Cairn: OS Grid Reference – SD 80678 66436

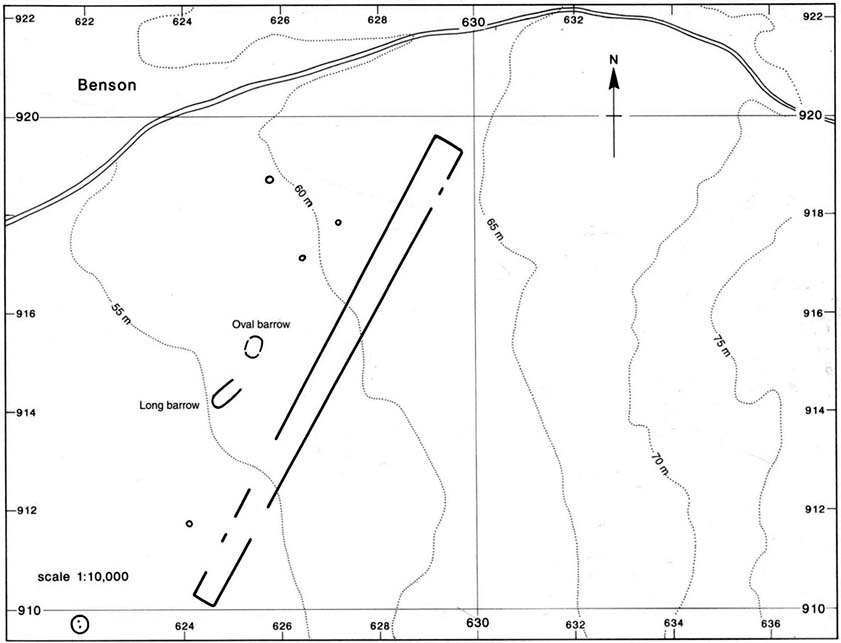
Follow the same directions as if you’re visiting the Apronful of Stones giant cairn, above Giggleswick. Walk past the giant cairn for a coupla hundred yards until you reach the large section of fallen walling, which you can clamber over and head towards the small rise of the Sheep Scar enclosure 100 yards in front of you. Walk to the far end of this walled enclosure and look down the slope to your left, for 50-60 yards where you’ll see a small rocky mound rising above the edge of the hollow footpath. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
This lovely old overgrown prehistoric cairn seems to one of what were once the remains of many other old tombs that scattered this grassy rocky plain, on the western ridge between Stainforth and Settle. Although there are what seems to be the remnants of others nearby, this particular stone heap, its edges buried beneath centuries of earth, is a fine little-known specimen that deserves attention after so long a period in the sleep of ignorant moderns. The cairn is found within an area that Harry Speight (1892) called the “Field of the Dead”, where he came across “traces and remains of human graves which carry us back to the far dim ages of unwritten history.” Whether he saw this particular cairn rising up above the edge of the old track that winds up from Borrins in the valley below, he doesn’t say — but I’d be amazed if the diligent Speight missed it!
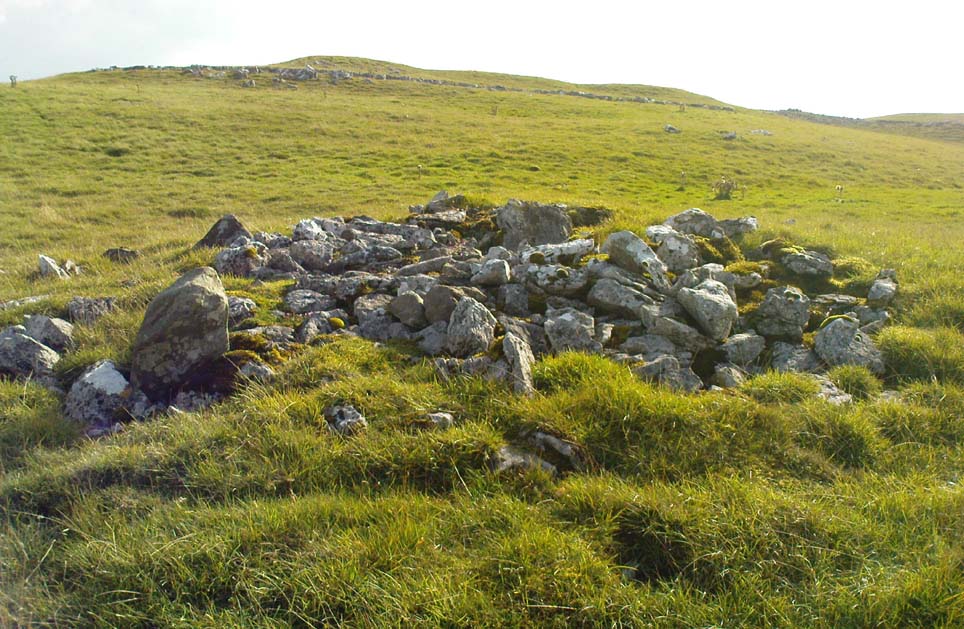


Standing more than a yard high, when Paul Horby and I paced this old ruin, it measured 10 yards by 12 yards across — though so much loose and overgrown stone was beneath the surface that it could be much bigger. The top of the cairn had come loose, perhaps explored by some antiquarian in times gone by, exposing a considerable mass of small rounded and misshapen rocks, typical of such constructions. When Harry Speight found the place more than a hundred years earlier, he described the situation much as we’d found it, telling of,
“other mounds of similar and smaller dimensions within the same area, some of which have been examined, but others do not appear to have been disturbed. Many of the barrows or ‘raises’ have at some time or other been carelessly dug into in the hope of finding valuables, and as doubtless in most cases nothing was found but rude chests or coffins, containing bones, these were tossed aside and no record of them deemed worthy of preservation.”
A situation we find still prevalent thanks to the ignorance of some archaeologists in some regions of Yorkshire to this day (despite what they tell folk). We could see nothing of any note in our brief look at this old cairn, except that it had the usual hallmarks of prehistory in its form, probably Bronze Age. Possible remains of other similar-sized cairns can be seen a little further up the slope on the northeastern edges of the enclosure. The prehistoric Sheep Scar Cairn Circle and other ancient remains scatter the fields all round here; something indicated by the place-name Borrins found in the woods below the ridge, meaning simply, ‘burial place.’ (Smith 1956: 57-8)
References:
- Smith, A.H., English Place-Name Elements – volume 1, Cambridge University Press 1956.
- Speight, Harry, The Craven and Northwest Yorkshire Highlands, Elliott Stock: London 1892.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian