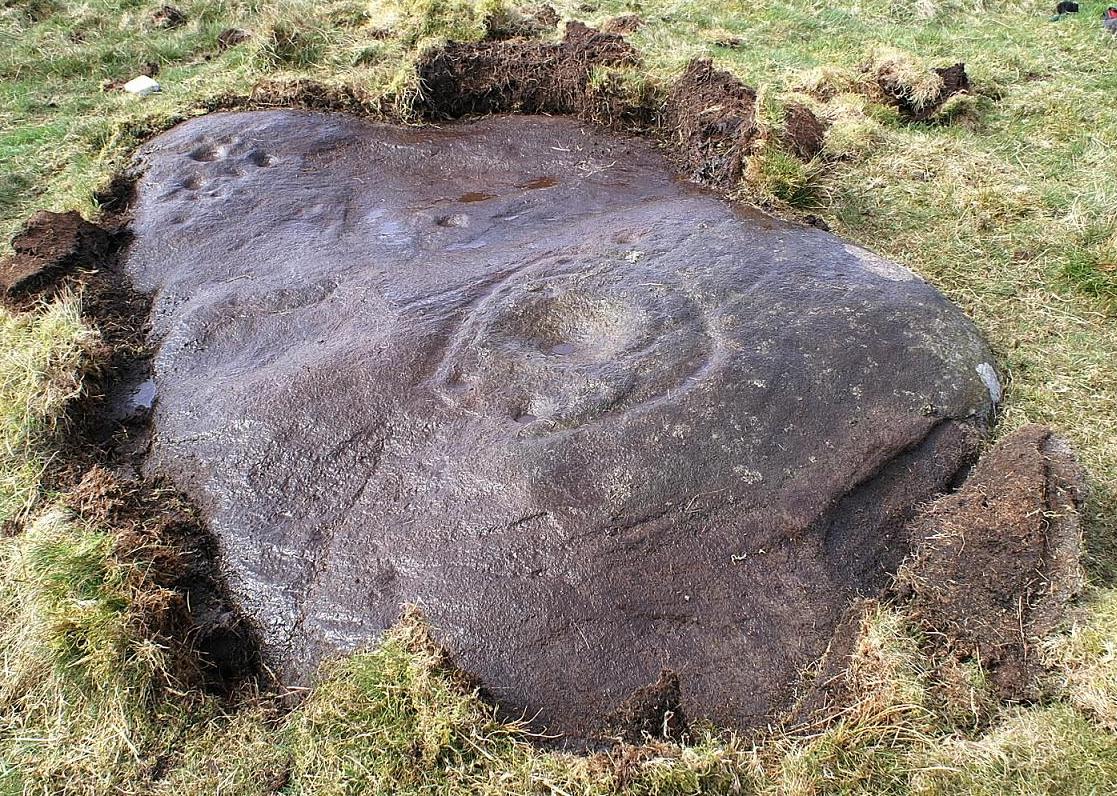
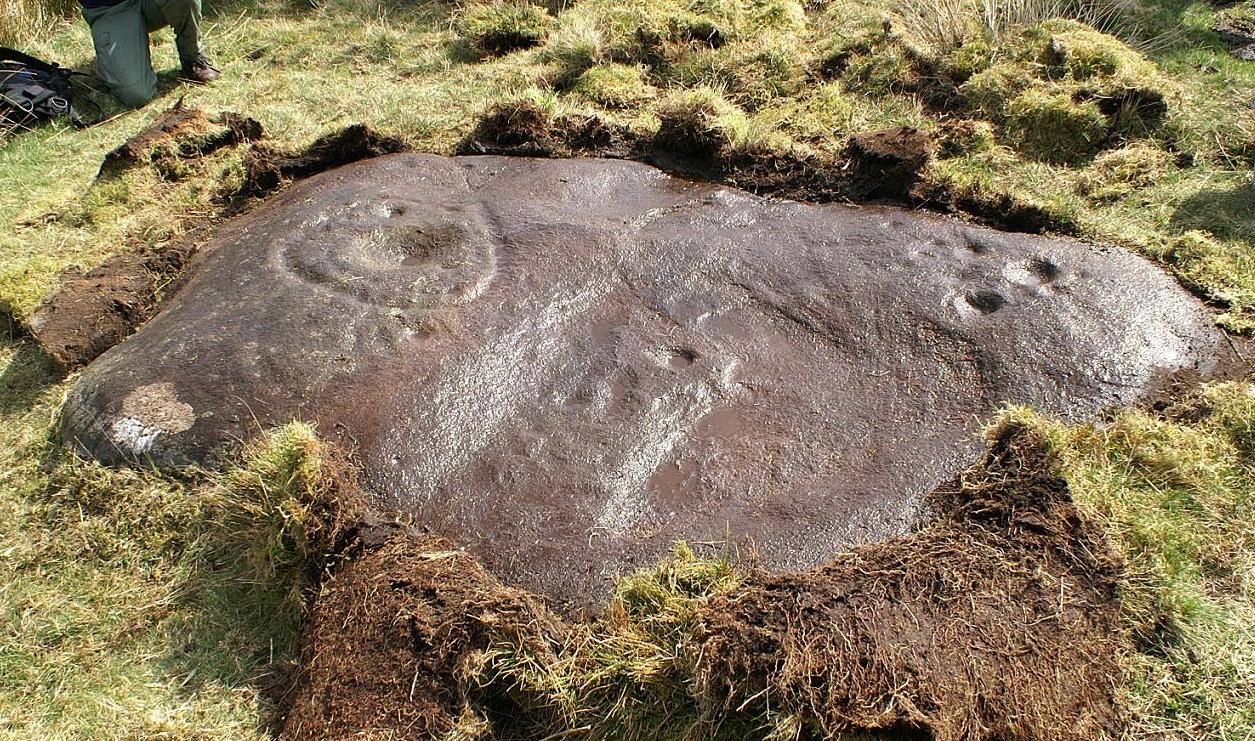
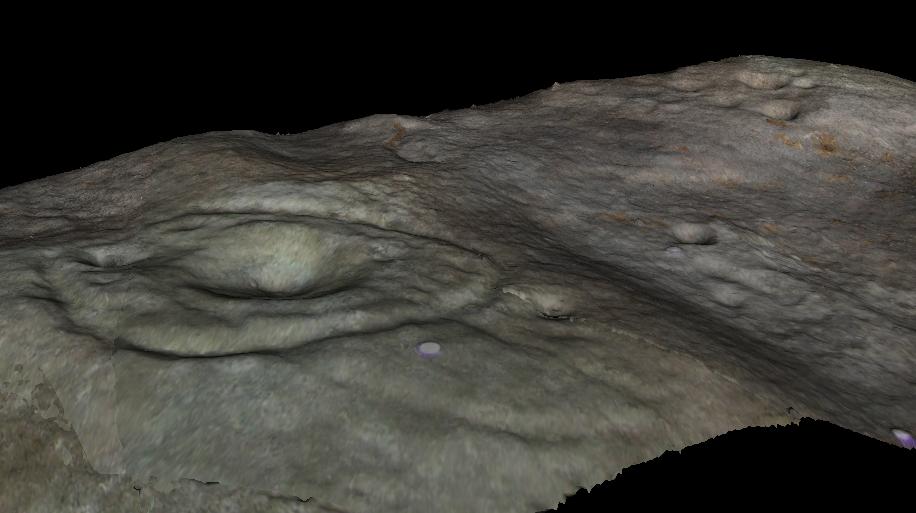
Cairn: OS Grid Reference – SE 11468 45224
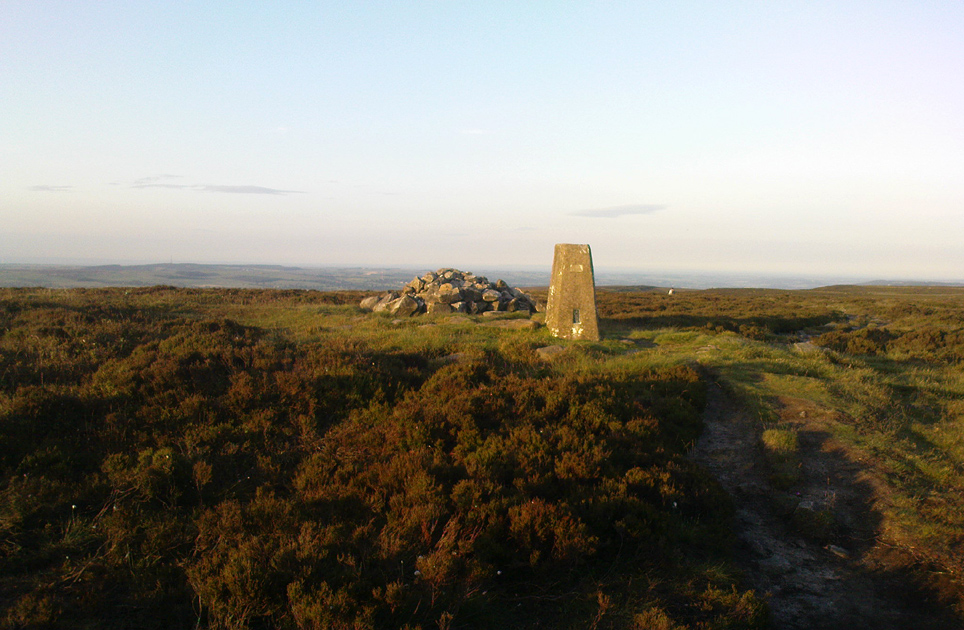

This is the highest point of the moors, 1320 feet up. There’s various ways of getting there: I’d favour the wander up to Twelve Apostles then taking the 15 minute walk west to the triangulation point which marks the spot. If you reach the large rocky outcrop of the Thimble Stones, you’ve gone too far; although you can walk past the Thimbles, if you’ve started your walk from the two radio masts atop of the moor where the old Roman road hits the dirt-track. Either way, unless you’re damn stupid, this is an easy spot to find!
Archaeology & History
Although today there’s little to be seen, when Collyer & Turner (1885) described the place it was 175 yards in circumference! Bloody huge! When Harry Speight got here in 1900, it had shrunk slightly to 150 yards. Now however, almost all the stones have been robbed. I first came here when I was just 11 years old and remember it was a decent size even then – at least as large as the Little Skirtful and Great Skirtful of Stones more than a mile to the east. Today however, unless you knew it was once a giant cairn, you wouldn’t give it a second look.
It’s quite appalling what’s happened to this site thanks to the sheer ignorance and neglect of the local archaeologist in tandem with his paymasters at Bradford Council: 90% of the site has been utterly vandalised and destroyed as a result of these incompetent idiots in the last 20 years. Nowadays, all you can make out here is the raised earth for about 10 yards surrounding the trig-point. It seems that most of the stones that comprised this giant cairn have been taken for use in walling, and to prop up the stupid paved footpaths which the local Council and its affiliated halfwits are slowly building o’er these hills.* Morons!
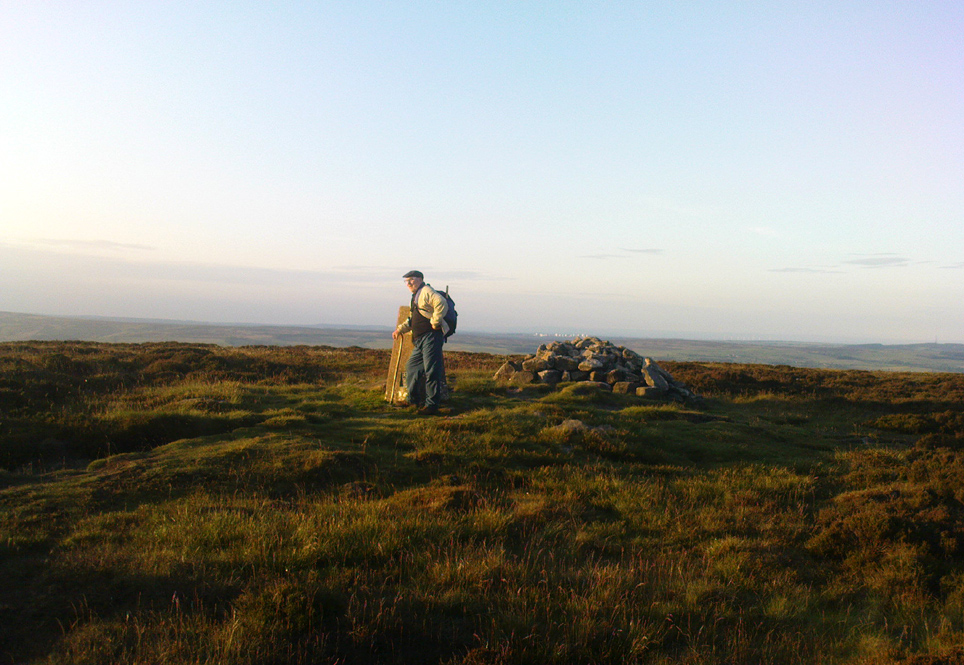

I’m not quite sure why it was called Nixon’s Station. It was J. Atkinson Busfield (1875) who mentioned this name, quite casually in his fine local history work, as if local folk had known it as such for sometime. There was also an inference of it being the resting place of some old general, but I’ve found nor heard anything more along such lines — though worra superb place for your spirit to roam free…..
If anyone has any old photos of this once giant prehistoric site, it would be good to see it in its old glory once again. When I wandered up here as a kid, I never carried things like a camera about (being a Luddite by nature!).
References:
- Busfield, J.A., Fragments Relating to the History of Bingley Parish, Bradford 1875.
- Collyer, R. & Turner, J.H., Ilkley, Ancient & Modern, Otley 1885.
- Speight, Harry, Upper Wharfedale, London 1900.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
* Anyone know exactly which idiots are responsible for the stone footpaths being laid over the moors here? They’re damn stupid and cause even more erosion and damage to the environment and prehistoric heritage up here, as anyone with an ounce of common sense can see. Can someone please get them stopped!?