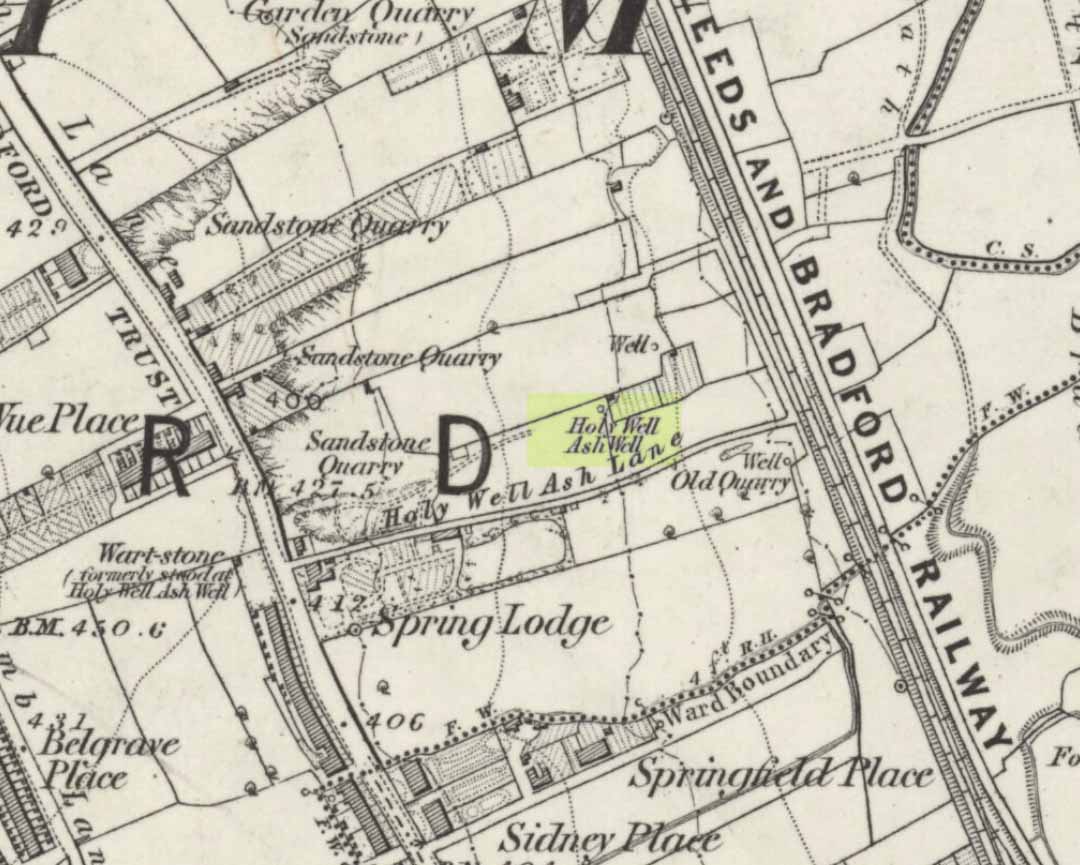
Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – TL 146 066
Also Known as:
- Holy Well of St. Albans
Archaeology & History
The ancient and once sacred water source was described in local place-names such as Holywell strete and Holywellbrugge from the 13th Century onwards; yet despite it being at the heart of one of the cradles of the English church, there are only scant accounts of the legendary well down the centuries. The most detailed essay on this site was written by Tony Haynes (1986) in the specialist holy well journal, Source, more than 20 years ago. Haynes tells as much as it known of the site, saying:
“Late in the seventeenth century, when John Churchill, future Duke of Marlborough, pulled down his wife’s house and built a new mansion in the middle of Holywell Hill, thus creating a major diversion, the Holy Well was a feature of his terraced gardens. Maps of the period show the site of the well to be a focal point of his lawns.
“In 1815, Shaw’s guide to the town states, ‘The holy-well is still held in some esteem for its purity and salubrious qualities’. The Duke’s residence later became the property of the Earl Spencers. It eventually fell into ruin and was demolished in 1837, and the original route of Holywell Hill was restored, no doubt much to the relief of contemporary coach and wagon drivers. After this time, the grounds were left to decay. Ten years later little remained of the gardens but a fishpond and the Duke’s ‘canal’ marking the original course of the River Ver.
“Of the Holy Well, in his History of St Albans published in 1893, Charles Ashdowne laments that: “It is now remembered only as a muddy depression, sheltered by the remains of a dilapidated wall and a mournful specimen of blackthorn.” Eventually the land was acquired by the St Albans School for Boys as a playing field. “The exigencies of athleticism necessitated the ground being levelled and turfed over,” Ashdown continues, “and it is much regretted that there is nothing to mark the site of what was essentially one of the most ancient of English Holy Wells.”
“This is confirmed by a Miss Lightfoot of Holywell Hill. In 1960, when she was 85, she wrote in a letter to Hertfordshire Countryside magazine: ‘I remember the well quite well, for as a child I often went round it. It was surrounded by a fence, inside was a tree, water and weeds – not very inviting.’
“The ‘Old boys’ of St Albans School recall, about fifty years ago, there being a concrete slab at one end of their football pitch which they knew as the site of the well. Their playing field fell into disuse in the 1960’s, but the exact site of the well was lost long before this.”
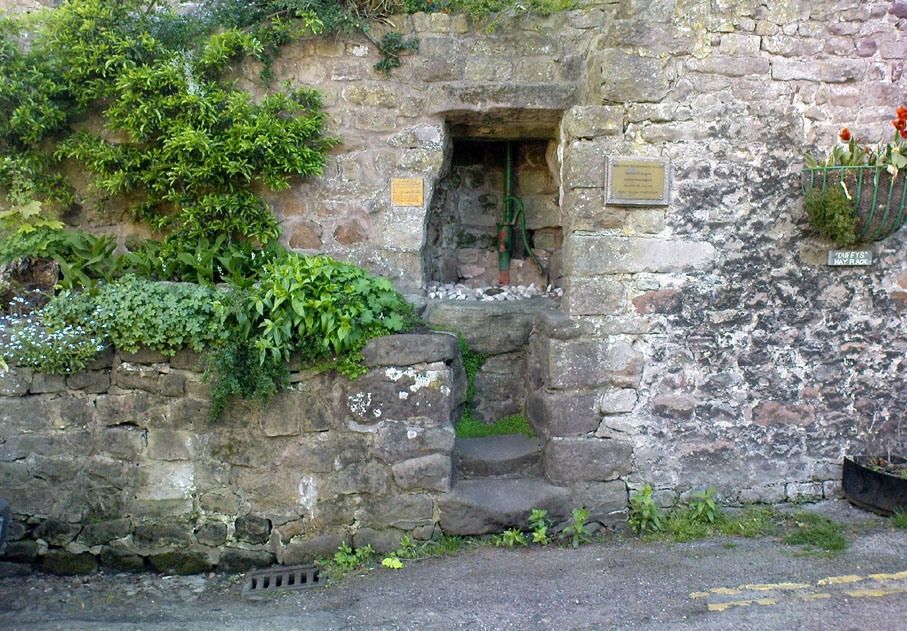
Naff all is visible here nowadays, apart from some concrete square bitta brickwork that betrays any sense whatsoever of a once sacred site. Very disappointing indeed…..
Folklore
As with a great many British holy wells, this all-but-forgotten site was named after one of the early christian martyrs — in this case from as early as the late 3rd century AD. A number of early folklore texts describe St. Albans story, with Vernon Brelsford (1958) telling:
“Tradition states that on his way to execution he walked up a neighbouring hill where he prayed for water to quench his thirst, whereupon a fountain of water sprang up under his feet. Here he was beheaded on June 23, AD 303.”
This date indicates the site probably replaced an earlier, heathen midsummer solstice custom at, or near this spot. Another tale tells that when St. Alban had been executed, the saint’s head rolled down the hill and into the waters of the well below. Mr Haynes (1986) described other early folklore which seems to relate to St. Alban’s Well, telling:
“An early reference to the well can be found in the writings of Brompton who lived in the time of Richard II. He recorded that the father of King Arthur, a British Prince, was severely wounded in the battles with the Saxons:
‘A long time he lay confined to his bed until at length he was cured by resorting to a well or spring not far distant from the city. at that time reputed to be salubrious; and for that reason, and for the cures thereby performed, esteemed holy; and blessed in a peculiar manner with the flavour of Heaven.’
“Two devout sisters built a shelter near the well. They served the weary pilgrims who trudged up the steep hill towards Alban’s shrine in the abbey, by dipping, or ‘sopping’ their bread in the holy water and offering it to the thirsty travellers. Hence was founded Sopwell Priory, nearby.”
References:
- Brelsford, Vernon, Superstitious Survivals, Centaur Press: London 1958.
- Gover, J.E.B., et al, The Place-Names of Hertfordshire, Cambridge University Press 1938.
- Haynes, Tony, “Well-Wishing in St. Albans,” in Source, no.6, 1986.
- Hope, R.C., The Legendary Lore of the Holy Wells of England, Elliot Stock: London 1893.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian