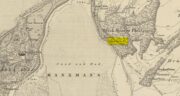
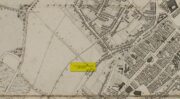
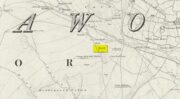
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid-Reference – C 30754 37541
Archaeology & History

This is an incredible find—dare I say a beautiful find—uncovered beneath the soil a few years ago on farmland close to the shore of Loch Swilly by one of the farm-workers. We were lucky inasmuch as when it was found he noticed curious markings on it. Informing the farmer, between them they peeled back the rest of the soil and found the incredible carving that we see here in Bettina Linke’s photos.
Etched onto a sloping stone overlooking the blue panorama that is Loch Swilly, this petroglyph has a 180º view of the landscape, from the southeast through to the northwest. This panorama—unimpaired by trees thanks to its proximity to the sea loch—was probably an important ingredient in the mythic function of the carving and is something we’ll return to shortly…
Local rock art specialist, Liam McLaughlin was informed of the discovery and, along with Bettina Linke, they met up with the farmer who showed them the carving. I have little doubt that they were very impressed by what lay before their eyes! They told that the rock,
“is aligned east-west with the visible motifs, apart from a few cup marks, situated at the western end of the outcrop. Interestingly, the northern half/leaf is little worn and individual peck marks, made millennia ago, are clearly visible, suggesting it may have been covered for most of the time. The southern half is clearly worn and smoothed out and therefor appears to have been exposed for a considerable amount of time.”


One of the most impressive elements in the overall design is the solar motif, i.e., a series of concentric rings (in this case three) with a number of ‘spokes’ reaching outwards as if to indicate the rays of the sun itself. This is shown clearly in one of Bettina’s photos here. This symbol is found on other neolithic carvings in Ireland: not least the incredible designs in the Newgrange complex where the solar alignment is unmistakable.
The discovery of the carving was reported to the Irish National Monument Service and added to the Heritage Environment Inventory where a detailed report was subsequently written, much of which is extracted here:
“The rock art panel is on an outcrop of bedrock, aligned east to west and slightly sloping in this direction towards Lough Swilly and Knockalla Mountains, also known as the Devil’s Backbone. It lies in an arable field near a field wall in rough ground. Visibility is good to the SE, S, W, and NW across Lough Foyle and the Fanad peninsula.”
On the northern section of the stone,
“There are three large motifs and well preserved with cup and pecking marks between them. There are traces of a fourth large motif on the east end but the rock surface has been eroded or damaged, making it impossible to ascertain the design of the motif.
“Starting from west to east, the top large motif has three rings and a diameter of 43cm. The centre cup mark is shallow and has a diameter of 5cm. There is second shallow cup mark between the 2nd and 3rd ring in the southern part of the motif. Its diameter is 3cm. One tail, is running from the inner ring outwards to the west and a second one is running towards the north. Peck marks, covering the motif, are still visible, particular in the rings.
“The motif below has four rings and a diameter of 39cm. The centre cup mark is very shallow and has a diameter of 4cm. And like in the above motif it has a tail running northwards. But a special mentioning has to be made of the unusual heart shape of its rings with the indentation to the south. Peck marks are still visible in the rings. As far as could be made out, there are five cup marks between those two motifs with diameters between 3cm – 5cm. This part also contains several single peck marks of about 1cm in diameter.
“The next large motif below has a diameter of 37cm, three rings and a centre cup with a diameter of 3cm. A tail appears to divide the motif into an eastern and western half. Another tail seems to run from the centre cup through the inner and middle ring towards east.
“Large peck marks of 1cm diameter cover the entire motif, which can be particular well seen in the embossed space between the middle and outer ring. There are more, large peck marks above the motif to the west as well as four possible shallow and small cup marks. Although the two closed to the motif, in what appears to be a twin configuration, could be two independent but slightly damaged peck marks.
“All of the three motifs on the northern wing leave the distinct impression that they may have been sun wheels with some spokes no longer visible or not visible during our visits.
“The southern wing:
“Like the northern ring the large motifs are placed in the western end of the wing with only a few cup marks on its eastern tip. The edges of the carvings are rounder and more worn, although some rings and cup marks are distinctively deeper. The latter might suggest that these motifs were carved at a different time and by different hands. It also appears that this wing was longer exposed than the northern one.
“The motifs are as followed from west to east: two deep cup marks on the northern side. Diameter for the upper one 5cm in diameter, for the lower one 4cm. There could be a shallow third one below and a damaged one to the south.
“Next in the centre of the wing is a large, three ringed motif with a diameter of 40cm and a centre cup mark, 3.5cm in diameter. Some of the photos show possible if faint tails or spokes, suggesting that this also could be a sun wheel motif. No visible peck marks. Below is a small double ring motif with a diameter of 17cm and a centre cup mark with a diameter of 2cm. Just below and to the south-east is a cup mark, circa 3 cm in diameter. Beside it to the east another cup mark about 5cm in diameter. There are one or two, maybe three circa 2.5cm cup marks in the white lichen area to the north-east of the small ringed motif. And some faint peck marks appear between the large 3 ring motif above and the small ringed motif close to the natural split of the bedrock. The next motif below is a deep double ring motif with a diameter of 26cm and a centre cup mark of 5cm. No tails or spokes could be detected. The white lichen area with up to three possible single cup marks is just beside it, close to the natural dividing crack.
“In the middle of the southern wing are faint traces which suggest that there could have been another motif, now destroyed, of an estimated diameter of 28cm.
“The eastern tip has one large cup mark of 10cm and 3 small cup marks between 2.5cm and 3cm. There might be a fifth but damaged cup mark.”
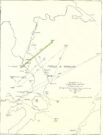

The fact that the stone itself is aligned east-west and pointing towards the outline of the Knockalla Mountains, suggesting “a solar/sunset alignment at the equinoxes” may well be true, but whether this was intended or not is another matter.
Intriguingly, one of the archaeo-astronony pioneers, Boyle Somerville (1909) wrote a article in the Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland about a number of summer solstice alignments he thought existed in this precise locale. Amongst them was one he found running from the standing stone at Cloghbane on the other side of Loch Swilly—known as the White or Rowan Stone—heading northeast to the small mountainous peak of Bulbin, approximately 7.1 mile away. Somerville found that,
“The outline of the mountains visible to the northward from Cloghbane shows two sight-lines that undoubtedly were used from this position. One is for the summer solstitial sunrise over the prominent peak Bulbin; the other is over a low and small but conspicuous round-topped headland, towards the mouth of the Lough, which is in line with an exactly similar hill behind it; their two summits being practically coincident, forming a single sky-line; so that, from Cloghbane, their angle of elevation by theodolite is the same.”

The first alignment is the relevant one here: it not only relates to the rising sun at solstice in 1000 BC, but our Glebe petroglyph lies right on the edge this alignment! (give or take a few yards) Whether or not this is a coincidence we cannot say for certain, but the ‘solar motif’ in the design would seem a strong indicator that implies some sort of solar function here.
As always with cup-and-rings, their non-linear designs tickle our minds with possibilities, probabilities and that there thing called the mysterious, which Einstein described as “the source of all true art and science…”
One final and important thing to anyone who may want to visit this site: please contact the farmer and ask his permission if you want to see it. Cheers. 😉

References:
- Lacy, Brian, “The Irish Archaeological Studies of Boyle Somerville, 1909-1936,” in Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland, volume 138, 2008.
- Lacy, Brian, et al, Archaeological Survey of County Donegal, Donegal County Council 1983.
- Somerville, H. Boyle, “Ancient Stone Monuments near Loch Swilly, County Donegal,” in Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland, volume 39, 1909.
Acknowledgements: Massive, huge huge thanks to Bettina ‘Grianan Swilly’ Linke for the superb photos and data for this site profile. And (although he doesn’t know it yet!) thanks are also due to the farmer and his employee who rediscovered the carving and to Liam McLaughlin who put pen to paper and told the rest of us about it.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian