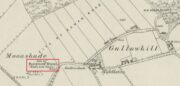
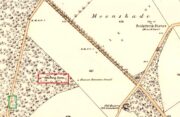
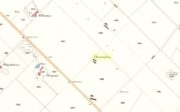
Standing Stone: OS Grid Reference – NS 60774 90383
Getting Here

Go up the B822 road from Fintry for literally 2.5 miles (about 500 yards below the small copse of trees that almost hide Balafark Farm above you) and at a very small ‘parking’ spot are 2 farm-gates. Go through the lower of the two and head downhill, crossing the small burn and up the other side for just over 100 yards where you’ll meet a very low, old and very overgrown wall. Keep your eyes peeled for it! Walk left along this wall, uphill, for another 100 yards till you meet a a dried-up dyke that runs downhill. 10-15 yards down this, a small stone greets you…
Archaeology & History
It’s difficult to call this a ‘standing stone’ and, as far as I’m concerned, is even more troublesome to cite it as a legitimate prehistoric monument. Nevertheless it is shown on the modern OS-maps as such and was listed by the Royal Commission (1963:1) lads in their standing stones inventory. But it’s really pushing it to be honest! They told us:
“This stone stands about 180 yds NW of a gate which opens off the Fintry-Kippen road, 340 yds N of its crossing of the Lernock Burn. It is triangular in profile and wedge-shaped in section, measuring 3’3″ both in height and breadth along its base, by 1’7″ in greatest thickness. It may well have been a boundary stone as it is near the corner of some ground which is enclosed by a turf dyke and has been cultivated.”


In truth, if we call this a standing stone, then there are hundreds of others that I’ve come across over the years—frobbling off-path across huge swathes of moorland—that must also be added to our prehistoric inventories, as the height of this isolated rock is echoed in countless others which are off the archaeological listings. One such stone ‘stands’ 100 yards northeast of here—although there are many others with much greater potential. …I think the only thing that may sway this as being a possible prehistoric upright is the fact that the top of the stone appears to have been broken off, albeit a few hundred years ago if the weathering is owt to go by. But a cursory look for any broken top-piece found nothing.
References:
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments Scotland, Stirling – volume 1, HMSO: Edinburgh 1963.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian