Timber Circle: OS Grid Reference – SD 57717 46004
Pretty easy to find, and a nice walk to boot! Head up to Bleasdale Church (worth a look in itself!), keep going up the path north to the aptly named Vicarage Farm. From here you’ll notice a small copse of trees on your left (east) heading to the hills. To those of you who like Predator, “it’s up there – in them trees…!”
Archaeology & History
On my first visit here in the company of John Dixon and other TNA regulars, my first impression was “this is a henge” – and noted subsequently that it’s been described as such by several writers. But the general category given to this fascinating place is a ‘timber circle.’
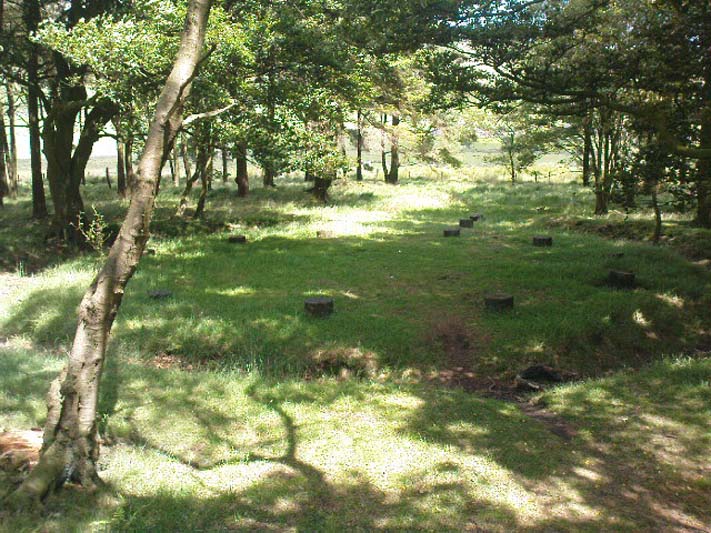

First discovered at the end of the 19th century and described in considerable detail by Mr Dawkins (1900), this is a gorgeous-looking monument was erected in at once a gentle and tranquil, aswell as an imposing natural setting, at the foot of Fair Snape Fell (to the northwest) and Bleasdale Fell (due southwest). These aspects of the landscape would have had obvious mythic importance to the people who built this ring amongst the trees. A condensed version of Dawkin’s material was described in J. Holden’s (1980) Story of Preston, that outlined this circle as being,
“a centre for religious worship in about 1700 BC. It was made up of a circle of timber posts which enclosed an area 45 metres in diameter. In the centre was a small mound surrounded by a ring of oak posts and a circular ditch. Inside the mound there was a grave that had in it two pottery urns filled with human bones and ashes. Examination of the contents of these urns shows that the bodies were wrapped in linen and burnt on a funeral pyre. A small ‘accessory’ cup was found inside one of the urns and this may have contained food or drink for the afterlife.”
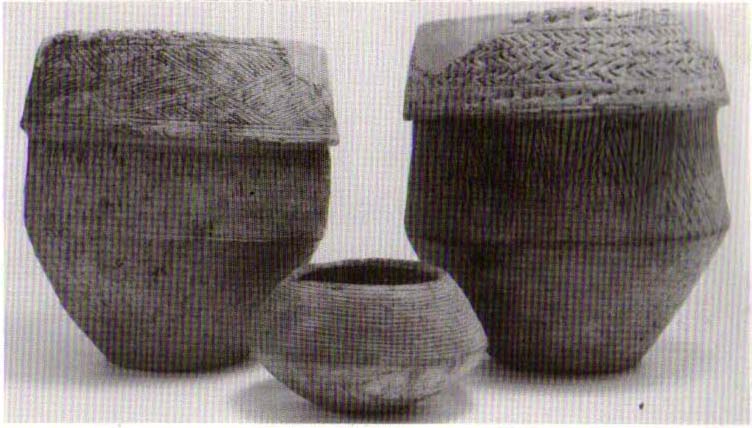


Located within a much larger circular enclosure, the internal Bleasdale ‘henge’ Ring consisted of a small circle of eleven timber posts near the edge of the ditch, and an entrance way to the east, to or from which was an avenue of further wooded posts that led to the edge of the larger enclosure. It gives the impression that this was some sort of avenue along which a ceremonial procession may have took place, strongly suggesting a ritual function. Robert Middleton (1996) told that,
“The post circle and barrow appear to respect each other (in date), whilst the enclosure may be later. The post circle has been dated to around 2200 BC, although the context and reliability of this date is unclear.”
Looking out eastwards from the middle of the internal henge-style ring and through the ‘entrance’ we find an alignment with a large notch on the skyline which, modern folklore ascribes, is where the midwinter sun rises — which is very believable, but I aint seen it proven anywhere yet.
A much greater and full excavation report of this site was written by Raymond Varley (2010), whose essay I urge fellow antiquarians to read.
References:
- Dawkins, W.B., ‘On the Exploration of Prehistoric Sepulchral Remains of the Bronze Age at Bleasdale,’ in Transactions of the Lancashire & Cheshire Antiquarian Society, volume 18, 1900.
- Dixon, John, Journeys through Brigantia – volume 8: Forest of Bowland, Aussteiger Publications: Barnoldswick 1992.
- Edwards, Ben, “The History of Archaeology in Lancashire”, in Newman, 1996.
- Gibson, Alex, Stonehenge and Timber Circles, Tempus: Stroud 1998.
- Holden, Jennifer (ed.), The Story of Preston, Harris Museum: Preston n.d. (c.1980)
- Middleton, Robert, “The Neolithic and Bronze Age,” in Newman, 1996.
- Newman, Richard (ed.), The Archaeology of Lancashire, Lancaster University 1996.
- Sever, Linda (ed.), Lancashire’s Sacred Landscape, History Press: Stroud 2010.
- Varley, W.J., ‘The Bleasdale Circle,’ in Antiquaries Journal, volume 18, 1938.
- Varley, Raymond, “The Bleasdale Bronze Age Timber Circle,” in Lancashire History Quarterly, 2010.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
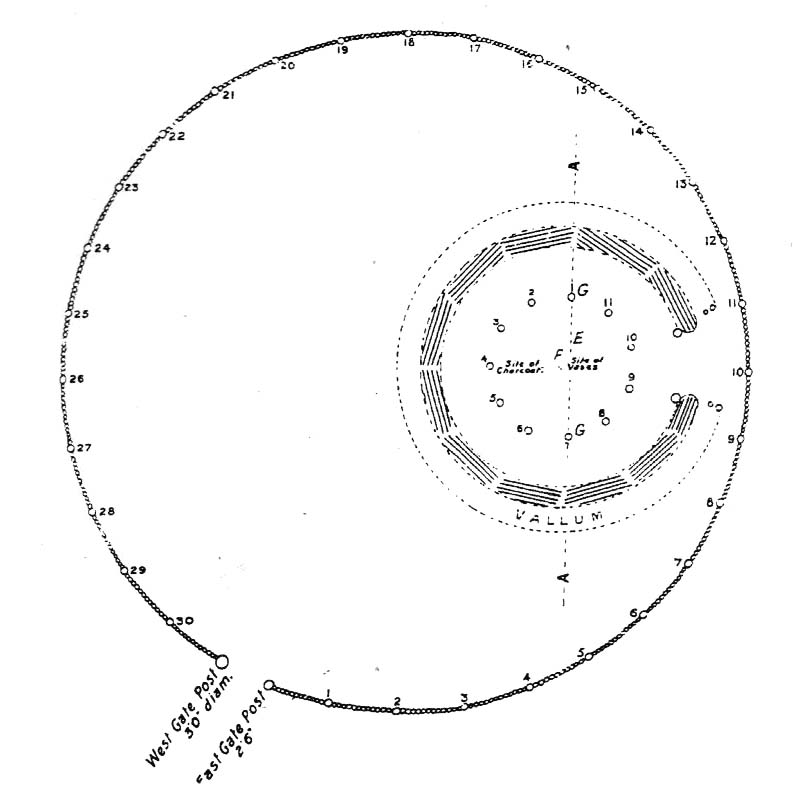
This complex palisaded circular monument was discovered and partly excavated in 1898/9 and later re-excavated in 1933/5.
The inner circle was seen to comprise of a circular mound, 11m. in diameter and 1m. high, surrounded by a single-causewayed ditch floored with birch poles 10-20cm in width. Originally these would have been in the form of woven hurdles. Eleven large oak posts (their position now marked by concrete pillars) formed a circle upon the mound, with an avenue of three poles on each side across the east facing causeway.
In the centre of the mound, at a depth of 56cm. was found a stone-lined cist containing two inverted cremation urns. One of the urns held a pygmy cup.
The above circular feature was surrounded by a palisade consisting of 22 large oak poles 8m. apart, between which were smaller diameter posts. The outer circle had an entrance on the south-east and what would have been a double gateway at the eastern end of the avenue.
A number of burned circular patches ( nine in all) of soil were found within the outer circle. They were around 3-4m. in diameter, suggesting round huts/buildings destroyed by fire. These structures are assumed to be of a type consisting of a centre post, roofed with ling thatch with stone or earthen walls plastered with animal dung and clay over a slightly excavated round pit.
The cinerary urns were 21cm in height, made from local clay, mixed with coarse sand. A radiocarbon date of 1810+/-90 BC (NLP-69) was obtained from timber recovered from the inner circle. If this date is correct, the well developed Pennine urns recovered from the cist are amongst the earliest collared urns to be found in Britain.
To conclude, what we appear to have at Bleasdale is an Early Bronze Age 11 circular village site with an off-centred communal hut, surrounded by a ditch, ouside of which would have been several other structures. The whole was enclosed within a palisade of oak pole construction.
Following the Indo-European custom, the dead were given to the earth inside the human habitation (the Knowth and New Grange passage graves are now known to have been built upon the foundations of circular habitations with dates 3900BC/3500BC resp.). The dear departed, who had been so close to the family in life, had to remain among them in deth also and share the group’s joys and struggles, food and drink. While living they had enjoyed nightly rest under the roof of the communal hut, dead the slept the eternal slumber beneath the domestic hearth.
The urns, and some of the posts,Are on display in the Harris Museum, Preston. Sadly the museum display is very poor and unenlightening, typical of most work undertaken by Lancashire Public Authorities in this (or any other!) field.
A great site to visit, and to discover other similar sites in the Bowland area see: ‘JOURNEYS THROUGH BRIGANTIA’ Volume 8. AUSSTEIGER PUBLICATIONS.
The Lancashire’s Sacred Landscapes book, edited by Linda Sever, is now advertised on Amazon and available to pre-order at £12.99 with a publication date of the 1st Feb!
Includes NEW information on BLEASDALE CIRCLE
Highly recomended!