Healing Well: OS Grid Reference – SD 71823 48265
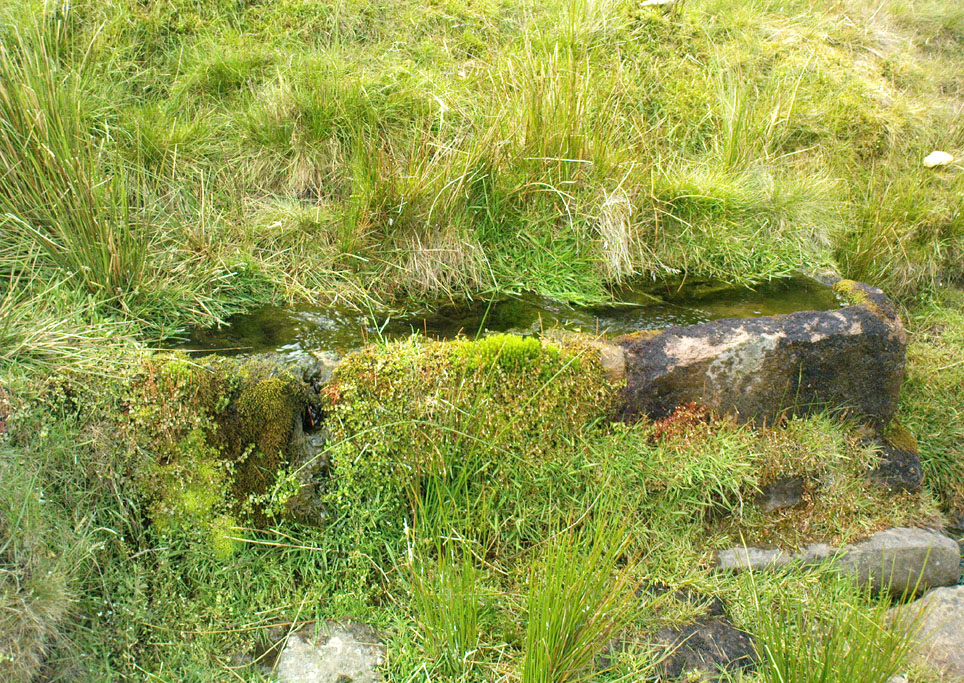

Take the B6478 road between Clitheroe and Newton, heading up north out of Clitheroe until you’re on the very top of the hill with fine views, mainly north and west. There’s a car-park about here, on the right-hand side of the road. From here, walk further along the road for about 200 yards, keeping your eyes peeled for the large stone trough at the left-hand side of the road. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
When we met up with John Dixon in the summer of this year, to wander on the nearby hills in search of old monuments, this was the first spot he showed us — and the waters were flowing nicely and tasted alright aswell! But its history is not widely know. Jessica Lofthouse (1976) described the place, saying:
“In the days of horse and pedestrian traffic none passed Walloper Well without stopping to ‘quaff the clear crystal.’ Long ago, hill men, hunters, forest wardens and farmers off to Clitheroe markets and fairs, pedlars, lead miners from the nearby workings, all met here. The name is thought-provoking. Why Walloper? From a word meaning a ‘fresh bubbling spring’, which this is, fresh from the moorside into stone troughs. Age, wartime army practice and vandalism of 1974 made renewal of the trough necessary, but the flow has been constant. One must drink, just as one throws pennies into the Roman fountain, to ensure one comes back again.
“The true derivation does not satisfy everyone. One can choose. A man and his wife climbed towards Walloper with raised voices, she nagging, he protesting. A pedlar watched them. “I’ll tell thee what I’d do if she were my wife. I’d wallop her, wallop her, wallop her well.” A song which every local singer was once compelled to have in his repertoire told the same story. The chorus sums up the reason for the name:
“…lovers of tell, each beau to his belle
The olden time story of Walloper Well.
The mason who built it in love with a maid
Who brought him his dinner one day, so tis said,
Was struggling to kiss her when over the Fell
A pedlar then passing cried, ‘Wallop her well’.”
References:
- Byrne, Clifford H., Mineral Springs and Holy Wells of North-East Lancashire, unpublished manuscript, 1972.
- Lofthouse, North Country Folklore, Robert Hale: London 1976.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian