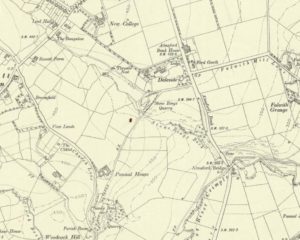
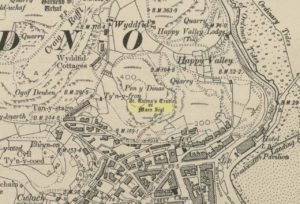
Standing Stones: OS Grid Reference – NS 65705 83932
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 45311
- Waterhead Stones
Getting Here

The Machar Stones
Of the 2 ways to reach here: one via the Crow Road, up to Waterhead Farm and then meandering through the forest—we took the other one! From the car park at the western end of Carron Reservoir, take the track into the forest. Stick to the track closest to the loch until, after crossing the small river bridge, veer right at the next junction 200 yards on. Another 600 yards (0.5km) along, take the right turn and walk all along this track to the very end. From here, take your feet down into the opening along the small burn and stick to this gap in the trees for 100 yards or so, where the gap in the trees veers left. Keep walking for another 200 yards.
Archaeology & History
These stones might take some finding, but they’re worth the effort if you like your megaliths. When Nina, Paul and I visited them yesterday, the meander turned into what have become known as Barmy Bennett Bimbles as we ventured off-path and into the forest, wading through marshland and getting our eyes poked out in the dense trees! And then the snow came. Twas gorgeous to be honest…

Machar Stones, looking SE

Machar Stones, looking west
Probably neolithic in origin, the Machar Stones are set upon an elevated rise above the confluence of the Bin Burn and the River Carron on what seems to be an enhanced artificial platform, akin to those which some stone circles and ring cairns are mounted upon. Around the edges of the stones themselves, the earth has been dug into at some point in the past, as evidenced by the distinct oval dip in the ground surrounding the stones; although I can find no antiquarian accounts describing such a dig. There is the possibility that these stones may once have marked the site of a prehistoric tomb.
Once you walk ten yards away from the stones in any direction, you begin to walk downhill. Sadly the trees presently obscure any view from the stones, completely silencing the panorama that quite intentionally awoke from here in centuries gone by, disabling any immediate visual landscape analysis or geomancy. The proximity of the two rivers was probably relevant in the construction of the stones; as may be the ridge between the Little and Meikle Bin to the southeast.
First described in Nimmo’s Stirlingshire (1817) as “a druidical remain…in the parish of Fintry, about the middle of the moor towards Campsie and northwest of the Meikle Bin”, another early account of these megaliths was in H.G. Smith’s (1896) work on the parish of Strathendrick, before the imposition of the modern ‘forest’ occurred and the views from the stones were unrestricted. After describing their geographical position, he told:
“On a comparatively level part of the muirland between the two rivers and under Meikle Bin, there are two old standing stones known locally as the Machar Stones, this name being derived from the Gaelic magh, a plain. The more northerly stones measures 8 feet in height, and the other is 5 feet 7 inches high. Little…is known of the origin of these standing stones… They were apparently in some way connected with the religious worship of the prehistoric inhabitants of the land. The general uniform direction in which they point, which is to the north of east, looking as nearly as possible to the quarter of sunrise at the summer solstice, seems to point to their having been erected by a race of sun worshippers.”

Machar Stones, looking NW
Around the same time, A.F. Hutchison (1893) gave a lecture on these and other Stirlingshire megaliths, giving slight variants on the heights of the monoliths, adding that “the two stones are standing in a line pointing to 220°.” Sadly, even the great authorities of Aubrey Burl (1993) and Alexander Thom (1990), in their respective tomes on the subject, were unable to define any astronomical alignments here. Hutchison puzzled about the seeming artificiality of the platform upon which the stones appear to have been set, though wrote how “geological authority pronounces it to be a quite natural formation.”
As to the name of the site, William Grant (1963) ascribes the word ‘Machar’ and its variants to mean “a stretch of low-lying land adjacent to the sand” or “low-lying fertile plain”—which doesn’t seem relevant here, unless it was so named by people living on the higher grounds. It seems odd… As does the alignment of the stones. When Nina Harris stood between the stones with a compass to work out the cardinal points, the stone that was leaning was due north of the upright stone. When she walked several yards away from them, the compass deviated and we were given a more northeast-southwest alignment from stone to stone. This isn’t too unusual as we find similar magnetic anomalies at other megalithic sites in Britain (see Devereux 1989), due to a variety of geophysical ingredients.

Royal Commission 1954 photo
Not that your bog standard archaeo-tomes ever mention magnetic anomalies, as basic physics is too complex a subject for your standard archaeo-types! Instead however, we just get the usual measurements and data-sets, much as the Royal Commission (1963) lads gave us after their visit here in 1954—but at least there was no forest when they came here! They were fortunate. “These two stones,” they told us,
“stand on a slight eminence in open moorland, half a mile ENE of Waterhead farmhouse and at an elevation of 850ft… Described by Nimmo’s editor as “a Druidical remain”, they have also been nown as the Machar Stones. The more northerly stone, a four-sided pillar of irregular section, has fallen almost prostrate and its whole length, 7ft 6in, is revealed. At the centre it measures 3ft in width by 2ft 6in in breadth. The other stone stands 4ft 6in further S. It is a slab…standing to a height of 5ft and measuring about 2ft in thickness. Its width is 2ft 8in at ground level, 3ft 8in at a point 2ft above this, and 2ft at the top.”
They posit the idea that the reason the taller stone is leaning at such an angle was due to there being a prehistoric cist nearby which had been ‘excavated’ by peoples unknown, who then took it upon themselves to explore the Machar Stones with similar venture.

The ‘cup-marked’ stone
In recent years it has been said that there are cup-markings on the leaning stone, seven of them apparently. When we visited yesterday they were difficult to make out. There were a number of ‘cups’ on the stone, but these were debatable and seemed more the result of conglomerate disintegration than man-made. A couple of them were perhaps ‘possibles’. However, the light was poor and I’d prefer another visit before making my mind up!
The Machar Stones are quite evocative megaliths, despite their lack of grandeur. Maybe it was the snow. Maybe it was the trees. Maybe it was me. Or probably a mix of all three and more; but this had a real feel to the place. Well hidden, miles from human touch or visits, awaiting just the occasional visitor—and in this weather (of floods, downpours, cold and snow) saturated humans would be the only sorts of crazy people whose spirits would risk getting completely lost to find them. And my god were they worth the effort! Paul, Nina and I thought so anyway!
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, From Carnac to Callanish, Yale University Press 1993.
- Devereux, Paul, Places of Power, Blandford: London 1990.
- Feachem, Richard, Guide to Prehistoric Scotland, Batsford: London 1977.
- Grant, William (ed.), Scottish National Dictionary – volume 6, SNDA: Edinburgh 1963.
- Hutchison, A.F., “The Standing Stones of Stirling District,” in The Stirling Antiquary, volume 1, 1893.
- Nimmo. William, History of Stirlingshire, Andrew Bean: Stirling 1817.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments Scotland, Stirlingshire – volume 1, HMSO: Edinburgh 1963.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, Archaeological Sites and Monuments of Stirling District, Central Region, Society of Antiquaries of Scotland 1979.
- Smith, H. Guthrie, Strathendrick and its Inhabitants from Early Times, James Maclehose: Glasgow 1896.
- Thom, A., Thom, A.S. & Burl, Aubrey, Stone Rows and Standing Stones – 2 volumes, BAR: Oxford 1990.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Nina Harris and Paul Hornby for their endurance and endeavor in locating these great old stones, in attendance with the great rain, snow and deep muddy bogs!
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian