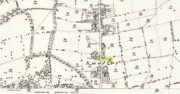
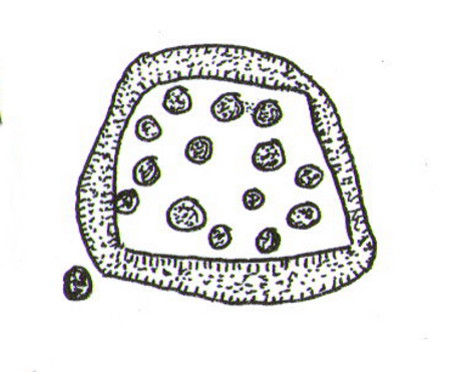
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – SK 3211 6866

From Holymoorside, take the long straight Loads Road running west out of the town into Longside Road. ¾-mile along, past Home View and just before Well Lane (on the right), there’s a public footpath sign pointing into the fields on your left. Walk dead straight, dead south along the wallside for 450 yards, then walk straight left again along the other wall until you reach the tiny bit of moorland less than 150 yards away. The carved rock is just on the other side of the stile at the edge of the old walling. You’ll find it.
Archaeology & History
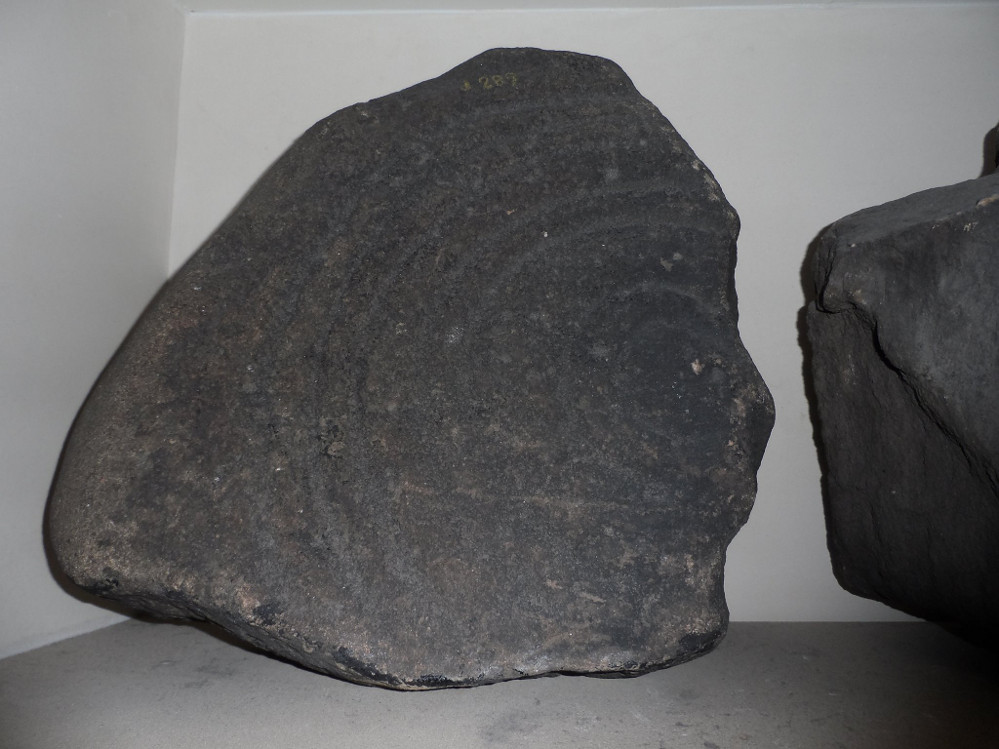
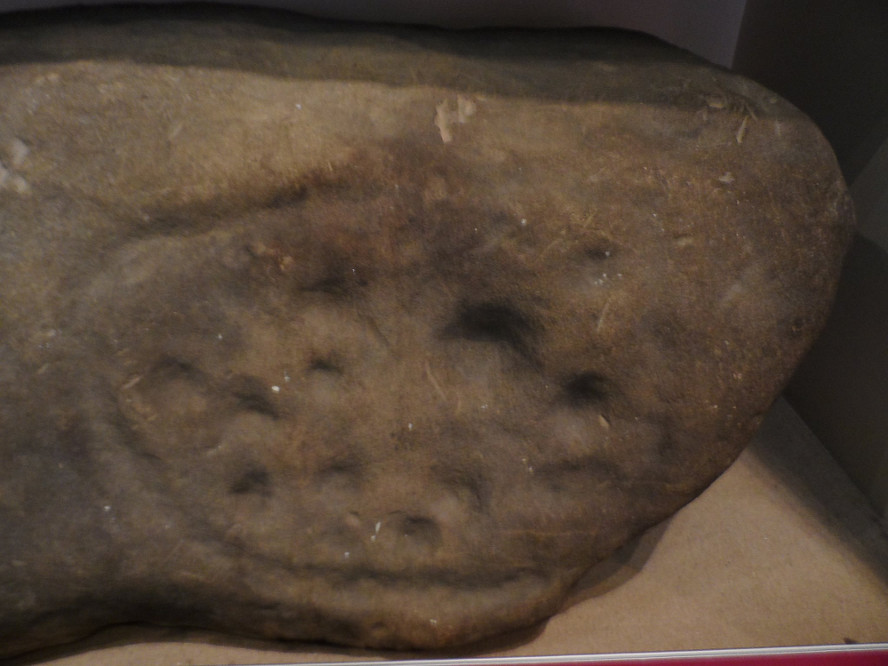
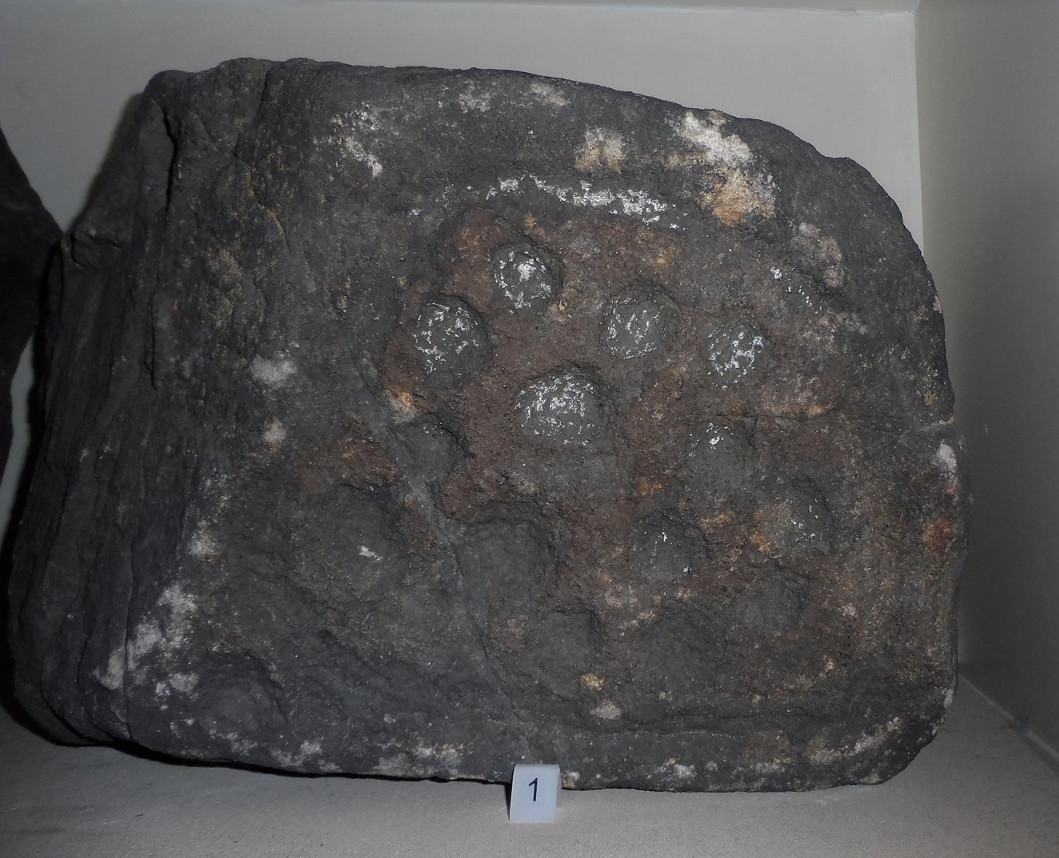
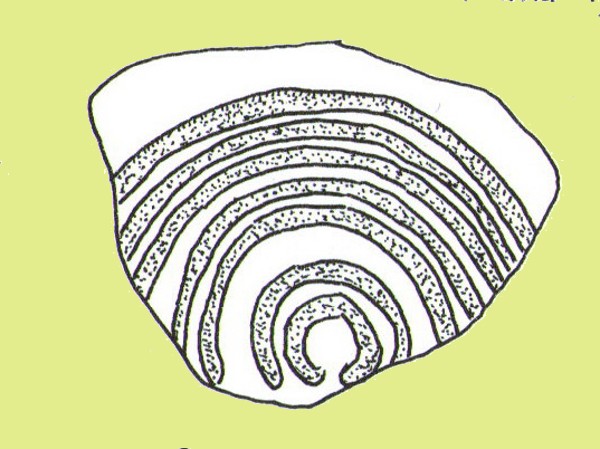
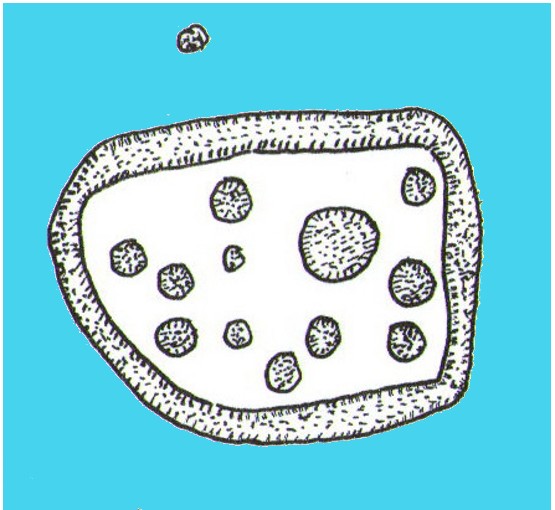
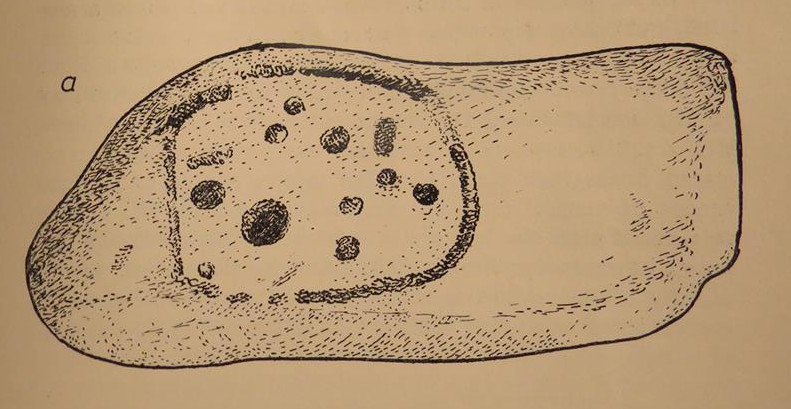
Rediscovered sometime in 2002, this would seem to be an isolated cup-and-ring stone. It was first mentioned in John Barnatt’s (2003) short gazetteer of Peakland petroglyphs, where he wrote,
“This irregularly-shaped small boulder was identified recently lying amongst post-medieval field clearance adjacent to a field corner and footpath… Its upper parts ar covered with 40-46 cupmarks. On the exposed irregular top they are badly worn and sometimes uncertainly identified. In one instance a cup is partly encircled by a worn ring, while a second partial ring nearby may be fortuituous. On a ledge near one edge of the boulder preservation is better and the cups are clearly defined and densely arranged.”
The stone looks as if it’s been moved into its present location, obviously for use in the walling. It’s original position would have been somewhere close by, but we know not where that might be.
References:
- Barnatt, John & Robinson, F., “Prehistoric Rock Art in Ashover School and Further New Discoveries Elsewhere in the Peak District,” in Derbyshire Archaeological Journal, 123, 2003.
Links:
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Geoff Watson for use of the photos in this site profile. It wouldn’t have been written without them.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian