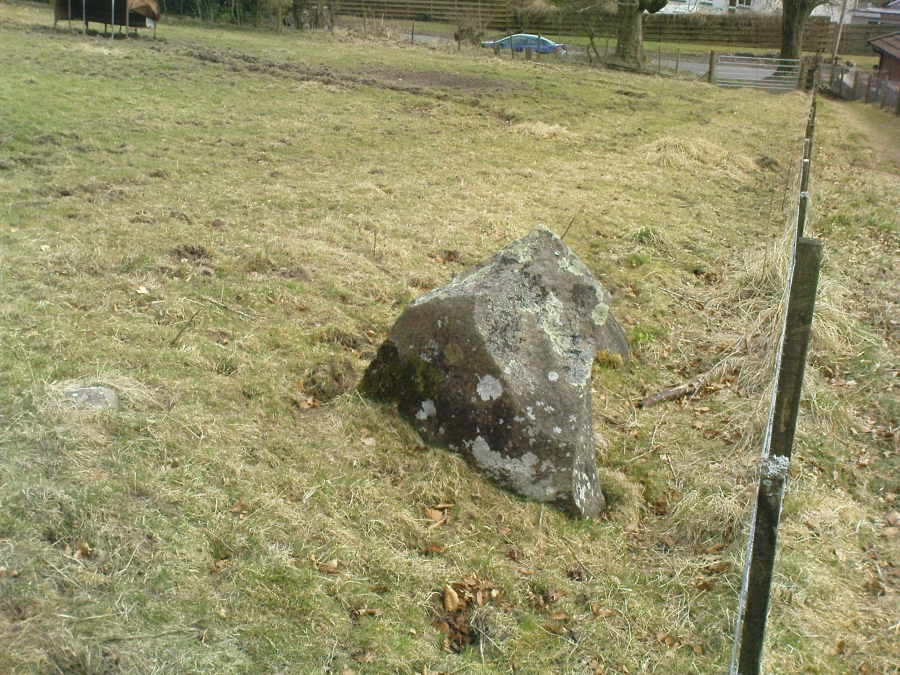
Legendary Rock: OS Grid Reference – NN 7081 2325
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 24876
- Dundurn
- Fillan’s Chair
- St. Fillan’s Bed
Getting Here
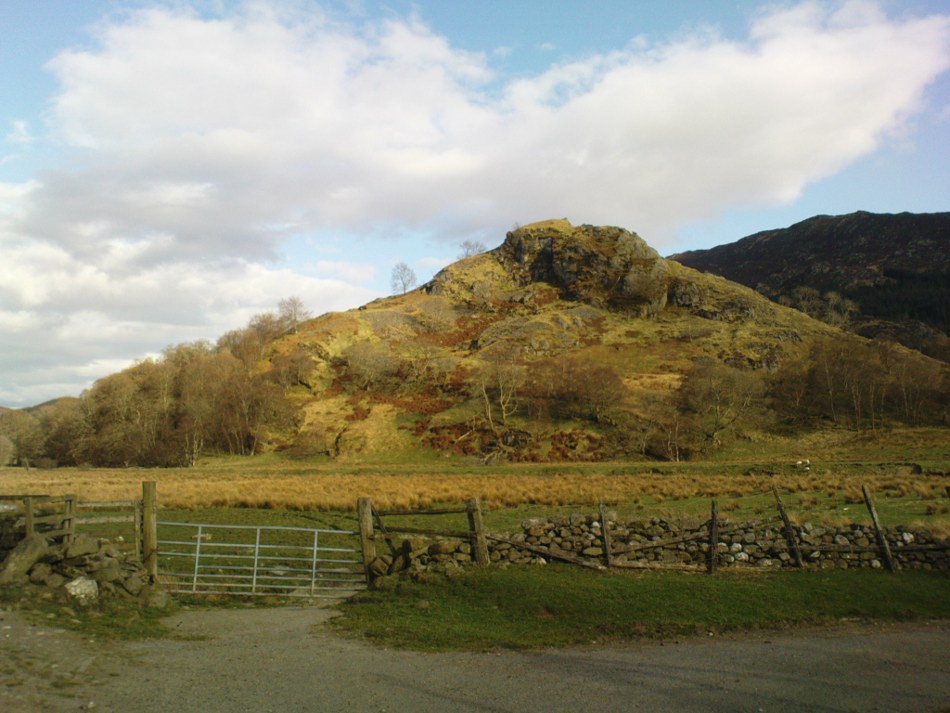

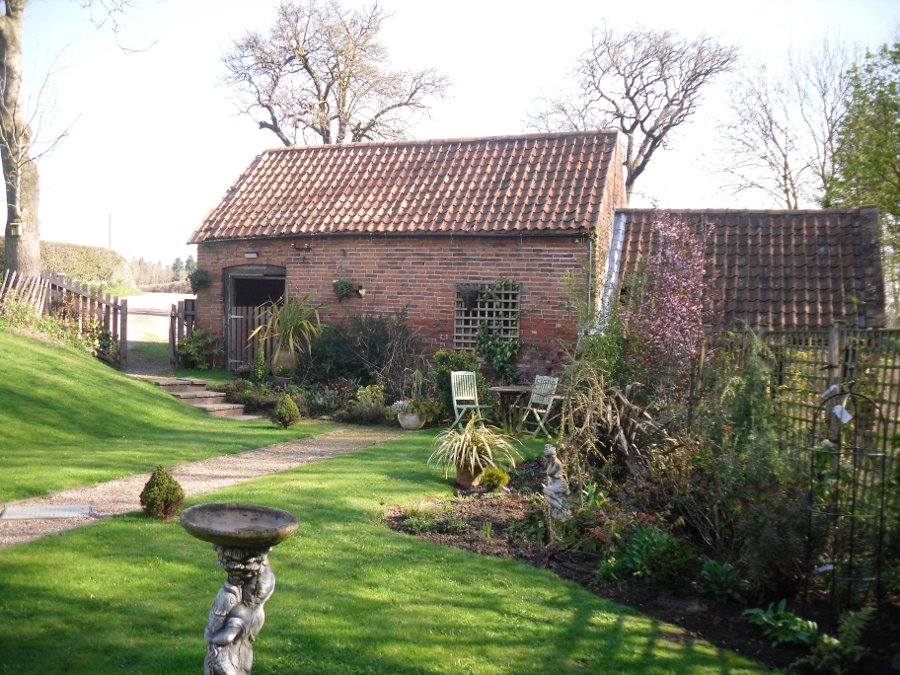
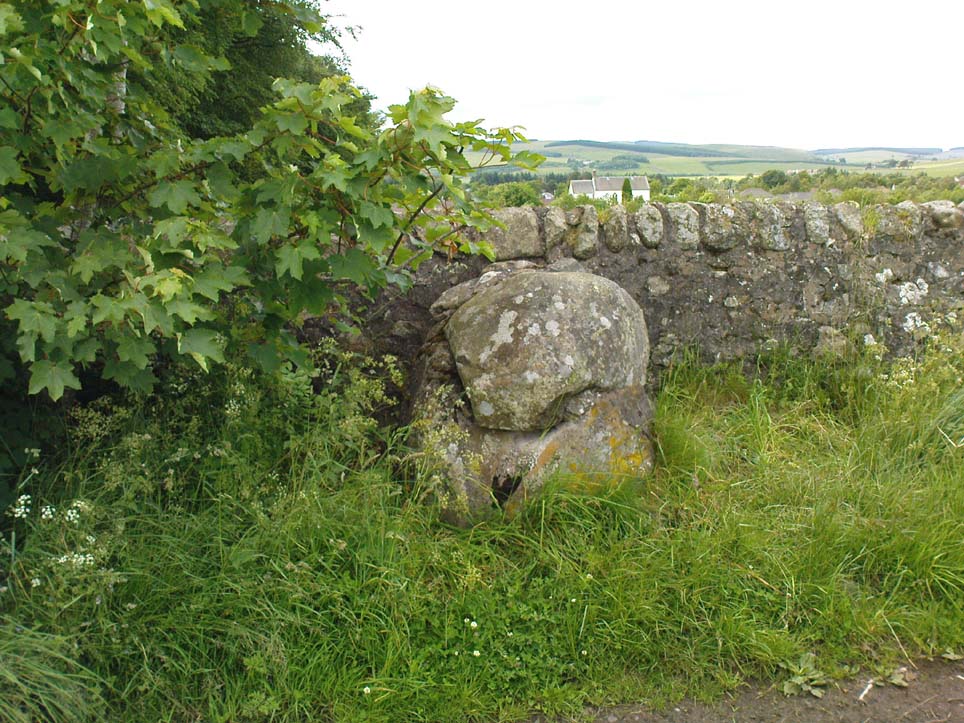
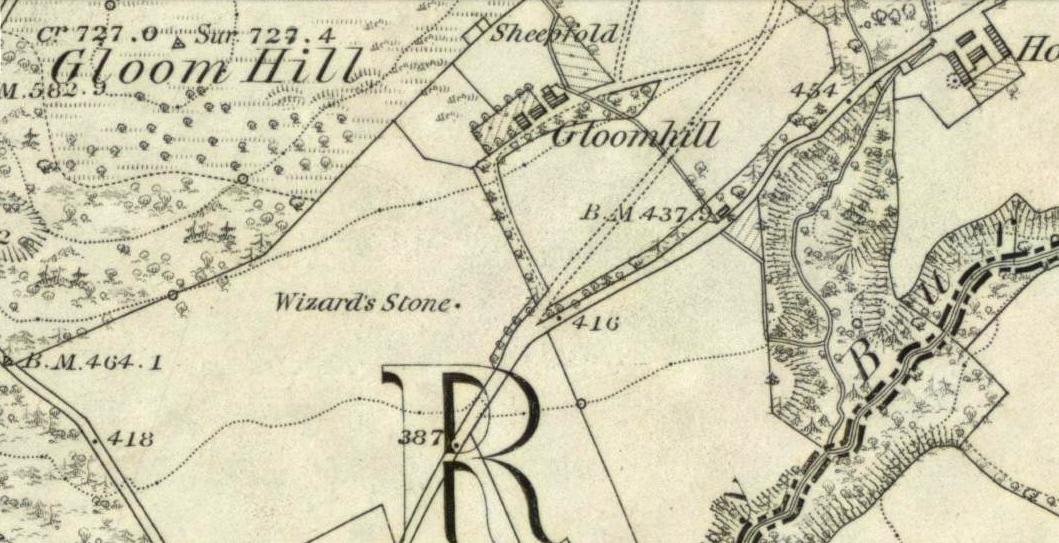
Not hard to find. Between the small towns of Comrie and St. Fillans along the A85 road, keep your eyes peeled for the small but rocky crags that rise in front of the background of dramatic mountains not far from the roadside to the south. It looks truly majestic even on a dull day. Just as you reach the eastern edge of St. Fillans village, take the small road over the river-bridge and go to the golf club. Walk past the golf club itself, keeping along the track that leads you to Dundurn hill. It’s easy enough. Then climb to the very top of the hill where you’ll find this curious, large, flat bed-like rock right in front of you!
Archaeology & History
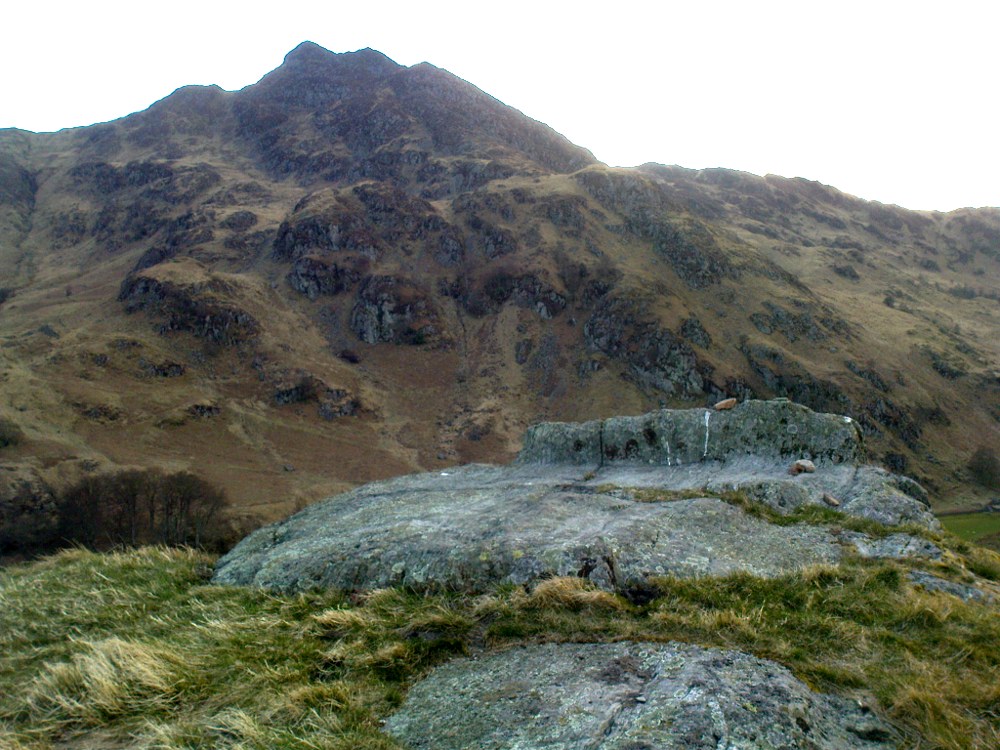

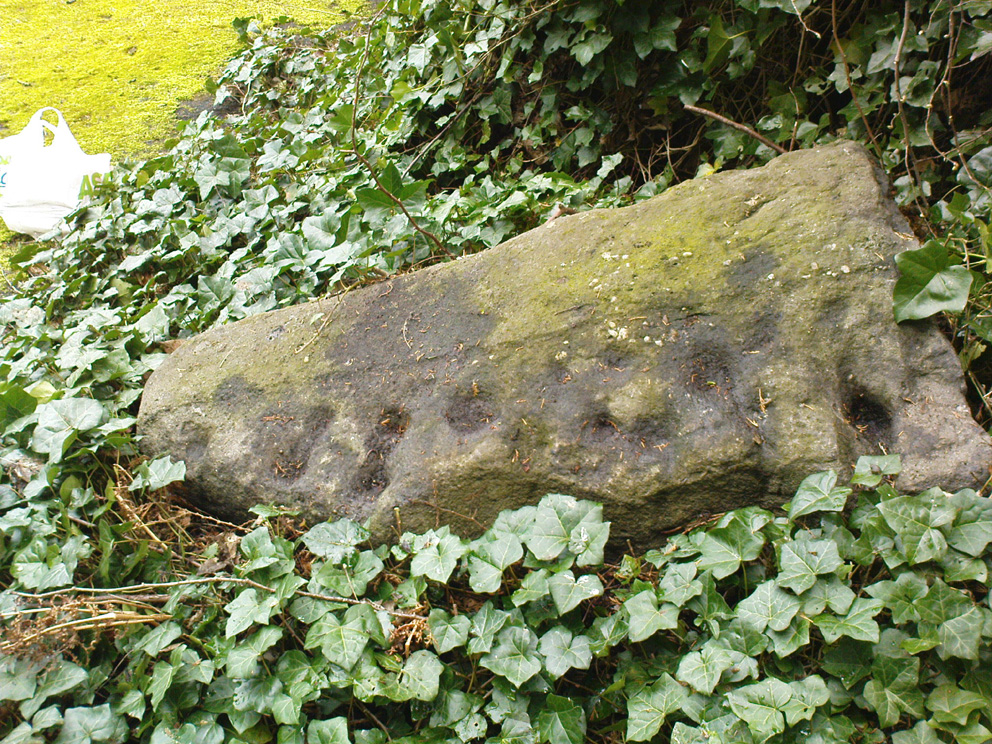
The archaeological data for St. Fillan’s Chair relates more to the folklore practices of the people upon Dundurn hill than anything else and ostensibly little can be said by such students. The place is more satisfying for geologists than archaeologists, who would adore the rocky fluctuations and geophysical propensities with greater verve than any archaeologist could muster! For this rocky bed-shaped feature is a fascinating structure whose only potential interest to archaeologists are what may be a couple of reduced cup-marks on the top of the stone (and even then, such potential rock art is more the province of religious historians and anthropologists than archaeologists).
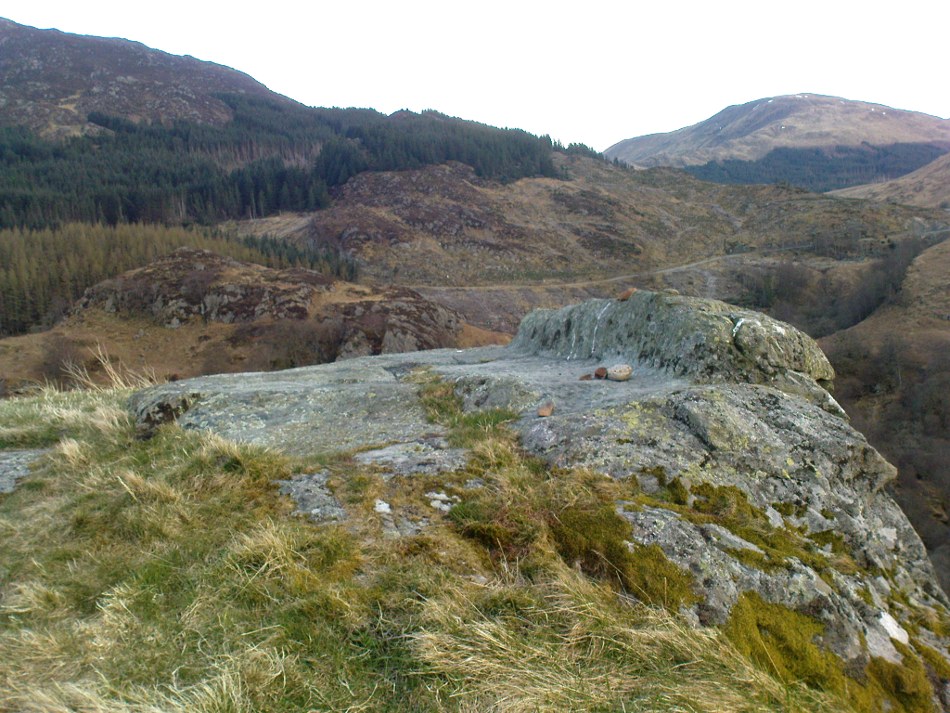
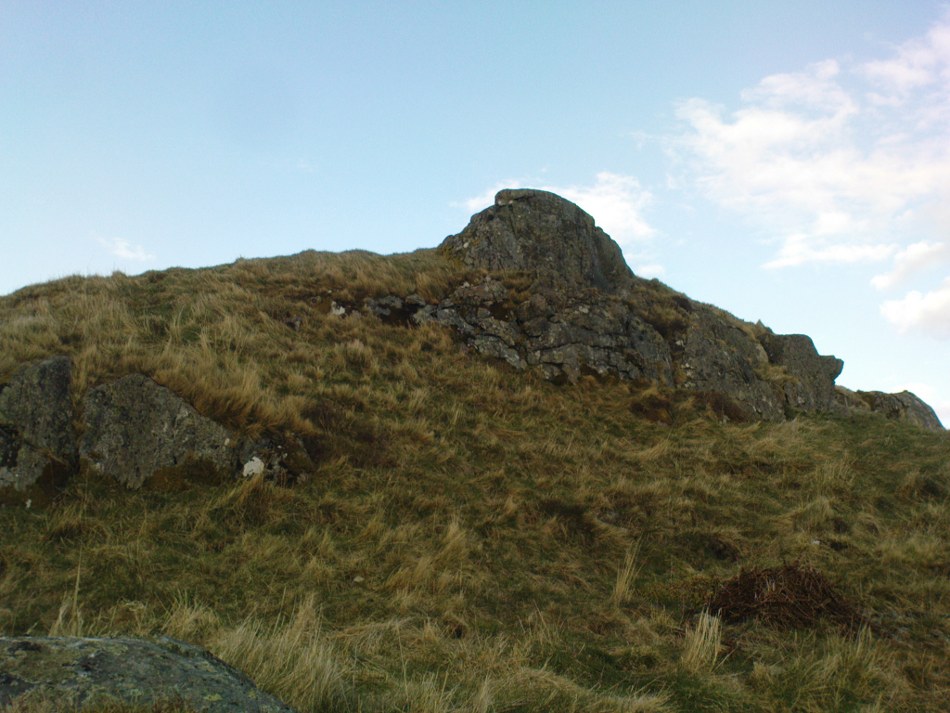


But this ‘bed’ or ‘chair’, as it was locally known, was – and it seems, still is – important in the social history of the area, as its folklore clearly tells. The ‘chair’ plays an important part in the holistic role of Dundurn as a hill, a fort, a healing centre, an inauguration site, and very probably an omphalos: a sacred centre whereupon the ordination of shamans, kings and the cosmos as a whole was brought to bear here… (these features will be explored in greater depth when I write a singular profile of Dundurn as a ‘fort’).
Folklore
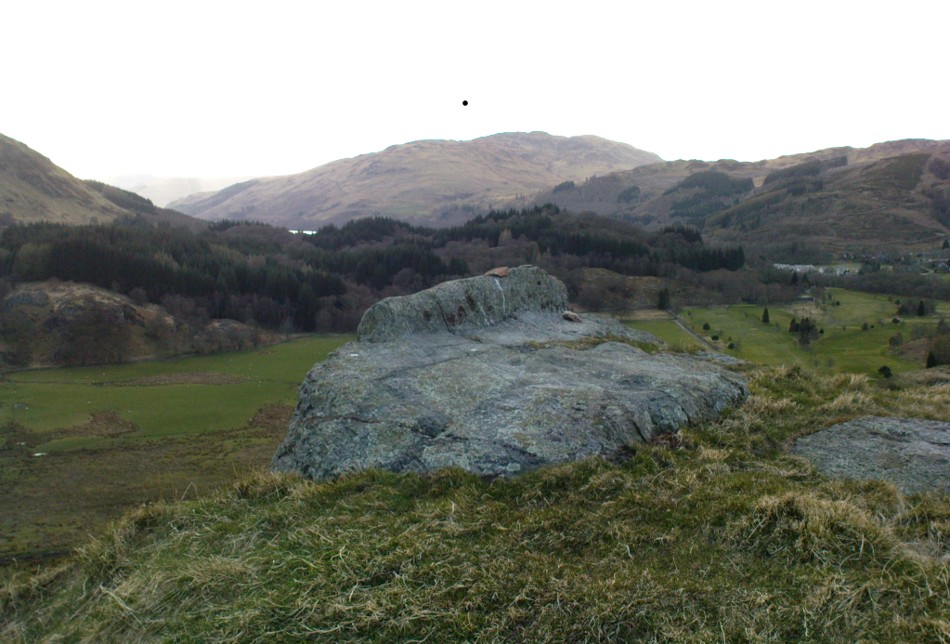

The character of St. Fillan was described by James Cockburn (1954) as “an Irish Pict” and the “son of a King – his father being Angus mac Nadfraich who died in battle in 490 AD.” Quite an important dood in his day! The relationship this early christian figure had with this Chair was in its supposedly curative properties. Yeah…you read it right: curative properties! As with countless rocks all over the world, some of Nature’s outcrop boulders were imbued with a spirit of their own and, when conditions and/or the cycle of the spirit ‘awoke’, healing attributes could be gained from the place. And such was the case at St. Fillan’s Chair, especially on Beltane morning (May 1). And some element of this traditional pilgrimage is still done; for when the author Marion Woolley and I visited the site on Mayday 2013, it was obvious that some people had been up earlier that Beltane morning and left some offerings of quartz stones on the top end of the bed.
The earliest written reference of this medicinal virtue was told in the Old Statistical Account of Perthshire (1791):
The rock on the summit of the hill, formed, of itself, a chair for the saint, which still remains. Those who complain of rheumatism in the back, must ascend the hill, sit in this chair, then lie down on their back, and be pulled by the legs to the bottom of the hill. This operation is still performed, and reckoned very efficacious.
More than a hundred years later, the sites was still being used and was described in similar vein in MacKinlay’s (1893) excellent study:
“On the top of green Dunfillan, in the parish of Comrie, is a rocky seat known in the district as Fillan’s Chair. Here, according to tradition, the saint sat and gave his blessing to the country around. Towards the end of last century, and doubtless even later, this chair was associated with a superstitious remedy for rheumatism in the back. The person to be cured sat in the chair, and then, lying on his back, was dragged down the hill by the legs. The influence of the saint lingering about the spot was believed to ensure recovery.”
The origins of this dramatic rite were probably pre-christian in nature and we should have little doubt that St. Fillan replaced the figure of a shaman or local medicine woman of some sort. The ritual “dragging down the hill” may be some faint remnant of initiation rites…
References:
- Cockburn, James H., The Celtic Church in Dunblane, Friends of Dunblane Cathedral 1954.
- Eliade, Mircea, Rites and Symbols of Initiation, Spring: Woodstock 1995.
- Finlayson, Andrew, The Stones of Strathearn, One Tree Island: Comrie 2010.
- Hunter, John, Chronicles of Strathearn, David Philips: Crieff 1896.
- MacKinlay, James M., Folklore of Scottish Lochs and Springs, William Hodge: Glasgow 1893.
- Shearer, John, Antiquities of Strathearn, David Philips: Crieff, 1883.
- Skene, William F., Celtic Scotland (3 volumes), Edmonston & Douglas: Edinburgh 1876-1880.
- Toulson, Shirley, Celtic Journeys in Scotland and the North of England, Fount: London 1995.
Links:
© Pual Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian