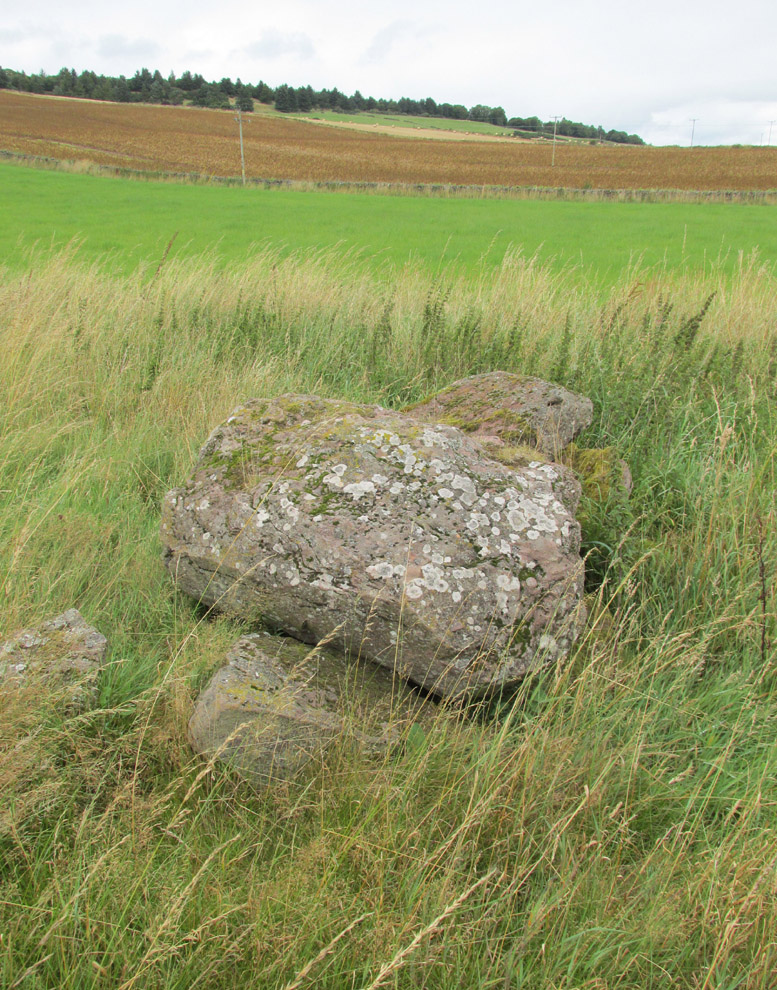
Cup-and-Ring Stone (lost): OS Grid Reference – NS 4469 2624
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 42713
- King Coil’s Grave Stone
- Old King Cole’s Stone (Morris 1981)
Archaeology & History
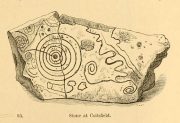
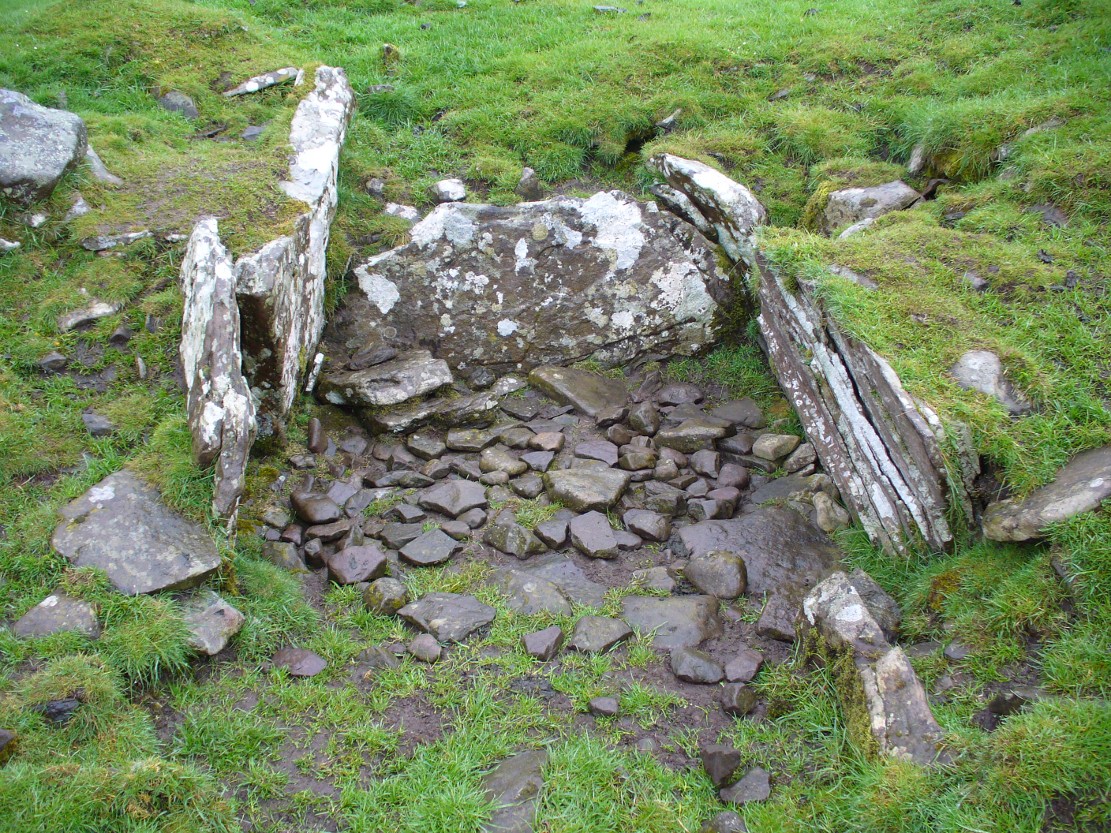
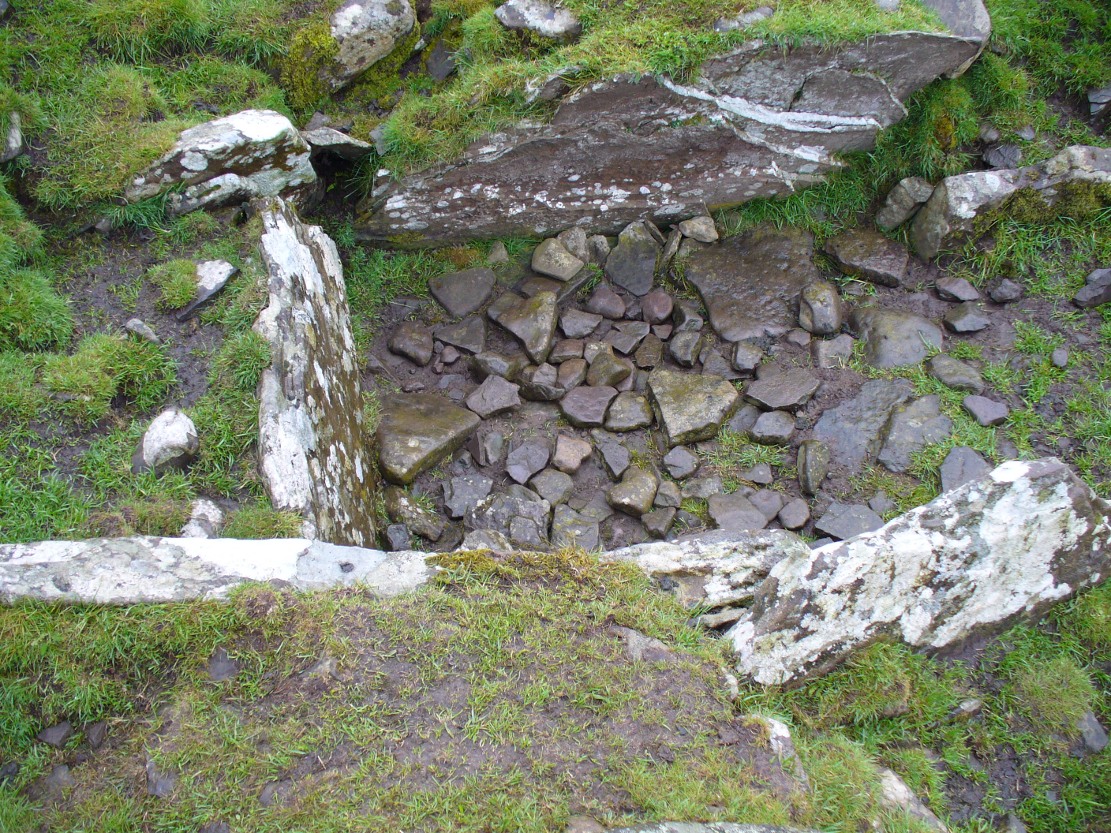
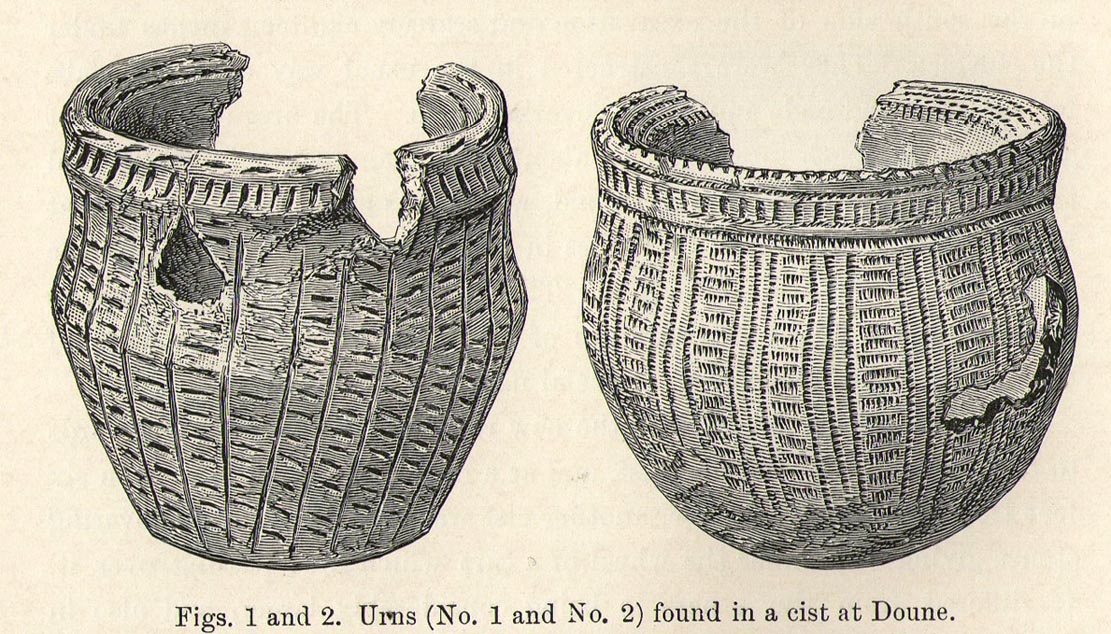
This fascinating and very ornate prehistoric carving was found on the underside of a grave-slab beneath Old King Coil’s Grave, or an adjacent prehistoric burial feature (we don’t know for sure). In Daniel Wilson’s (1851) superb early work on prehistoric Scotland is a detailed drawing of this ornate petroglyph—similar in design and form to those found across the waters in Ireland—copied “from a drawing presented to the Royal Society of Edinburgh by Colonel Hugh Montgomery of Shielmorly, in 1785.” Mr Wilson informed us that,
“It formed the cover of a cist, discovered in digging a gravel-pit at Coilsfield, in Ayrshire, and underneath it was found an urn filled with incinerated bones. The dimensions of the stone were about five feet in length by two and a half feet in breadth”
A few years later Sir James Simpson (1866; 1867) wrote and published the earliest (and still one of the finest) books on aboriginal rock carvings in the British Isles, and all but echoed what Wilson had described. He added a further description of the designs that were carved onto the stone, telling us that,
“it had cut upon it a series of concentric circles, consisting of six rings placed around a central cup, the rings traversed by a straight radial groove. On the drawing are marks of other cups and rings, or rather volutes, and a number of angular lines… This sculptured stone covered an urn…”
Following the descriptions of our early authors, many archaeologists and antiquarians explored the site but could find little else about the carving. In Ron Morris’ (1981) most recent survey, he told us that it was,
“a gritstone slab, 1½m by ¾m (5ft x 2½ft), possibly broken after carving, had on one side (not now known if this was the inner of outer face); a cup-and-six-complete-rings with radial groove from the cup – diameter 50cm (20in) – 5 other cups-and-rings, mostly partly broken off or incomplete, an irregular ‘reversed-S-shaped’ single spiral with 3 convolutions at each end, other irregular grooved figures, 4 cups and about 7 ‘dots’ (6 of these are in the cup-and-six-rings).”

The Royal Commission at Canmore tell us that “the present location of the food vessel and cist cover is unknown”; yet the rock art researcher Ronald W.B. Morris (1981) reported the petroglyph was “said to have been given to the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland but (is) now missing”; whilst the local writer E.H. Letham (1900) told us “the urns were conveyed to Eglintoun Castle.” This aint good. Has anyone subsequently found out what became of it?
Folklore
The tumulus of King Coil’s Grave was the legendary resting place of the “Old King Cole” of popular rhymes. There were two such northern kings in ancient times and, as William Robertson (1889) said, “the only difficulty is to say which of the King Coils he was, whether the Coilu who lived three hundred and thirty years before Christ; or Coel, King of the Roman districts, who must have lived in the third century.”
References:
- Letham, E.H., Burns and Tarbolton, D.Brown: Kilmarnock 1900.
- Morris, Ronald W.B., The Prehistoric Rock Art of Southern Scotland, BAR: Oxford 1981.
- Morris, Ronald W.B. & Bailey, Douglas C., “The Cup-and-Ring Marks and Similar Sculptures of Southwestern Scotland: A Survey,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 98, 1966.
- Morrison, Alex, The Bronze Age in Ayrshire, Ayrshire Natural History & Archaeology Society 1978.
- Robertson, William, Historical Tales and Legends of Ayrshire, Thomas D. Morrison: Glasgow 1889.
- Paterson, James, History of the County of Ayr – volume 2, Thomas Stevenson: Edinburgh 1852.
- Simpson, J.Y., “On Ancient Sculpturings of Cups and Concentric Rings,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 6, 1866.
- Simpson, James, Archaic Sculpturings of Cups, Circles, etc., Upon Stones and Rocks in Scotland, England and other Countries, Edmonston & Douglas: Edinburgh 1867.
- Smith, John, Prehistoric Man in Ayrshire, Elliot Stock: London 1895.
- Wilson, Daniel, The Archaeology and Prehistoric Annals of Scotland, Sutherland & Knox: Edinburgh 1851.
- Young, Alison, “Cup-and-Ring Markings on Creag Ruenshin, with Some Comparative Notes,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 72, 1937.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian