Hillfort: OS Grid Reference – NS 97105 89923

Take the A907 road between Clackmannan and Comrie and, close to Bogside Farm at the roadside, but on the other side of the road where the bridge crosses a burn, take the dirt-track uphill and into the woodland. About 300 yards up (before you hit the signs pointing you to the farm) , walk uphill into the trees on your left until the ground levels out. Look around! (and best visited between December and May, before the bracken covers the place)
Archaeology & History
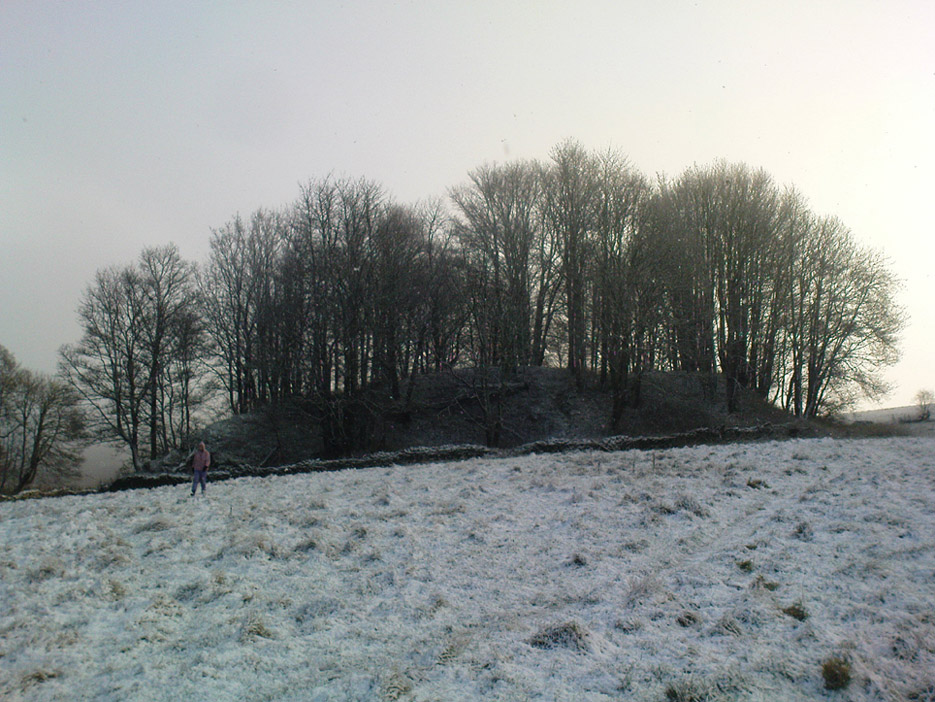
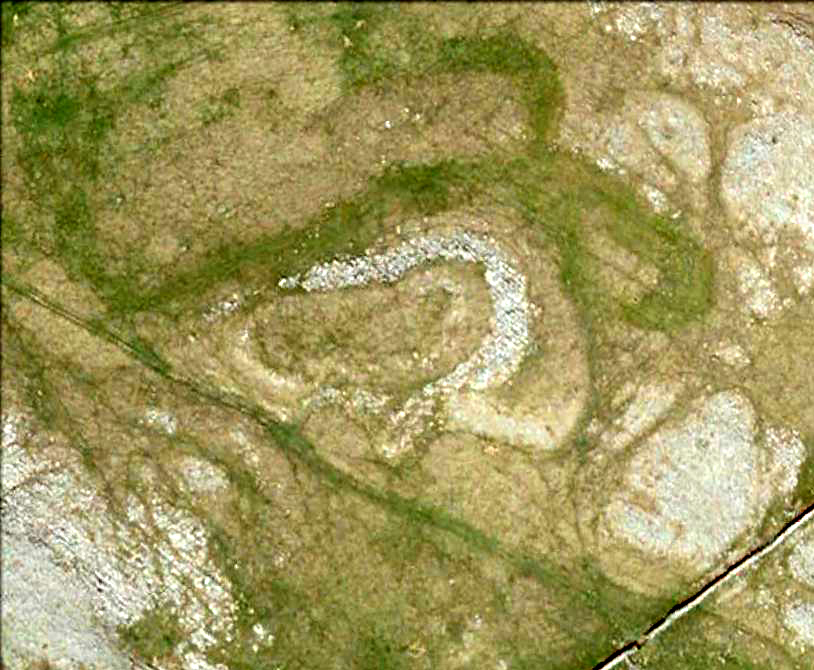
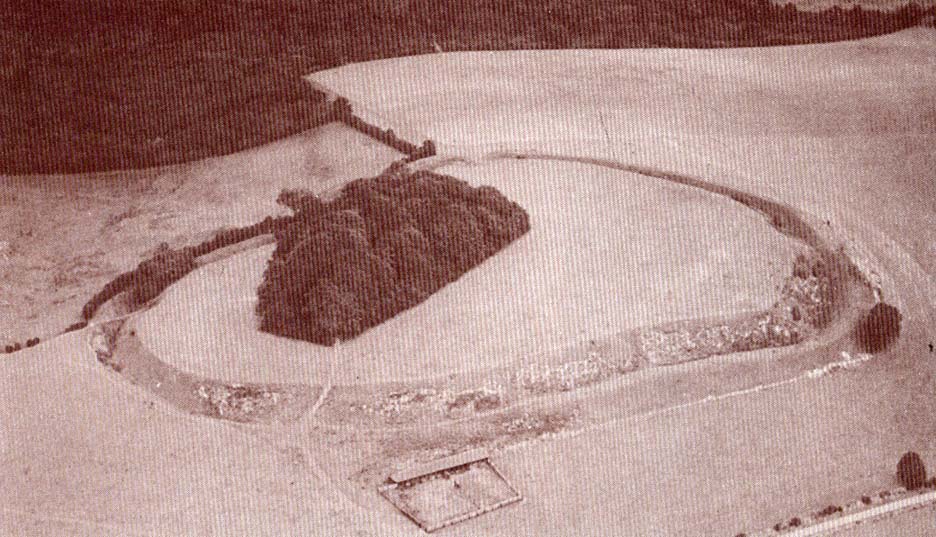
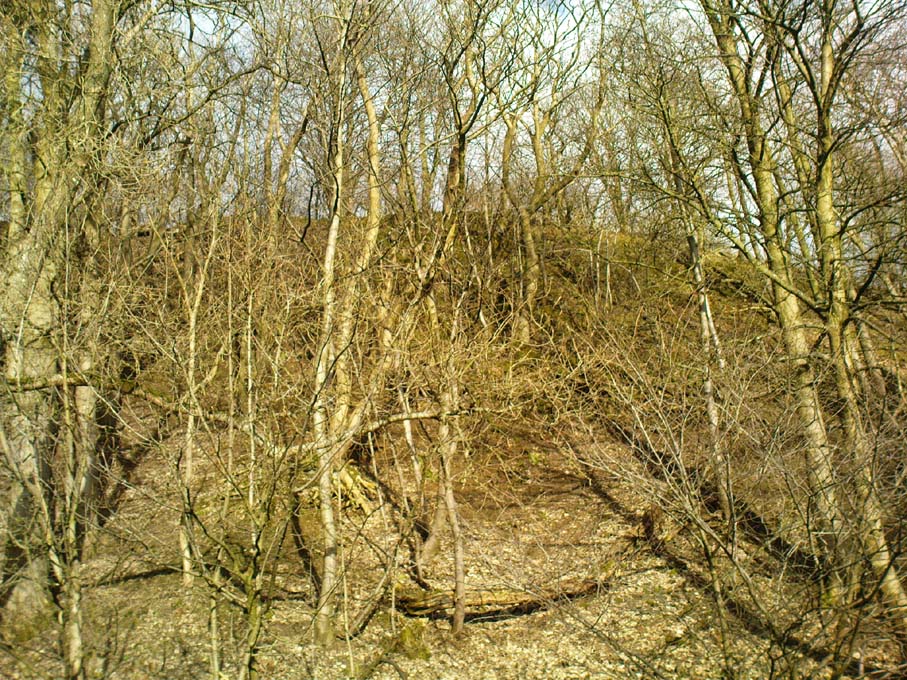
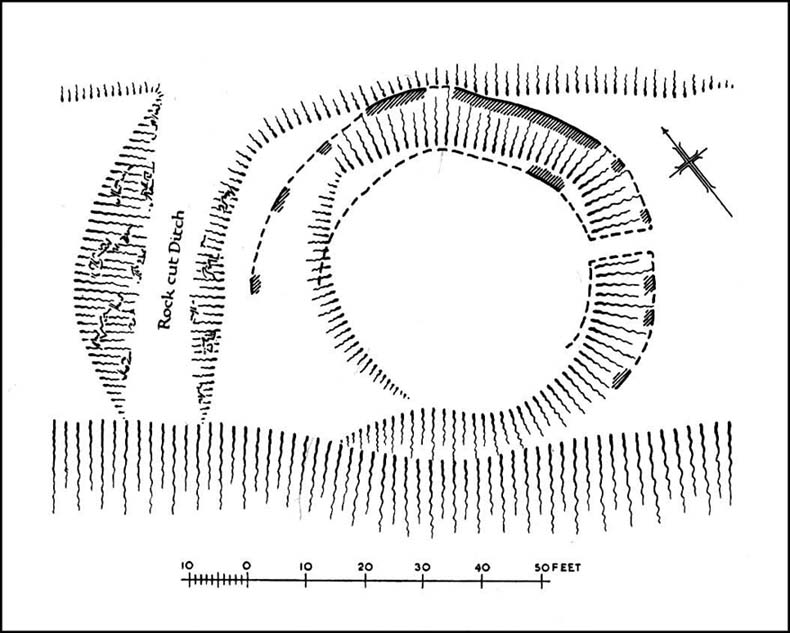
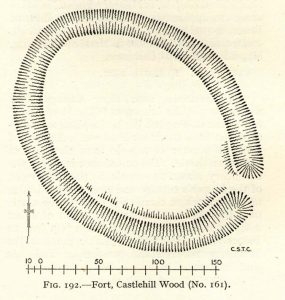
Visiting this site is pleasure in itself. Situated in an open forest, with traditional pine trees in abundance, there are scattered amidst the edges of this large oval-shaped Iron Age structure, the aged boughs of ash and beech, centuries old, along its edges and throughout the woods. It is a truly superb setting! When visited by the Royal Commission lads in April, 1925, they found the remains here in good condition. A few years later in their impressive Inventory, they told:
“In Castlehill Wood, about 250 yards to the southwest of Bogside Railway Station, and at an elevation of 200 feet above sea-level, is a small plateau of very regular oval form with its major axis northwest and southeast. It is surrounded by a single ditch, the well-marked enclosure thus produced having a maximum measurement of 185 by 135 feet. At the southeast the ditch has been left uncut in order to provide a passage for entrance. This passage has been about 20 feet wide, and at its inner end there are on either side faint traces of a low mound, which in all probability once ran right round the edge of the enclosure and which may have been palisaded.”
Sadly when I came here a few days ago, much of the was very overgrown with bracken and other vegetation, making it impossible to see the site properly and preventing any decent photos. We’ll go back here in a few months time to get better images!
Folklore
This site was mentioned, albeit briefly, in David Beveridge’s (1885) magnum opus on the history of Culross. With equal brevity he noted several standing stones in the region, saying how tradition afforded them a Danish origin. This site was the same for
“a tradition prevails that after the battle of Inverkeithing the Danish army or a portion of it retreated to a station in the north of Culross parish, where they erected the earthwork or camp of Castlehill, still existing near the Burrowine Farm.”
References:
- Beveridge, David, Culross and Tulliallan: Its History and Antiquities – volume 1, William Blackwood: Edinburgh 1885.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments, Scotland, Inventory of Monuments and Constructions in the Counties of Fife, Kinross and Clackmannan, HMSO: Edinburgh 1933.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian