Settlement: OS Grid Reference – SE 1492 5378

From Blubberhouses church by the crossroads, walk up the slope (south) as if you’re going to Askwith, for 100 yards or so, taking the track and footpath past the Manor House and onto the moor. Once you hit the moorland proper, take the footpath that bears left going down into heather and keep going till you hit the dead straight Roman Road path running west onto Blubberhouses Moor. Go on here for nearly a mile until you hit the valley stream with its Eagle Stone down on your left. Walk downstream, past the Eagle Stone, and cross over 100 yards down until you’re back on the level ground with the scatter of bracken and heather. You’re here!
Archaeology & History
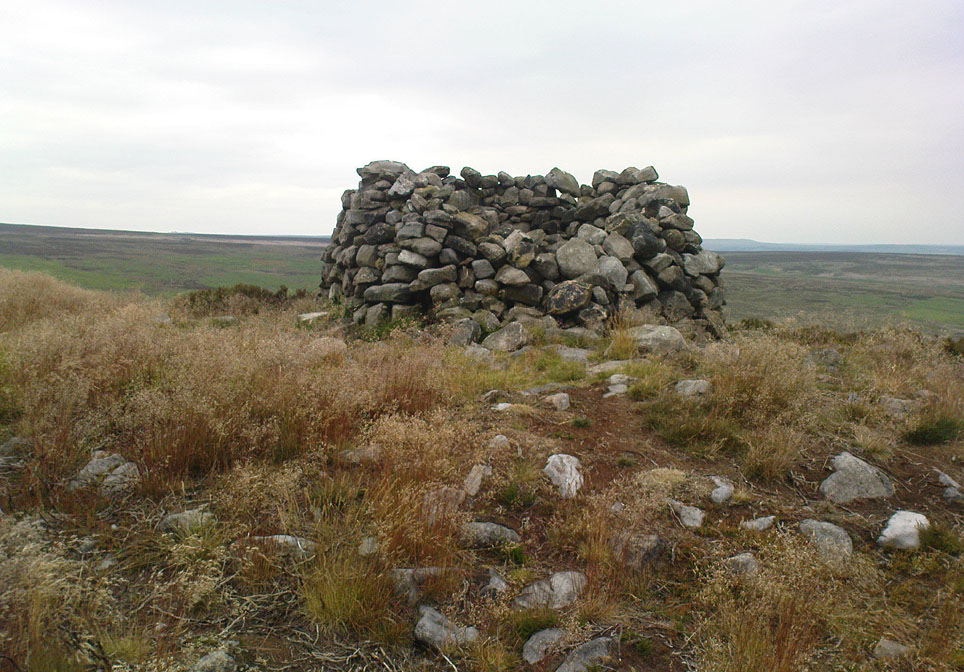
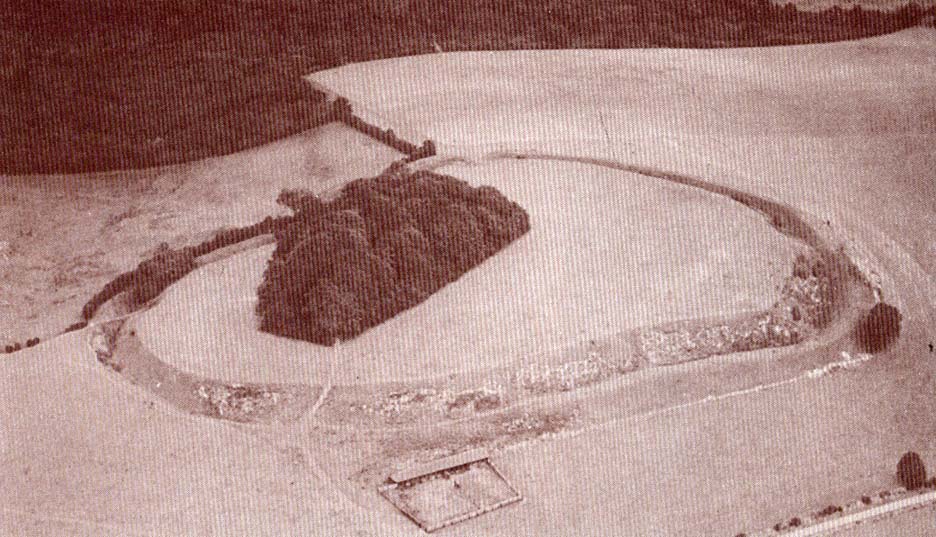
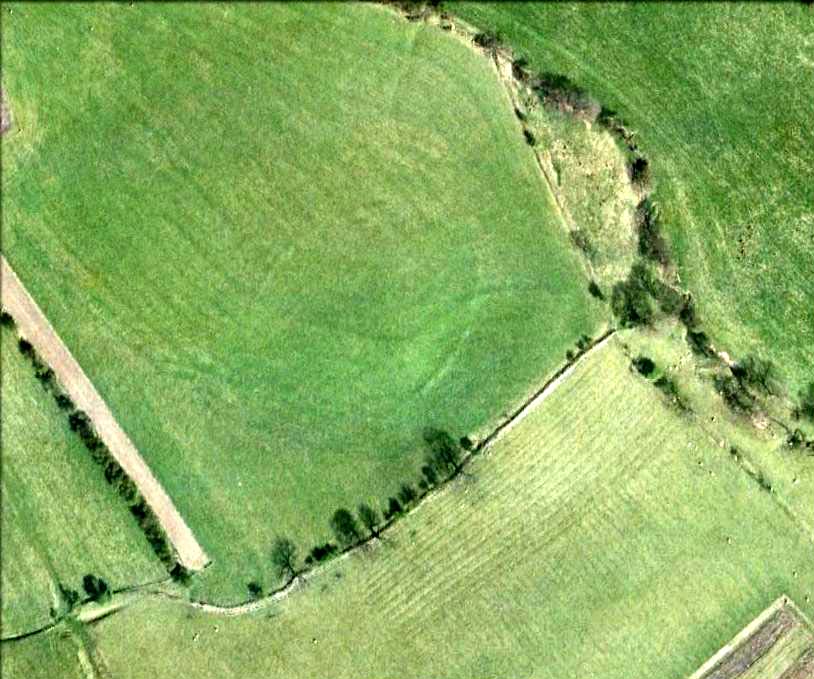
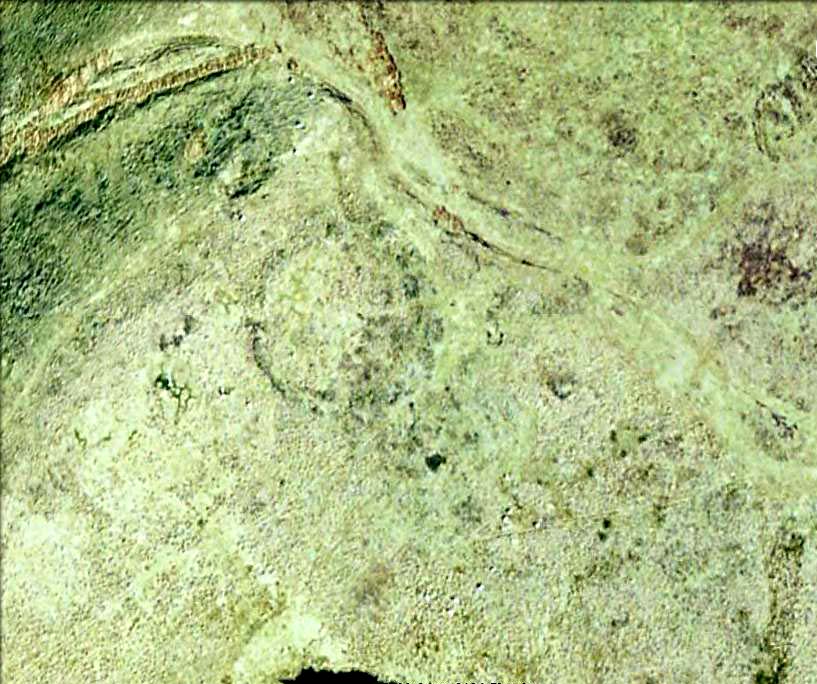
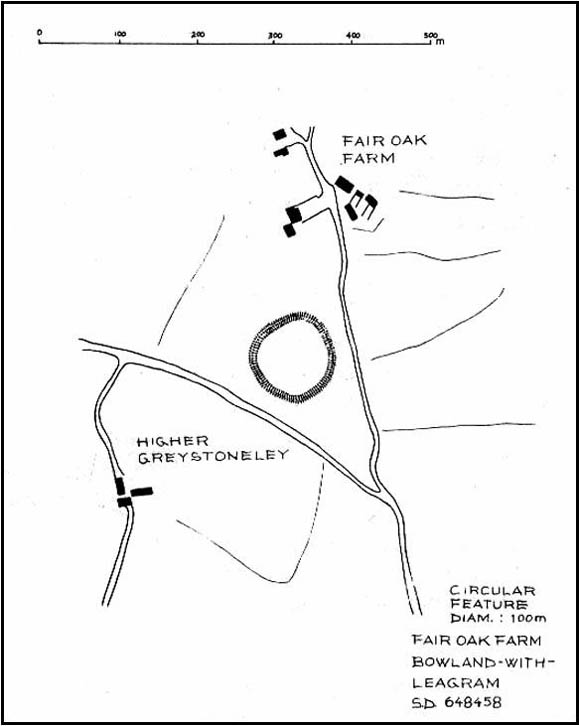
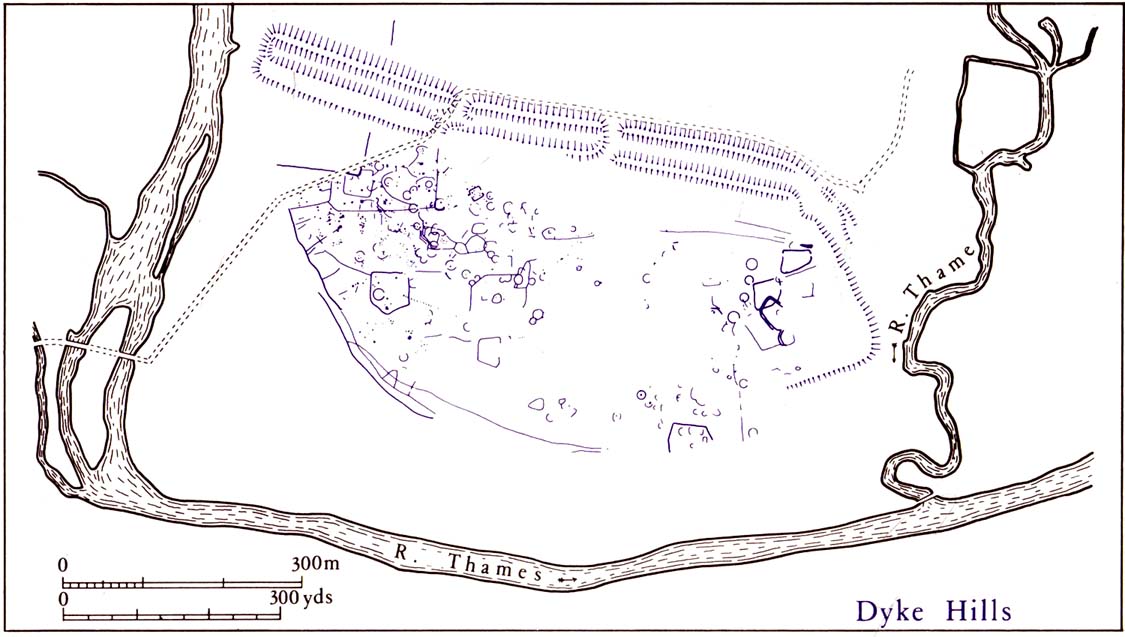
On the other side of the stream a short distance southeast of the large cup-marked Eagle Stone is a curious site, first described by Eric Cowling (1946) as “a series of enclosures of varying size and roughly circular shape” which he ascribed as a Bronze Age settlement. Certainly we have a rather extensive scattered group of walled structures just as he described, but not all of the walling here seems typical of local Bronze Age constructions. Cowling suggested the remains to be “useful for protection, herding and for shelter,” though admitted archaeological excavation would be the best way to ascertain their specific nature. Such undertakings have yet to be done — and I wouldn’t hold your breath either.
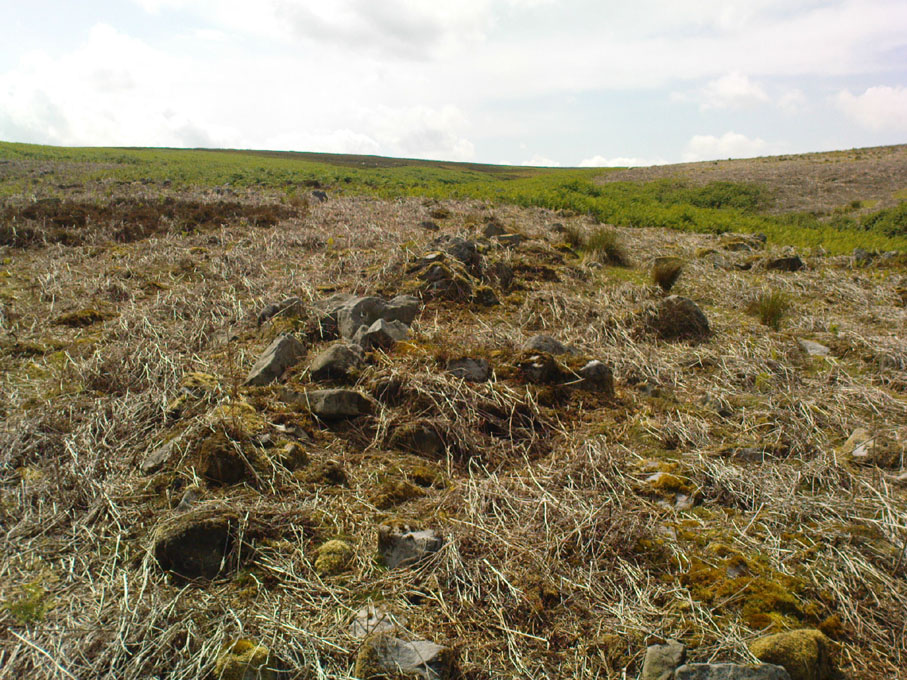
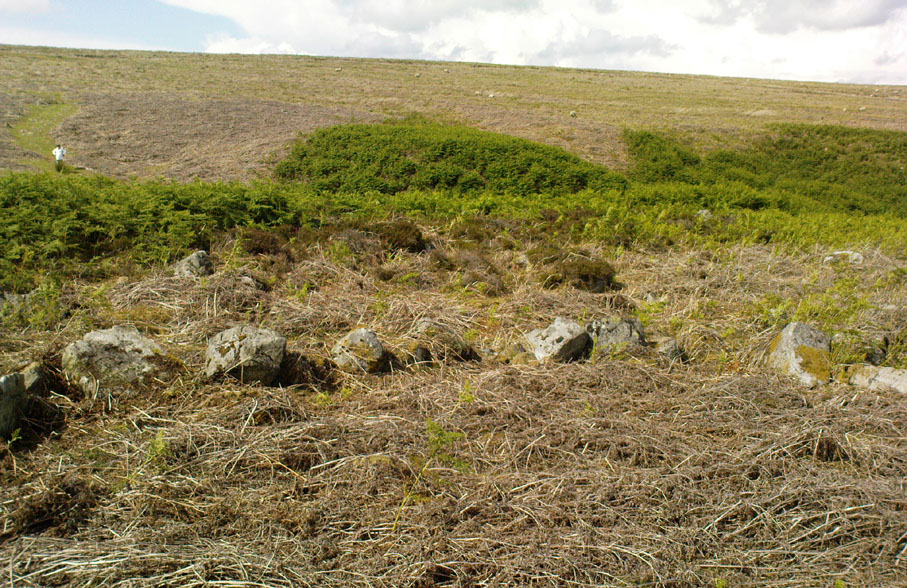


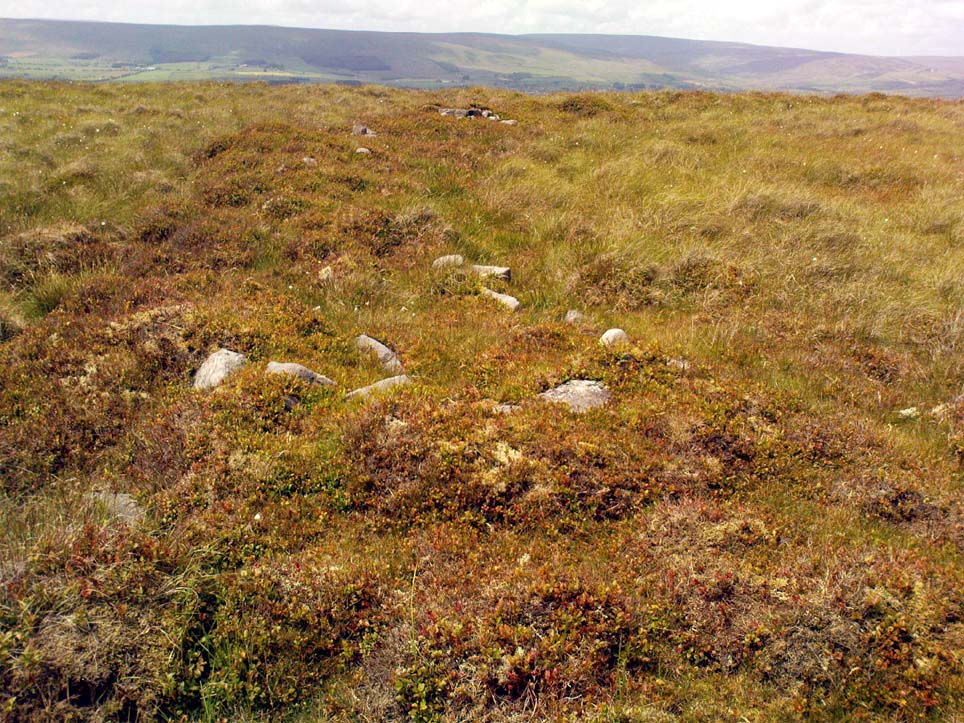
Although he described some of the walls here as nearly four-feet tall, when Graeme Chappell and I first ventured here in the winter of 1990, the walling wasn’t quite as high. There are a number of individual tall stones sat in the walls that stand three-feet tall, with some that have been cut and dressed in more historic times. Who did this and when is unknown. However, if we visited this place when all the vegetation has been cut and burnt back at the end of winter and early months of Spring — a fact not lost on Cowling when he first found this place — we would gain a much clearer picture of things here.
Some sections of lower walling above the streamside appear to be prehistoric in nature, but many other parts of the walled structures across this flatland plain have a much later look and feel about them, illustrating that the site may have been used well into post-medieval periods. This seems increasingly obvious where we find a number of the stones cut at sharp angles, with some having distinctive quarried grooves in them. However, I can find no historical records to verify this at present.
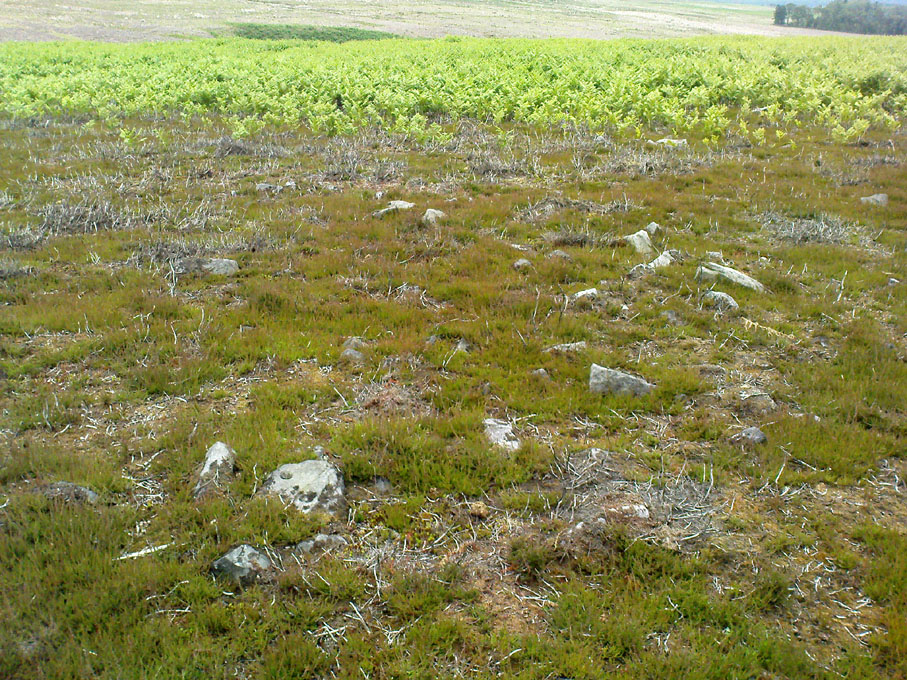
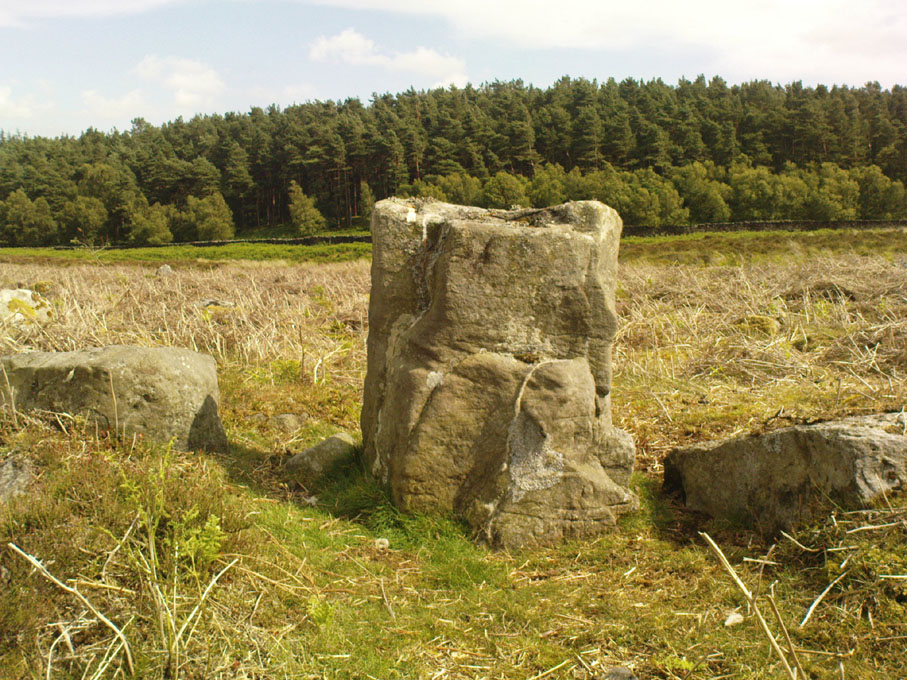


If we walk up the slight slope westwards however (before bracken and heath grow) there are more distinct prehistoric remains in the form of typical hut circles with low walls emerging from deep peatlands — although even these have been cut in one or two places by metal tools. My view of this little-known but large settlement arena is that we’re looking at a site initially built in the Bronze Age period, continuing to be used by local tribespeople throughout the Iron Age and, as the cut stones clearly show, was a village that was certainly made use of in the last millenium. But until someone comes along here and gives the site the attention it deserves, we’re not gonna know…
On the southern fringe of the copious walled structures we also find a very curious medicinal chalybeate spring that may have been of some importance to those who once lived hereby. A ‘standing stone’ and prehistoric cairn can also be seen close by.
References:
- Cowling, E.T., Rombald’s Way: A Prehistory of Mid-Wharfedale, William Walker: Otley 1946.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian