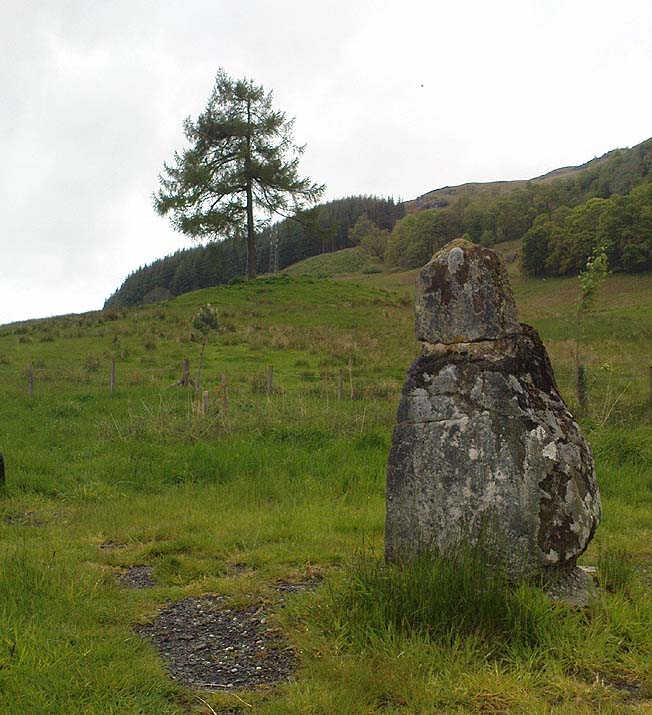
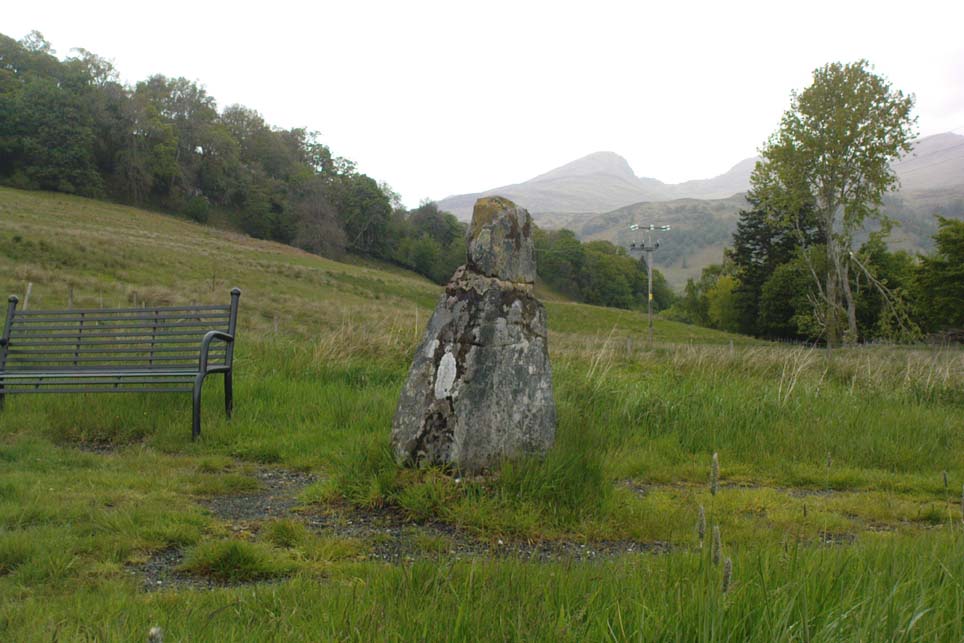
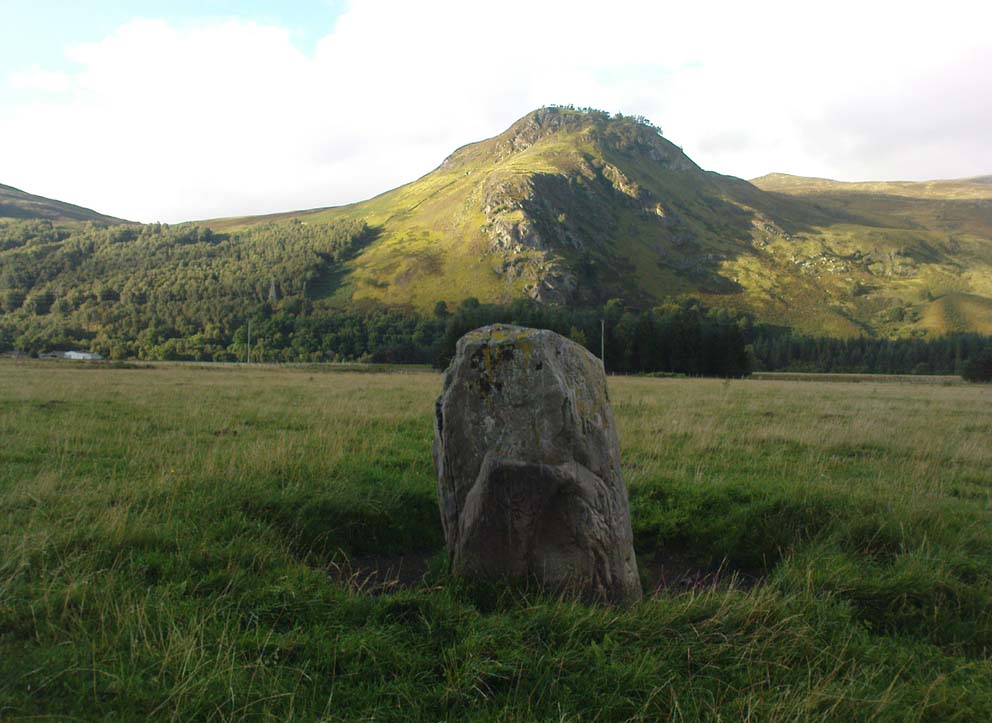
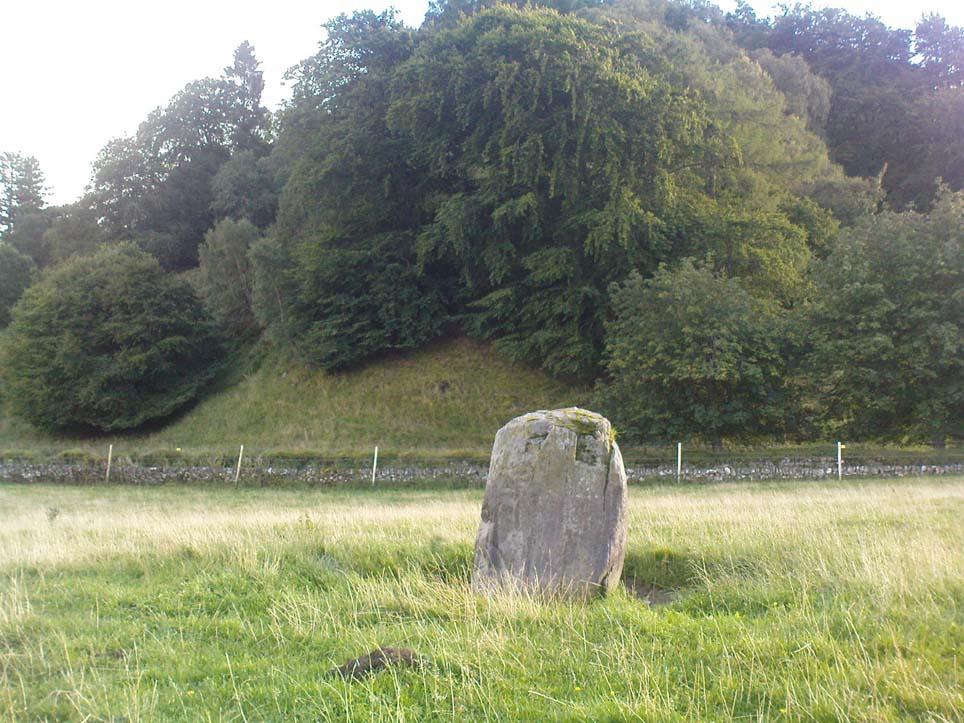
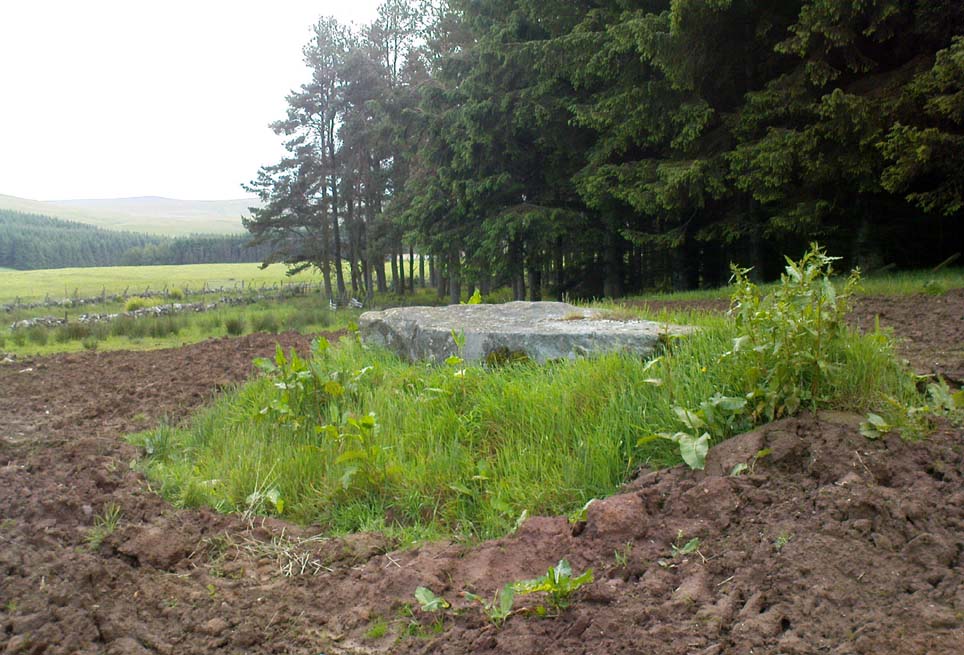
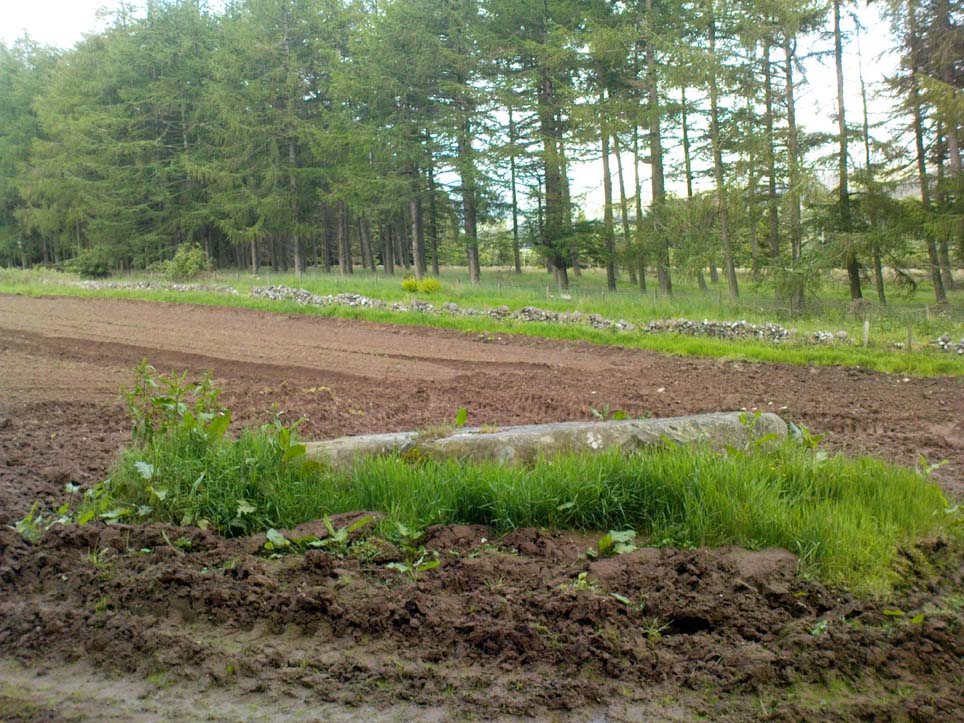
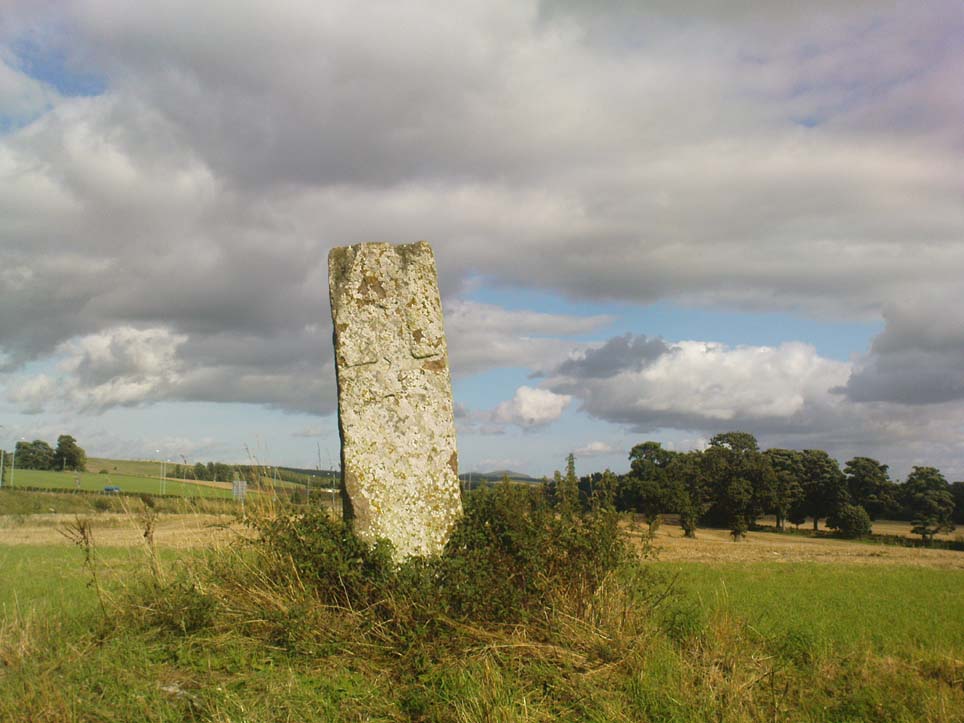
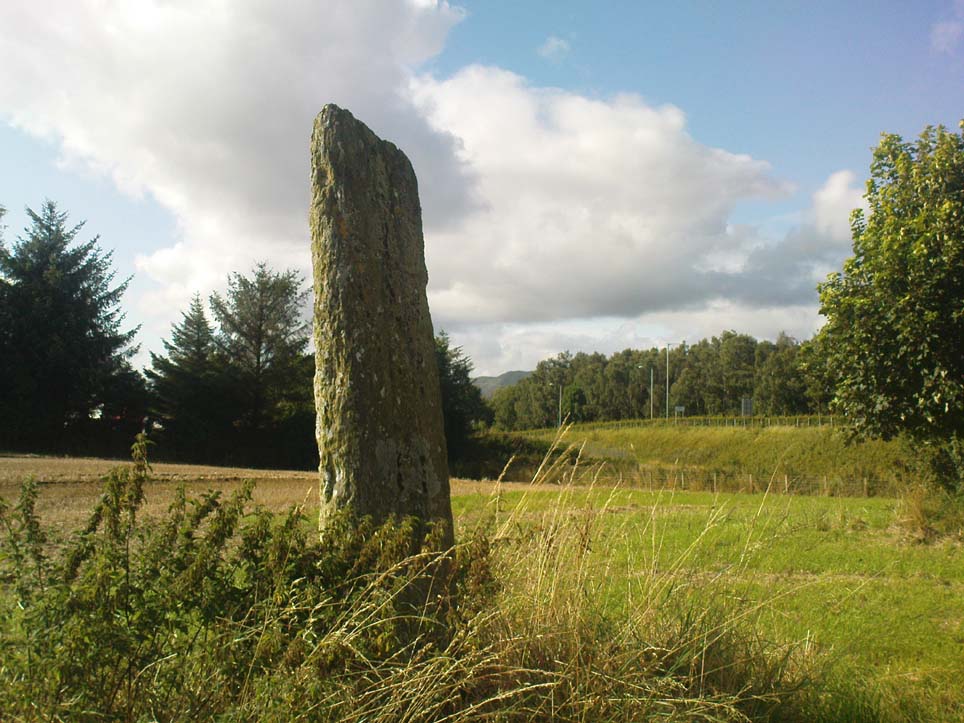
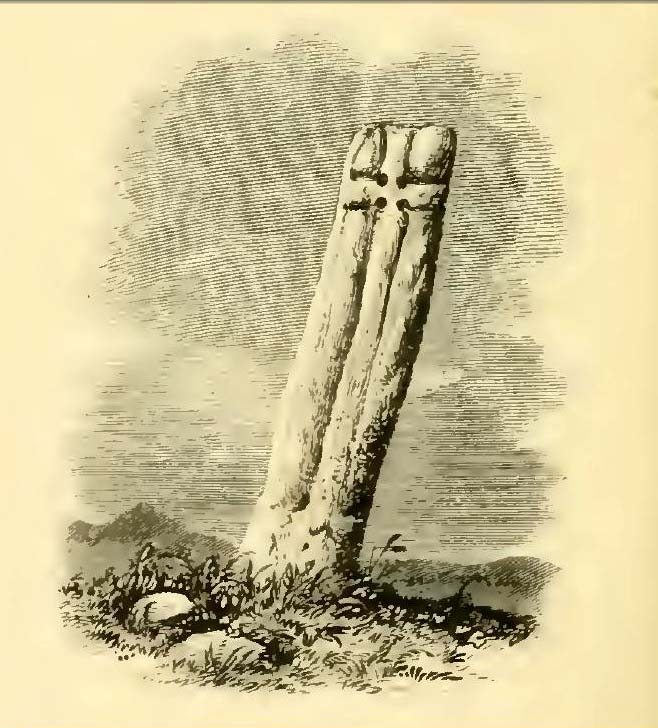
Legendary Rock: OS Grid Reference – SN 1770 1874
Also Known as:
- Chair of St. Canna
- St Canna’s Chair
Archaeology & History
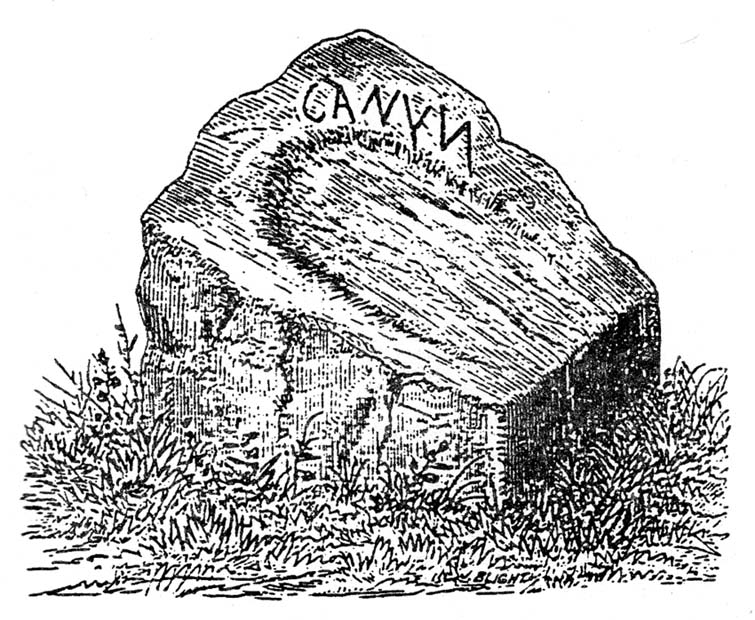

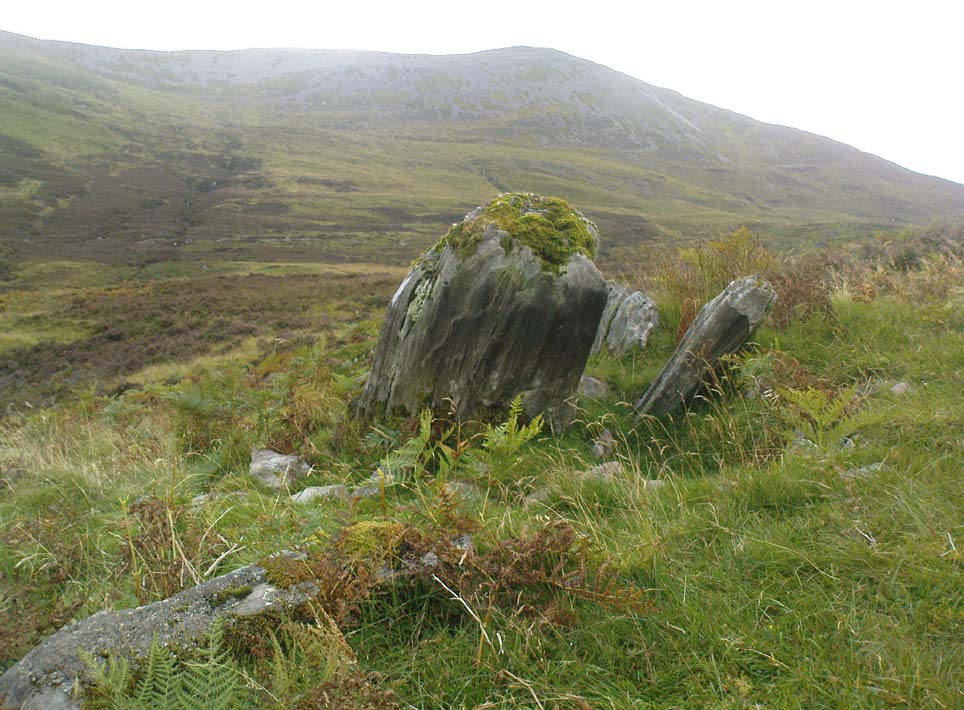
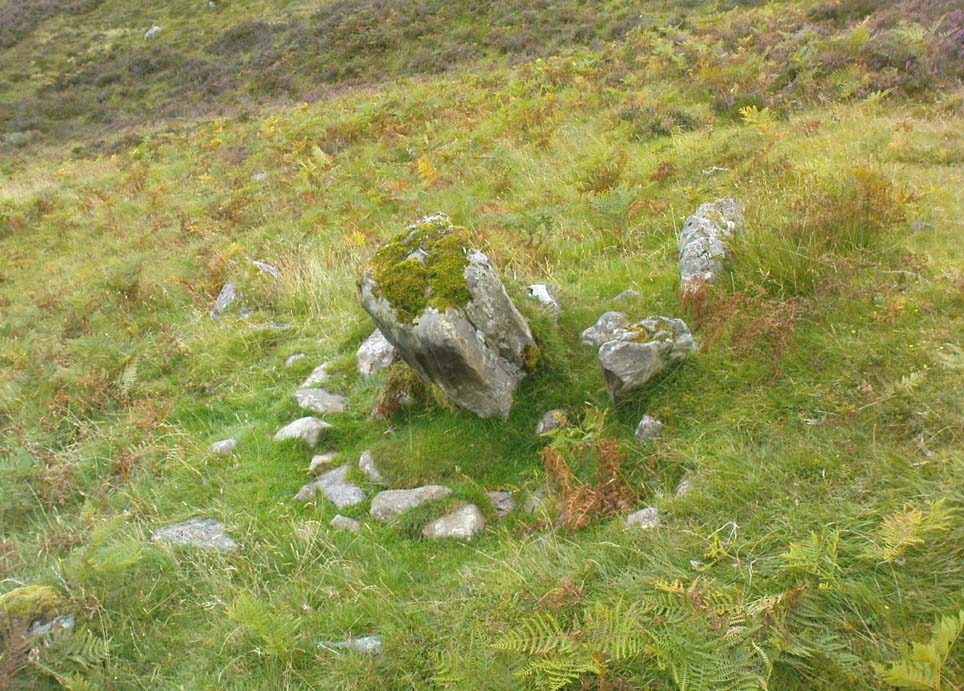
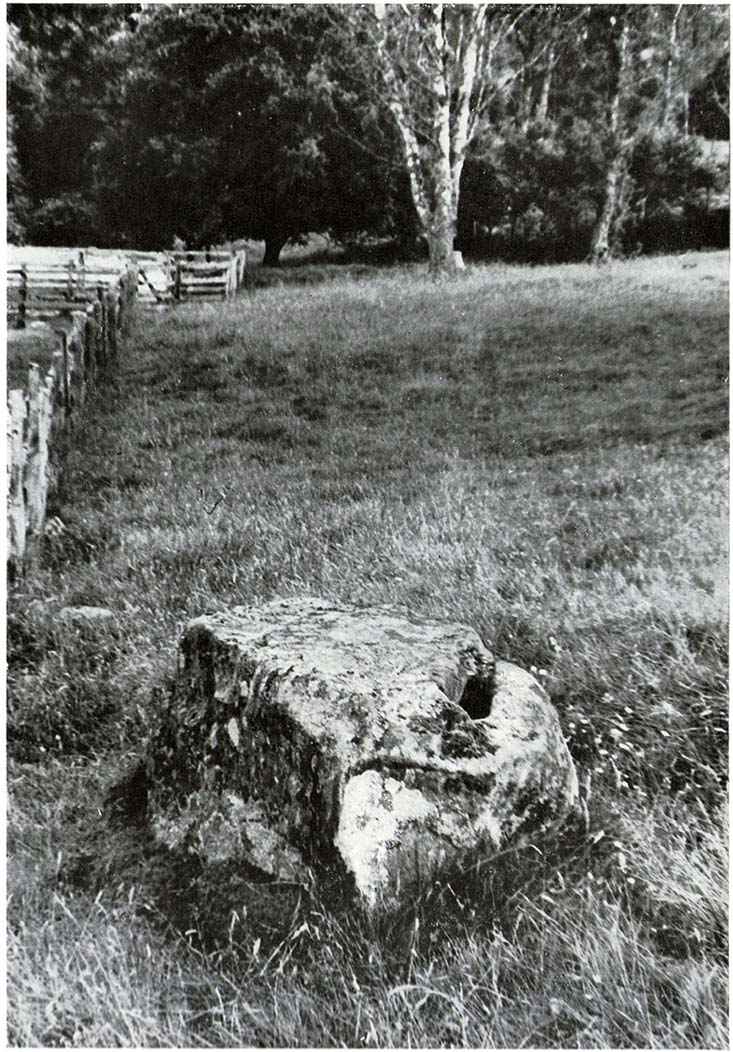
This once important healing stone that was moved a short distance (from grid reference SN 1775 1875 to SN 1770 1874 according to officials) to its present spot, around 1925, whilst having a long history according to the folk traditions of Carmarthenshire, was previously questioned as an authentic site by none other than Prof John Rhys (1875), following his visit to the site in the 1870s. Although Rhys seemed an isolated voice, some modern archaeologists have also questioned its veracity. It’s difficult to say precisely what the original nature of the stone may have been, but it was certainly accommodated in medieval times as a healing stone and used in conjunction with a pagan well – which was of course, accommodated by the Church. If the stone itself had a megalithic pedigree, as some have believed, we know not what it may have been…
As Janet & Colin Bord (2006) wrote, the stone “still survives, but to the casual observer it looks like any other abandoned block of stone,” sitting innocuously within the ring of trees surrounding the church. An early account of the stone was written by E.L. Barnwell (1872), who told:
“The present church of Llangan in Carmarthenshire is a wretched structure, built in 1820, and is about to be removed, as the population has long since migrated to some distance from it, and in a few years even the memory of Canna’s church having once existed here may cease. There is, however, a relic still left, which we trust will not be overlooked by the local authorities, as indeed it seems to have been hitherto ; for no notice occurs of it in the account of the parish in Lewis’s Topographical Dictionary or any other work. This relic is a rude stone, forming a kind of chair, lying in a field adjoining the churchyard, and about thirty or forty yards from it. When it was removed to its present position is unknown. There was also a well below the church called Ffynnon Canna; and there is still a small brook available, if required, for following the rules prescribed to those who wish to avail themselves of the curative powers of the saint’s chair. It appears that the principal maladies which are thus supposed to be cured are ague and intestinal complaints. The prescribed practice was as follows. The patient first threw some pins into the well, a common practice in many other parts of Wales, where wells are still thought to be invested with certain powers. Then he drank a fixed quantity of the water, and sometimes bathed in the well, for the bath was not always resorted to. The third step was to sit down in the chair for a certain length of time; and if the patient could manage to sleep under these circumstances, the curative effects of the operation were considerably increased. This process was continued for some days, even for a fortnight or longer. A man aged seventy-eight, still living near the spot, remembers the well and hundreds of pins in it, as well as patients undergoing the treatment; but, about thirty or thirty- five years ago, the tenant carried off the soil between the well and the watercourse, so as to make the spring level with the well, which soon after partly disappeared, and from that time the medical reputation of the saint and her chair has gradually faded away, and will, in the course of a generation or two, be altogether forgotten.”
Folklore
In Wirt Sykes (1880) classic text, he told us that the field where the original Canna’s Chair may have been, possessed fairy-lore that we find at other sites, usually ascribed as prehistoric. He wrote:
“In the middle of this parish there is a field called Parc y Fonwent, or the churchyard field, where, according to local tradition, the church was to have been originally built; but the stones brought to the spot during the day were at night removed by invisible hands to the site of the present church. Watchers in the dark heard the goblins engaged in this work and pronouncing in clear and correct Welsh these words, “Llangan, dyma’r fan,” which means, “Llangan, here is the spot.””
References:
- Allen, J. Romilly, The Monumental History of the Early British Church, SPCK: London 1889.
- Baring-Gould, S. & Fisher, John, Lives of the British Saints – volume 2, London 1907.
- Barnwell, E.L., “Canna’s Chair,” in Archaeologia Cambrensis, volume 3 (4th Series), 1872.
- Bord, Janet & Colin, Cures and Curses: Ritual and Cult at Holy Wells, Heart of Albion: Wymeswold 2006.
- Breverton, Terry, The Book of Welsh Saints, Bro Morganwg: Glyndwr 2000.
- Davies, Jonathan Ceredig, Folk-lore of West and Mid-Wales, Welsh Gazette: Aberystwyth 1911.
- “D.M.”, “Canna’s Chair,” in Archaeologia Cambrensis, volume 4 (4th Series), 1875.
- Rhys, John, “On Some of Our Inscribed Stones,” in Archaeologia Cambrensis, volume 4 (4th Series), 1875.
- Sikes, Wirt, British Goblins, Sampson Low: London 1880.
- Sharkey, John (ed.), Ogham Monuments in Wales, Llanerch: Felinfach 1992.
- Westwood, J.O., Lapidarium Walliae: The Early Inscribed and Sculptured Stones of Wales, Oxford University Press 1879.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian