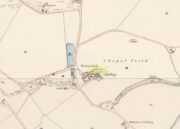
Tumulus (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – TL 60 62
Archaeology & History
This is one of many long lost prehistoric tombs that were known to have existed in and around the Newmarket race-course, but unlike the Newmarket tumuli 1 – 4 which were all on the first OS-map of the area, this one had been destroyed before the Ordnance Survey lads came here. As a result we don’t know its exact whereabouts.
Described in both the Cambridge Chronicle and Gentleman’s Magazine in 1827, the accounts even then were talking about it in the past tense, albeit pretty recently. The race-course at Newmarket was being modified, leading to the destruction of our ancient landscape—and with it, this tumulus. In those days however, such destruction was deemed as an ‘improvement’, as Sylvanus Urban (1827) tells at the start of his account:
“The improvements making in the exercise ground at Newmarket, Cambridgeshire, have led to some discoveries which may, perhaps, tend to the elucidation of the hitherto obscure origin of the entrenchment commonly called “The Devil’s Ditch.” In removing one of the monumental remains denominated barrows, or tumuli, which are numerous in this neighbourhood, the skeleton of a person was found deposited near the surface, whose remains were too recent to be associated with the area of its place of interment; but, upon clearing away the earth to the centre of the mound, a discovery was made of an urn, of rude construction and materials, containing ashes, together with some beads, which, it is presumed, formed the ornaments of the person to whose honour the barrow was dedicated. There were also found two coins, supposed to be Roman, and a fragment of a cup, of far superior manufacture to the urn, lying promiscuously at the depth of about two feet.”
A summary of this was included in Babbington’s (1883) archaeological survey. But in Cyril Fox’s (1932) list of barrows near Cambridge he seemed to confuse this “tumulus on Exercise Ground” (no.16) with what he thought was another tumulus (no.17), which he described as, “Exact site unknown. Contained a cremation interment. Burnt bones and sherds of Bronze Age type, also Roman sherds.” The two are the same thing.
References:
- Babbington, Charles C., Ancient Cambridgeshire, Cambridge Antiquarian Society 1883.
- Fox, Cyril, The Archaeology of the Cambridge Region, Cambridge University Press 1923.
- Royal Commission Ancient Historical Monuments, Inventory of Historical Monuments in the County of Cambridgeshire – Volume 2: North-East Cambridgeshire, HMSO: London 1972.
- Urban, Sylvanus, “Domestic Occurrences,” in Gentleman’s Magazine, September 1827.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian