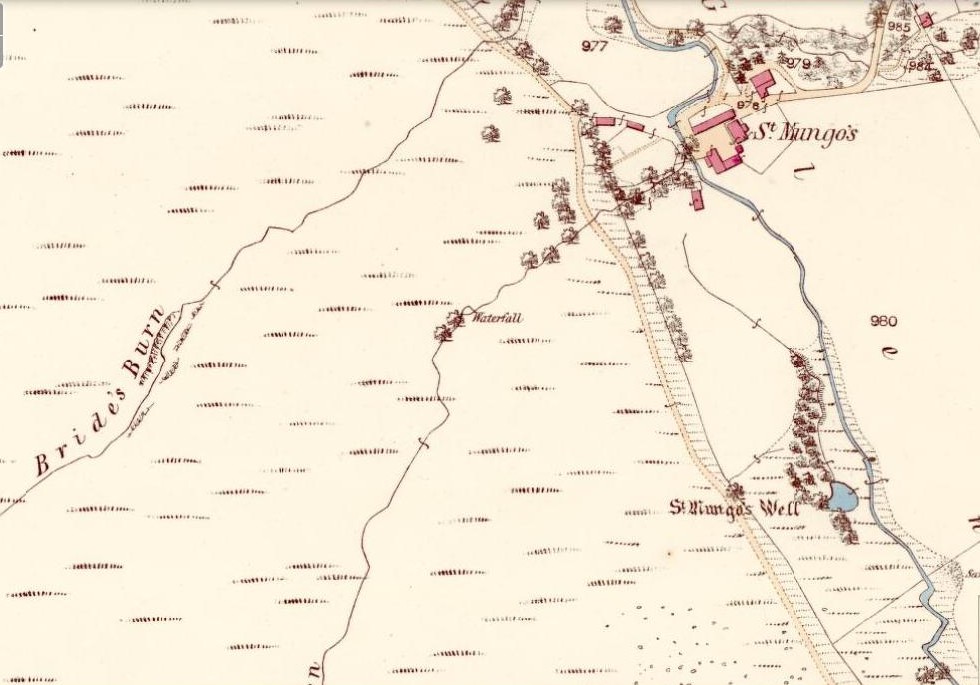
Holy Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NS 589 648
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 44288
- St. Tenew’s Well
- St. Theneu’s Well
Archaeology & History
Whilst I’m in Glasgow (big thanks to Aisha!) I thought I’d check out any remaining heathen sites that might still be visible. Many have perished of course, beneath the weight of religious industrialism—this one included. Even when the Ordnance Survey lads came here in 1858, it had already been destroyed. All that we now know of it comes from the writings of the earlier historians like Walker (1883), Renwick (1921) and co.
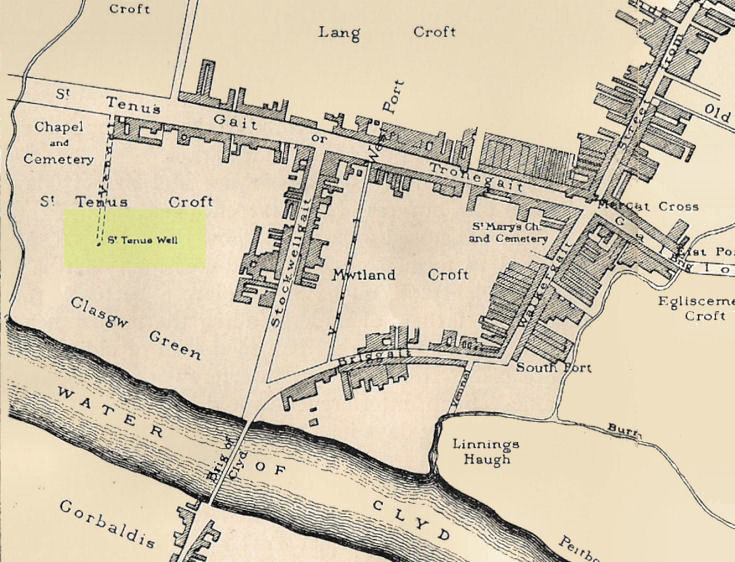
Known in early records as St. Theneu (mother of the legendary St. Mungo, who also had sacred wells dedicated to him in Glasgow, Gleneagles and much further afield), trackways and burns hereby were also named after this curious character, and a chapel was also commemorated to her, which fell into ruin several centuries ago. Its position was highlighted on a late-16th century sketch of Glasgow village—as it was then—immediately south of the chapel, just north of the River Clyde. The best description we have of it comes from a detailed paper on the holy wells of Glasgow by a Mr Brotchie (1920), who told:
“Where the subway station of St. Enoch’s Square stands…there was at one time the well of St. Tenew, the mother of St. Kentigern or Mungo. It is thus described by a writer in 1750, “The ruins of a small chapel stood beside the well whose waters were sheltered by a bush, on which were to be seen, especially in early summer, bits of rags of all kinds and colours, while in the well itself enterprising boys were wont to get small coins. The rags and the coins were the offerings of people, principally women, who came to drink of the waters of St. Tenew’s Well, and left these trifles as thank offerings.”
“This ancient well of St. Tenew stood near a chapel erected over the tomb of St. Tenew, and the ground in its vicinity remained sacred in the eyes of the faithful as the last resting place of the holy woman who had watched the infant steps of the great apostle of the Cambrian Britons, St. Mungo, the patron saint of Glasgow. The Trongate and Argyle Street, which now stretch westwards from the cross, were in old times a country road leading to St. Tenew’s chapel, kirkyard and holy well. In a deed of 1498 mention is made of “the blessed chapel where the bones of the beloved Tenew, mother of the blessed confessor, Kentigern, rest.” When M’Ure wrote his History of Glasgow in 1736, the remains of this old chapel and kirkyard were described as standing “in a solitary spot in the country surrounded by cornfields.” Looking westwards from St. Tenew’s Well in 1750, a writer describes the scene as “open country, pastures and cornfields, rude-looking country homesteads, barns and other farm buildings, and enclosed kailyards,” where now stand the busy arteries of Jamaica Street, the Caledonian Railway Station, and the miles of tenements that stretch westward to Anderston, Finnieston and Partick.
“We have a comparatively recent record of the holy well of St. Tenew in the statement of the late Mr Robert Hart, who told M’George that he had been informed by an old man, a Mr Thomson, who had resided in the neighbourhood of St. Enoch’s Square, that in the beginning of the last century, say 1800, he recollected the well being cleaned out, and of seeing picked from the debris at the bottom many old coins and votive offerings. St. Tenew’s Well was a holy well. For centuries it was a place of pilgrimage and was much resorted to for cures, especially in pre-Reformation days. In 1586, James VI, addressed a letter to Mr Andrew Hay, commissioner for the west of Scotland, condemning the practice of people making pilgrimages to wells and chapels, but the royal edict was powerless to stop the practice and St. Tenew’s Well was resorted to by people in trouble as long as it was in existence. The road that led to it was known up to the 15th century as St. Tenew’s Gait or path. Indeed, it was so named till 1540, when the name of Trongate begins to make its appearance in old city deeds. This name, of course, owes its origin to the granting in 1490 by James IV, to the Bishop of Glasgow of the privileges of a free tron in the city—hence our Trongate of today.”
References:
- Bennett, Paul, Ancient and Holy Wells of Glasgow, TNA 2017.
- Brotchie, T.C.F., “Holy Wells in and Around Glasgow,” in Old Glasgow Club Transactions, volume 4, 1920.
- Eyre-Todd, George, History of Glasgow – volume 2, Jackson Wylie: Glasgow 1931
- MacGeorge, Andrew, Old Glasgow, Blackie & Son: Glasgow 1880.
- Renwick, Robert & Lindsay, John, History of Glasgow – volume 1, Maclehose Jackson: Glasgow 1921.
- Walker, J.R., ‘”Holy Wells” in Scotland”, in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume17, 1883.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian