Standing Stone: OS Grid Reference – NM 86681 03320
Also Known as:
- Achadh nan Carradh
- Achnacarra
- Canmore ID 22802
Unless you’re venturing down the tiny Loch Awe roads, the easiest way here is to turn right off the A816 Lochgilphead-Oban road, 1½ miles north of Kilmartin. Go along this winding minor road for literally 2½ miles where, after coming out the tree-lined road, just past the small Loch Ederline, the fields re-appear on both sides of the road. Just here, where the trees end, just a few hundred yards before the hamlet of Ford, in one of the field on the left, you’ll see a tall upright stone. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
I was very fortunate, many years ago, to live in the old farmhouse of Auchinellan in the trees by this ancient stone. It became a companion of mine many-a-time, as I sat with it in rain and mist and darkness sometimes, beneath the bright Moon. It always had a good feeling about it. And so when a small bunch of us visited here again recently, it was almost as if I’d never been away. Tis a magickal part of our landscape.


Standing ten-foot-tall on a grassy plain with craggy hills all round, this old fella once had a companion close by its side—a stone one! Accounts of it are curious to say the least, with one telling us that it was only “a few inches high” – which is just daft. The now-lost stone was in fact about six-feet tall and the story of its disappearance was that it was moved into the grounds of Auchinellan House where I used to live, somewhere in the garden. I could never find it, and local folk told me that the old fella who lived in the mansion would have known about it, but died shortly before I moved in. Clive Ruggles (1984) told that it could be found at grid-reference NM 8653 0268, but that would be smack bang on the manor house.
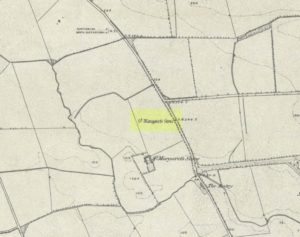
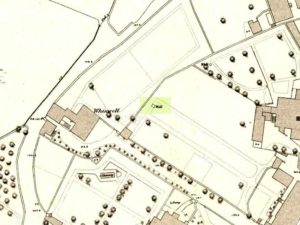
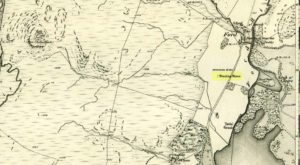
As far as I can tell, the first written testimony of this stone was by the Ordnance Survey lads after they’d visited here in 1871 and, several years later, highlighted it on their maps. (above) On this is clearly shown, just yards apart, the two standing stones. Much later, when the Royal Commission (1988) doods did their survey, they described the stone in their usual brief way:
“Situated on the top of a slight rise in a pasture field 270m SW of the Ford Hotel, there is a standing stone which measures 0.7m by 0.55m at the base and rises with straight sides to a flat top at a height of 3m…”
The site was included in Thom’s (1990) major survey on prehistoric stone rows where, again, only a brief description is given, saying:
“On a terrace near Loch Ederline is a standing stone which leans to the E. It is 9ft 6 (2.9m) high.”
It’s a beautiful place in a beautiful setting and is one of countless prehistoric monuments in this part of Scotland. Well worth having a look at.
Folklore
The Gaelic names for this site—Achnacarra and Achadh nan Carradh—means “the field of the burial stone”, which relates to the folklore of the stones reputedly marking the place of an ancient grave.
References:
- Campbell, Marion, Mid Argyll – An Archaeological Guide, Dolphin: Glenrothes 1984.
- Campbell, Marion & Sandeman, M., “Mid Argyll: An Archaeological Survey,” in Proceedings Society of Antiquaries Scotland, volume 95, 1964.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, Argyll – Volume 6: Mid-Argyll and Cowal, HMSO: Edinburgh 1988.
- Ruggles, Clive L.N., Megalithic Astronomy, BAR: Oxford 1984.
- Thom, Alexander, Thom, A.S. & Burl, Aubrey, Stone Rows and Standing Stones – volume 1, BAR: Oxford 1990.
Acknowledgements: Big thanks to Neens Harris, Paul Hornby & Frank Mercer. And the stunning resource of Scotland’s 1st edition OS-maps is Reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
Links:
- Auchinellan (Ford) Stone on The Megalithic Portal
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian