Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – NN 8445 5002
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 25672
- Chapel Rock Spring
- Fuaran Creig a’ Chaibeul
- St. Cuthbert’s Well

The best way to find this site, in the middle of the large woods up the slopes, is to follow the circular mile-long tourist path that runs through it. Take the B846 road out of Aberfeldy over the bridge towards Dull and Weem. As you go through Weem, watch closely for the signpost directing you into the trees of Weem Rock and Woods on the right. Follow this tiny road up until you reach the parking circle in the edge of the trees. Follow the directed footpath up into the woods & keep to the winding track, up, zigzagging, and up again, until it levels out a bit and runs below the large long crags. Tis beneath here you need to be!
Archaeology & History
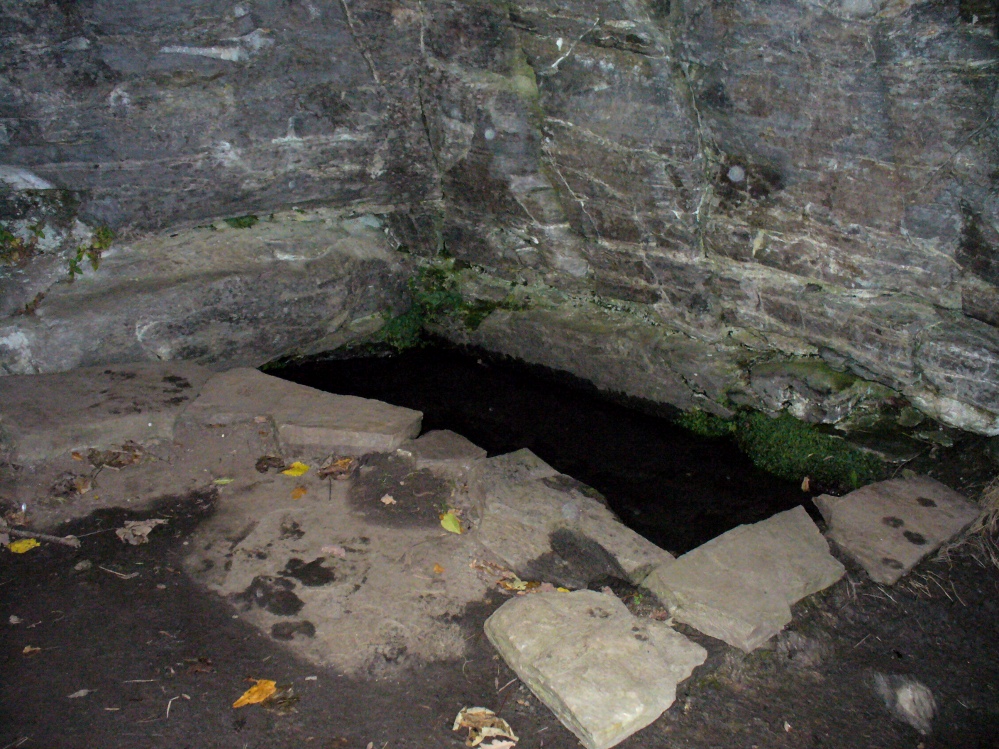

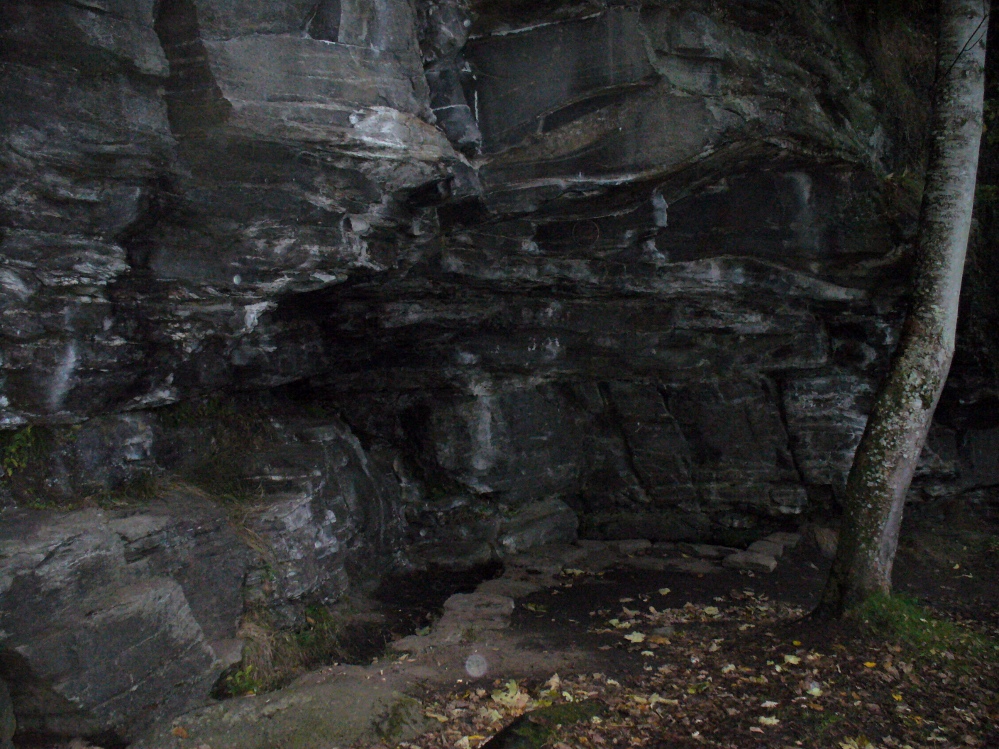
Not far from the curious Weem Wood carvings, hidden beneath one section of the long high crags in remains of the ancient forest, is this trickle of fresh water which collects into a small stone-lined pool. (a small round plaque which reads ‘St. David’s Well’ on the cliff-face above the waters is helpful) It’s in a truly lovely setting, with a small ‘cave’ about 50 yards west along the same footpath and a modern carved ‘cross’ in front of it.
The well was formerly known as St. Cuthbert’s Well (date: 20 March) who, so legend tells, lived nearby—probably at the christian-druid college at Dull, a mile west of here. It was he who collected the waters from the rock face into the small pool we see today. This used to be known as St. Cuthbert’s Bath. But several centuries after the saint’s death, the local laird, Sir David Menzies, came and restored the well and gained a reputation for spending much time living hereby, sometimes in the small cave along the edge of the cliffs. It was to him that the New Statistical Account wrongly dedicated the waters to in the 19th century—but the title has stuck!
Described in several old local history works, the site was included in the giant folklore tome on Scottish waters by MacKinlay (1893), who wrote the following:
“In the wood clothing the steep hill of Weem, in Perthshire, is St. David’s Well, said to be named after a former laird who turned hermit. The spring has a considerable local fame, and many have been the wishes silently breathed over its water. Part of an ancient stone cross lies at its margin, and on it the visitor kneels while framing his or her wish.”
Nothing of this ‘cross’ can now be seen, but it is said that its remnants are housed at Weem church in the village below. Also in the 19th century, occasional christian gatherings were held here and as many as fifty people came “for religious services.” Thomas Hunter (1886) reported that “a collection of human bones” were found near the well in front of the crags. There is also what looks like a newly cut large cup-marking with two carved lines reaching out from it, heading towards the well, on a small ledge of stone close to the pool.
Folklore
Folklore tells that once, long ago, dragons lived in these old woods—overcome no doubt by the incoming christians who stole and denigrated the olde peasant ways of our ancestors. In bygone times, locals used the waters here for their health-giving properties. As Ruth and Frank Morris (1982) told,
“it was an ancient wishing well which was still visited in 1954, when such objects as pins and buttons and an occasional penny was thrown in.”
References:
- Ferguson, Malcolm, Rambles in Breadalbane, Thomas Murray: Glasgow 1891.
- Hunter, Thomas, Illustrated Guide to Perthshire, Robertson & Hunter: Perth 1886.
- MacKinlay, James M., Folklore of Scottish Lochs and Springs, William Hodge: Glasgow 1893.
- Morris, Ruth & Frank, Scottish Healing Wells, Alethea: Sandy 1982.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian