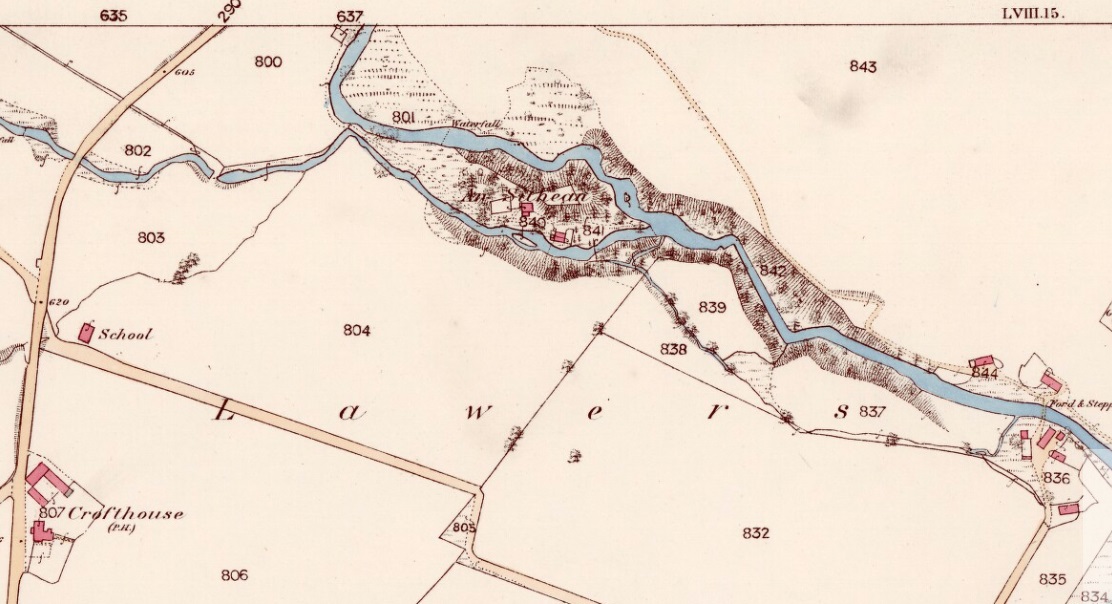
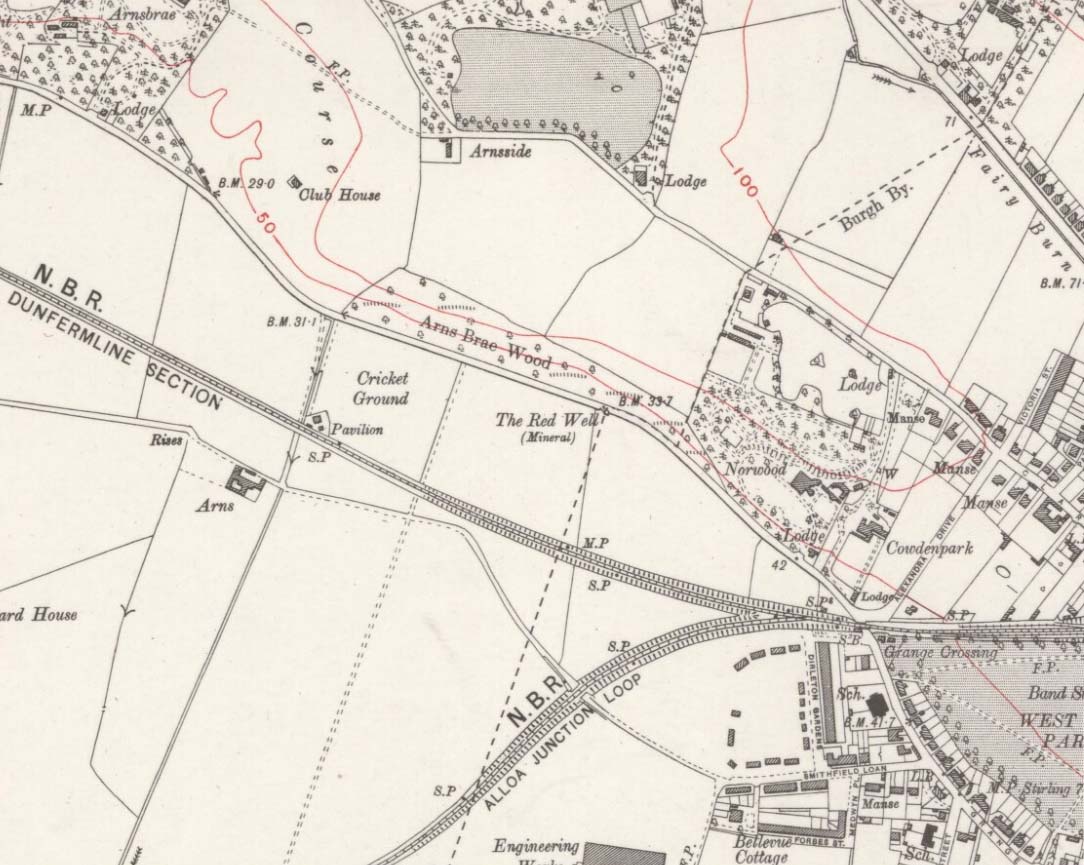
Sacred Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 0973 4091
Archaeology & History
Once found in a cluster of three little wells all very close to each other near the top of the field where the Crossflatts roundabout joins up with the Aire-Valley trunk road, this is an intriguing site if you happen to be a pagan, or have an interest in druidism — and for one main reason: its name. When I first came across a reference to the place about 25 years ago, the only piece of information I could find about it came from the arduous detailed researches of the Victorian industrial historian J. Horsfall Turner who, unfortunately, neglected to record much of the fading folklore in the region at his time. Marked on the 1852 6-inch Ordnance Survey map, ‘Lund’ was a bit of an etymological curiosity, and Mr Turner (1897) thought the well’s name was little other than that of a local mill owner, whose nickname was ‘Lund’ Thompson. He was guessing of course…and I thought little more about it…
Years later when looking through A.H. Smith’s (1961-63) magnum opus on the place-names of West Yorkshire, I found that he didn’t include the Lund Well in his survey. However, an eventual perusal of Kenneth Cameron’s (1996) work told that in Old Norse place-names (and there is a preponderance of such places scattering Yorkshire and Lancashire), lund or lundr was a “‘small wood, grove,’ also had a meaning, ‘sacred grove’.” The word is echoed in old French, launde, meaning ‘forest glade’. In A.H. Smith’s (1954) earlier etymological magnum opus he said that the word derives from a “small wood, grove, also a sacred grove, one offering sanctuary.” However, Margaret Gelling (2000) urged caution on the origin of lund as a sacred grove and erred more to the usual English tendency of depersonalizing everything, taking any animistic attribution away from its root meaning; but we must urge caution upon her caution here! Neither Joseph Wright (English Dialect Dictionary, vol.3 1905) nor William Grant (Scottish National Dictionary, vol.6, 1963) have entries for this word, so we must assume the Scandinavian root word origin to be correct.
One vitally important ingredient with the Lund Well is its geographical position. For across the adjacent River Aire the land climbs uphill—and a few hundred yards above we reach the well-known and legendary Druid’s Altar, with its Druid’s Well just below. This association is what suggests our Lund Well may have had a real association with a “sacred grove of trees”, as—despite us knowing very little about them—we do at least know that druids performed rites in sacred groves. In Greenbank’s (1929) historical analysis of the Druid’s Altar, he was left perplexed as to the origin of its name as all early accounts and popular culture assigned it this title, and so he opted for the probability that the druids did indeed once perform rites here. If this was true, then our seemingly innocuous Lund Well once had a much more sacred history than anyone might have thought. Sadly, through their usual ignorance of such matters, the industrialists destroyed it….
References:
- Cameron, Kenneth, English Place-Names, Batsford: London 1996.
- Gelling, Margaret, Place-Names in the Landscape, Phoenix: London 2000.
- Greenbank, Sydney, The Druid’s Altar, Bingley, R.G. Preston: Bingley 1929.
- Smith, A.H., English Place-Name Elements – volume 2, Cambridge University Press 1954.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the West Riding of Yorkshire – 8 volumes, Cambridge University Press 1961-63.
- Wainwright, F.T., Scandinavian England, Phillimore: Chichester 1975.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian