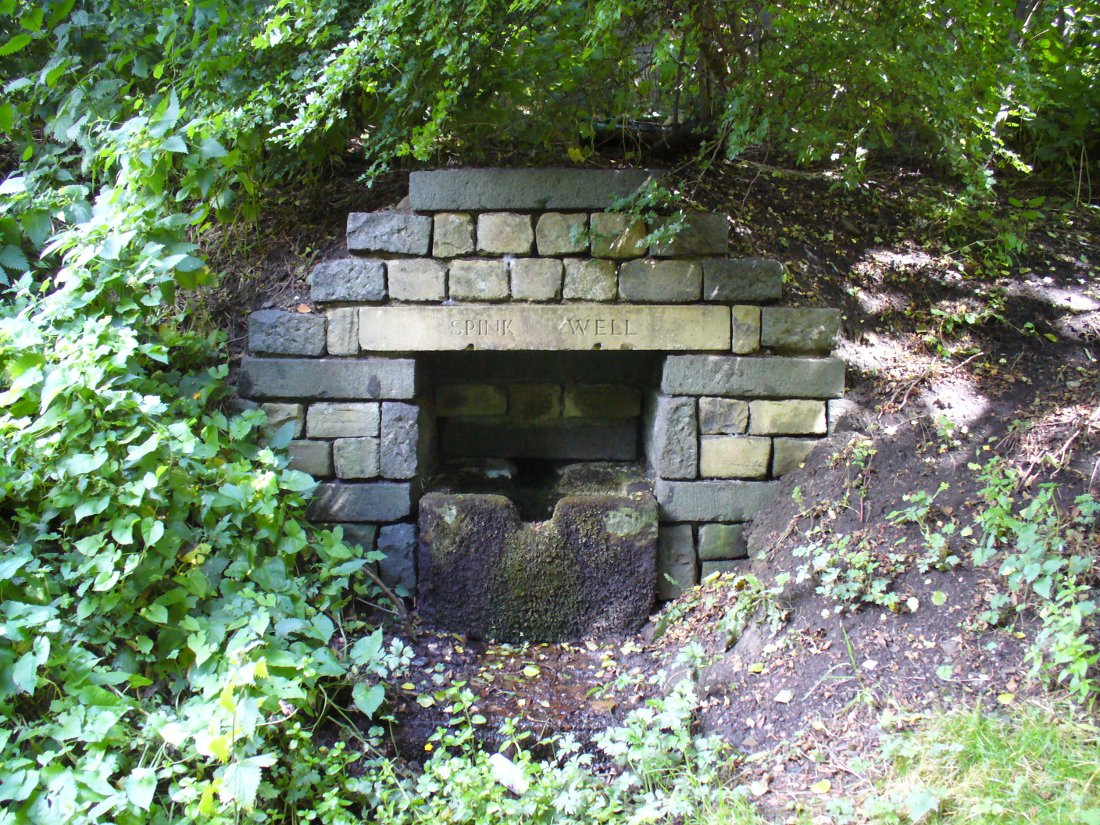
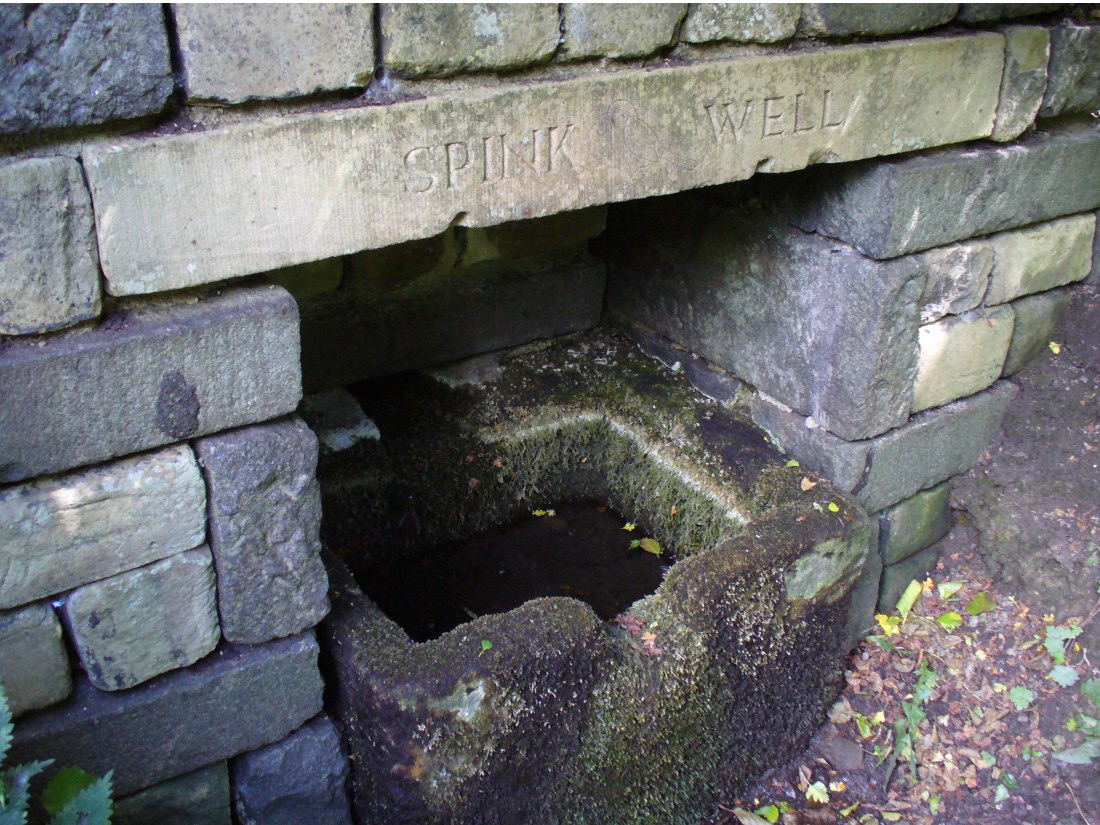
Sacred Well: OS Grid Reference – SD 34908 37119
Also Known as:
- Wrangdom Well
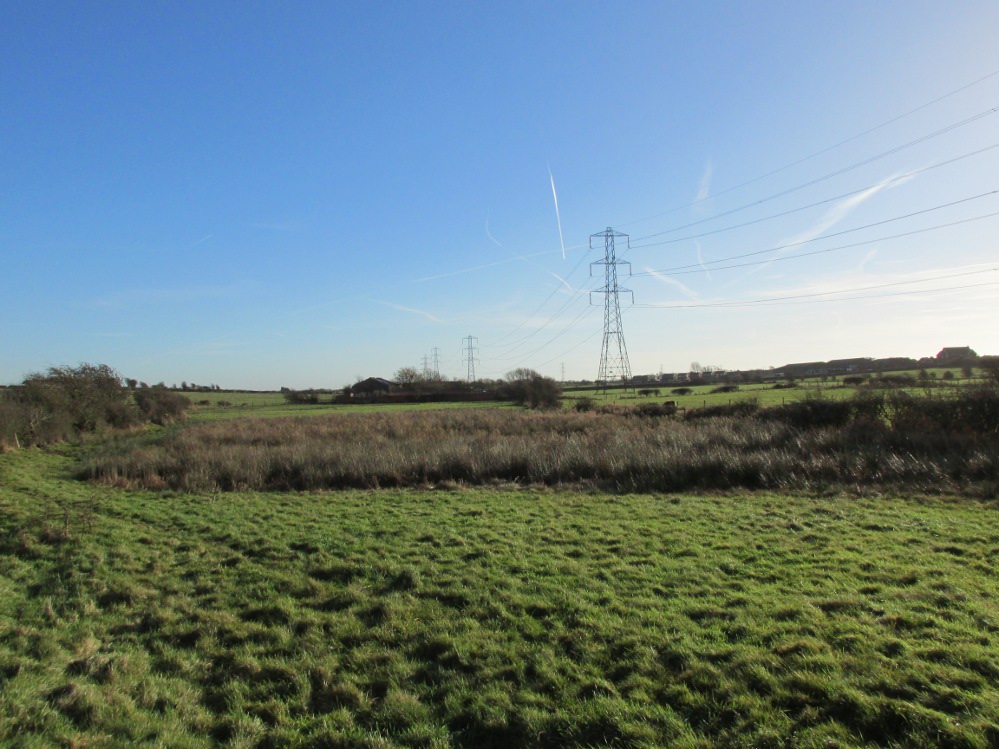

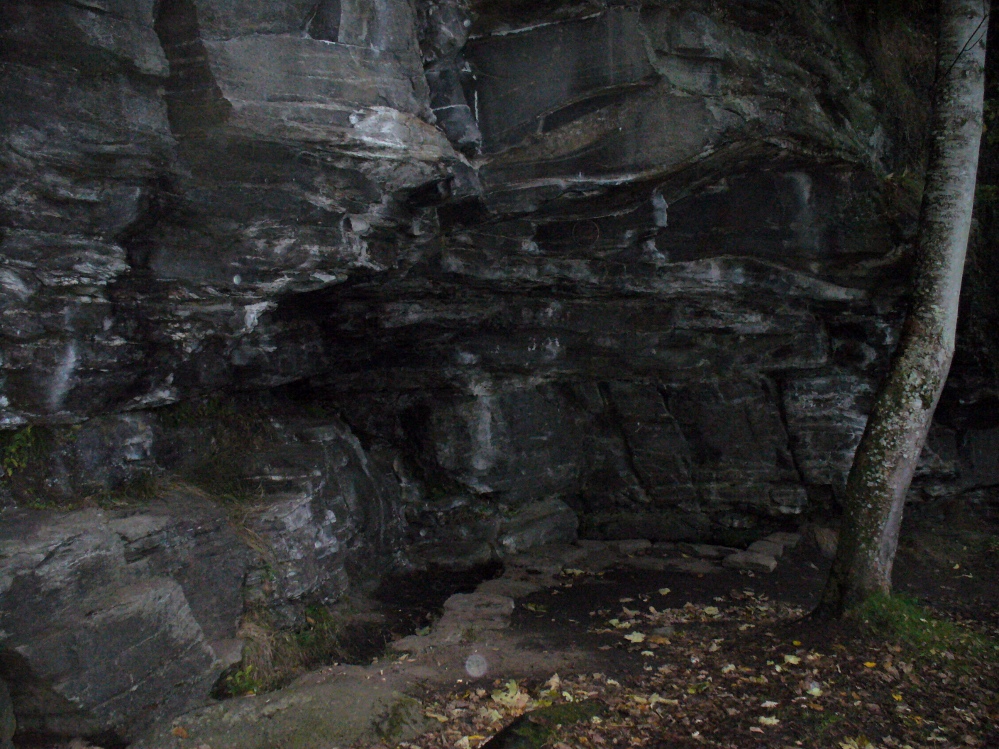
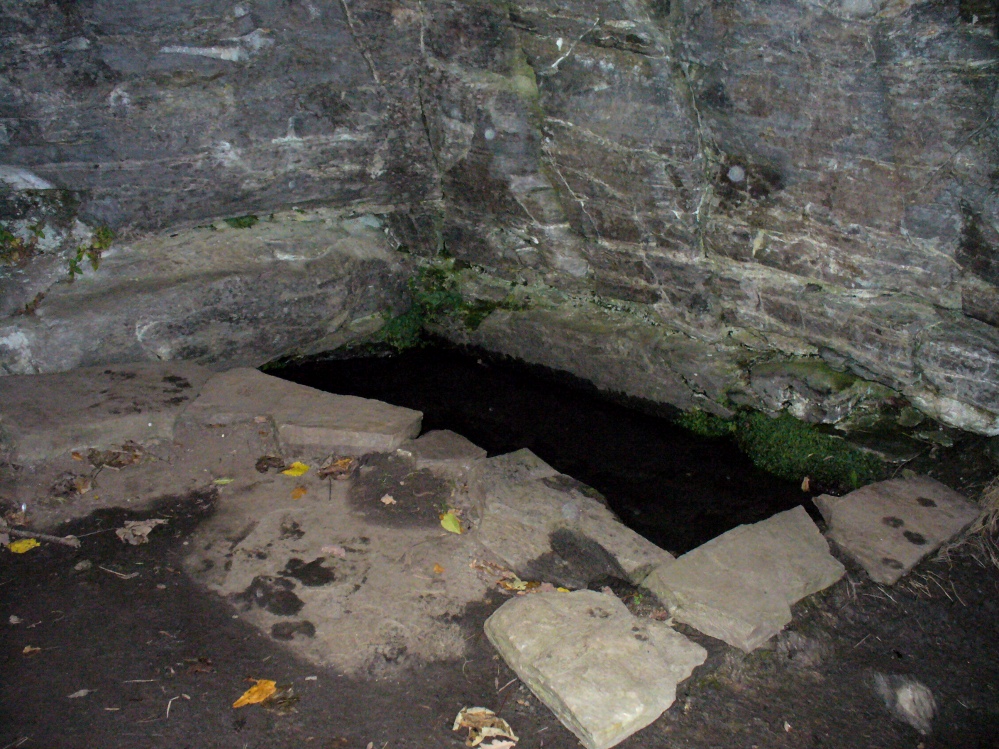
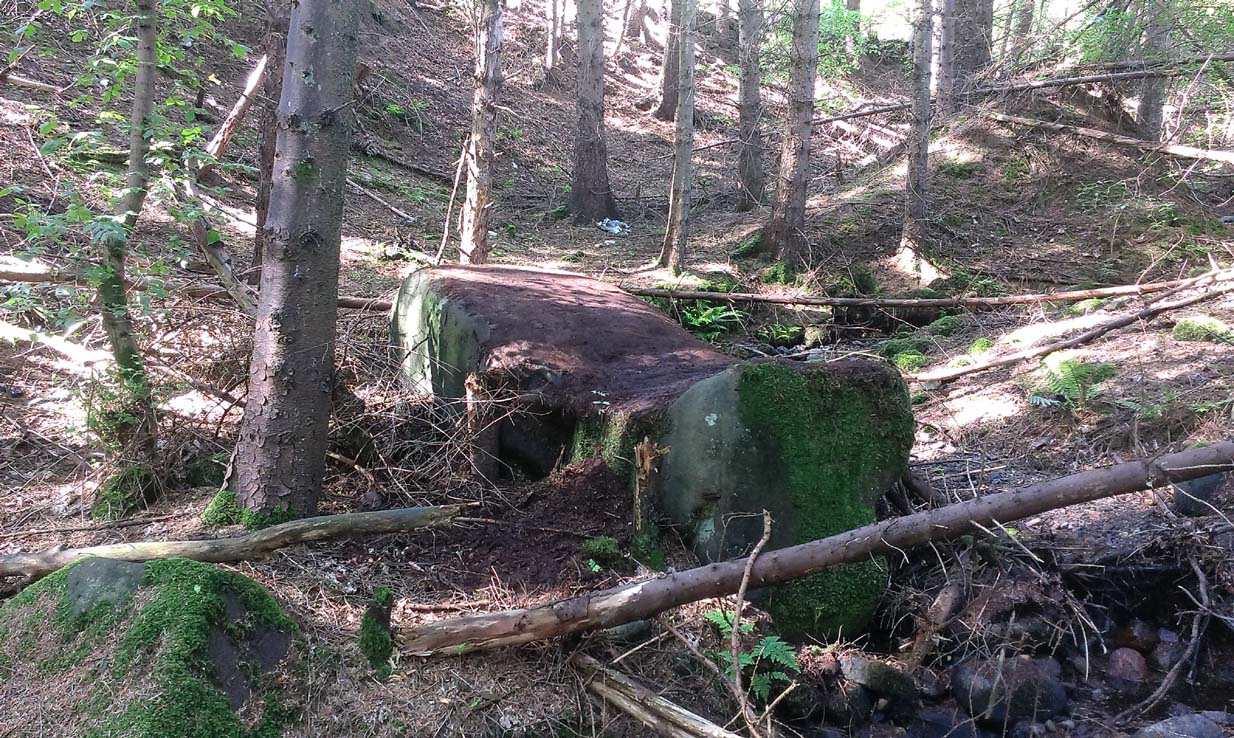
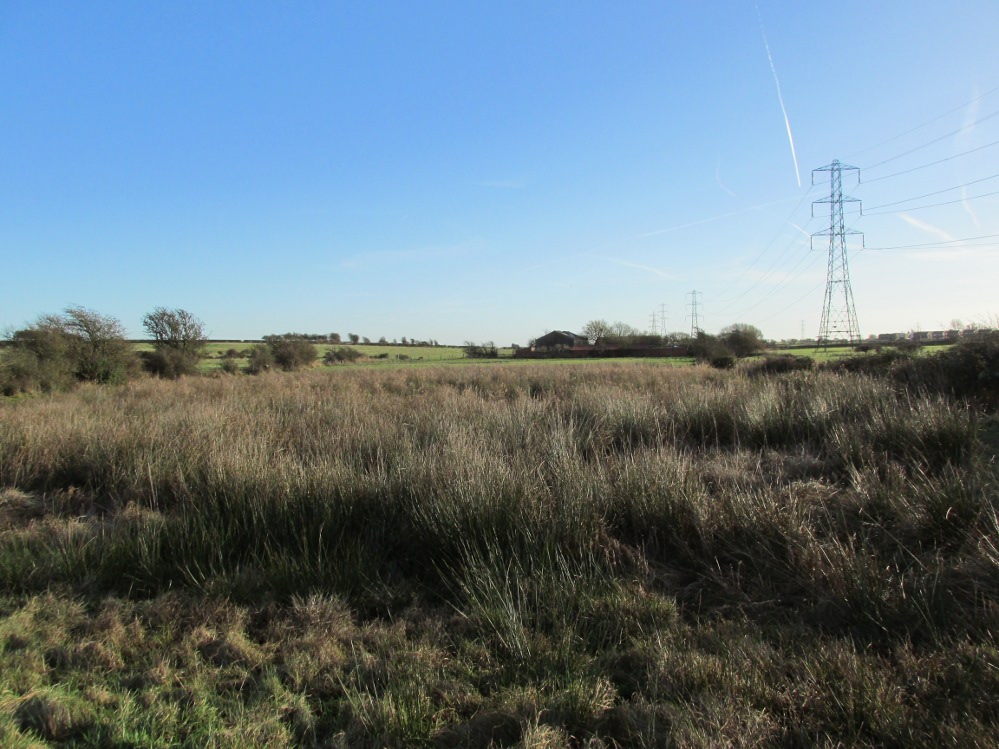
One and a half centuries of neglect have not been kind to the Wrangdomwell, which is now in the middle of a large area of swampy land, reached from Staining village along Mill Lane, turning right at the windmill then walking along Smithy Lane. Just before a derelict piggery on the left go into the field, and Wrong Well Meadow is on the right at the back of the piggery, with the spring issuing from the boggy ground. Be prepared to cross barbed wire fences, and to meet some friendly ponies.
Archaeology & History
Were it not for the researches and writings of an eccentric cleric, this site would almost certainly now be lost to history. The Reverend William Thornber recorded, in his 1837 History of Blackpool that:
“The fairies of our fathers…were kind good natured creatures, at times seeking the assistance of mortals, and in return liberally rewarding them. They had a favourite spot between Hardhorn and Staining, at a cold spring of water, called Fairies’ Well to this day.”

Writing in a paper published in 1851, Thornber described the Fairy Well or Wrangdomwell in the context of the “Teanlas”, the enormous Hallowe’en bonfires (4) that were still at that time being lit at ritual cairns of stones in parts of west Lancashire. One of these fire cairns once adjoined the Fairy Well, which in 1850 was still being visited for its,
“sovereign virtue for healing the diseases of men and cattle. To succeed in obtaining a cure, the patient, escorted by his friends, was made to pass through the cairn, then he was sprinkled or dipped in the well, and lastly, he made an offering of a shell, pin, a rusty nail or a rag, but principally three white stones burnt in the Teanla fire. It is surprising in what numbers pieces of iron may be picked up. I have found since the meadows were ploughed, nails, an old shaped knife, leather thongs etc.”
Thornber wrote that the cairn no longer existed, and gave no precise location for the well.
Looking at the area between Hardhorn and Staining on the 1891 25″ OS map revealed only one ‘spring’; in land parcel 295. This parcel of land is recorded in the Schedule to the 1839 Tithe map as ‘Wrong Well Meadow’, occupied by Thomas Dobson, and owned by ‘School of Marton’, a charitable endowment established in 1717. Adjoining Wrong Well Meadow are Old Meadow and Nickers Meadow (‘Old Nick’?), which might appear to show the Wrangdomwell as in the past having been part of a larger heathen ritual locality. Notwithstanding this, the Church was happy to take its tithe.
References:
- Thornber, William, The History of Blackpool, Smith Market Place: Poulton-le-Fylde 1837 (republished in 1985 by the Blackpool and Fylde Historical Society).
- Thornber, William, ‘Traces of the Britons, Saxons and Danes in the Foreland of the Fylde,’ in Proceedings and Papers of the Historic Society of Lancashire and Cheshire, Liverpool 1852.
- Tithe Map & Schedule Transcript, ‘The Township of Hardhorn with Newton’ Surveyed by Thomas Hull in 1838, with Schedule dated 1839.’
- Michelle Harris & Brian Hughes, in their ‘The History of the Wyre from Harold the Elk to Cardinal Allen‘ (4th ed. 2007) p35, write – “According to Tom C. Smith’s ‘History of the Parish of Chipping‘ published in 1891: ‘Teanlaes was the name given to fire celebrations, observed until quite recent years on May 1st, Midsummer Day, August 31st, and November 1st.’ These dates, it should be said, are at variance with Henry Taylor who, in his 1899 publication ‘Ancient Crosses of Lancashire’, quotes Atticus as saying: ‘The ceremony observed on Teanlow night, the last night of October, consisted of making bonfires on all the neighbouring hills.'”
Acknowledgements: My thanks to the staff of the Local Studies Department, Borough of Blackpool Library Services for their assistance.
© Paul T. Hornby, The Northern Antiquarian