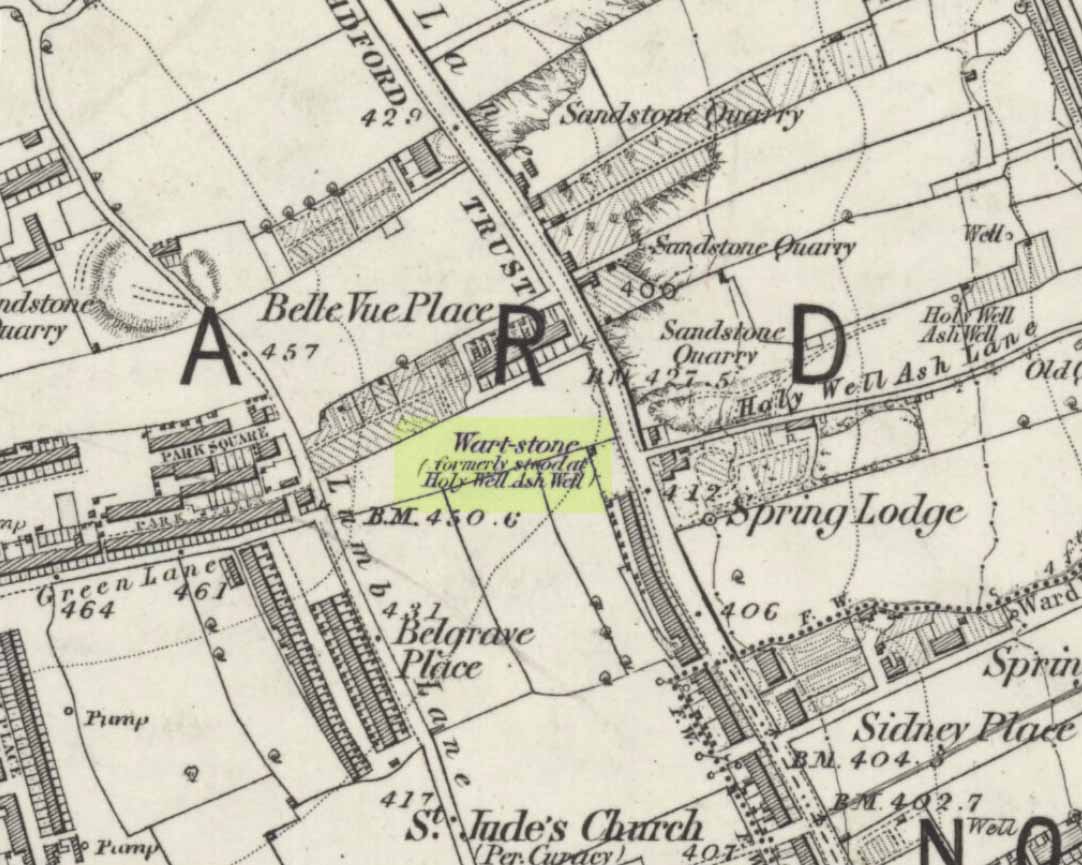
Stone Circle (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 138 403
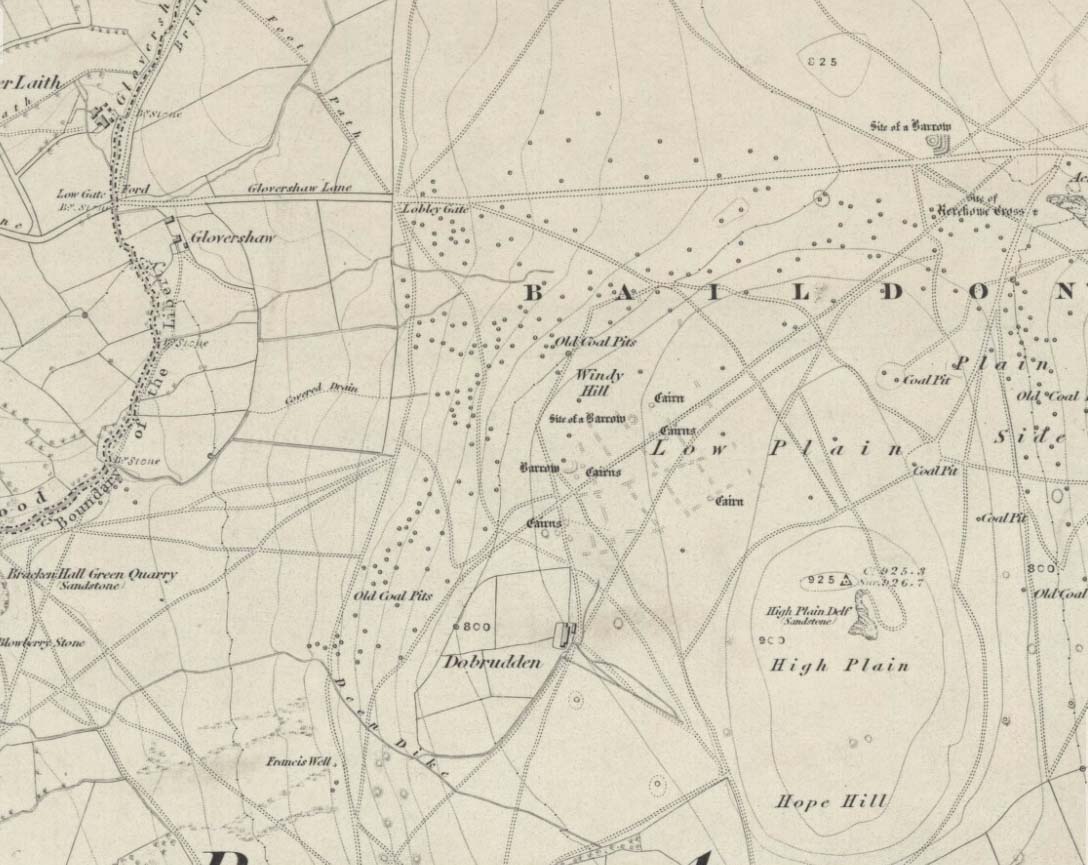
Archaeology & History
The early northern antiquarian, J.N.M. Colls (1846), described visiting a ‘druidical circle’ of stones due east of the Dobrudden prehistoric graveyard, but it seems to have been completely destroyed soon after he wrote his essay, with the stones taken away for use in road-building. He told that here was,
“a double circle of stones, the outer ring numbering eighteen, with six stones making up the inner circle.”
…and his illustration shows just that! It’s possible that this inner ring may have covered a burial. Harry Speight — aka, ‘Johnnie Gray’ (1891) — is the only other writer I’ve found that refers to the megalithic remains up here, although he gave no additional details.
The site was to be found across the High Plain and Windy Hill, on the western edge of Baildon Hill, where there was once a greater profusion of seemingly neolithic and Bronze Age remains. Another possible early reference to the site is in Collyer & Turner’s Ilkley (1885), where they talk of a circle “on the highest part of the eastern moor,” fifty-six feet across with a similar appearance to the Pennythorn Hill circle, although they describe it as overlooking the hamlet of Sconce, which is hardly possible from the Windy Hill side of Baildon Moor.
The site looked across the horizon from south, through west to north and if used astronomically would have been used to observe sun and moonset times. Although we find a number of cup-and-ring stones in the vicinity, it really does seem that this site has bit the dust!
References:
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Chieveley 2001.
- Colls, J.N.M., ‘Letter upon some Early Remains Discovered in Yorkshire,’ in Archaeologia 31, 1846.
- Collyer, Robert & Turner, J. Horsfall, Ilkley, Ancient and Modern, William Walker: Otley 1885.
- Gray, Johnnie, Through Airedale, from Goole to Malham, Elliot Stock: London 1891.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian