Cup-Marked Stones: OS Grid Reference – SE 13830 45195
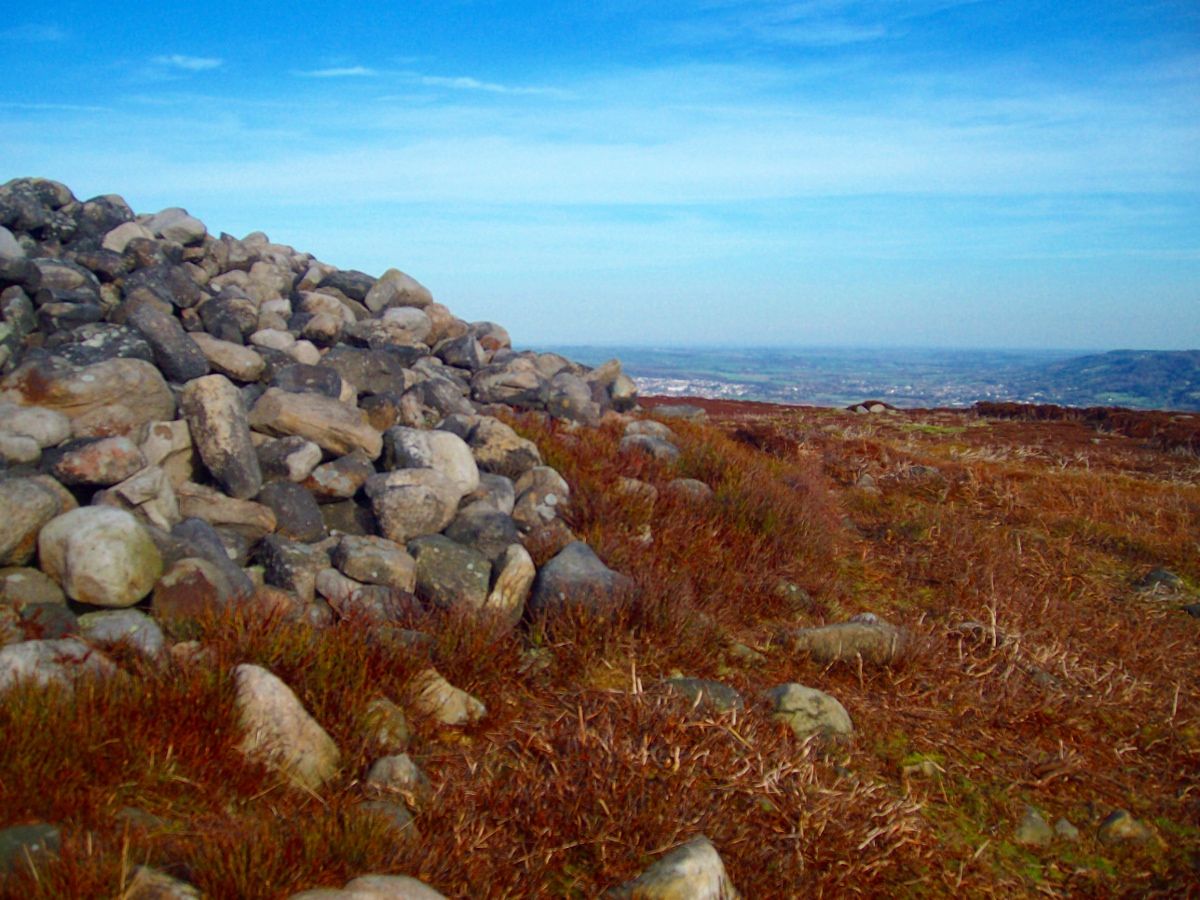

Also Known as:
- Carving nos. 391a, 391b, 391c, 391d
- Little Skirtful of Stones’ Carvings
Getting Here
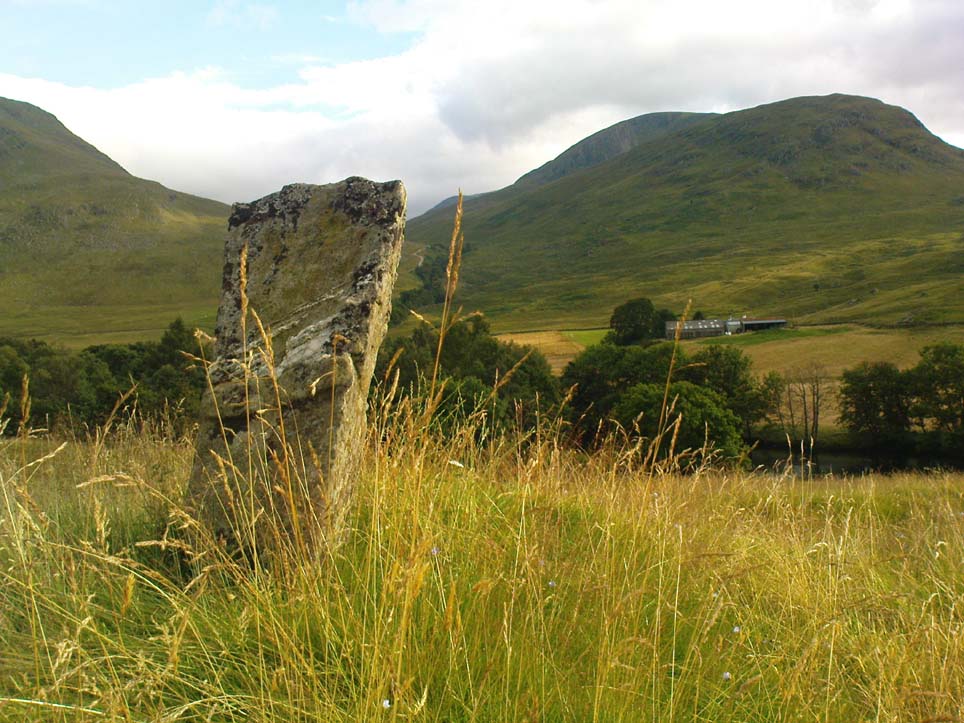
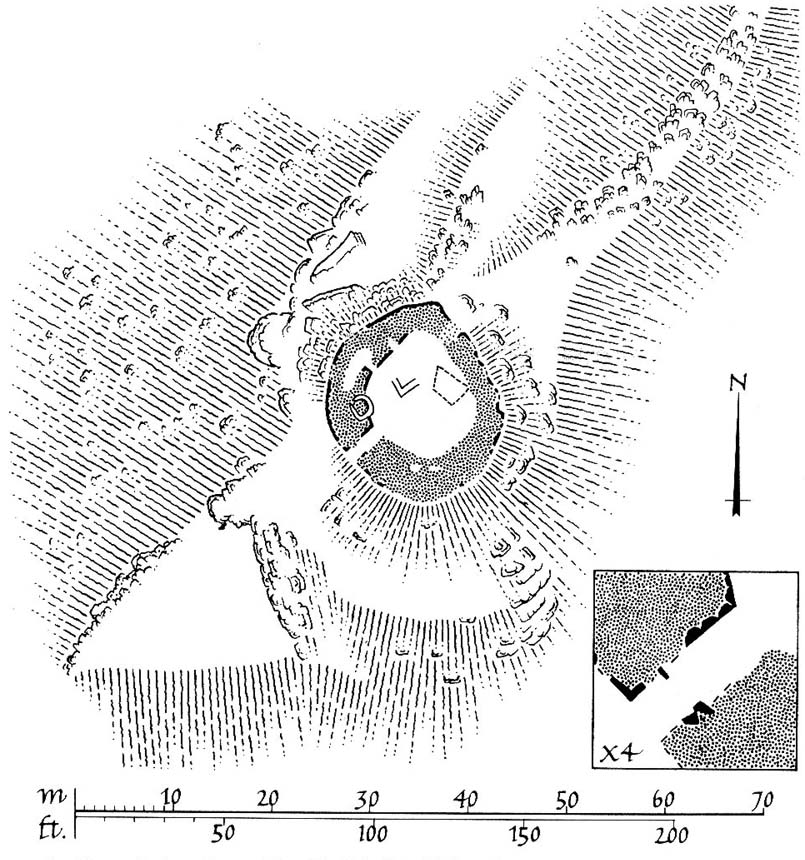
Follow the directions to reach the Little Skirtful of Stones giant prehistoric cairn. Once here, look for the singular rocks out of the many thousands which make up the giant cairn, mainly from the middle to the northern-half of the cairn, and you’ll find them amidst the mass!
Archaeology & History
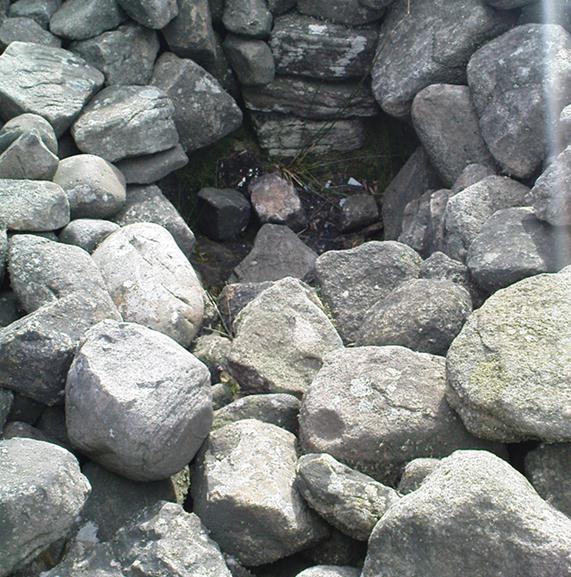

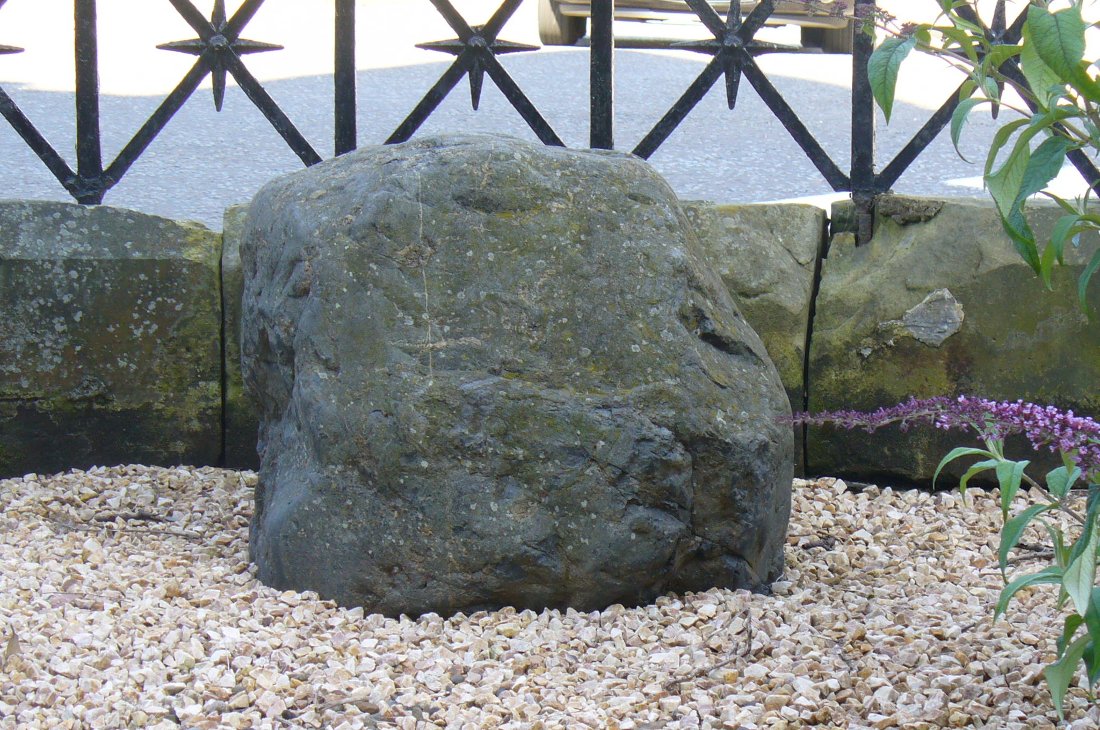
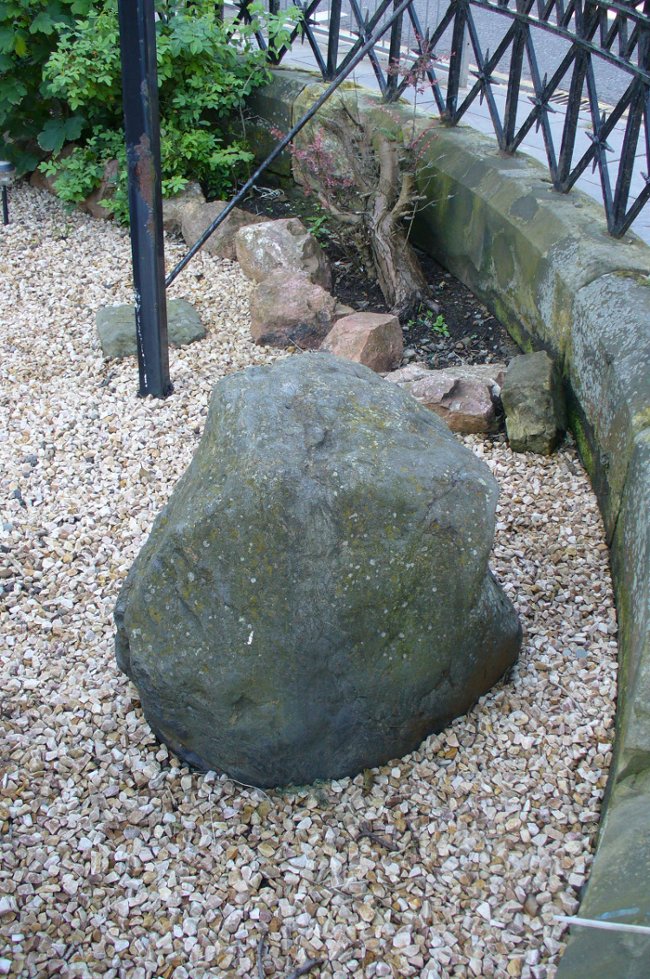
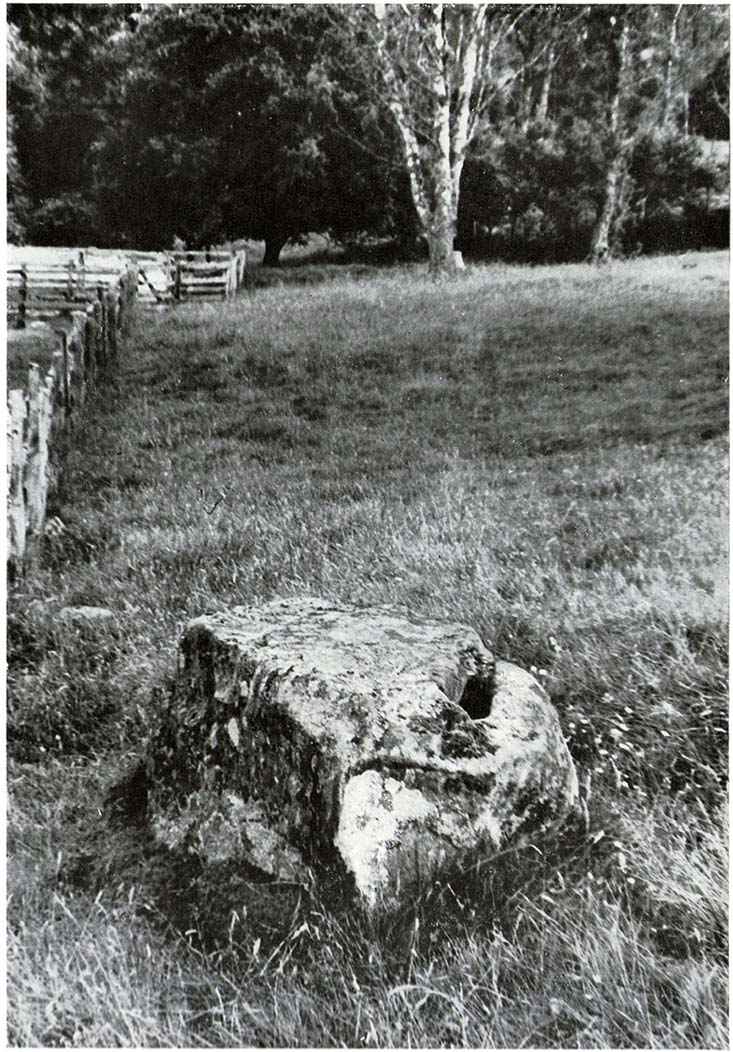
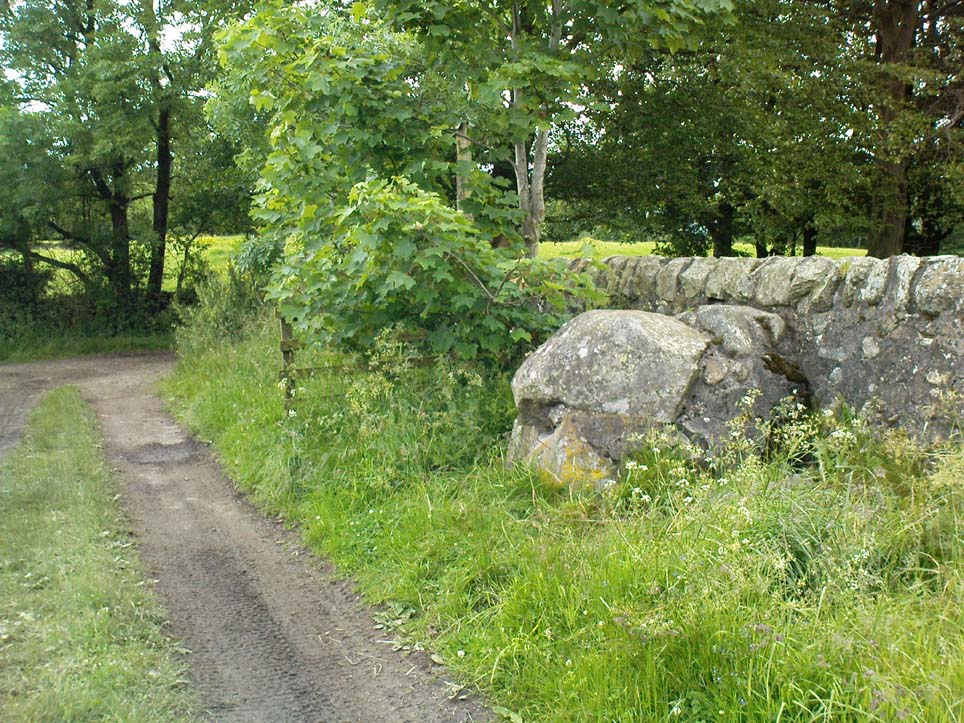
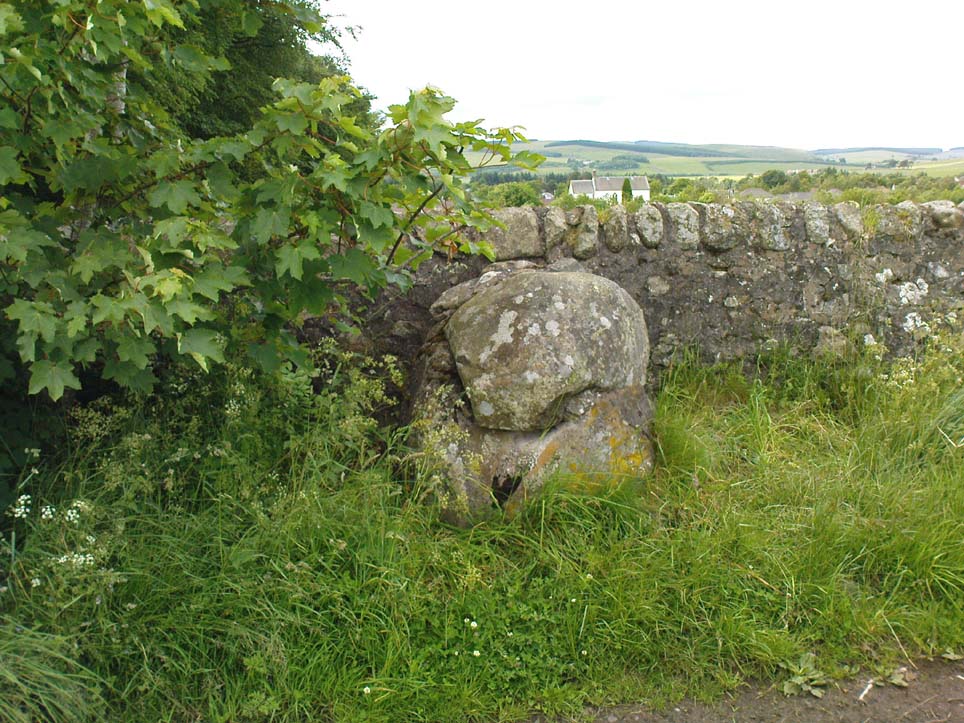
Despite the task sounding difficult, it’s not too hard locating the cup-marked rocks within this giant cairn. As I recall there should be five of them, though the Boughey & Vickerman (2003) survey only list four and I only have photos of four of them as well…so I reckon age is probably getting to me at last! There could very well be more of them amidst this massive tomb. But we certainly can’t rely on the Boughey & Vickerman (2003) survey for the carvings at this site as they give the wrong grid references for each of the cup-markings listed, with them all being a kilometre east from the site of the tomb itself! Awesome! God knows what their cartographer was on when he did the profiles for these carvings! (there are plenty of spliff-butts scattered over this moor…..) Not only that, but the position they cite of the relative cup-markings within the cairn are also wrong.
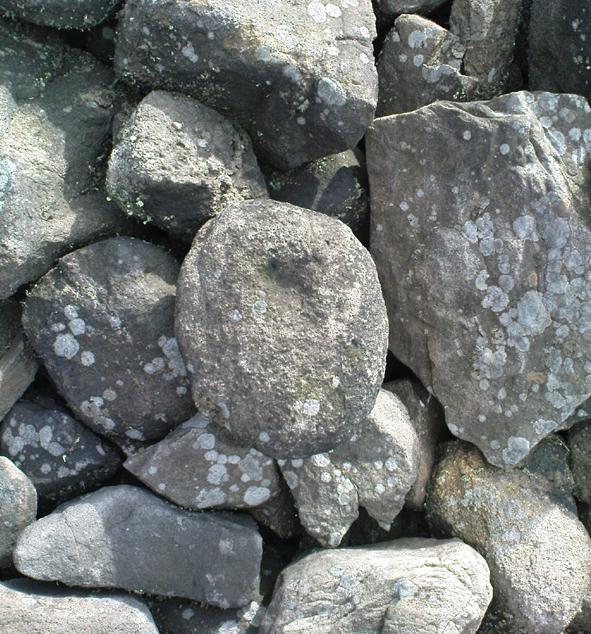
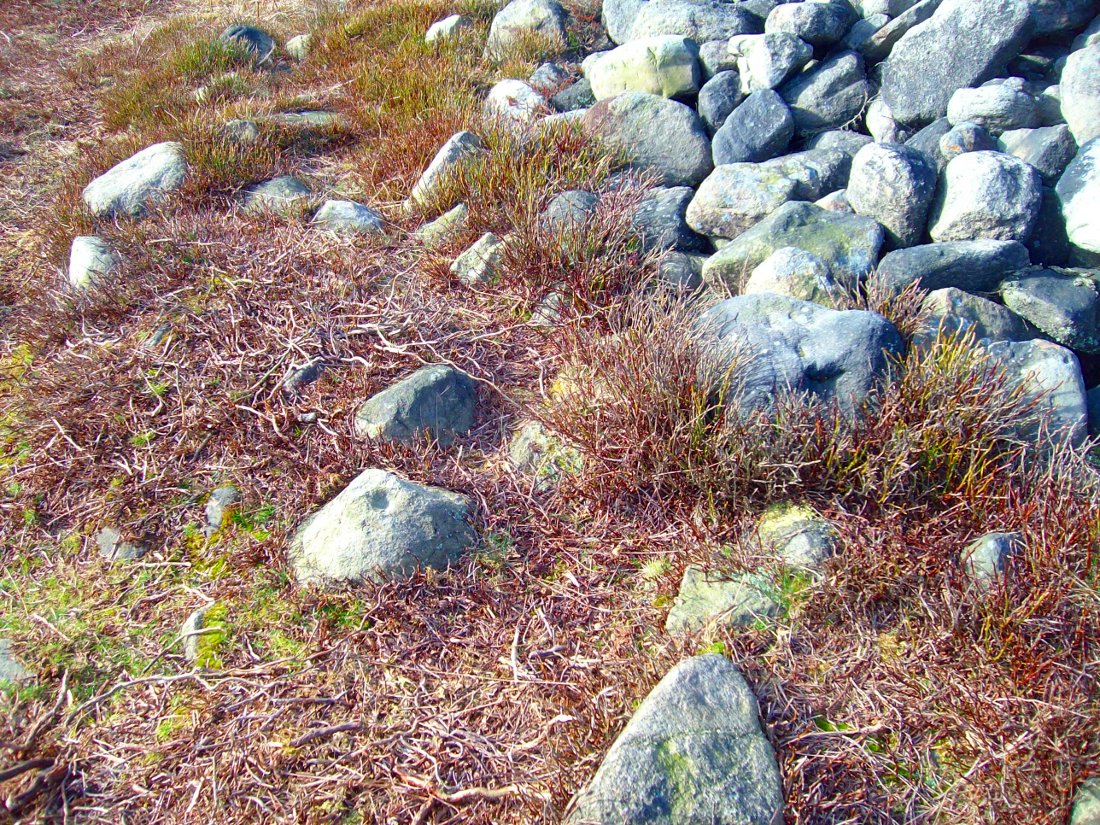


But for those of you who like to know the archaeological data, here’s what was said: Carving 391a is a “small rock towards SW edge of cairn, with single worn cup”; but this stone is actually closer to the northern section of the cairn. Carving 391b was told to be a “small dome-shaped rock at extreme S edge of cairn with single, small clear cup at top of dome.” This again is more on the northern section of the cairn, away from the centre. Carving 391c was described as a “small oval, rounded rock at N edge of cairn, with single, broad, shallow worn cup.” Whilst carving 391d which was told to be a “small rock at SSE edge of cairn, with single small worn cup.” However, we have to take into account that any errors about their position may simply be down to the fact that the small rocks have been moved.
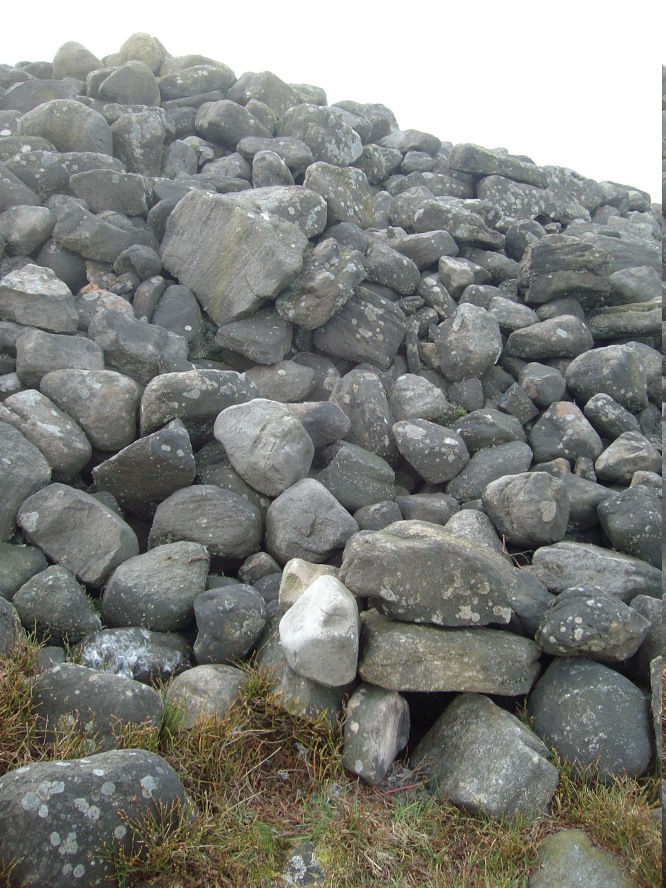
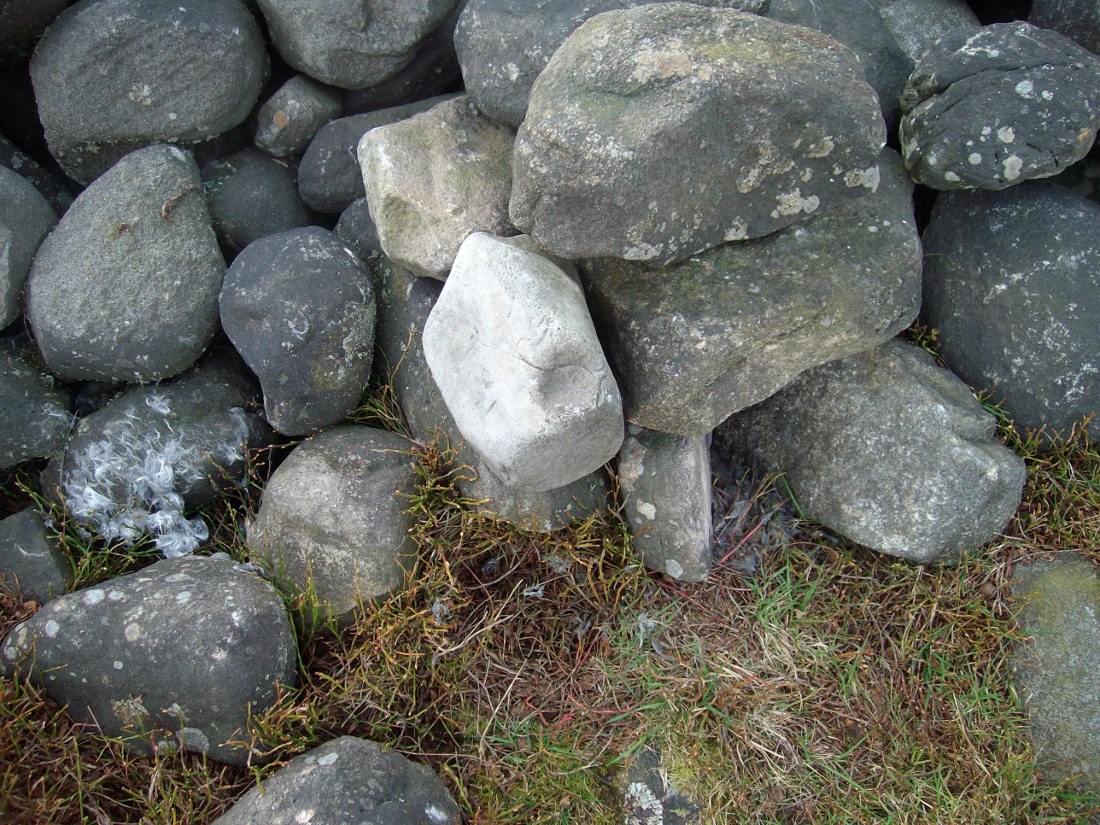


As you’ll see in the photos here, one of them is actually near the very centre of the cairn, with the cup-marking etched into the edge of the small rock itself. I’m not quite sure if this is the additional fifth carving in the cairn, or whether it’s one of those wrongly ascribed as being in another position. It’s hard to tell, as the local Ilkley Archaeology team don’t publish their findings and information on-line as they should do and unless you’re in their little club they’re hard to get info out of. So this will have to do for the time being I’m afraid. Also note how one of the cup-marked stones is of a rock-type different to the local millstone grit.
Folklore
The creation myth of the Little Skirtful itself tells that the giant Rombald (who gives his name to the moor) was in trouble with his wife and when he stepped over to Almscliffe Crags from here, his giant wife – who is never named – dropped a small bundle of stones she was carrying in her apron. Harry Speight (1900) tells us of a variation of the tale,
“which tradition says was let fall by the aforementioned giant Rumbalds, while hastening to build a bridge over the Wharfe.”
Variations on this story have said it was the devil who made the site, but this is a denigrated christian variant on the earlier, and probably healthier, creation tale. Similar tales are told of the Great Skirtful of Stones, 500 yards south.
The cluster of portable small stones with single cup-marks on them relates to traditions found in other cultures in the world where, usually, women would carry such items in their aprons and deposit them at or on the tomb, in honour of the ancestor or spirit known to be resident at the sacred site. The folklore found at the Little Skirtful (and Great Skirtful too) of Rombald’s wife dropping the rocks here and forming the giant tomb, probably derive from variants of this same honorary practice.
References:
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Chieveley 2001.
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock Art of the West Riding, WYAA 2003.
- Cowling, Eric T., Rombald’s Way, William Walker: Otley 1946.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian