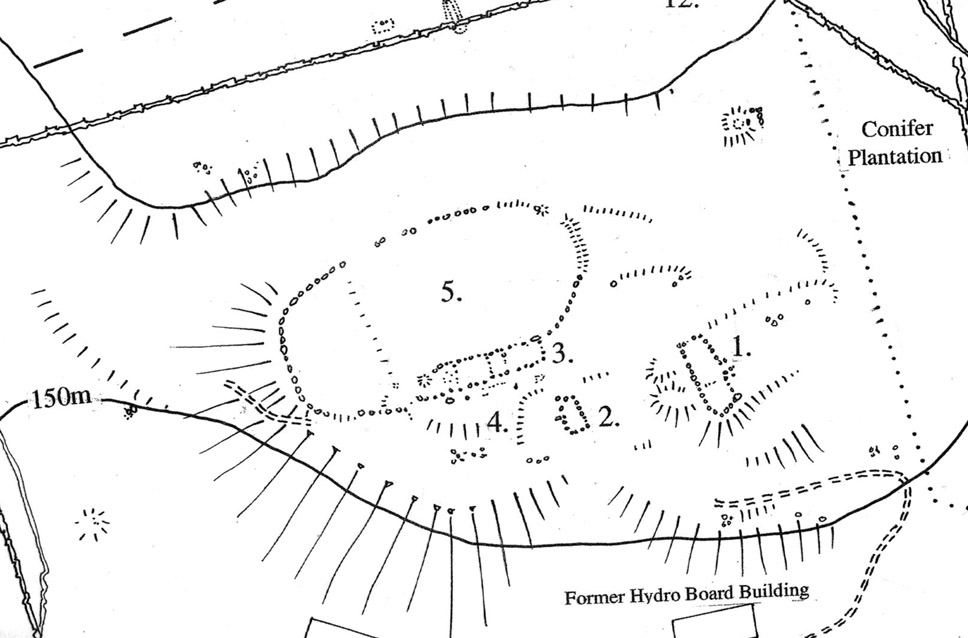
Enclosure: OS Grid Reference – NN 5325 3607
Take the single-track Glen Lochay road down past the Bridge of Lochay hotel at the edge of Killin, as if you’re gonna visit the superb cup-and-ring carvings opposite Stag Cottage (or Duncroisk 1). Immediately past the garden of Stag Cottage is a small copse of trees and a couple of old wartime-looking buildings in the field above the roadside. Go up past these buildings and onto the rise at the back. You’re here.
Archaeology & History
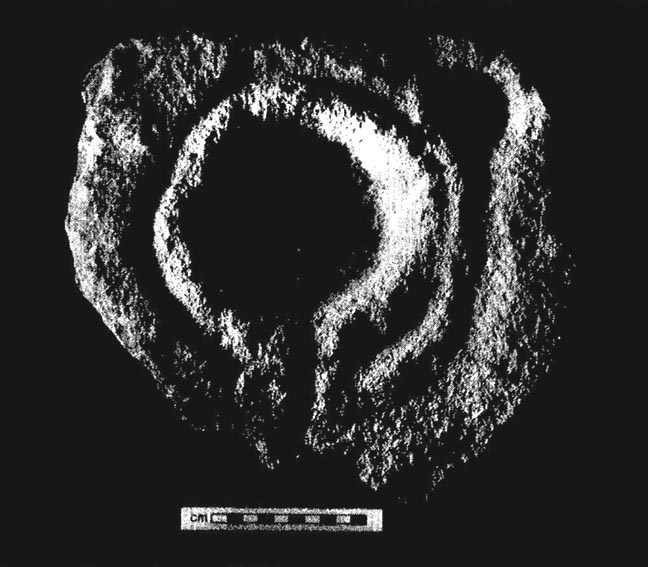
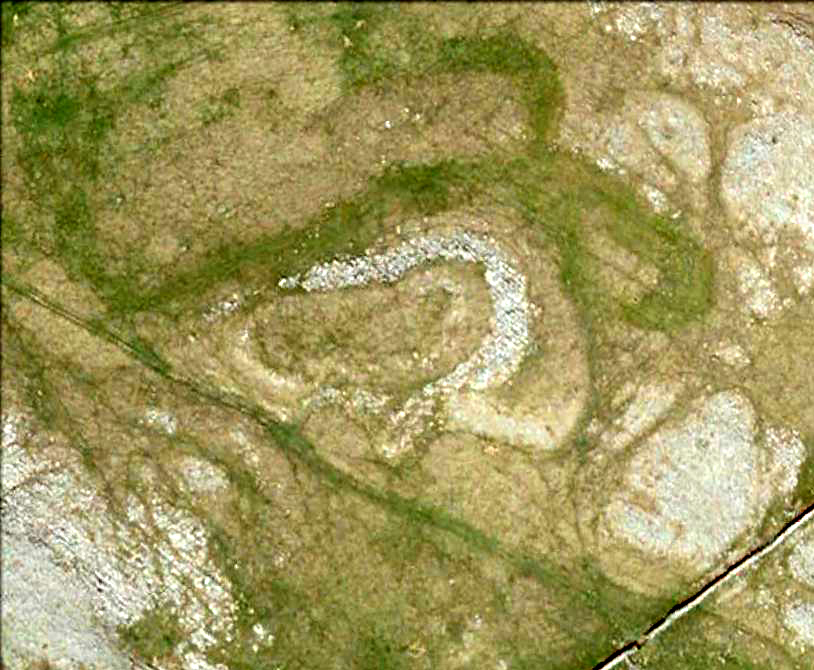
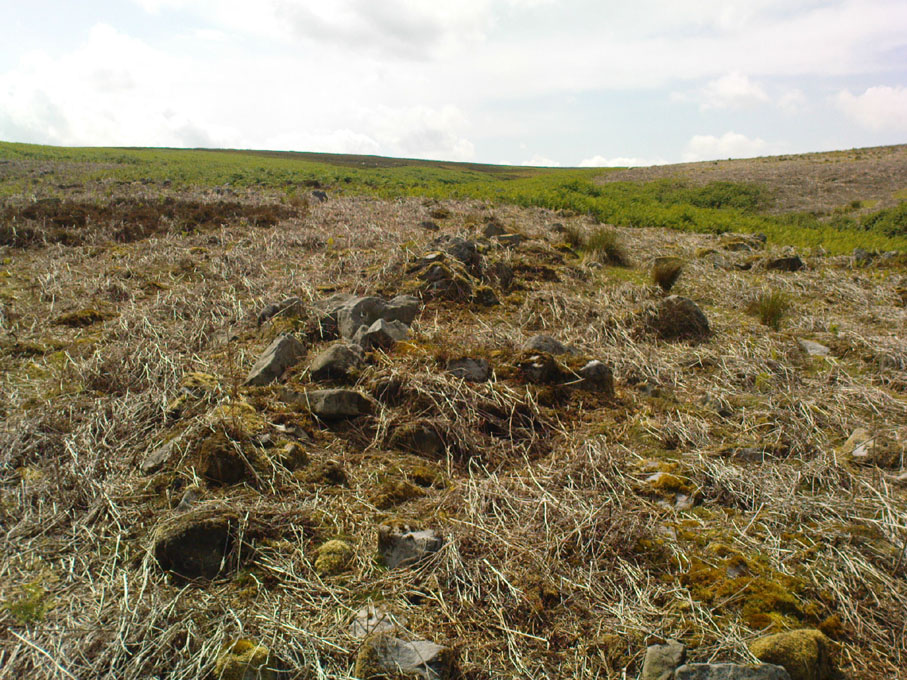
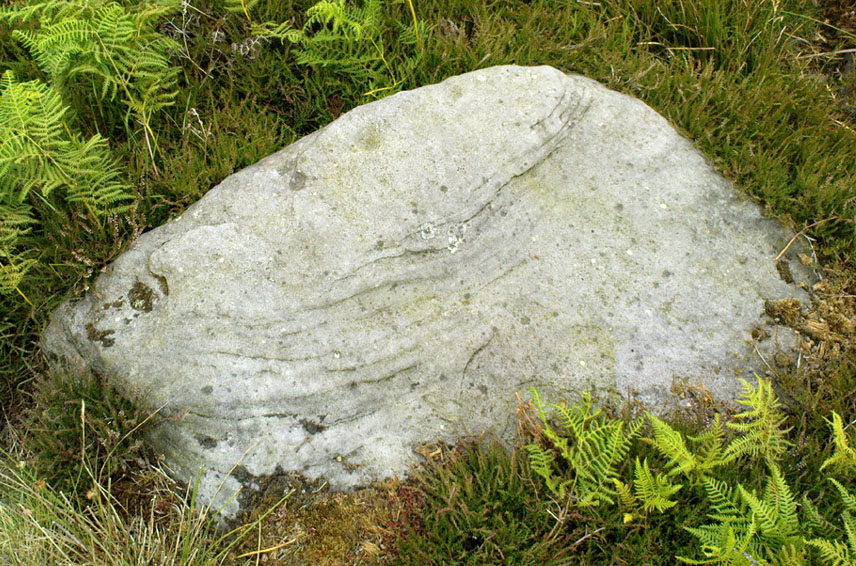
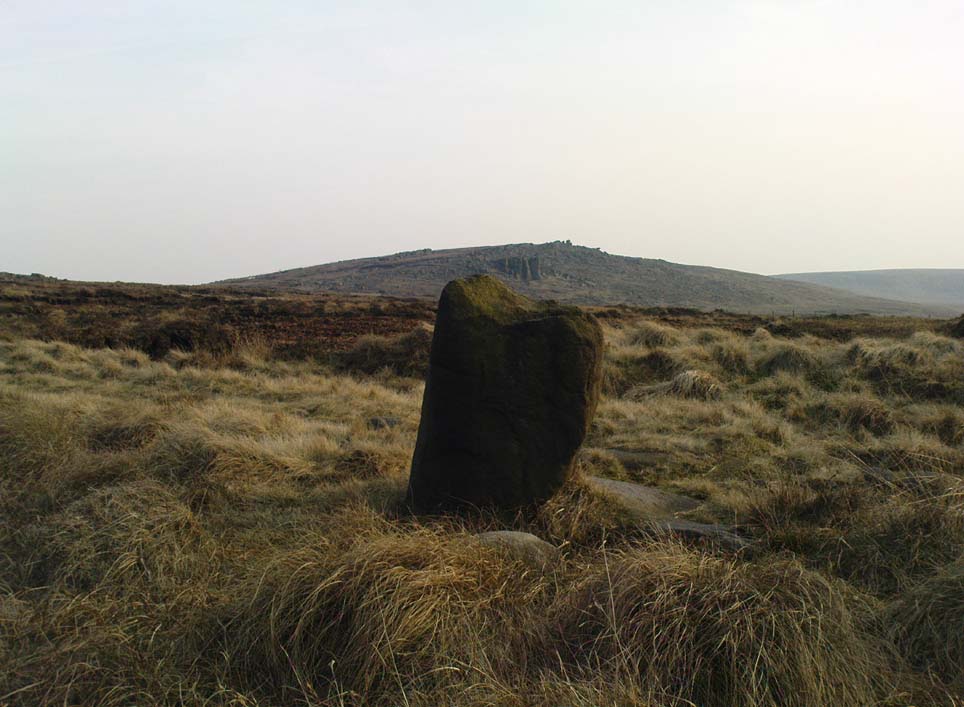
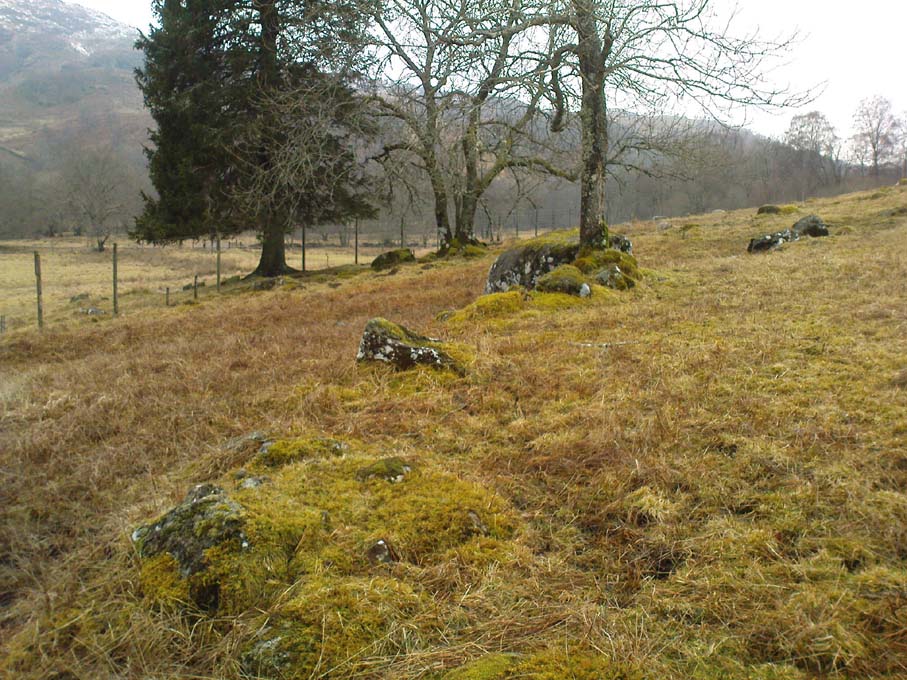
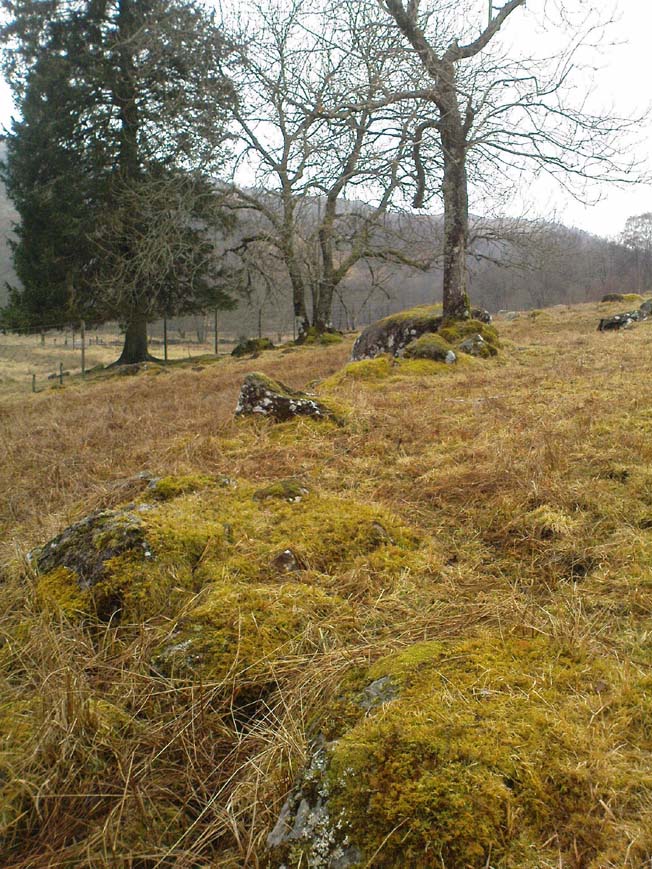
This is a fascinating site of multi-period historical usage, which Dugald MacInnes (2001) thinks may have its origins in the early Bronze Age or neolithic; but which I reckon was probably first used in the Iron Age. Either way, we have here a large interesting well-preserved prehistoric stone enclosure, that has yet to be excavated. I first came across it whilst gathering firewood from the adjacent copse and was quite puzzled by what seemed to be an extensive curved line of ancient walling running from its east to northeastern section, typical of prehistoric Iron Age walled structures common in northern England and beyond. I must have paced back and forth along a 75 yard length of this section of walling a half-dozen times, wondering what the hell this place was. And the more I looked at this section of the enclosure, the greater my conviction grew that this was constructed in prehistoric times. And thereafter came the puzzle.
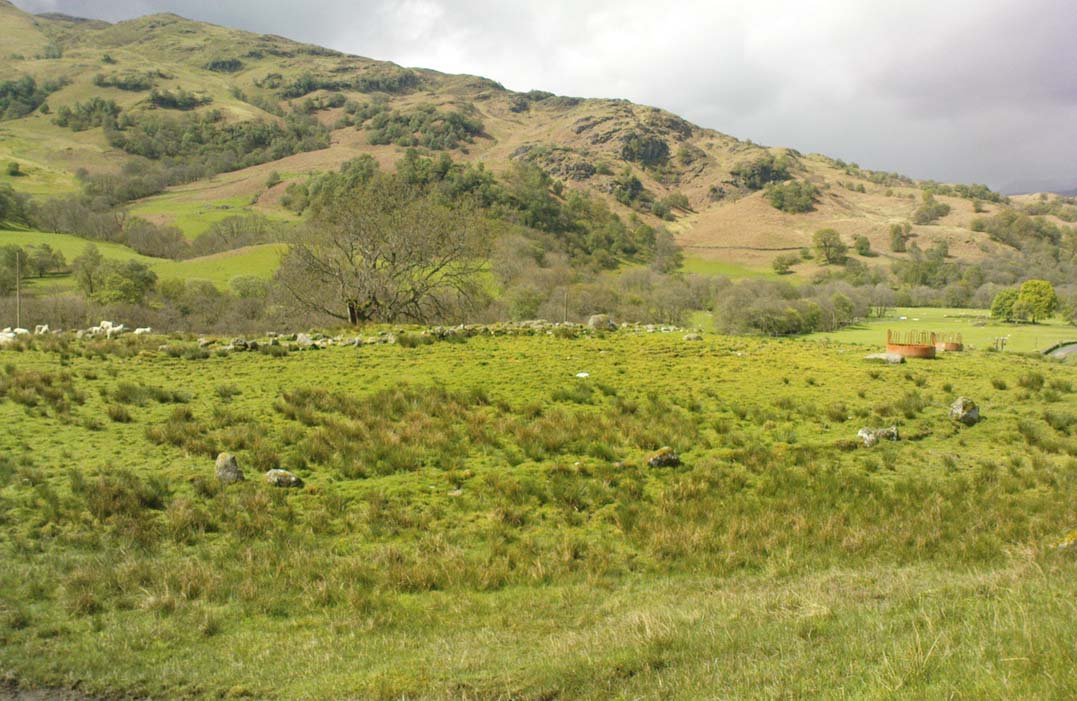


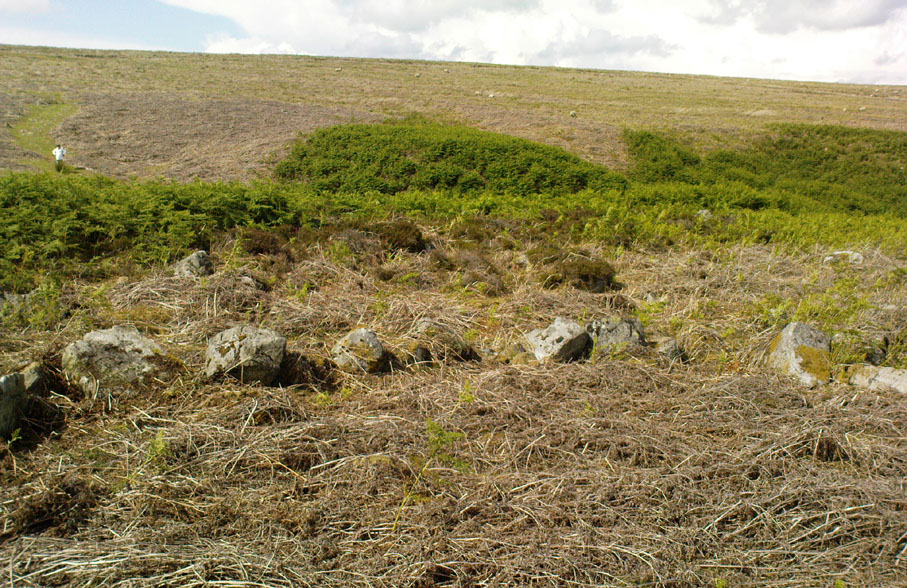
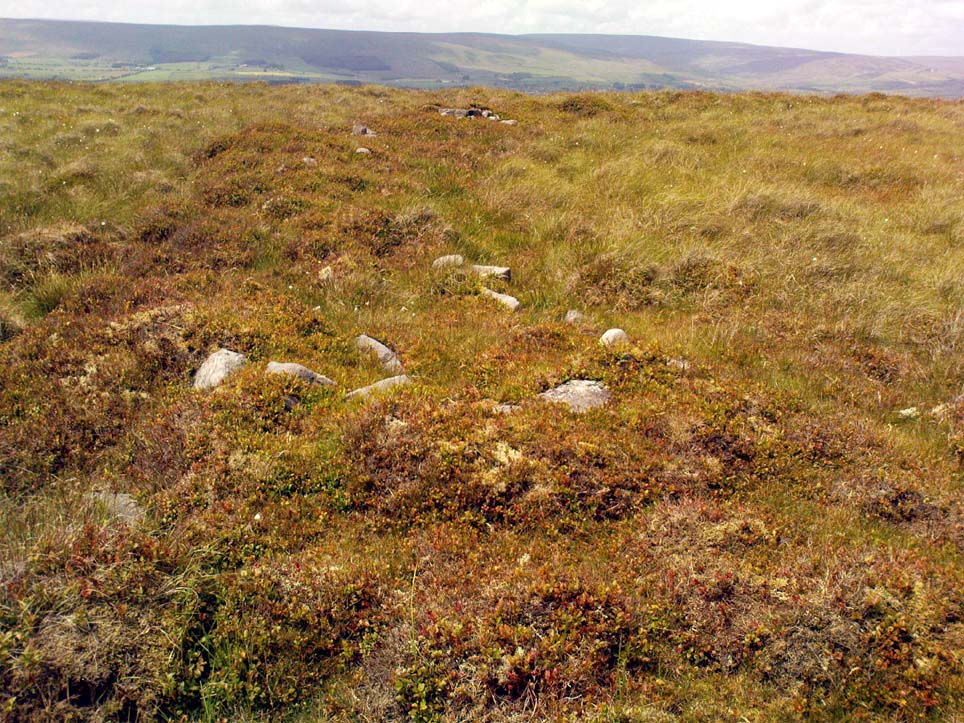
For along the southern walled section were a number of much more modern medieval and much later walled sections, including the remains of buildings that looked barely Victorian in age and nature. The site was obviously being used presently by the local farmer for his cattle. And so it became obvious that here was a large oval-shaped stone-walled enclosure or settlement that had been used over and over again through many centuries, with its origins seeming to be Iron Age in nature. Measuring approximately 195 yards (178m) in circumference, the structure has a maximum E-W diameter of 78 yards (71m) and N-S measurement of 44 yards (40m).
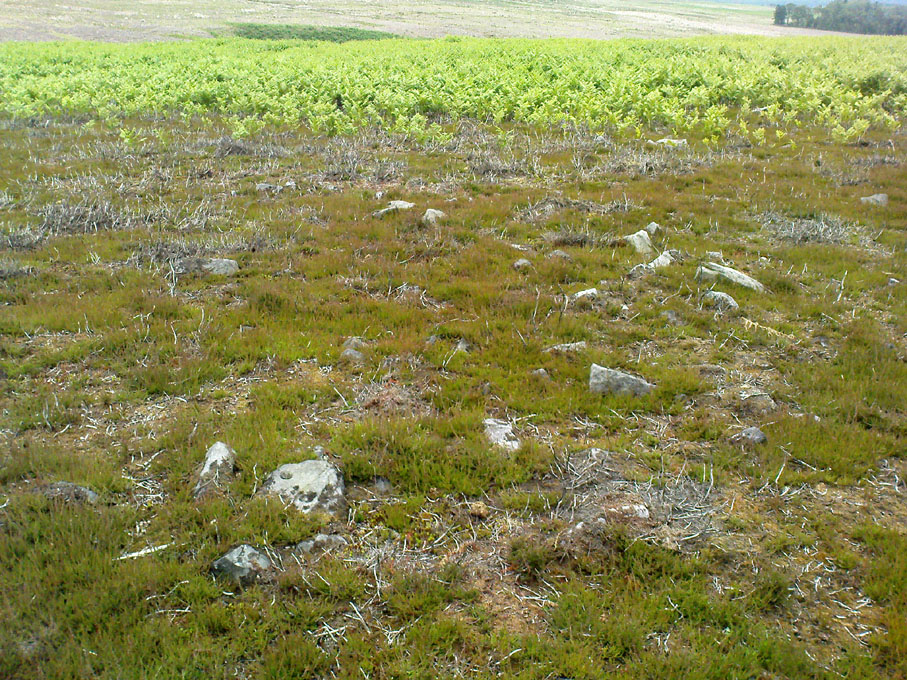
The mass of evidence for prehistoric activity is all round this hidden enclosure, with the fascinating clusters of cup-and-ring stones of Duncroisk and Corrycharmaig close by. The small standing stones of Tirai 600 yards NW, and a similar prehistoric enclosure at Tullich ¾-mile NW show ample evidence of prehistoric man in this part of Glen Lochay.
Despite the size of the place, no literary reference of it occurs before MacInnes and his team came here. His description is as follows:
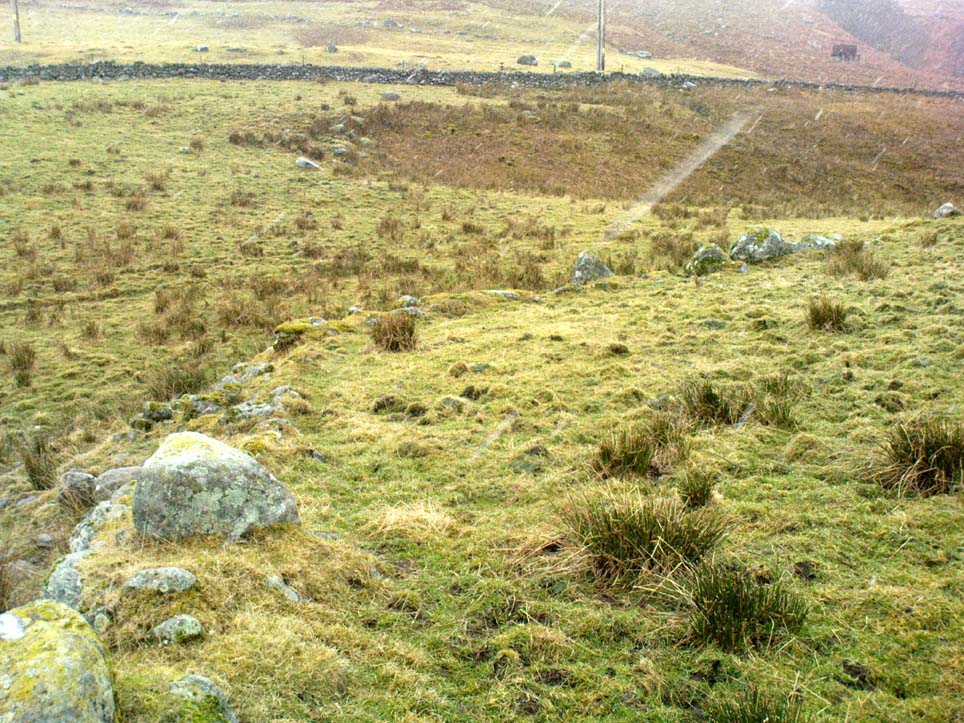
“An oval enclosure, its boundaries formed principally from large water-worn boulders interspersed with drystone walling and in part by an earthen bank in the easternmost section, sits atop of a natural terrace about 155m OD. The terrace slopes steeply to the west and south and cut into the western slope is a track, the course of which cannot be determined beyond the extent of the slope. This track displays revetment in the form of stone coursing.
“The SW corner of the enclosure is angular rather than the rounded character of the other sections. The W and SW sections are composed of coarsely constructed stonework in which large, 1m wide, often 1m high, water-worn boulders at two to three metre intervals, are interspersed with smaller boulders which form crude drystone coursing.
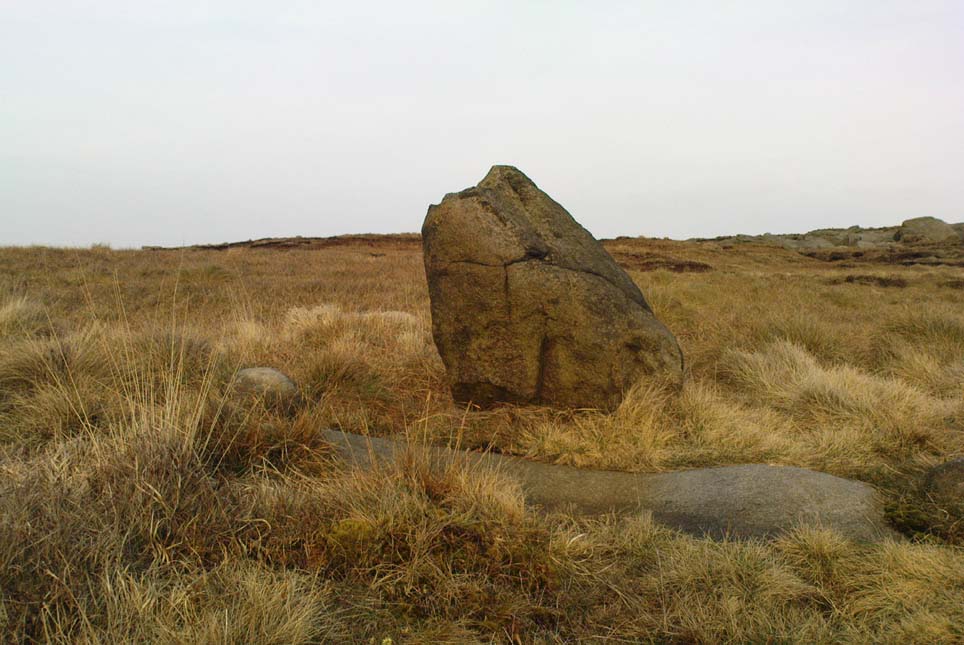
“The NE section is formed largely of large boulders, one of which is 1.5m in width and 1.2m high by 0.8m wide. Sections of the northern part would appear to be robbed out, perhaps to construct the modern wall which lies about 25m to the north. There are no remaining large boulders there, however, which could indicate their absence in the original construction of the enclosure. The central section of the northern perimeter may be constructed of two outer skins of boulders, forming a wall about 0.9m wide, 0.4m high on its exterior, but reducing to 0.3m on its interior side. Two sections could possibly be filled with a rubble core.
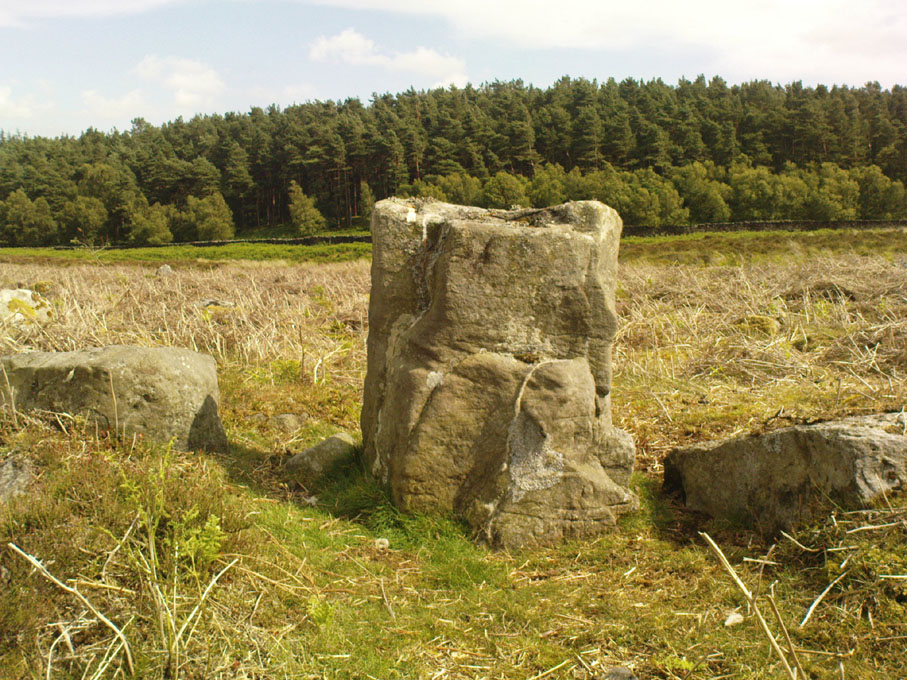
“The E section is formed by a low 0.3m high earthen grass-covered bank with occasional boulders. This bank is about 0.2m high relative to the interior, but is about 0.5m to.0.8m high on its exterior side. The NW side shows on the western side more evidence of double skin, rubble construction. Close inspection of the stonework around the perimeter of the enclosure has revealed no evidence of shot-holes. However a monolith situated in the NE has been split, but this would appear to be natural. The interior of the enclosure is more or less level and grass-covered. There is however, a slight drop in level in the western third of the interior. This is defined by a linear slope which may be a lynchet.”
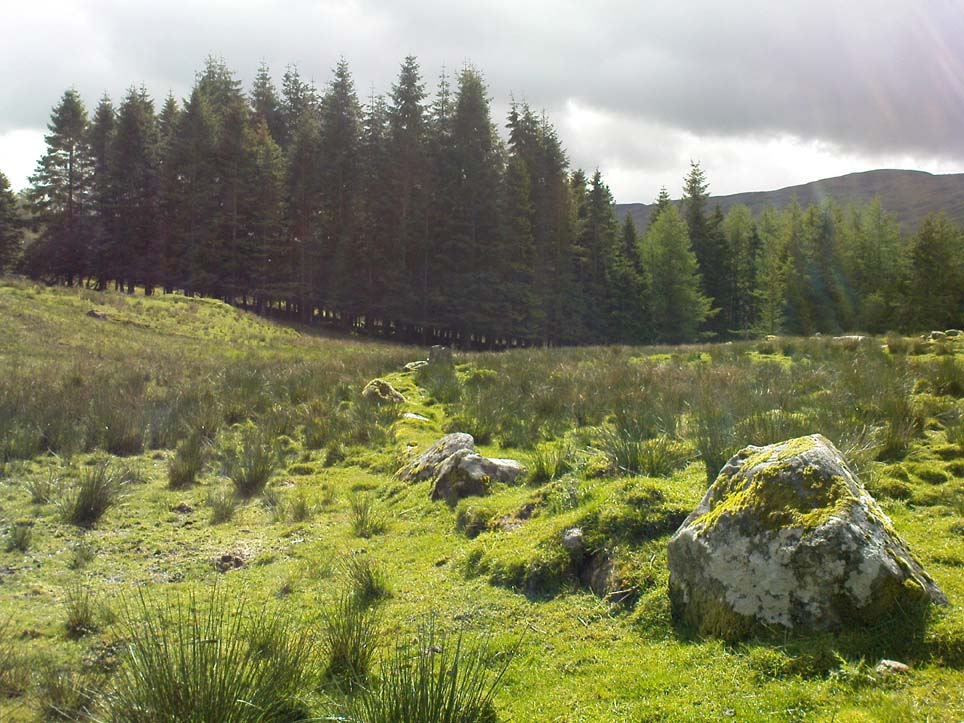
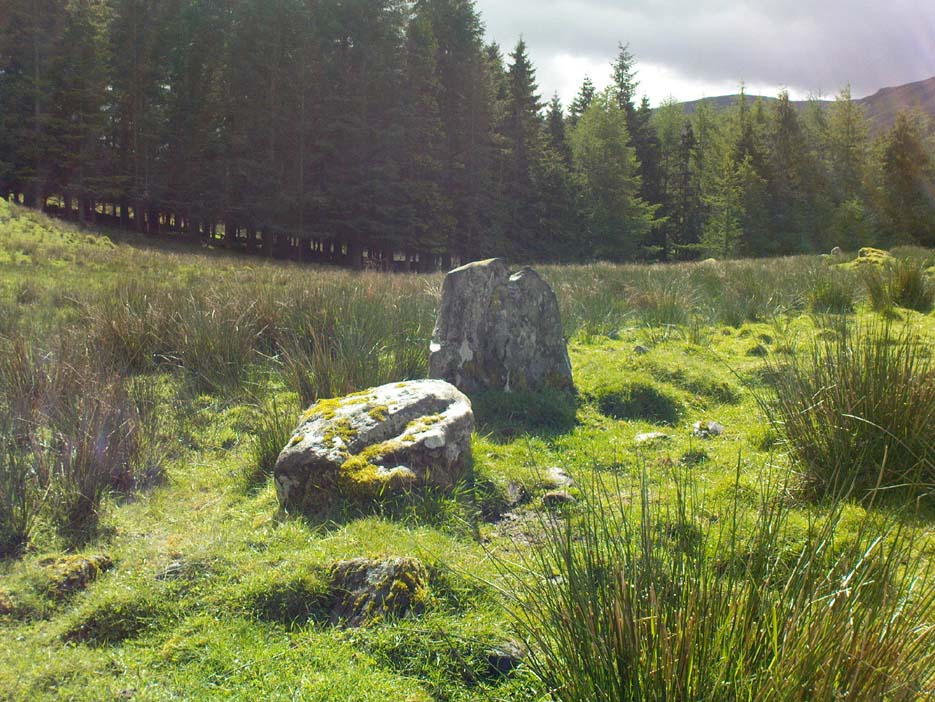


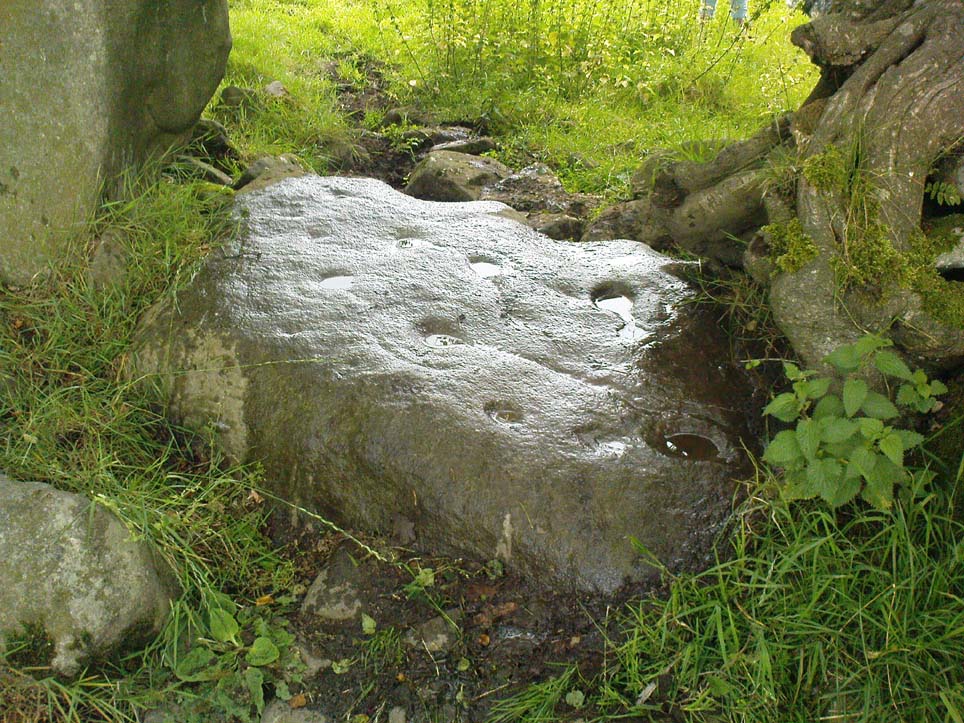
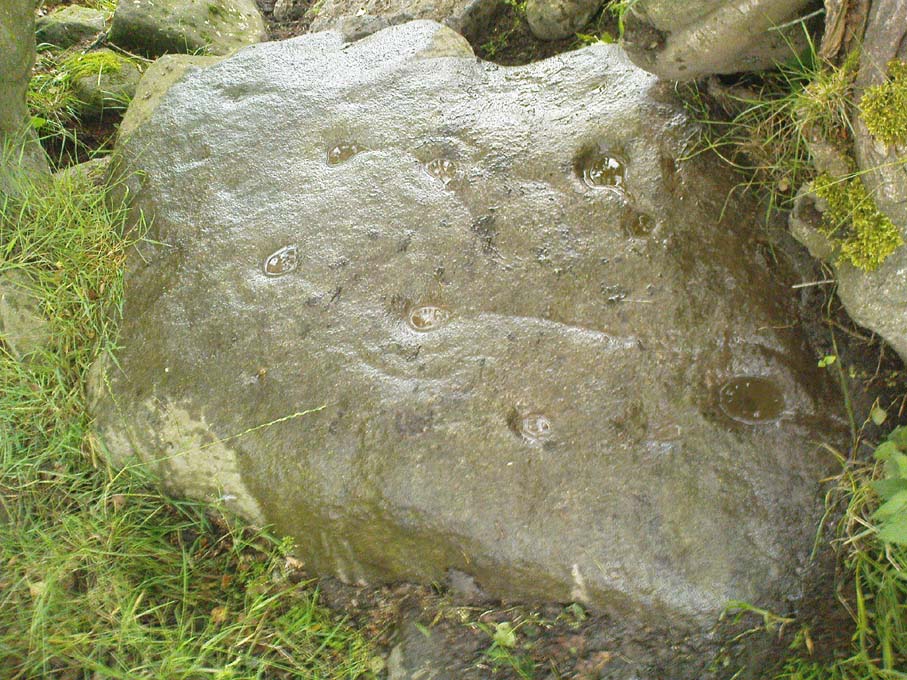
Northeast of the enclosure about 40 yards away is the normal drystone walling running along the sloping hillside. But more intriguingly to archaeologists is the second line of much more ancient walling 76 yards (70m) further up the grassy slope, running at an angle across and uphill in a northwesterly direction. This line of walling has a distinctly Iron Age flavour to it and is composed of some very large upright monoliths, almost Bronze Age in nature! It continues into the next field for some 400 yards and onto Duncroisk Burn — the other side of which we find another line of ancient walling with an impressive cup-and-ring stone incorporated.
There’s tons more to be said of this region…
…to be continued…
References:
- MacInnes, Dugald, An Archaeological Field Survey of a Deserted Settlement at Duncroisk Farm, Glen Lochay, Association of Certified Field Archaeologists: Glasgow 2001.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian