Hillfort: OS Grid Reference – NS 8094 9566
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 47113
- Wallace Monument Fort
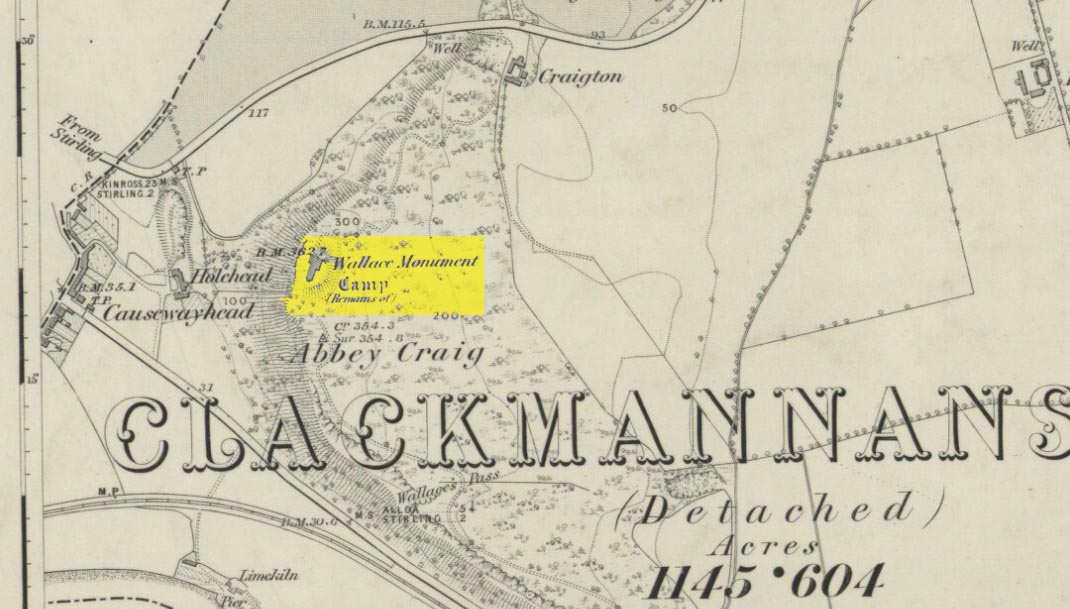
Most folk visiting here are coming from Stirling city. There are various buses to get here, which head out over Stirling Bridge along Causewayhead Road (the A9) for half-a-mile where, at the roundabout and the William Wallace pub, go straight across up the minor road, zigzagging back on itself, until you reach the signs for the Wallace Monument. Follow the well-defined footpath and, once on top of the hill, walk round the back of the mightily impressive tower.
Archaeology & History
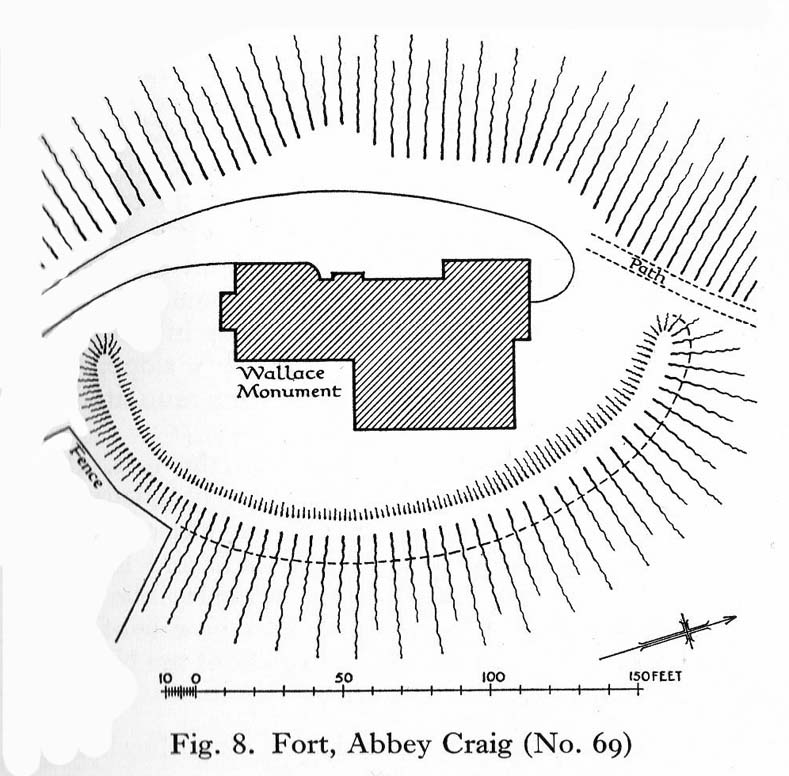
Located right where the impressive Wallace Monument proudly stands, this prehistoric precursor to Sir William Wallace’s memory was where Scotland’s legendary hero and his men cast a clear and easy view over Bannockburn, where the halfwit english came for a fight—and deservedly lost! The structures that used to be inside the now denuded hillfort would, no doubt, have been used by Wallace’s men; but much of those prehistoric remains have now been destroyed. The visible remains of the fort can be seen round the back of the Wallace Monument: elongated rises of overgrown walling that run almost all the way round, getting slightly higher as you approach the more northern edges, like a semi-circular enclosure.

The site was described very briefly in William Nimmo’s (1880) early survey of the area, where he told that in 1784, “eleven brazen spears were found on the Abbey Craig, by a Mr Harley”, which he thought came from the time when the earlier ‘castle’ stood here. He was probably right. Many years later, the prehistoric remains were included in the county survey of archaeological sites by the Royal Commission lads (1963), who told that, near the north end of the summit of Abbey Craig,
“there is a fort which has been damaged by the construction within it of the Wallace Monument. All that remains is a substantial turf-covered bank, cresentic on plan and 260ft in length, the ends of which lie close to the brink of the precipice that forms the west face of the hill. The bank stands to a maximum height of 5ft above the level of the interior and presumably represents a ruined timber-laced wall, since numerous pieces of vitrified stone have been found on the slopes immediately below it.
The entrance to the fort presumably lay between one end of the bank and the lip of the precipice, but both the areas concerned have been disturbed by the construction of the modern approaches. The interior of the fort measures about 175ft from north to south, by about 125ft transversely and the interior is featureless.”
The fort was probably built sometime in the early Iron Age; so the next time you visit this fine spot, check the remains out round the back of the tower—and remember that our ancestors were living up here 2500 years ago!
References:
-
Aitchison, N.B., “Abbey Craig Rampart’, in Discovery & Excavation, Scotland, 1981.
- Feacham, Richard W., Guide to Prehistoric Scotland, Batsford: London 1977.
- Hogg, A.H.A., British Hill-Forts: An Index, BAR: Oxford 1979.
-
Nimmo, William, The History of Stirlingshire – volume 1 (3rd edition), T.D. Morison: London 1880.
-
Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments Scotland, Stirling – volume 1, HMSO: Edinburgh 1963.
-
Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, Archaeological Sites and Monuments of Stirling District, Central Region, Society of Antiquaries of Scotland 1979.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian