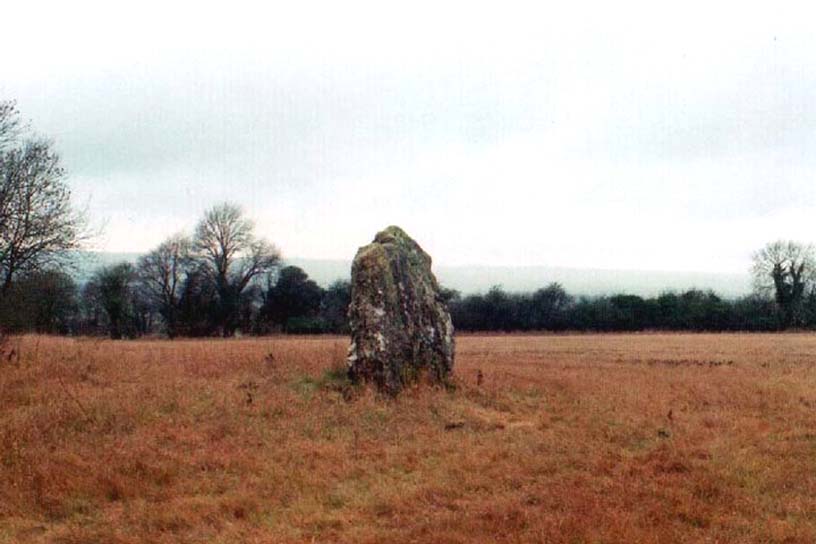
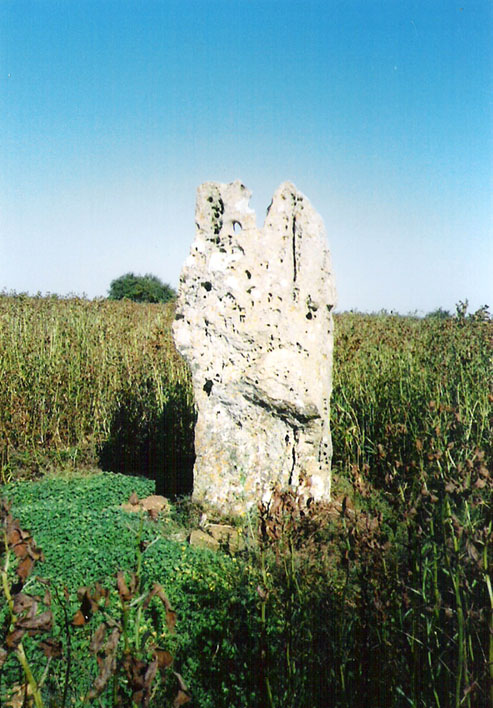
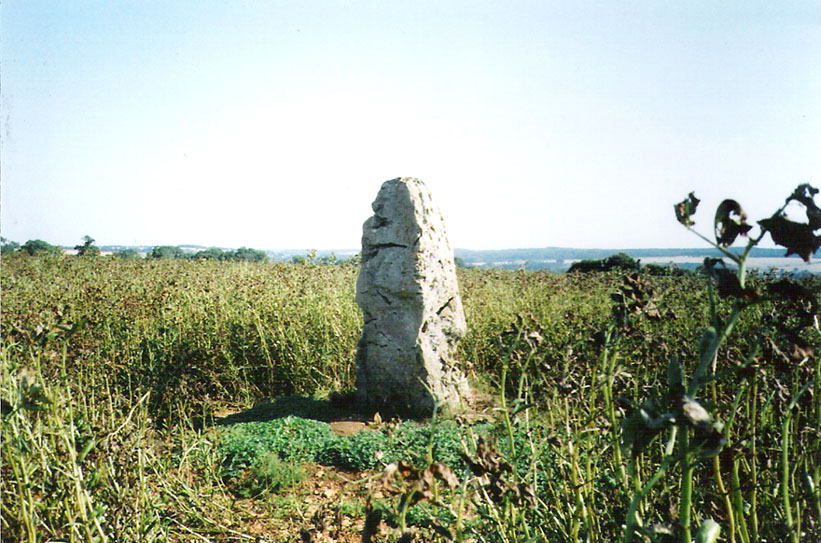
Chambered Tomb: OS Grid Reference – SP 29936 30841
Also Known as:
- Five Knights

Follow the directions to reach the Rollrights stone circle, from Chipping Norton. Walk past the entrance to the circle along the road for a coupla hundred yards, keeping your eyes peeled looking into the field on your right. You’ll notice the large rocky mass of these Knights a hundred yards down in the field, which can be reached by a footpath running straight along the old hedge from the roadside straight to the collapsed tomb.
Archaeology & History
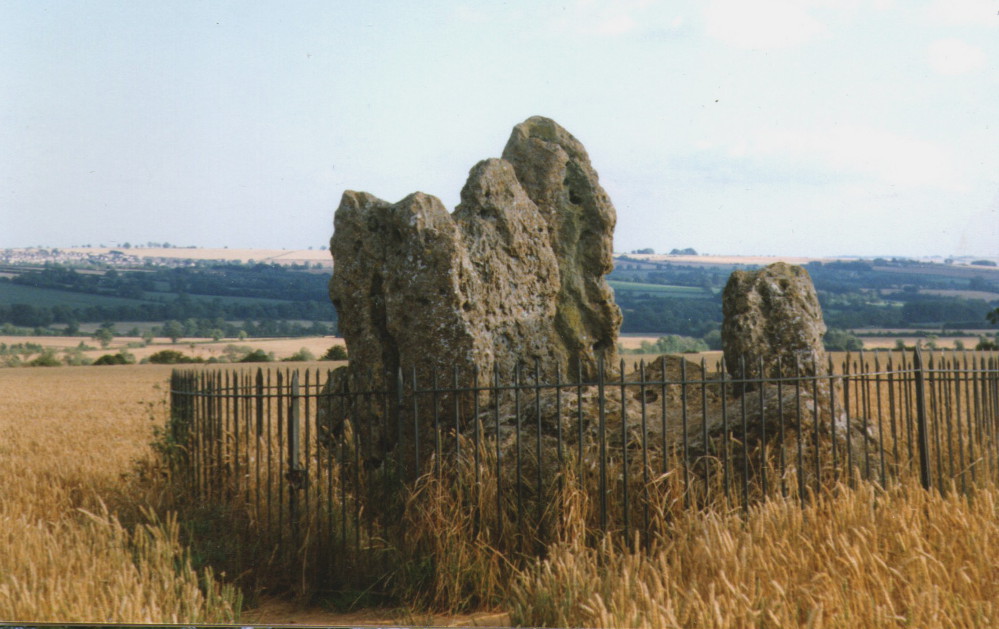

A brilliant site—albeit nowhere like how it once was—where I slept a few times when I lived in the old hut at the Rollright stone circle down the road. A field-mouse lived here when I slept at the place and, hopefully, its ancestors still reside hereby (Rollright Trust’s poisons notwithstanding!). On my first encounter with the little fella, I felt him running into my waist-side whilst laying, dozing in the old tomb. He nudged into me—then again —and yet again; before I leaned over to see what was going on! And the little mouse looked up at me, without a care in the world, as if to say, “What are you doing lying on my path!? Can I get past please?” (though I’d not had a bath for a good 3 months, so didn’t smell like any modern human, which I think explained his total lack of fear)
Laying there, I smiled at the little fella, who then decided to jump up the side of my waist and walk over the top of me to get to the other side! He jumped down into the grasses and disappeared! However, a few minutes later, I felt another tiny ‘thud’ at my side and looked down to see the same lovely mouse wanting to go back along his obviously traditional route – and looking up at me again, whiskers twitching inquisitively, realised I was still here; and so once again took it upon himself to climb over the scruffy smelly human-sort who was blocking his route!
He was a gorgeous little mouse and we got to know each other quite well over the unwashed springs and summers I slept here….. But anyway, that’s not what you folks are interested in hearing about! Back to the archaeo-shit
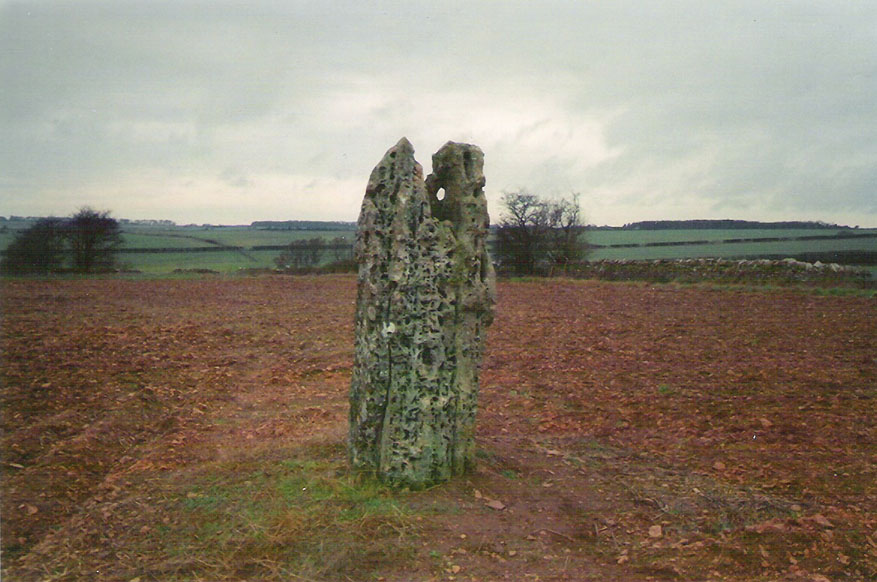
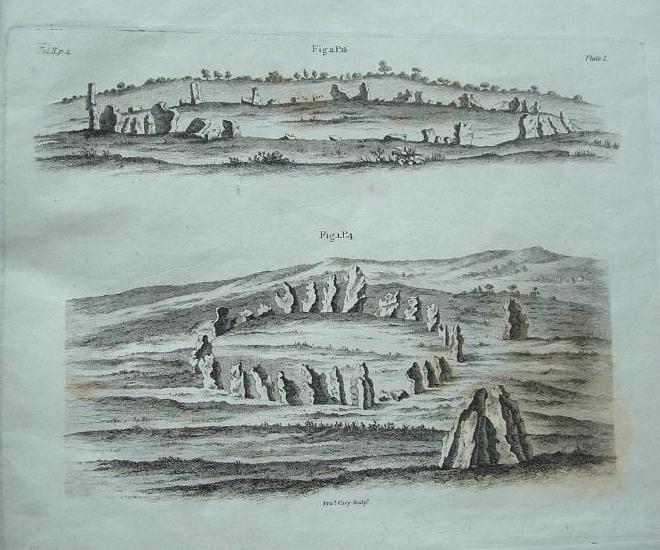
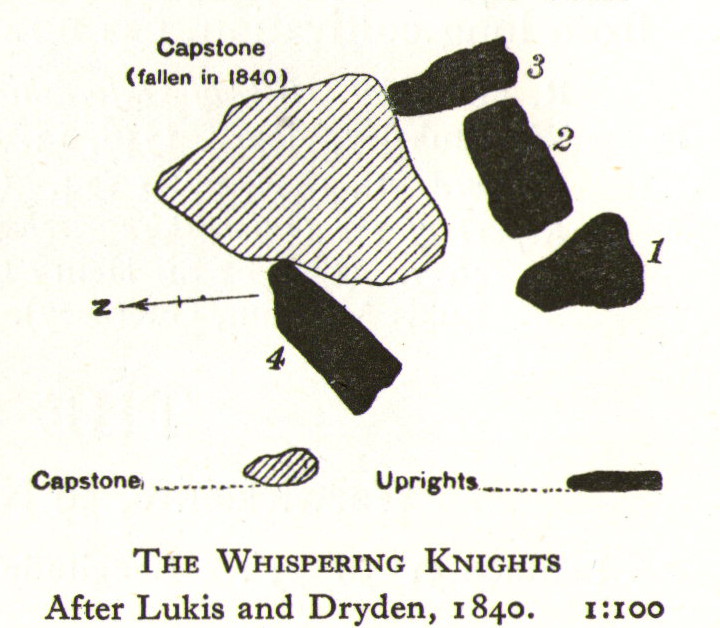
The Whispering Knights is one of the main sites in the cluster known collectively as the Rollright Stones, which also comprises of the standing stone commonly called the King Stone, plus the King’s Men stone circle a coupla hundred yards down the road from the Knights. They all sit atop of the ridge which separates the counties of Oxfordshire and Warwickshire along the edge of the prehistoric road known as the Jurassic Way. The sites are non-contemporaneous having been erected over a period of many centuries. The Whispering- or Five Knights are by far the oldest part of the complex dating from a period never previously anticipated. They comprise of four upright megaliths in close proximity, and a fifth fallen stone which is said to be the capstone on the original monument. This stone alone weighs some 10 tons.
The general archaeological opinion is that the place is a ‘portal dolmen burial chamber’ of which the capstone has fallen. The Oxford archaeologist George Lambrick (1988) postulated the stones to have been covered with a mound of earth, but any evidence supporting this has long since gone.
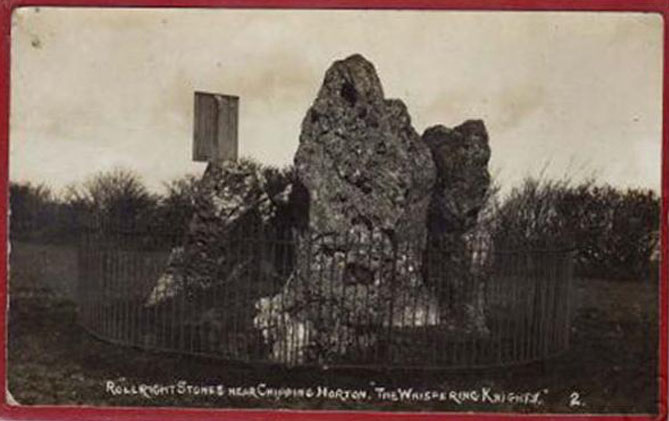
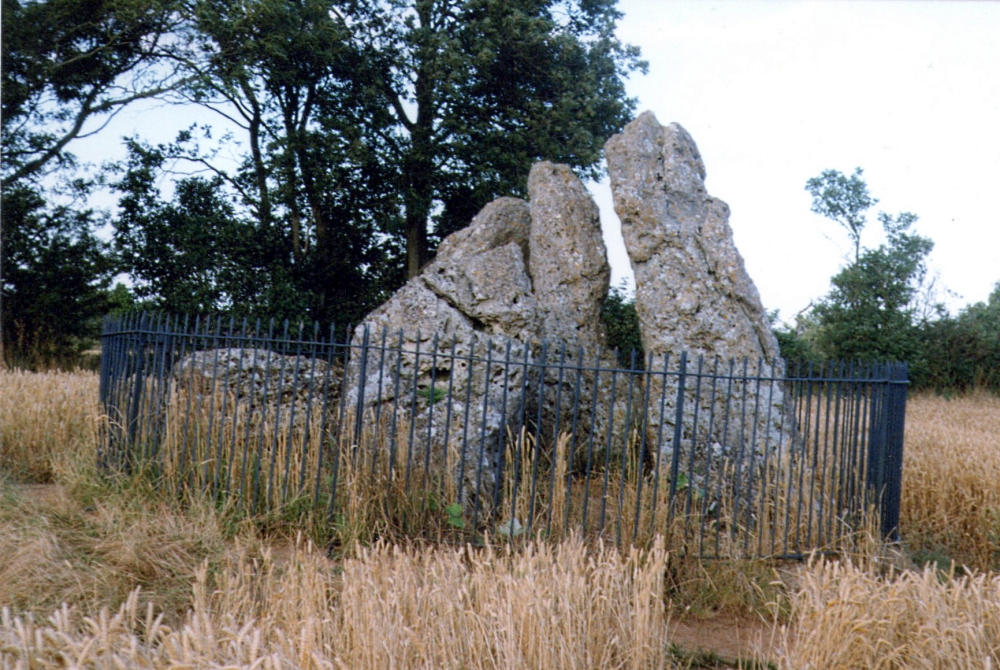


This great monument was initially thought by archaeologists to have been built sometime around 1800 BCE—a favourite date of academics for many an unexcavated site for many decades—until they turned their astute attention to the place in the 1980s. And what they found was astonishing. Well…astonishing for the archaeologists! Affirming the local folk tradition that the Knights were the “oldest monuments in Oxfordshire,” the dates truly went back. Way back! Datable remains at the site gave results from between 3500 and 3800 BCE: two thousand years earlier than anyone had ever expected of them.
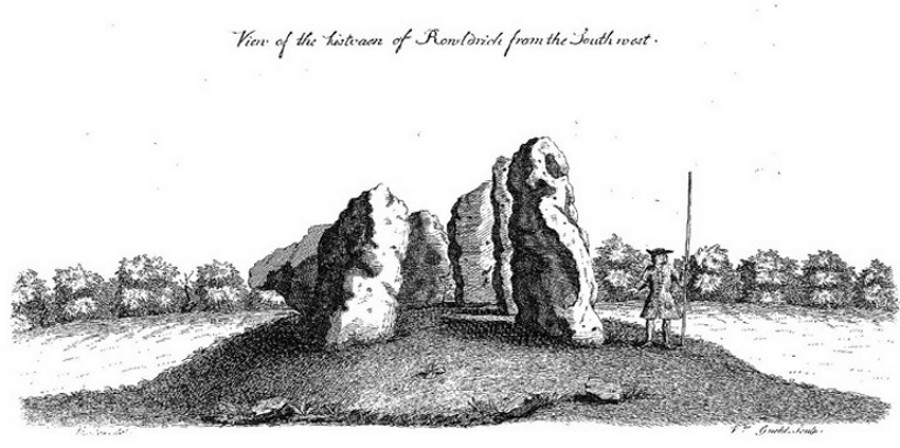
Although five stones remain of the site, when the great William Stukeley (1743) visited the Whispering Knights, he described six of them to be visible with the great stones here to be sat upon a tumulus, saying:
“Tis composed of six stones, one broader for the back part, two and two narrower for the sides, set square to the former; and above all, as a cover, a still larger. The opening is full west to the temple or Rowldrich. It stands on a round tumulus, and has a fine prospect southwestward down the valley, where the head of the Evenlode runs.”
O.G.S. Crawford (1932) told us of a description which Sir Henry Dryden gave of the Knights in 1898, when he wrote:
“About 356 yards E from the (Rollright) circle and S of the road, is the dolmen about to be described, called the Five Whispering Knights. It is in a ruinous state. It now consists of four stones, upright, or nearly so, and one prostrate, all of coarse limestone…
- Height, 8ft 3ins (4ft by 2ft 6ins)
- ” , 7ft 3ins (3ft 6ins by 1ft 10ins)
- ” , 6ft 7ins (3ft 8ins by 1ft 4ins)
- ” , 5ft 4ins (4ft 9ins by 2ft)
- Capstone (then fallen), 8ft 4ins by 5ft 9ins, by 2ft 4ins
“The chamber appears to have been about 5 feet 6 inches W and E, and the same N and S. If, as usual, there was an entrance, with or without a passage, it was probably to the ENE… There is not, so far as I know, any record of remains having been found in this dolmen. In a small stone pit about 700 feet NE by E from the circle it is stated that 12 skulls were found in 1835. In another stone pit near it was found in 1836 an urn and beads…”
During the last century, very little has really changed at the Knights. The ring fencing surrounding the stones has kept it pretty much protected, despite it ruining all sense of healthy ambience. But they have gained greater and greater attention the older they have got. Archaeologists are not the only ones exploring the site. Fascinated astronomers, engineers and architects have been and seemingly uncovered other mythic ingredients here.
When the legendary Alexander Thom came here, he used the archaeological data that was being espoused at the time, which said the Knights and the Rollright stones had both been built around 1750 to 1800 BC. With these dates as his guide, he found that someone standing at the centre of the Rollright circle, on the morning of the equinoxes—March 21 and September 21—the sun would rise right above the Whispering Knights. And the effect, he thought, was a notable one: with the light from the rising sun going straight through a hole in one of the stones in the circle as it rose up behind the Knights. It would have looked both spectacular and eerie in the rising mists of first light, like a laser cutting through the still morning air… However, although Thom’s measurements were very accurate, the archaeologists had got their dates wrong. Very wrong! For the Whispering Knights were about 1500 years older than the stone circle—and so the alignments Thom pronounced, based on the archaeologist’s erroneous proclamations, were also incorrect.
There may be other alignments connected to the Rollright complex. In a survey of the site as part of the Dragon Project experiments conducted here in June 1980, Leslie Banks and Christopher Stanley flew over the place and found, adjacent to the Whispering Knights, a quite distinct “trace of two dark green parallel lines in a field of ripening corn” running northwest to the roadside. To this day nobody quite understands the nature of this enigmatic alignment:
“In the absence of excavation we can only speculate,” said Stanley. “But the most likely explanation is that it is what archaeologists refer to as a Cursus. Cursuses are thought to be prehistoric religious processional ways.”
As with many of the alignments described here, the jury is still out on this one!
Folklore
The folklore here is prodigious! The prime story of the neolithic tomb of the Whispering Knights tells that originally they were in fact a group of traitors who moved away from a King and his army in ages past, and who were plotting against him, when the great Witch of Rollright (a southern version of the great cailleach, found in more northern counties, Scotland and Ireland) turned them all to stone (this tale is intimately bound up with the King’s Men stone circle and the associated King’s Stone).
Another tale tells how the King Stone and the Whispering Knights venture, at midnight, less than half a mile south to drink from a spring in the small woodland at Little Rollright Spinney, although it is difficult to ascertain precisely which of the two springs the stones are supposed to visit. In some accounts, the stones reputedly drink from the well every night, but others tell that they only go there at certain times of the year, or on saint’s days. When Arthur Evans (1895) wrote of these tales he described there being a “gap in the bushes… through which they go down to the water,” but the terrain has altered since his day.
Other accounts imbuing the stones with life tell how they only ‘awaken’ when disturbed by humans. A story well-known to local people is that of when the Knights had its capstone removed one day by a farmer who used it to build a bridge across the stream at Little Rollright. As Evans told us,
“it took a score of horses to drag it down the hill, for at first it would not move, and they had to strain and strain to get it along till every bit of the harness was broken. At last they got it to the brook by Rollright Farm, and with great difficulty laid it across to serve as a bridge. But every night the stone turned over back again and was found in the morning lying on the grass.”
Three nights of this led the farmer to think he should replace the stone which, so the fable goes, took only one horse to move it back uphill and into position. A variation of the same tale was told by T.H. Ravenhill, who wrote:
“The Lord of the Manor of Little Rollright desired to possess the King’s Stone in order to bridge Little Rollright brook. So he dug it up and tried to cart it away, but found that he had not enough horses. He hitched on more, and yet more, and still he found that he could not move the stone. Finally he succeeded and hauled the stone away to the Manor House. The same night he was alarmed by strange sounds about the house, which he attributed to the presence of the King’s Stone, and decided, therefore, to replace it on its mound. No sooner had he harnessed the first horse to the cart than it galloped away up hill with ease, taking with it the stone, which leapt to position on reaching its resting place.”
There are still more variations that are worth mentioning. One from 1876,
“said that a miller in Long Compton, thinking the stone would be useful in damming the water of his mill, carried it away and used it for that purpose, but he found that whatever water was dammed up in the day disappeared in the night, and thinking it was done by the witches (at Long Compton) and that they would punish him for his impertinence in removing the stone, he took it back again; and, though it required three horses to take it to Long Compton, one easily brought it back.”
In yet another version, the stone was wanted by a local farmer for his outhouse. In taking it downhill, the horses that pulled his wagon died and the vehicle itself was irreparably damaged. It got even worse for the poor chap: his crops failed, his family were taken ill and his cattle died. Eventually when all but his last horse remained, he made another cart and it pulled the stone back uphill with ease. Thereafter, so the tale goes, all his adversities stopped and he lived a normal life. In one version of this tale, the great monolith was said to have been taken north-north-west down to the stream at The Hollows, Long Compton. Tales such as these are, once more, found throughout the world.
The truth of these stories was seemingly unquestionable to some local people in the 19th century,
“one man going as far as to say that there were those now living who had spoken to men who had helped to bring the stone down and up again.”
In William Stukeley’s day, one Farmer Baker was so troubled by his actions that he couldn’t rest until he returned the old stone.
The doyen of the early geodelic sciences or Earth Mysteries movement, John Michell, suggested how the legends of megaliths moving of their own accord harked back to ancient days when the people of those times were more attuned to the terrestrial magnetic flows of the Earth.
The Whispering Knights were also a place where “young girls of the neighbourhood (use it as) a kind of primitive oracle.” One local told Arthur Evans that around barley harvest the young women of the district visited the Five Knights to listen to them whisper. One at a time they would rest their ears against the strange shapes of stone and, if fortune and conditions were right, they would hear the future told. This mass of animistic lore is very revealing indeed, telling us much about the way our peasant ancestors viewed the living world around them. (Eliade 1958)
In more recent times, the site has been explored by dowsers and ley hunters, who claim to have found a veritable bags of fascinating lost material around the Knights. Although originally ‘leys’ were described by Alfred Watkins as quite acceptable prehistoric trackways linking site to site to site, in recent years the original theory has been ignored and superceded with a host of almost incredulous fluctuations. Leys these days can run just about anywhere – and do!
One writer who tells about the leys around Whispering Knights is Lawrence Main. (1997) He dowsed and found a ley running south to the famous White Horse at Uffington. Roy Cooper (1979) was the first person to write about this alignment and extended it further north to the impressive and legendary Brailles Hill. That one seems reasonable. However,
“Other leys I dowsed,” said Main, “Linked the King Stone, the stone circle, and the Whispering Knights with each other; the King Stone with Banbury Cross; the Whispering Knights with Hook Norton church; and the stone circle with the churches at Todenham and Stretton-on-Fosse.”
Another dowsing ley hunter is Dennis Wheatley (not The Devil Rides Out dood). He wrote a couple of short works on his lengthy experiments at the Rollright stones and reported how he found a
“tangential aerial energy course…across the country (which) latches on to a solitary standing stone, six miles south, known as the Hawk Stone.”
Perhaps of greater importance here is that Wheatley also discovered how,
“all of the Rollright ring’s stones engage in aerial energetic cross-talk with the King Stone producing a triangulation of energy lines.”
This cross-talk of Wheatley’s involves more than seventy energy lines running between the circle and the King’s Stone. He tells us that a greater “aerial cross-talk” also occurs between the circle and the Knights; and “a lesser energetic triangulation” runs between the King and the Knights.
Along similar lines are the findings of the dowser Reginald Smith. (1980) Beneath the Whispering Knights he claimed to have found,
“a concealed spring which runs underground to the northwest and may betoken a consecrated site; but 100 feet to the east there seems to be another blind spring with issue to the northeast.”
…to be continued…
References:
- Bennett, Paul & Wilson, Tom, The Old Stones of Rollright and District, Cockley Press: London 1999.
- Burl, Aubrey, Great Stone Circles, Yale University Press: New York & London 1999.
- Cooper, Roy, ‘Some Oxfordshire Leys,’ in The Ley Hunter 86, 1979.
- Crawford, O.G.S., Long Barrows of the Cotswolds, John Bellows: Oxford 1932.
- Devereux, Paul, Places of Power, Blandford: London 1990.
- Devereux, Paul, The Sacred Place, Cassell: London 2000.
- Eliade, Mircea, Patterns in Comparative Religion, Sheed & Ward: London 1958.
- Evans, Arthur J., ‘The Rollright Stones and their Folklore (3 parts),’ in Folklore Journal, 1895.
- Gelling, Margaret, The Place-Names of Oxfordshire – volume 2, Cambridge University Press 1971.
- Graves, Tom, Dowsing: Techniques and Applications, Turnstone: London 1976.
- Grinsell, Leslie V., The Ancient Burial Mounds of England, Methuen: London 1936.
- Lambrick, George, The Rollright Stones: The Archaeology and Folklore of the Stones and their Surroundings, Oxford Archaeology Review 1983. (Reprinted and updated in 1988.)
- Main, Lawrence, Walks in Mysterious Oxfordshire, Sigma: Wilmslow 1997.
- Ravenhill, T.H., The Rollright Stones and the Men Who Erected Them, Little Rollright 1926.
- Robins, Don, Circles of Silence, Souvenir Press: London 1985.
- Smith, Reginald A., ‘Archaeological Dowsing,’ in Graves, Tom (ed.), Dowsing and Archaeology (Turnstone: Wellingborough 1980).
- Stanley, Christopher C., ‘A Rollright Processional Way?’ in The Ley Hunter 90, 1981.
- Stuart, Sheila, Lifting the Latch, Oxford University Press 1987.
- Stukeley, William, Abury: A Temple of the British Druids, London 1743.
- Thom, Alexander, Megalithic Sites in Britain, Oxford University Press 1967.
- Wheatley, Dennis, The Rollright Ring, Braden Press: Swindon n.d. (c.1990)
Links:
- The Whispering Knights on The Megalithic Portal
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian