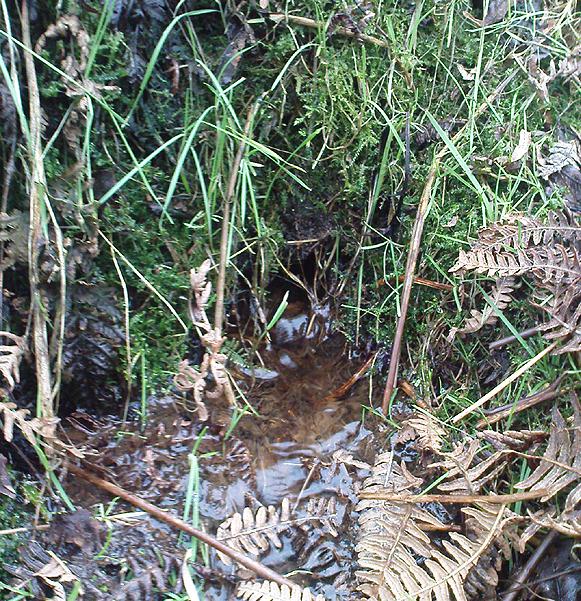
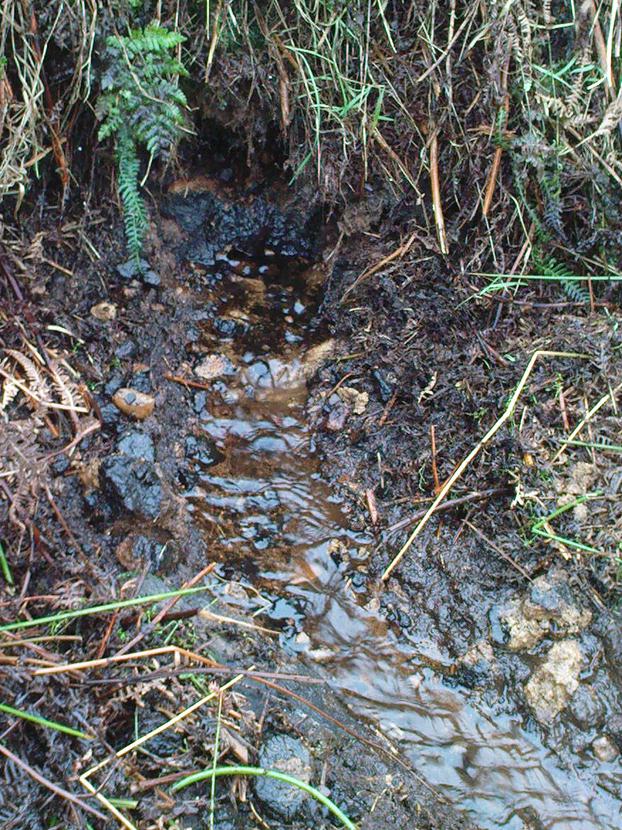
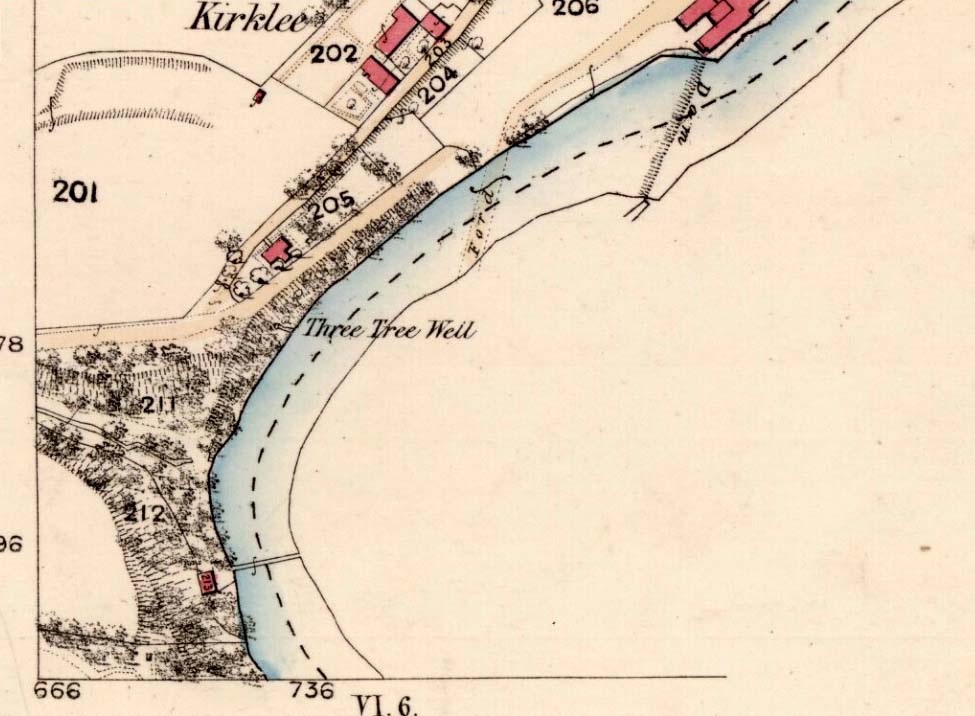
Healing Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NS 56728 67797
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 164370
- Three Tree Well
Archaeology & History
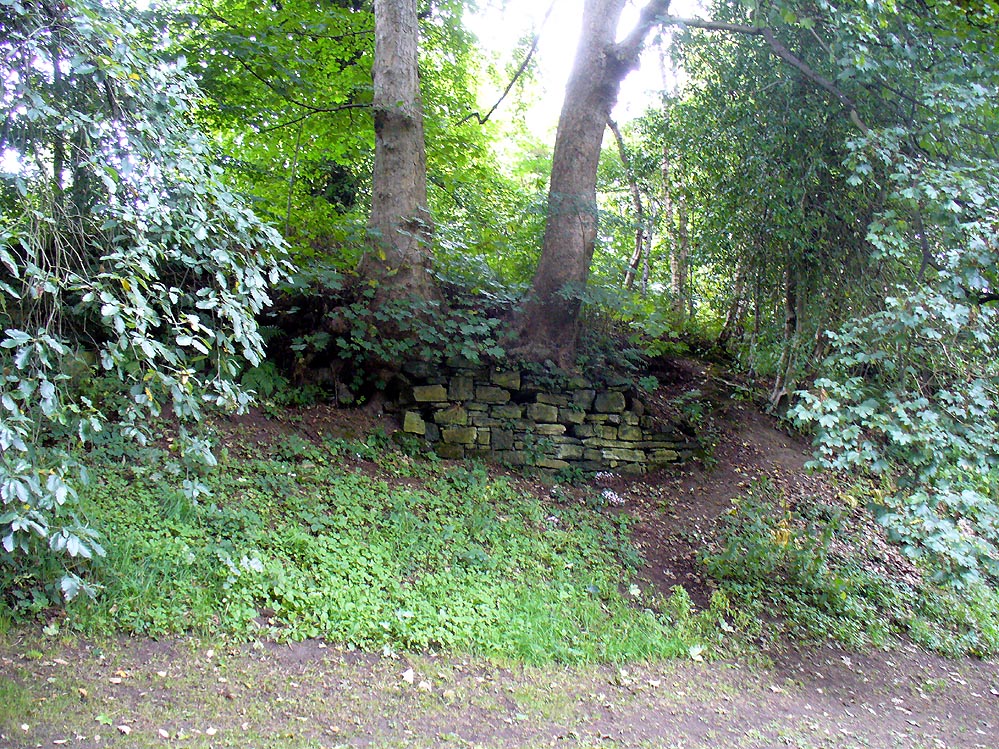

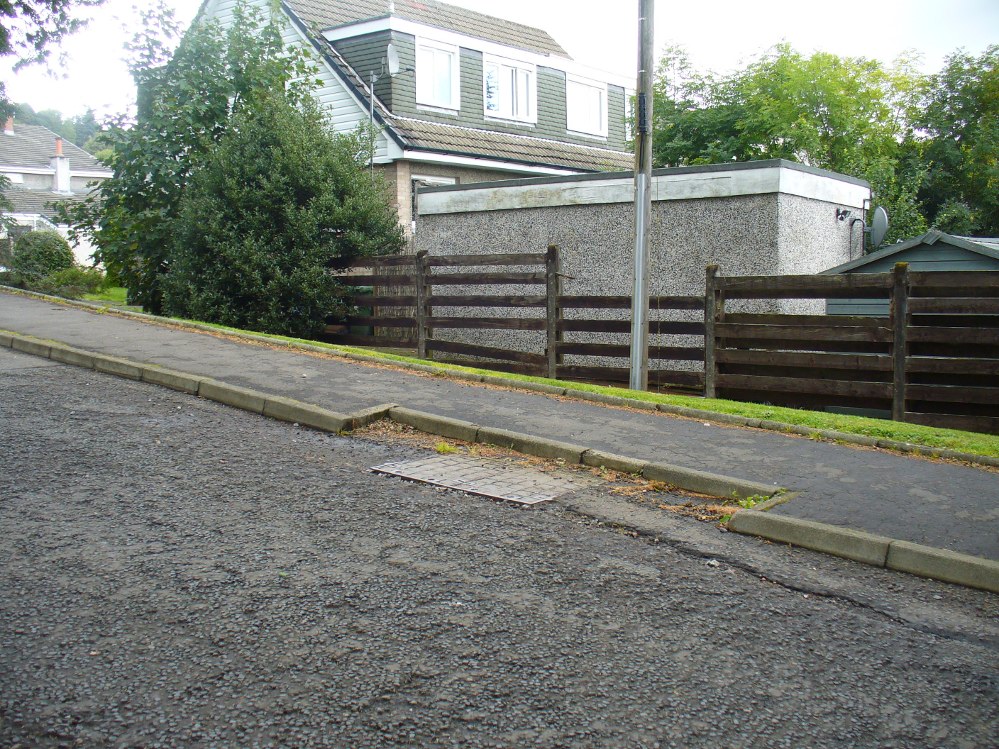
The demise of this old healing spring of water occurred a few generations ago by the look of things. Marked on the earliest Ordnance Survey maps—erroneously as the ‘Three Tree Well’, as Mr McDonald (1860) will soon explain—it was located on the west side of the River Kelvin, halfway between the Kirklee footbridge and the ancient ford, but the only remains we can see of it now appears to be the brick-walling above which a pair of sycamore trees rise, or perhaps beneath the man-hole cover on the path lower down.
…But it wasn’t always this way… Known to be a chalybeate, or iron-bearing spring (which are always regarded as tonics in local lore, fortifying the blood general health), when the local writer Hugh McDonald (1860) wrote about it in his wonderful Rambles round Glasgow in the middle of the 19th century, he cast a picture of the area that few Glaswegians would recognise today—and a damn good swipe at the incomers trying to alter the names of traditional places:
“At the western extremity of the Botanic Gardens a narrow passage, in popular parlance called “the Kyber Pass,” leads over a green knoll to the volley of the Kelvin at the famous “Pear-tree Well.” …The scenery of the Kelvin in the vicinity of the Pear-tree Well is of the most romantic and beautiful description. The banks are bold, and in many places fringed with masses of foliage to the water-lip; while the rustic bridge, the lonely cottage, and the picturesque mill, seem planted by the very hand of taste, along the meanderings of the rippled and murmuring stream, wherever they are likely to produce a telling effect… Altogether the scene and its accessories present the very choicest of those harmonious combinations of colour and form which the landscape limner loves to gaze upon, and fondly endeavours, in the pride of his skill, to transfer to the living canvas. No wonder it is that Kelvin Grove has long been the favourite haunt of our City lovers, and the favourite theme of our local poets; for Nature has, indeed, strewn its recesses with charms as fresh and beautiful as though it were situated far from the dwellings of men, instead of almost under the wing of our most dinsome and dusky of towns.
“The Pear-tree Well issues from the bottom of a steep and thickly-wooded bank, which, at this point, rises gracefully from the rocky bed of the streamlet. The crystalline and deliciously cool water is collected into a considerable cavity in the earth; immediately over which three large trees—a plane and two handsome ashes—raise on high their umbrageous heads, while their sturdy roots, in serpent-like convolutions, twine around the watery hollow beneath, as if to defend it from the intrusion of the penetrating noonday sun. Some suppose that it is from this trio of sylvan guardians that the fountain has received its name — and that the ‘Three-tree’ and not the ‘Pear-tree’ Well is its proper denomination. The advocates of the latter theory further remark, that there is no pear-tree in the vicinity, and that consequently the popular name is probably but a corruption of “Three-tree.” There is high authority for saying that names are things of slight consequence; but however that may be, we are inclined, in the present instance, to be conservative of the old name for this favourite well, and to retain it in spite of all attempts at innovation. Whether from langsyne associations or not, we shall not attempt to discover, but Pear-tree Well sounds most musically on our ear — and we should be loath to have it suppressed by the word-coinage of any crotchety theorist; and besides, who can tell what kind of trees may have formerly graced the locality? A perfect orchard of the pear tribe may, at some past period, have clothed the banks of Kelvin for anything that these violators of a time-honoured name—”these men who are given to change”—know to the contrary. No, no! Pear-tree Well it has been, and Pear-tree Well to us, at least, it must remain. We had as lief meet an old friend with a new face, as an old haunt with a new name.
“Having done our devoirs to the spirit of the fountain, by draining a bicker of the translucent water, which, by the way, is slightly impregnated with iron, we sit ourselves down on the bank above, under the ashen tree, when one of two friends with whose company we have been honoured, inspired by the half-gelid beverage, bursts suddenly out with—
“Let us haste to Kelvin Grove, bonnie lassie, O.”
“We of course join heartily in the measure, which has for many years been highly popular in the west of Scotland, and which we naturally enjoy with double zest, amid the scenery to which it refers…”

The great historian and romantic, J.A. Hammerton (1920) even passed here, telling how sufferers of disease relied upon its curing waters to heal them. It is just such a pity that this picturesque medicinal spring and its rivulet are with us no more…
References:
- Brotchie, T.C.F., Glasgow Rivers and Streams: Their Legend and Lore, John Maclehose: Glasgow 1914.
- Brotchie, T.C.F., “Holy Wells in and Around Glasgow,” in Old Glasgow Club Transactions, volume 4, 1920.
- Hammerton, J.A., Wonderful Britain: Its Highways and Byways – volume 1, EBC: London 1920.
- McDonald, Hugh, Rambles round Glasgow, John Cameron: Glasgow 1860.
- Millar, A.H., By-gone Glasgow, Morison Bros: Glasgow 1896.
- Pagan, James & Stoddart, J.H., Relics of Ancient Architecture and other Picturesque Scenes in Glasgow, David Bryce: Glasgow 1896.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Nina Harris for guiding us to the spot where this old well could once be seen.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian