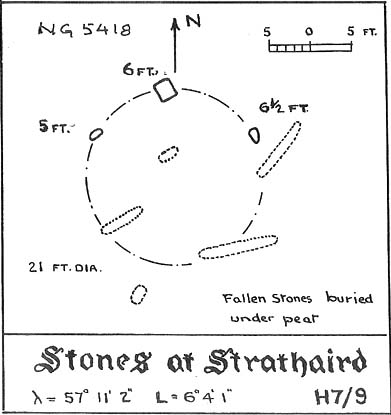
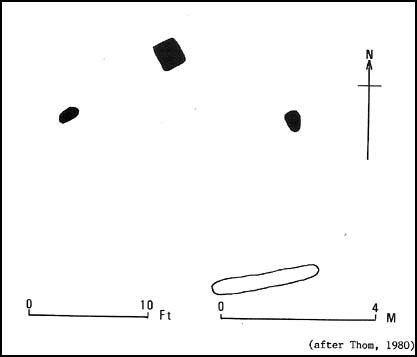
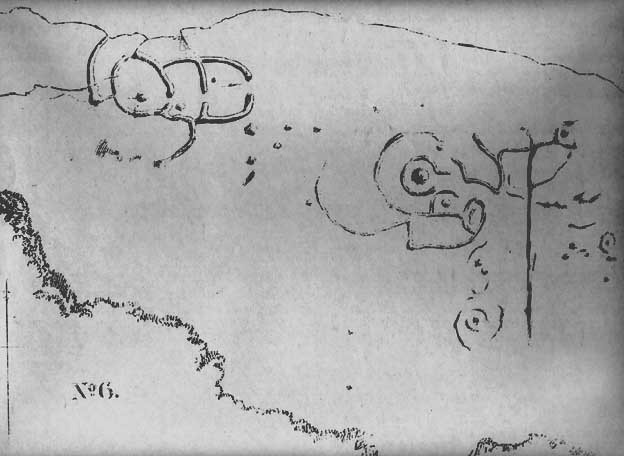Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – SK 2254 6264
Also Known as:
- Grey Ladies
- Hartle Moor Stone Circle
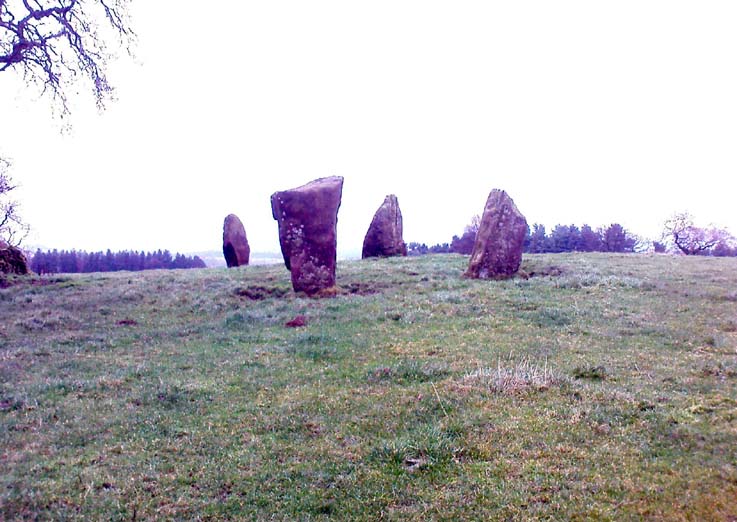

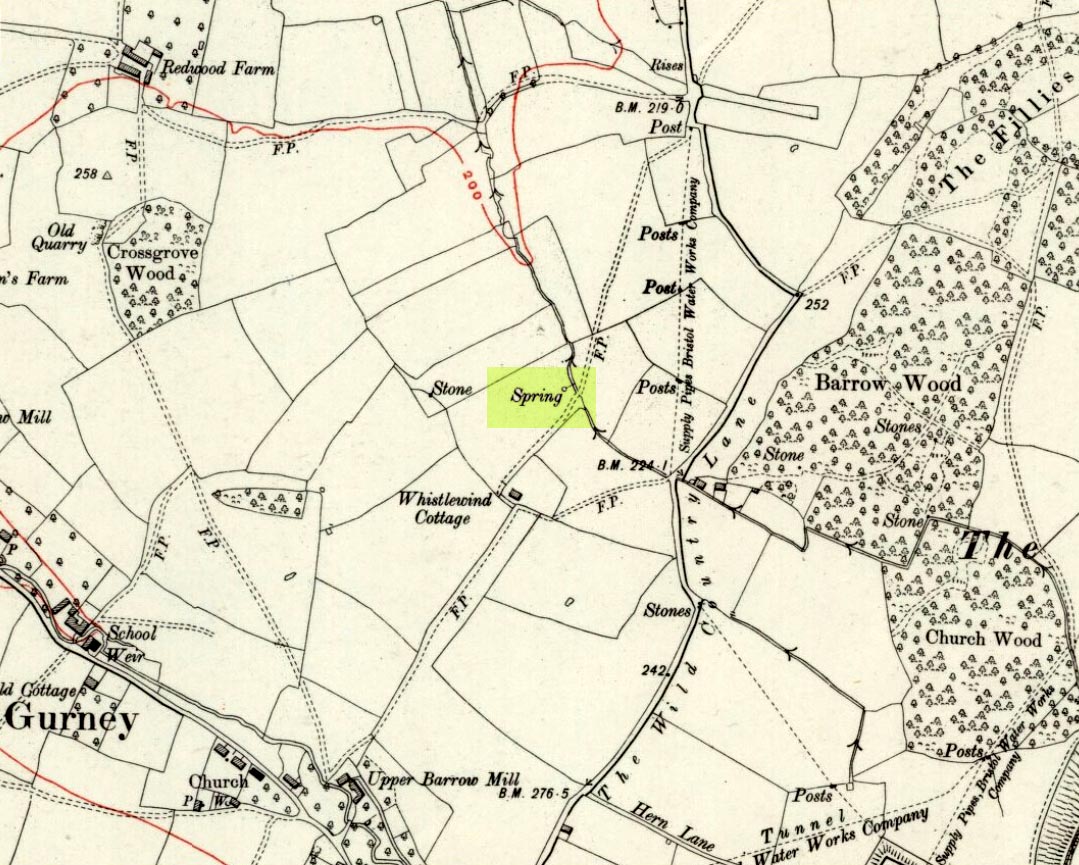
From Bakewell take the A6 Matlock road, follow this till just past the signs for Haddon Hall where you take a right (the first major junction) for Youlgreave the B5056. After about 1km take the first left over the bridge. You then take the first right turn: a steep lane with restriction signs (don’t worry there’s access for cars but no wide vehicles). Take the first left you come to by the barn and then just follow the road, up through the woodland where the lane narrows then shortly after you’ll see Robin Hood’s Stride to your left. Park a little way after the field gateway and look across the field to your left. The stones are visible from the road.
Archaeology & History
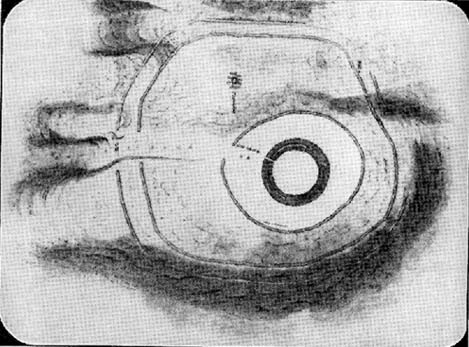
This is a fine-looking ring of stones — though perhaps the word ‘ring’ is slightly misleading here, as only four of (apparently) nine originals still remain and they are, by definition, more in a square-shape than a circle! But it’s a lovely site. When Geoff brought us here for the first time only last weekend, despite the dark clouds and cold grey day, along with the fact that we’d been sleeping rough the night before and got soaking wet through, there was a subtle feel to this place which my shivering senses still touched. Only just though…!
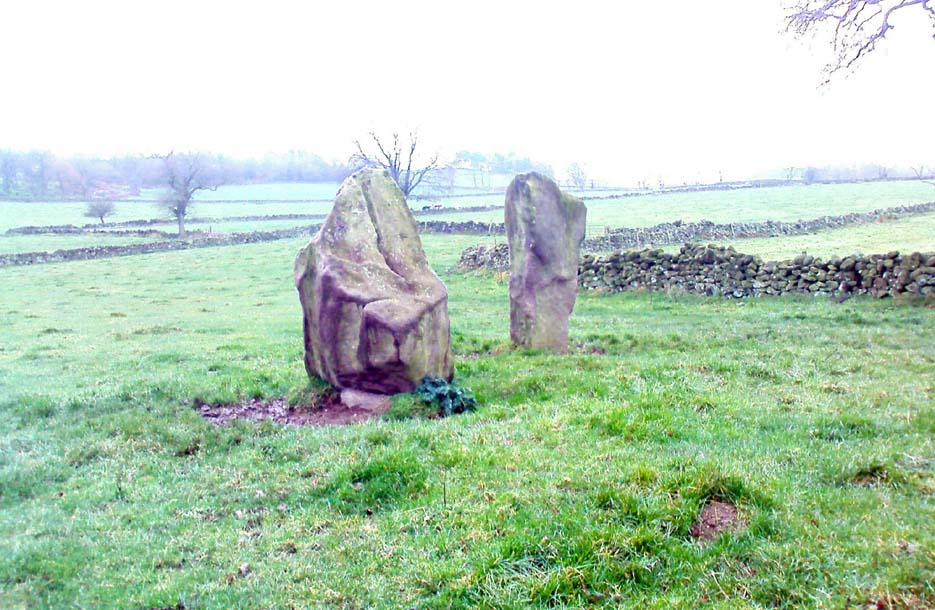

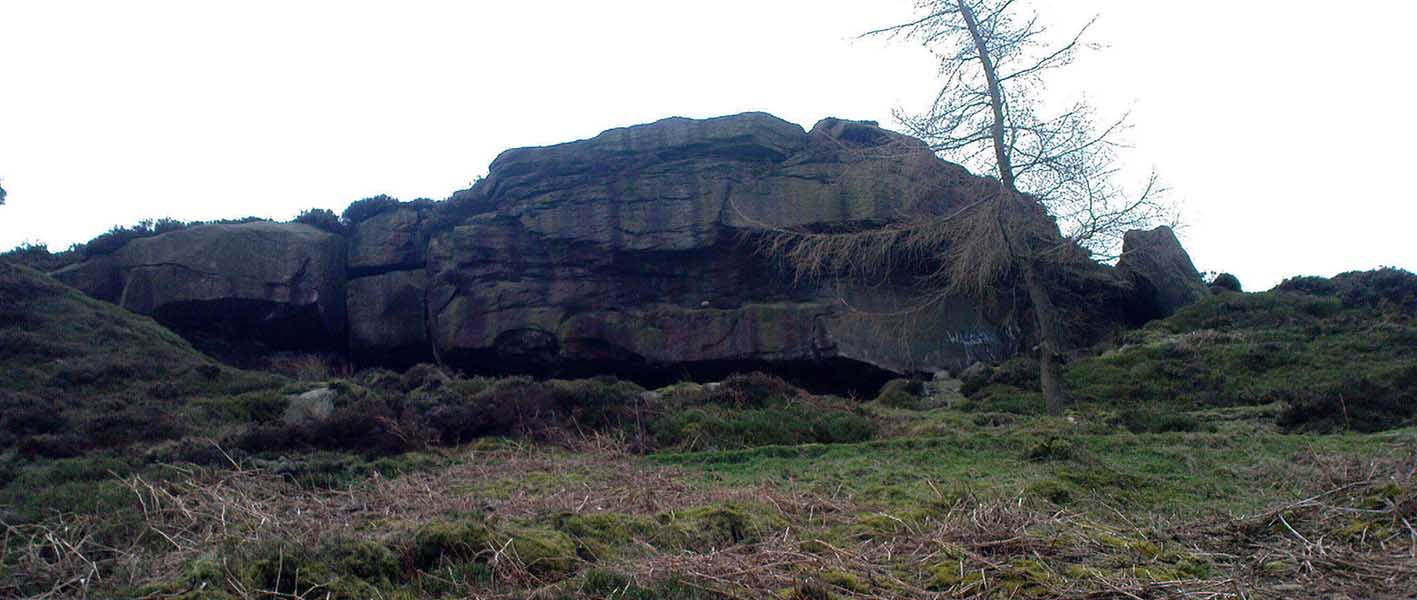
Mebbe it was the rising crags of Robin Hood’s Stride to its immediate south? Or the quietly hidden companionship with other stones and sites in the locale? I don’t really think so. There was something a little more about its own genius loci that tingled very slightly on the rise in the field upon which the circle sits. Some people would, perhaps, acquaint my sense of a subtle genius loci here to the various leys or ley-lines that have been drawn through here by other writers— but it wasn’t that.
When earlier writers came here, they too had various inspirations of differing forms. John Barnatt’s (1978) early impressions of the place had him signing astronomical events in and around the remaining stones here, despite knowing that the site had been damaged. In later years he revised his early notions — as most of us do as our perspectives are enriched — but the astronomy is still assumed here. As Clive Ruggles (1999) told:
“Other rings are located where natural features coincide with astronomical events, such as Nine Stone Close in Derbyshire…from which the Moon at the southern major standstill limit, sets behind the gritstone crag of Robin Hood’s Stride to the SSW, between ‘two stubbly piles of boulders jutting up at either end of its flat top.'”

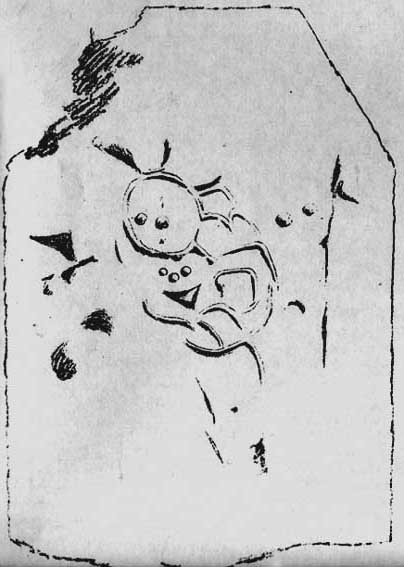
The stones that remain here are quite tall, between 6½ and 8 feet tall. One of them seems to have originally been taken from a stream or river-bed. They stand upon the small rise in the field and has diameters of 40 and 45 feet respectively. Aubrey Burl described there being seven uprights still here in 1847, and the early drawing of the site near the end of the 18th century by Major Hayman Rooke highlights 6 stones around the spot where the circle now stands. In J.P. Heathcote’s (1947) summary, he wrote that,
“Bateman, in his Vestiges, says an excavation in 1847 yielded some indications of interments in the form of ‘several fragments of imperfectly-baked pottery, accompanied by flint both in a natural and calcined state.’ In 1877, Llewellyn Jewitt and Canon Greenwell…turned their attention…to the Nine Stones. They dug at the foot of the second highest stone and the Canon directed a good deal of digging within the circle, but nothing special turned up. The area in the circle is now quite level, but it is probable that there was, as Bateman says, a tumulus in the centre.”
This latter remark is the impression I got of the place. Tis a really good little site. All around here are a number of other sites: cup-marked stones, enclosures or settlements, prehistoric trackways, and more.
Folklore
One of the old names of this site was The Grey Ladies. This came from the well known tale found at other sites across the world, that some ladies were dancing here at some late hour and were turned into stone. A variation on this theme told how Robin Hood stood on the nearby rock outcrop to the south and pissed over the landscape here, “where seven maidens upon seeing it turned to stone.” In this case, Robin Hood replaced an older, forgotten account of a giant, who forged the landscape and the sites around Harthill Moor.
Another tale — whose origins and nature are allied to that of the petrification of the Grey Ladies — narrated with considerable sincerity by local people, was that the circle was a place where the little people gathered and where, at certain times of the year, “fairy music and the sight of hundreds of dancing shapes around the stones” would happen.
Said by Rickman and Nown (1977) to be “Derbyshire’s most magical ancient site,” they thought the site was on a ley that linked up with Arbor Lowe, less than 5 miles west, crossing a couple of tumuli on its way.
References:
- Barnatt, John, Stone Circles of the Peak, Turnstone: London 1978.
- Burl, Aubrey, A Guide to the Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 1995.
- Clarke, David, Ghosts and Legends of the Peak, Jarrold: Norwich 1991.
- Heathcote, J. Percy, Birchover – Its Prehistoric and Druidical Remains, Wilfrid Edwards: Chesterfield 1947.
- Rickman, Philip & Nown, Graham, Mysterious Derbyshire, Dalesman: Clapham 1977.
- Ruggles, Clive, Astronomy in Prehistoric Britain and Ireland, Yale University Press 1999.
- Thom, A., Thom, A.S. & Burl, Aubrey, Megalithic Rings, BAR: Oxford 1980.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian