Settlement: OS Grid Reference – SU 5735 9364
Also Known as:
- Dorchester Dykes
- Dorchester Fort
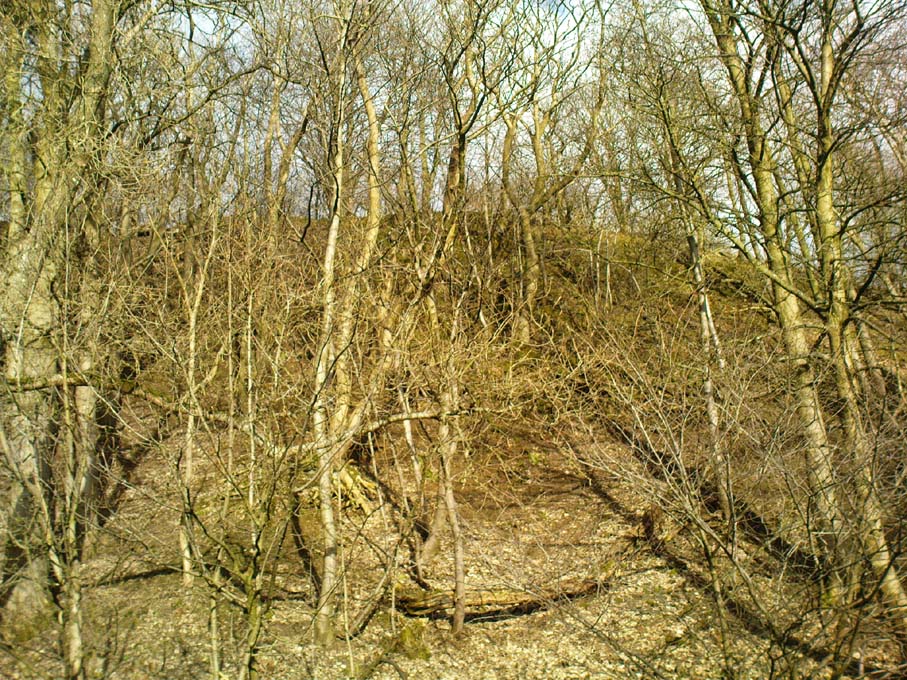
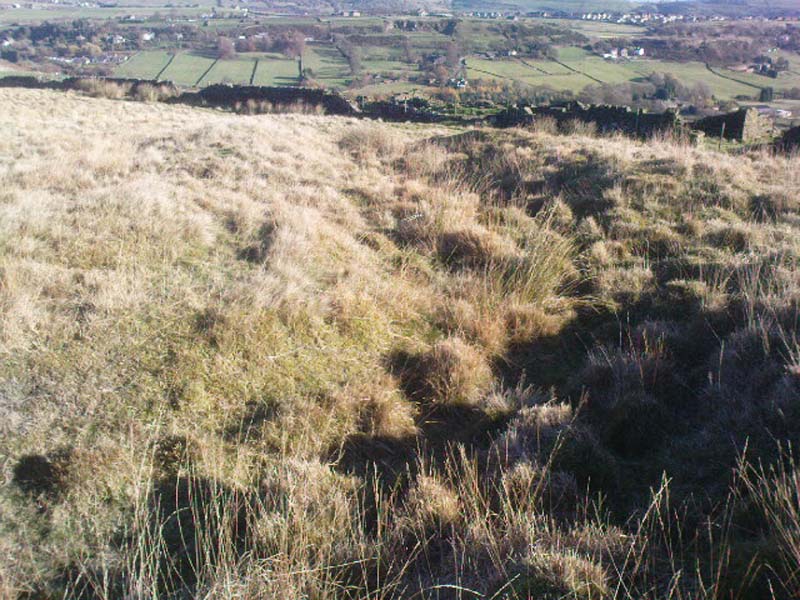
Easy to find. From Dorchester town centre, take the road at the bottom of town where the church is and walk along to the end where a footpath takes you into the field. Once here you’ll note a rise in the land at the end, stretching away to the west and the River Thames. That’s your Dyke Hills!
Archaeology & History
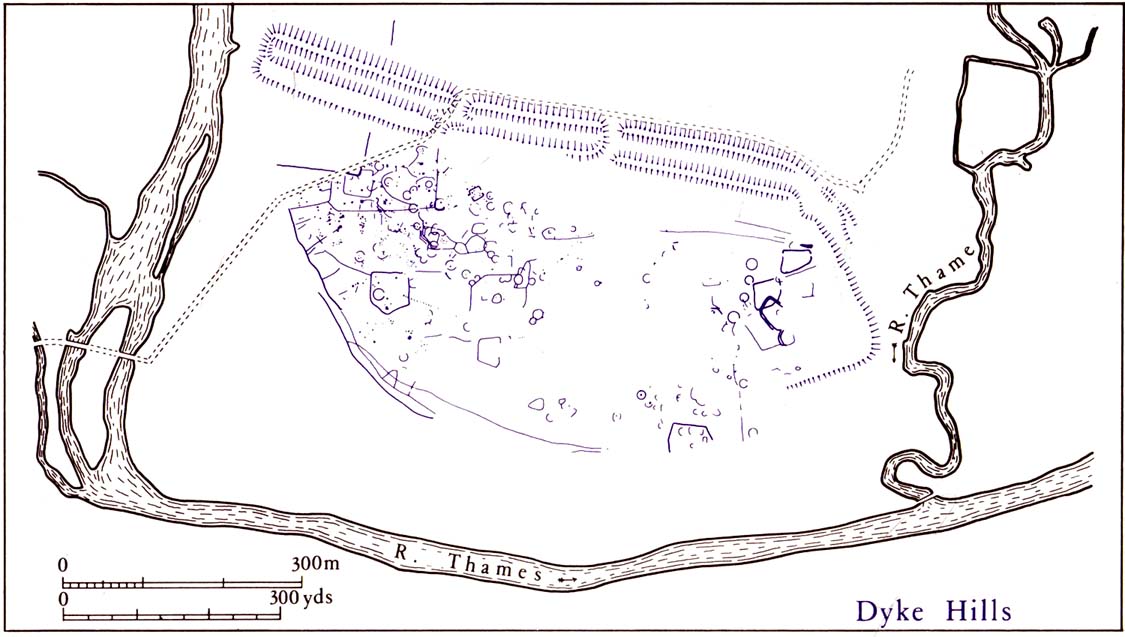
This site is another example of the considerable neglect shown to the prehistoric archaeological remains in and around the Dorchester region, despite Jean Cook (1985) describing the place as “a site of major local, regional and national importance.” Which is a pity, as the site here was once huge and it seems that much could have been learned from here. (you’ve gotta ask: do those doods who allegedly work for English Heritage care more for the ancient sites, or the money their organization gets?)
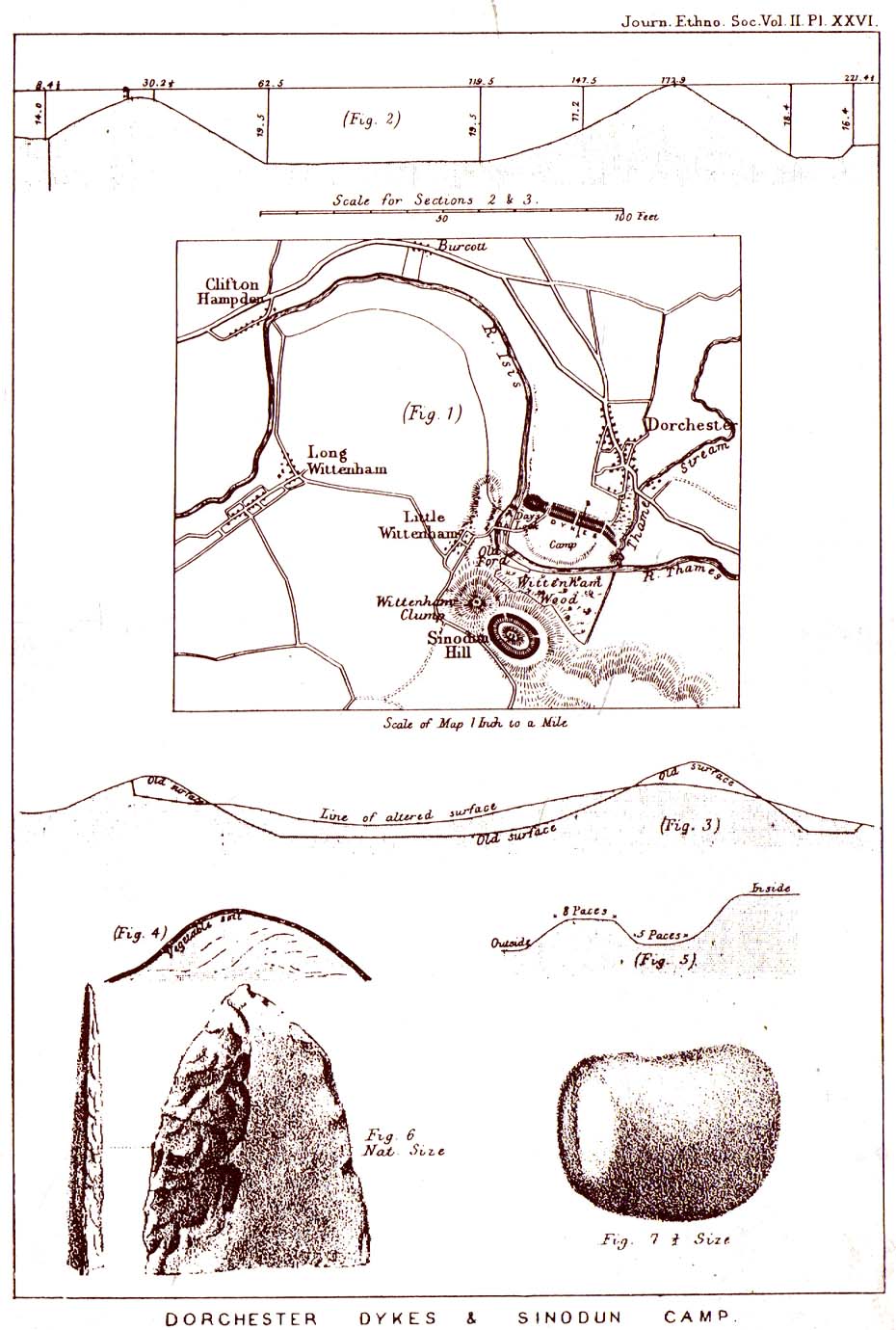
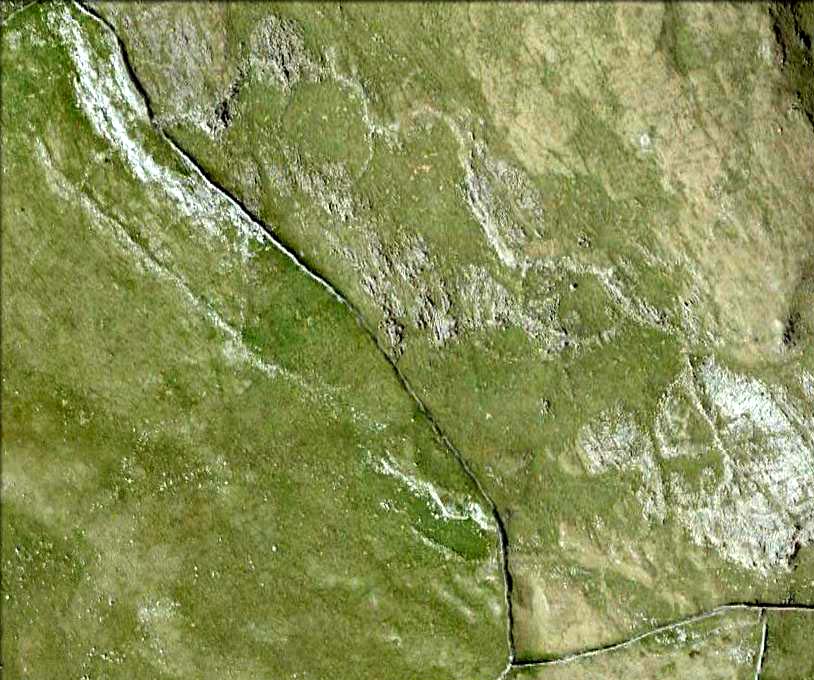
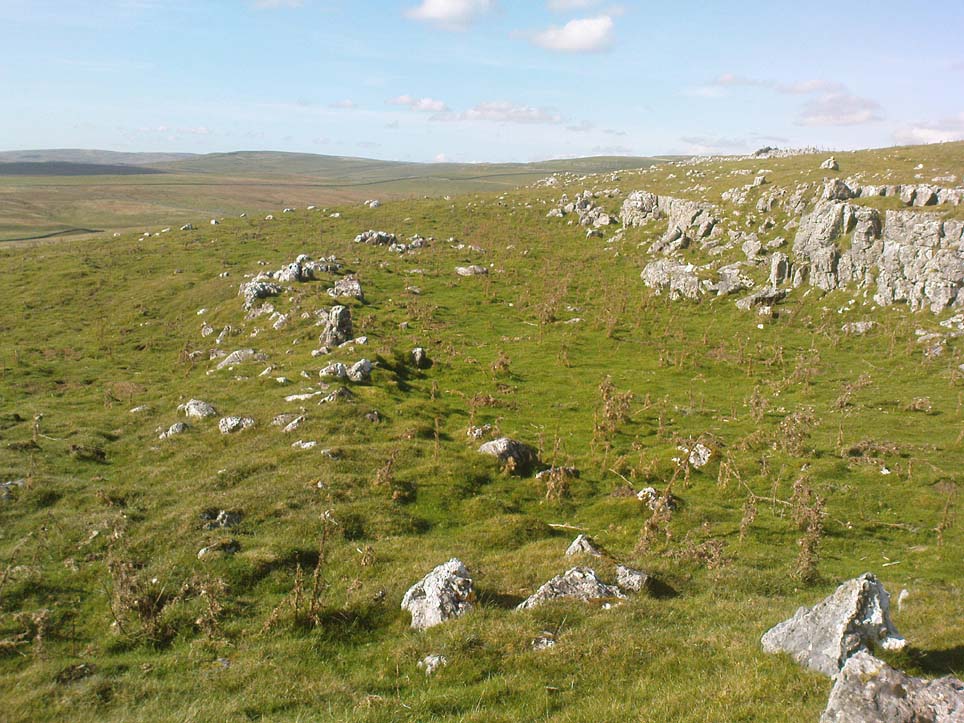
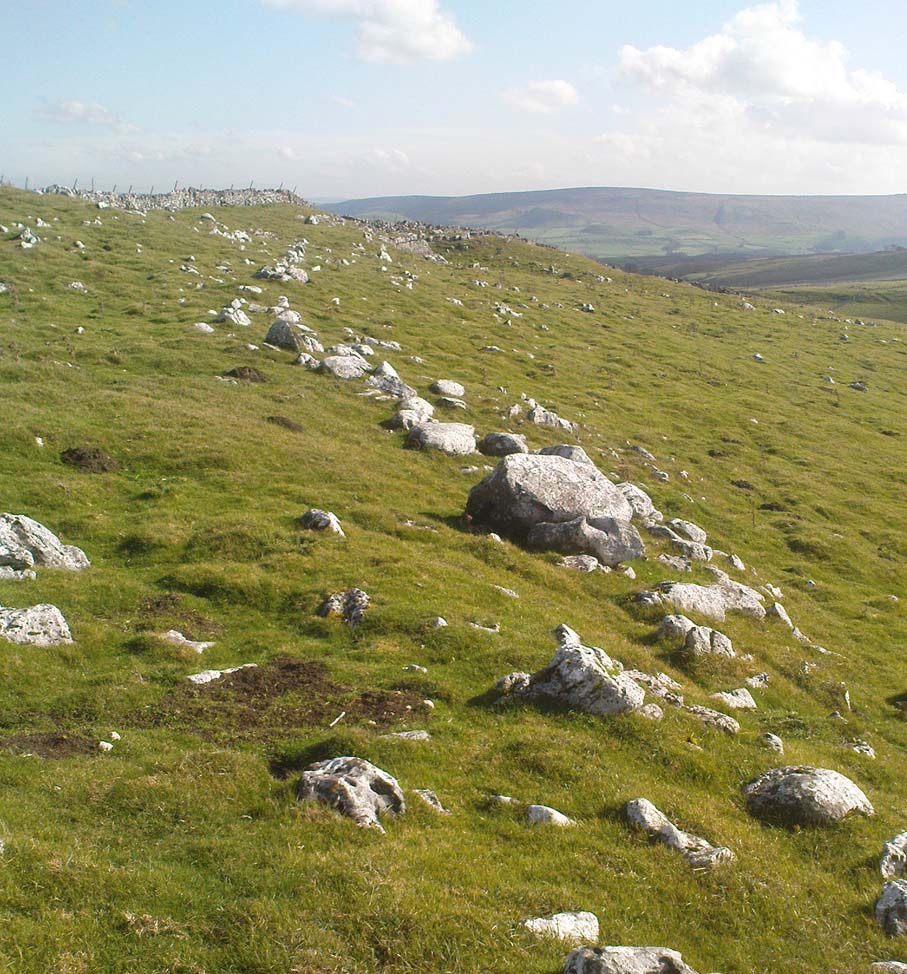
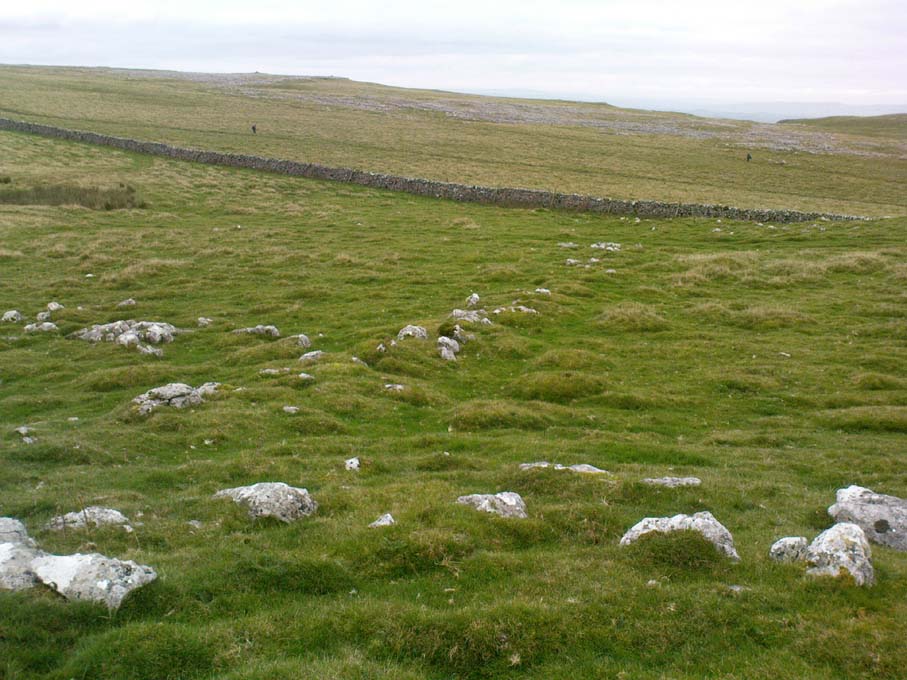
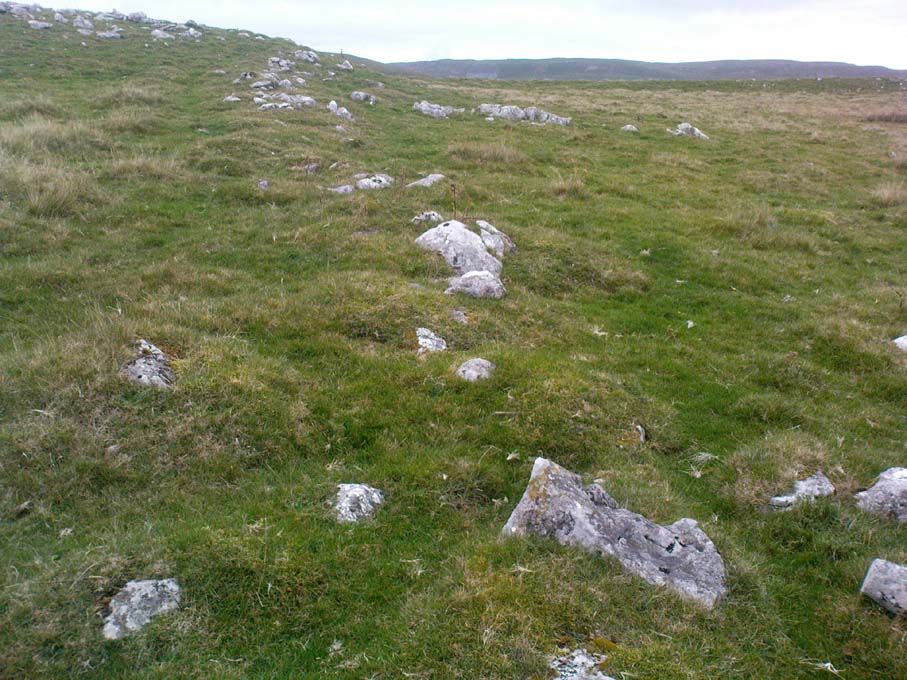
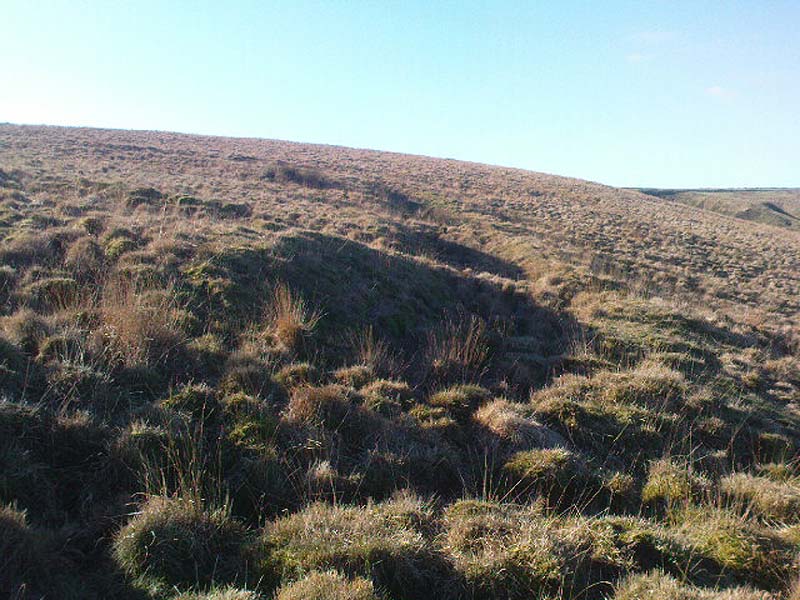
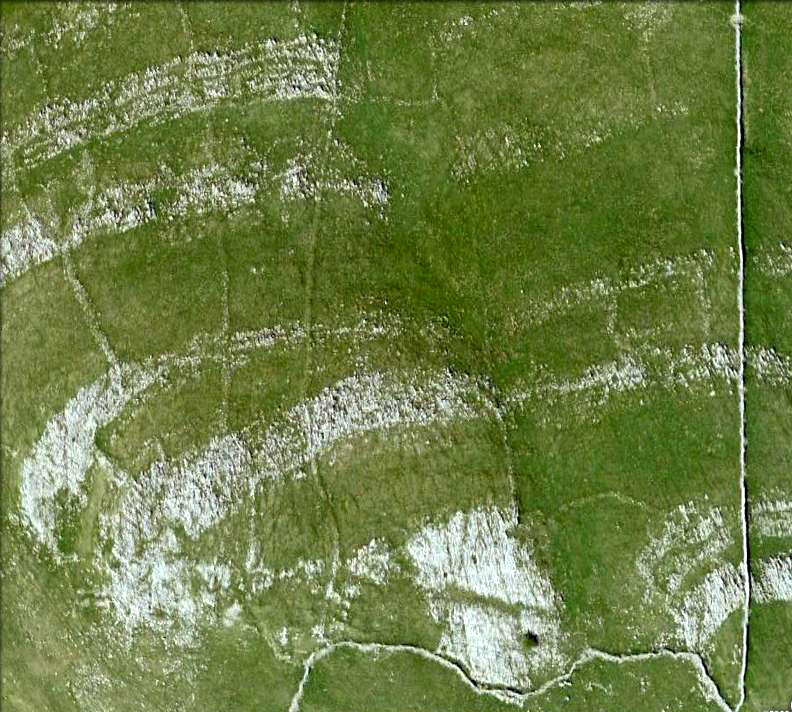
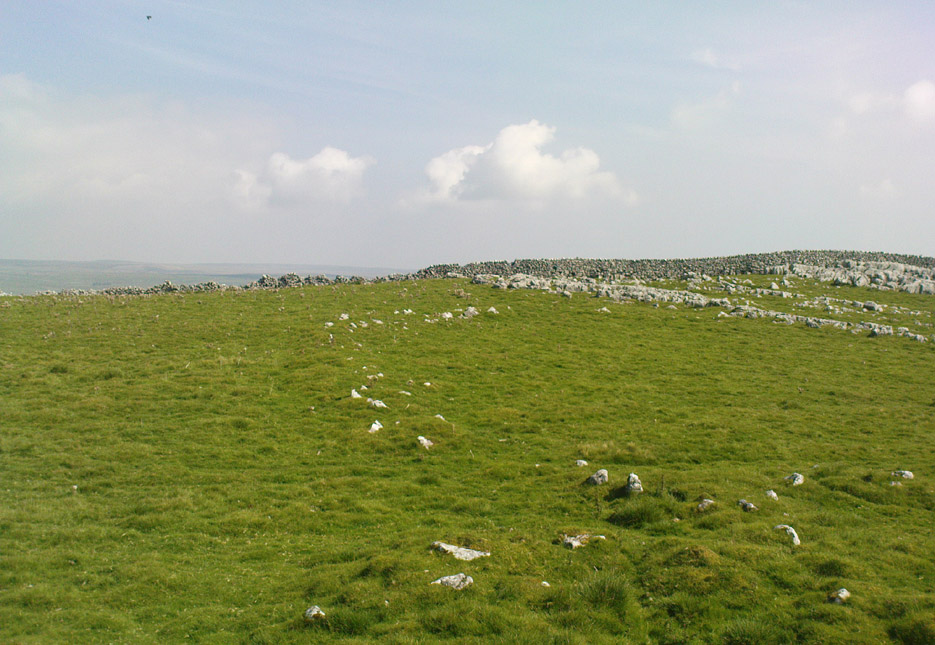
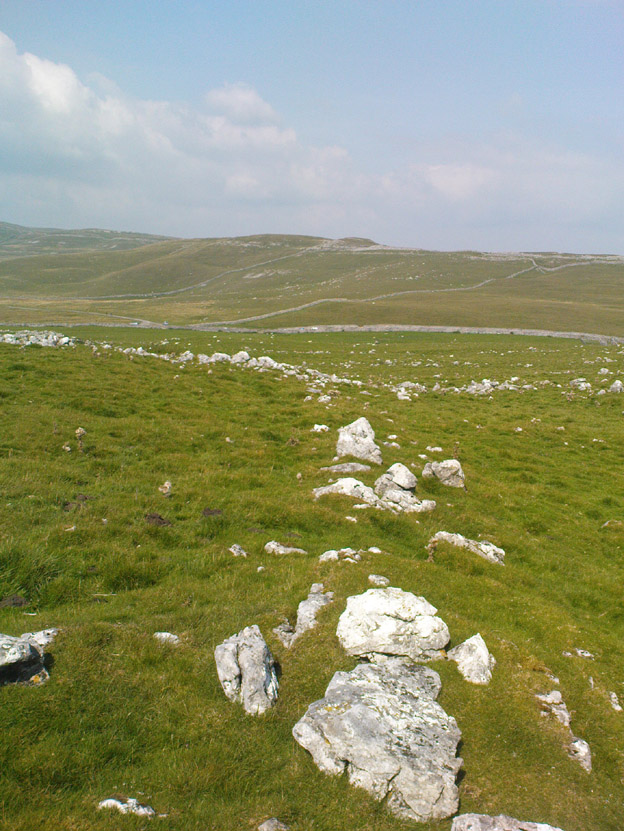
It would seem that the majority of the site was Iron Age in nature, with snifflings of Bronze Age remains scattered here and there. The primary position of the massive dykes and construction of internal domestic structures immediately below (south) of the dykes, was hemmed in on all sides by the surrounding River Thames and one of its tributaries, giving the place an excellent position in terms of food, plus shelter and protection from any intrusive tribes or hungry winter animals.
The first excavation at the huge dykes that define the northern edge of this ‘monument’ was done in 1870 by the renowned General Pitt-Rivers, then later Colonel Lane-Fox (at the time the Secretary of London’s Ethnological Society), as they were very concerned about the damage that was being inflicted upon the site, when the local landowner allowed sections of the banking to be “reduced for cultivation.” An article in the Saturday Review magazine on July 2, 1870, told of these concerns and what was written — as Jean Cook so rightly tells — “has a depressingly modern ring to it”:
“…the fortress at Dorchester and the fortress on Sinodun (Castle Hill) are among the most speaking monuments of the earliest history of our island, and till lately they were among its most perfect monuments. But it is a grievous truth that while we are writing, the dykes at Dorchester are being levelled. Hitherto the neighbourhood ground has been grazed and the harmless sheep is no foe to history; but it has lately occurred to the owner of the ground hat a few shillings more of yearly profit might be gained by turning pasture land into arable; and to such a sordid motive as this these precious antiquities are at this very moment being sacrificed. At least a third of the dyke has already been lowered, and will gradually be utterly destroyed beneath the yearly passage of ruin’s merciless plough share. Such wanton destruction naturally aroused the indignation of men of taste and knowledge, especially in the neighbouring University. A vigourous appeal to the owner to stay his hand was made by some of the most eminent Oxford residents, and an attempt was made to call public attention to the subject by describing the state of the case in various newspapers…”
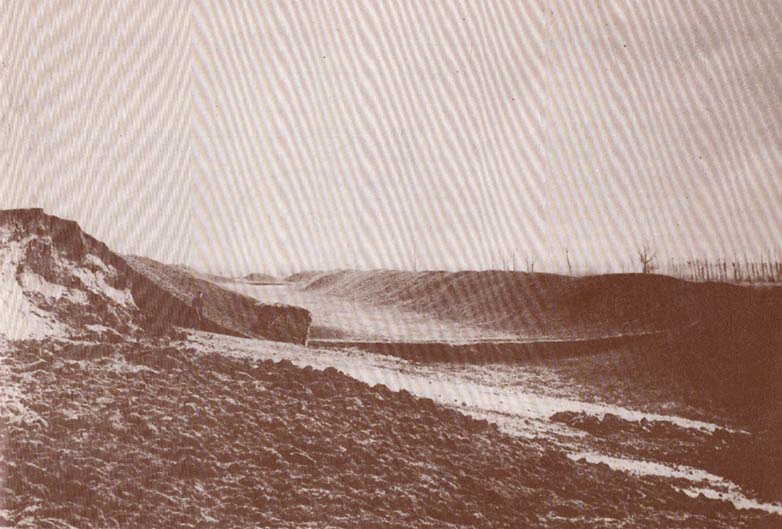
But the digging into the dykes continued. For some time at least — until Colonel Lane-Fox himself went to the see the landowner and “persuaded” him to stop what he was doing. A method we should always keep in mind ourselves…
The modern state of the Dyke Hills is summarised once again in Jean Cook’s (1985) fine survey of the region, where she wrote:
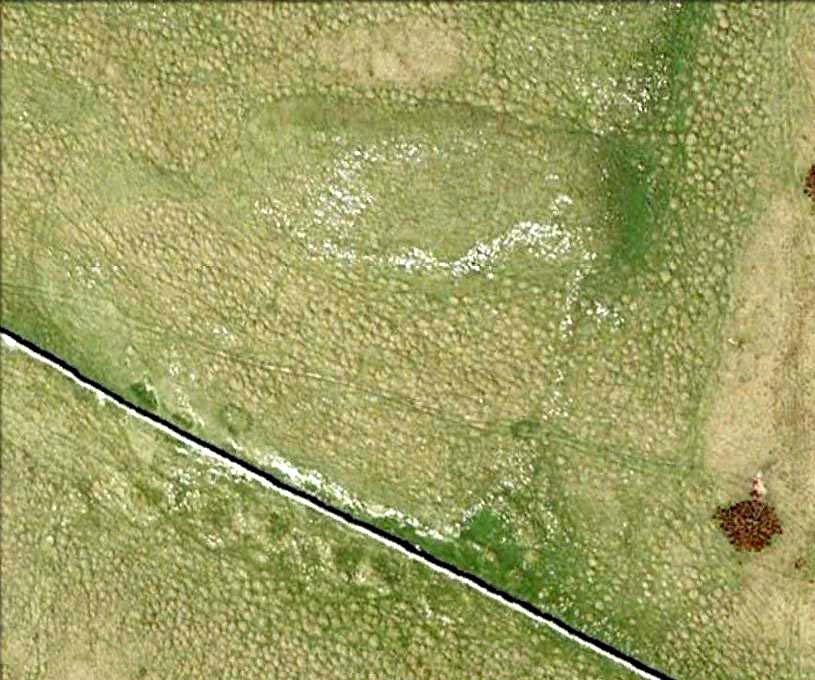
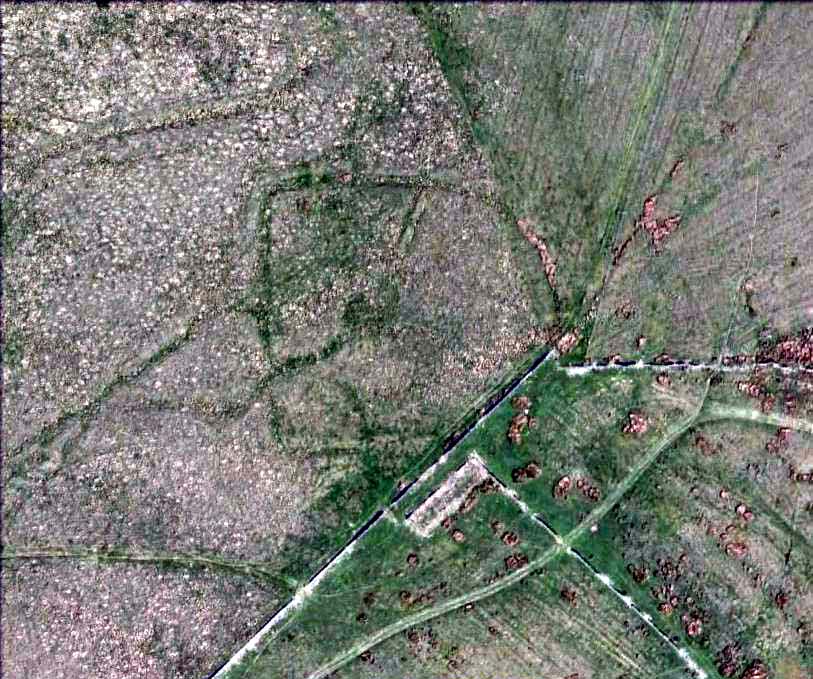
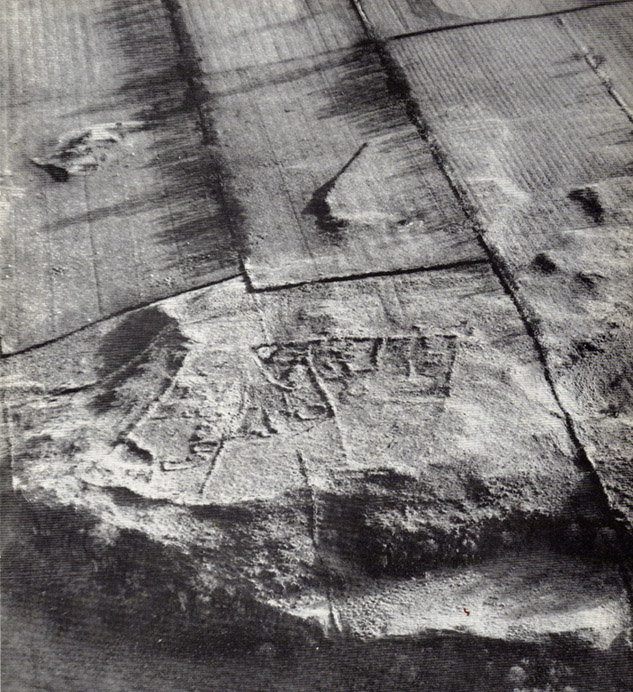
“This great enclosure, known to archaeologists as an oppidum, covered 46 hectares (c. 114 acres) and as defended by a massive double bank and ditch to the north and to the east. The southern and western boundaries have all but disappeared, but can be traced in lines of modern field boundaries beyond which the Thames forms a natural boundary. The interior is (now) empty, but cropmarks reveal that it is full of enclosures, pits and circular houses aligned along a regular pattern of internal roads. Although there has been no scientific excavation within Dyke Hills, ploughing of the site has produced one of the densest concentrations of Iron Age coins in Britain.”
It would appear that this site was of considerable importance for local tribes and would have been home to powerful chiefs and impressive-looking shamans! The large Castle Hill site immediately across the river would have had obvious links to this once-omportant prehistoric settlement.
References:
- Cook, Jean, “Before the Roman Conquest,” in Dorchester through the Ages, Oxford University 1985.
- Cook, Jean & Rowley, Trevor (eds.), Dorchester through the Ages, Oxford University 1985.
- Williams, Geoffrey, The Iron Age Hillforts of England, Horace Books 1993.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian