Holy Well. The cross may thus have been a Wayside Cross showing the way to this Holy spring which is remembered as being propitious in the cure of rheumatism.”
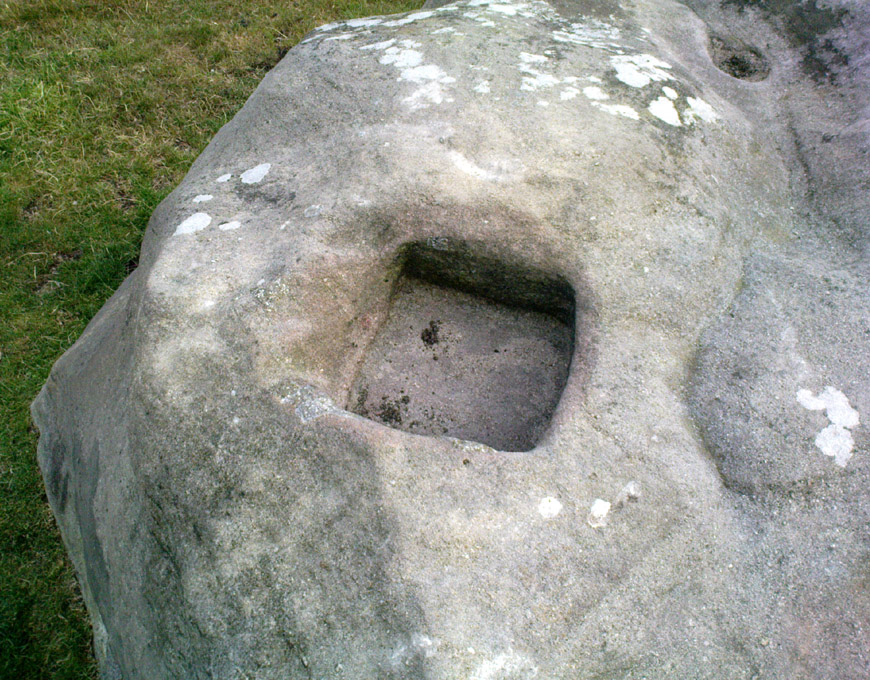

This may be so; but I suspect earlier, heathen remains upon the moors here to explain the curious position of both this and another cross-base some 400 yards away. Some dubious cup-marks can be seen by the side of the stone hollow; and other dubious ones have been found on the moors above here. There is folklore of a lost stone circle on the hills above here, and a scattering of little-known faerie lore, indicating hidden sites and lost myths. These ingredients are more likely the reasons that Herders Cross was erected here, overlooking the countryside south and west, with the holy hill of Pendle rising in the centre of the distant landscape…
References:
- Byrne, Clifford, A Survey of the Wayside Crosses in North East Lancashire, unpublished 1974.
- Taylor, Henry, The Ancient Crosses and Holy Wells of Lancashire, Sherratt & Hughes: Manchester 1906.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian