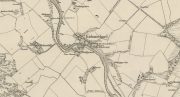
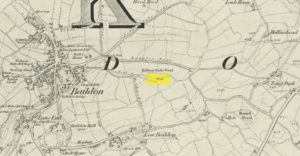
Standing Stones (destroyed): OS Grid Reference — NO 4128 1769
Also Known as:
- Dairsie Stones
Archaeology & History

Recent archaeological investigations at the site which has become known as the Dairsie Hoard—where many pieces of broken Roman silverware were seemingly deposited in one spot, adjacent to a dried bog “which may arise from a former spring” of water—brought about the discovery of much earlier megalithic remains. The position of two previously unrecorded standing stones were found during the archaeological dig here. In the most recent edition of Current Archaeology, Fraser Hunter (2018) described the position of the Roman silverware close to some ancient pits or sockets in the ground. This “group of features was…intriguing”, he told,
“for two of them contained stumps of standing stones, one in association with probably Bronze Age pottery. This hoard had been buried in a memorable, perhaps even a sacred site, between an intriguing wet spot on one side and, on the other, two standing stones, which were already ancient by the time the silver was buried. Such burial of valuables in association with prehistoric monuments can be readily paralleled elsewhere. It suggests this silver was placed under the care of the gods, probably as a sacrifice rather than a burial for safekeeping.”
Two thousand years before the Roman silver deposit had been deposited, megaliths here stood. Sadly they’re long gone, leaving more questions than answers as usual…
References:
- Hunter, Fraser, “Solving a Silver Jigsaw,” in Current Archaeology, 335, February 2018.
Acknowledgments: Many thanks to Paul Hornby for use of his photo in this site profile.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian