Long Cairn: OS Grid Reference – NS 51839 78157
Getting Here
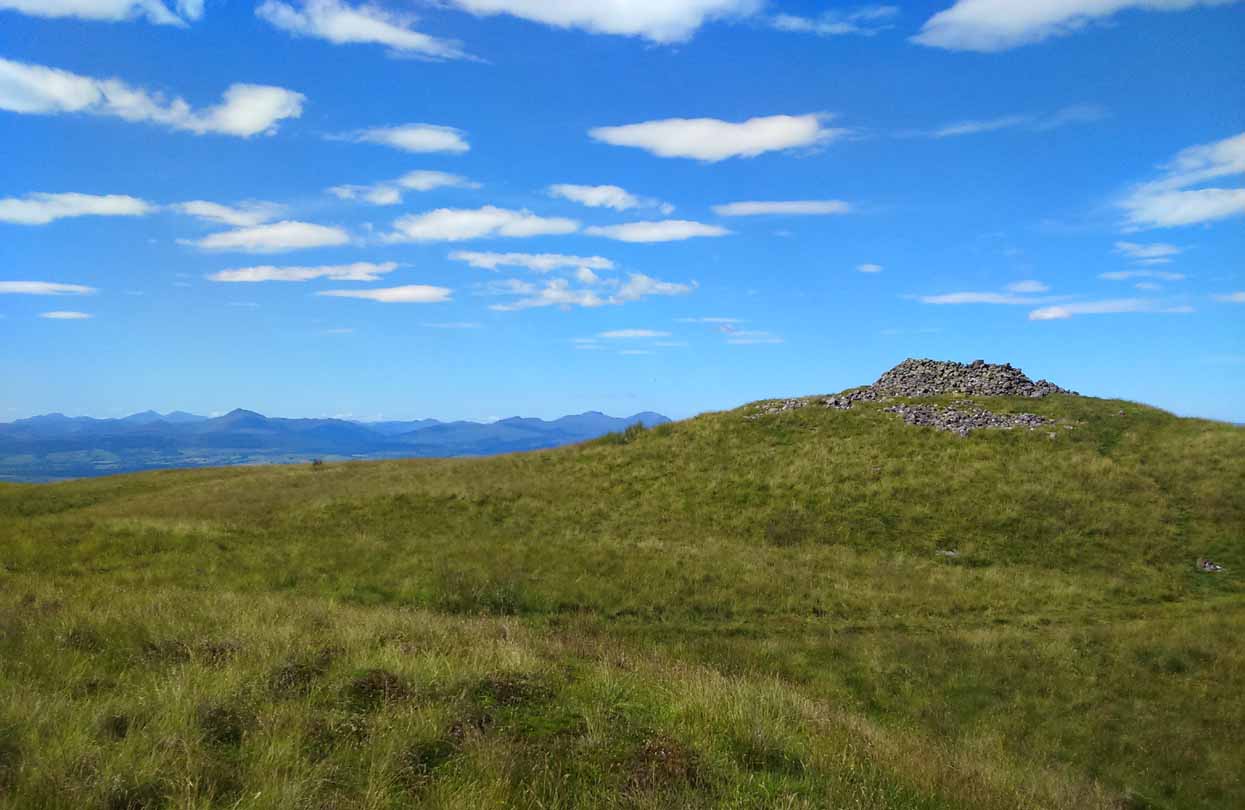
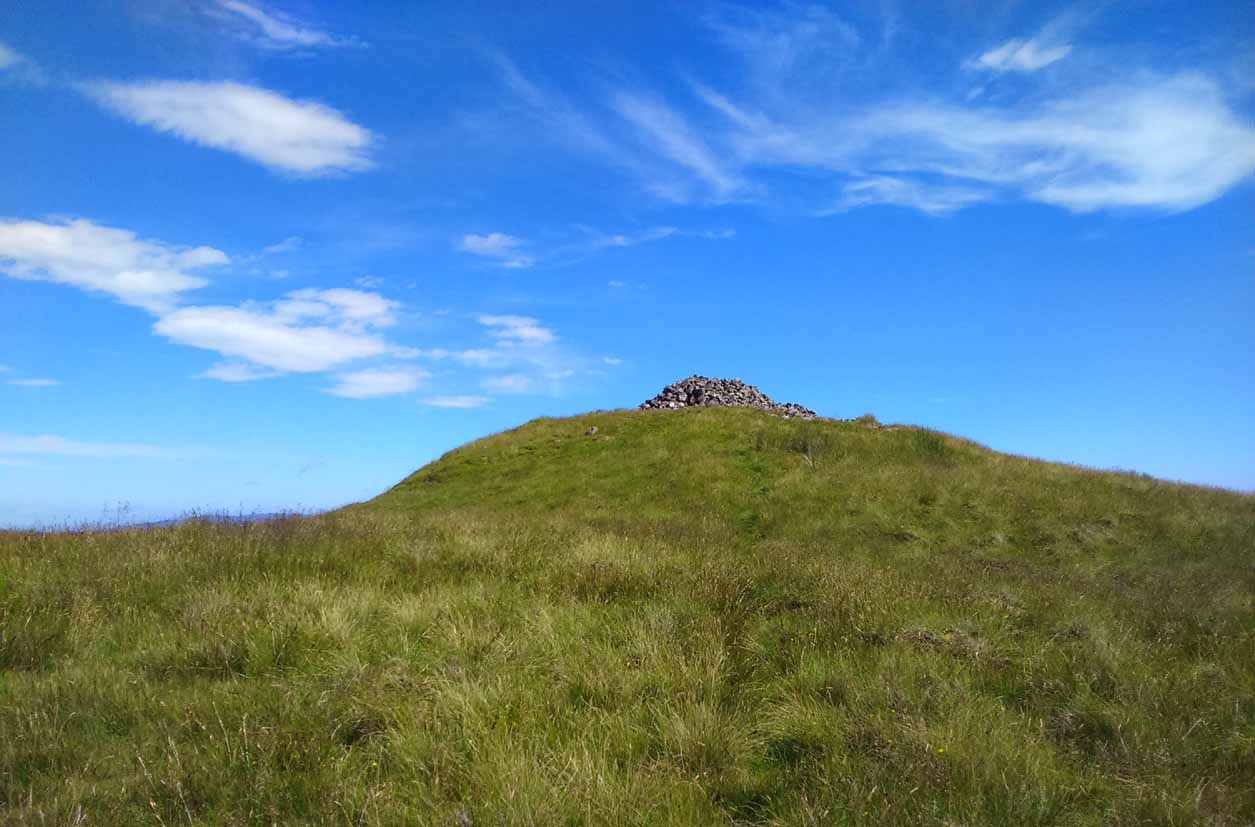
Take the A809 road several miles north out of Glasgow, between Bearsden and Drymen. Once out of the suburban sprawl, passing Milngavie, you’re heading to the famous Carbeth hutters. Before this, note the gold course on your right (east). Park here and cross the road where a gate and overgrown footpath takes you onto the grassy hills. Keep to the fence-side for about 700 yards until it veers downhill. Don’t walk downhill! Keep in the same direction into the short grasses and, veering gradually left, downhill for a couple hundred yards ahead and, across a small boggy area, you’ll note some large upright stones in front of a mound. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
There is no previous reference to this site which was found, quite fortuitously, by Nina Harris of Organic Scotland a few years ago. She visited the site a number of times, puzzling over the curious line of possible standing stones at the edge the grass-covered mound—wondering if it was anything at all. A few months ago she took us to see the place…
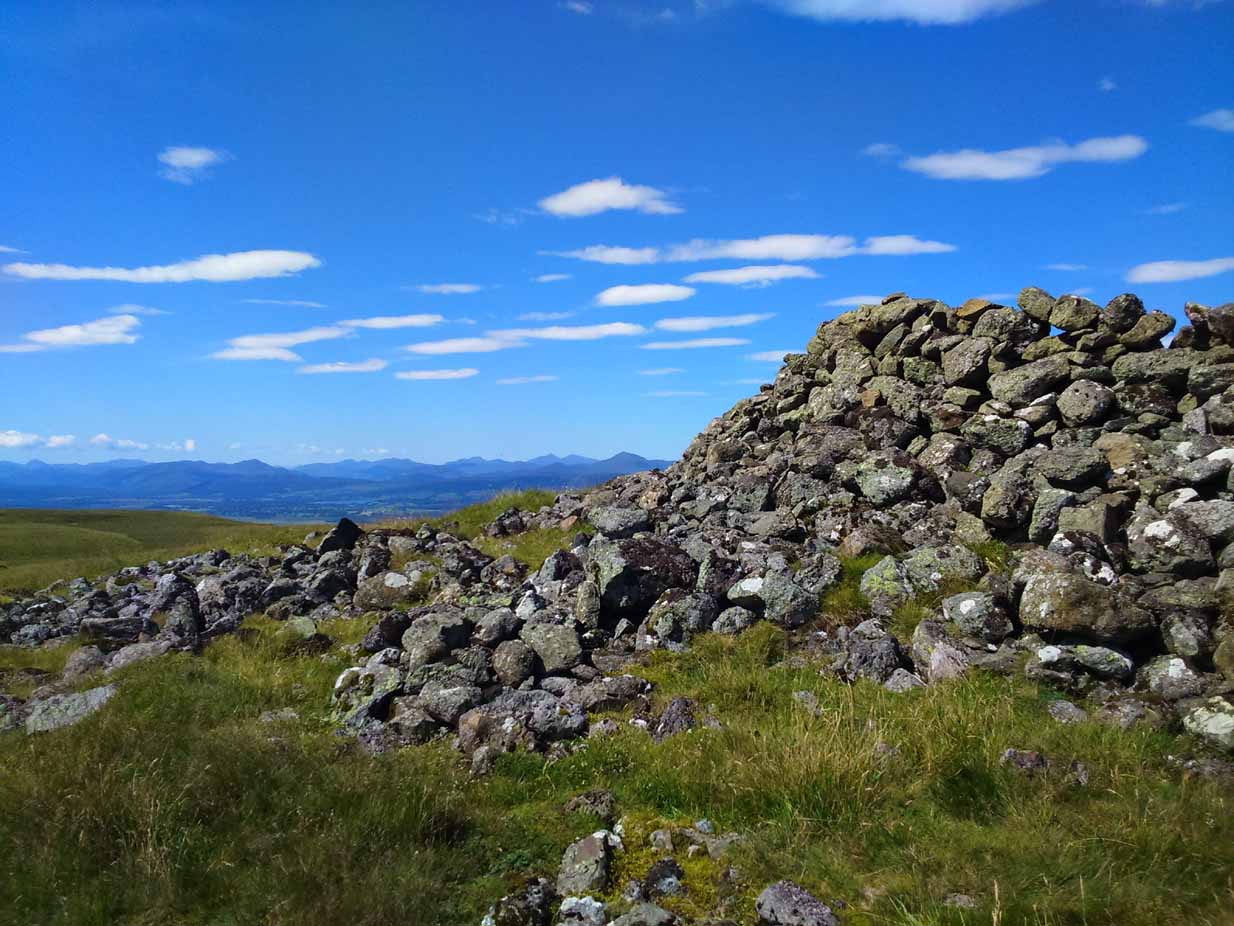
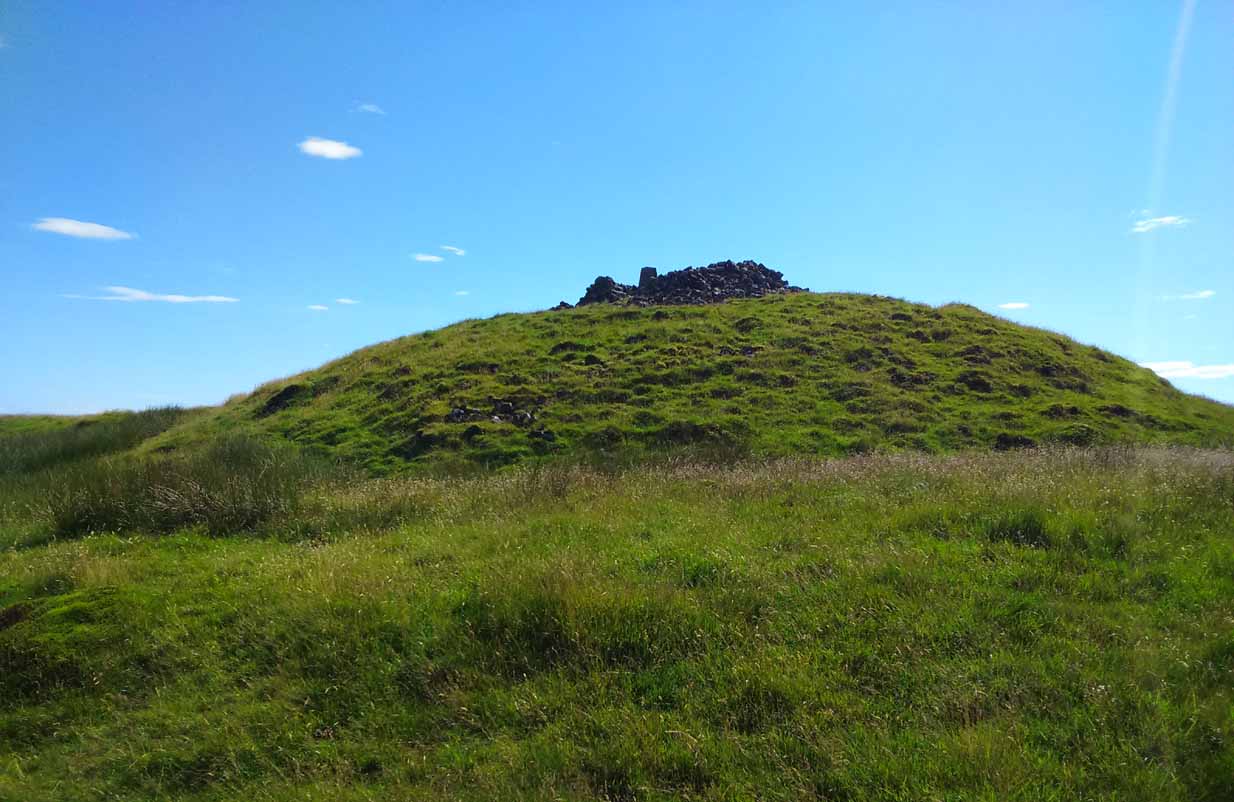
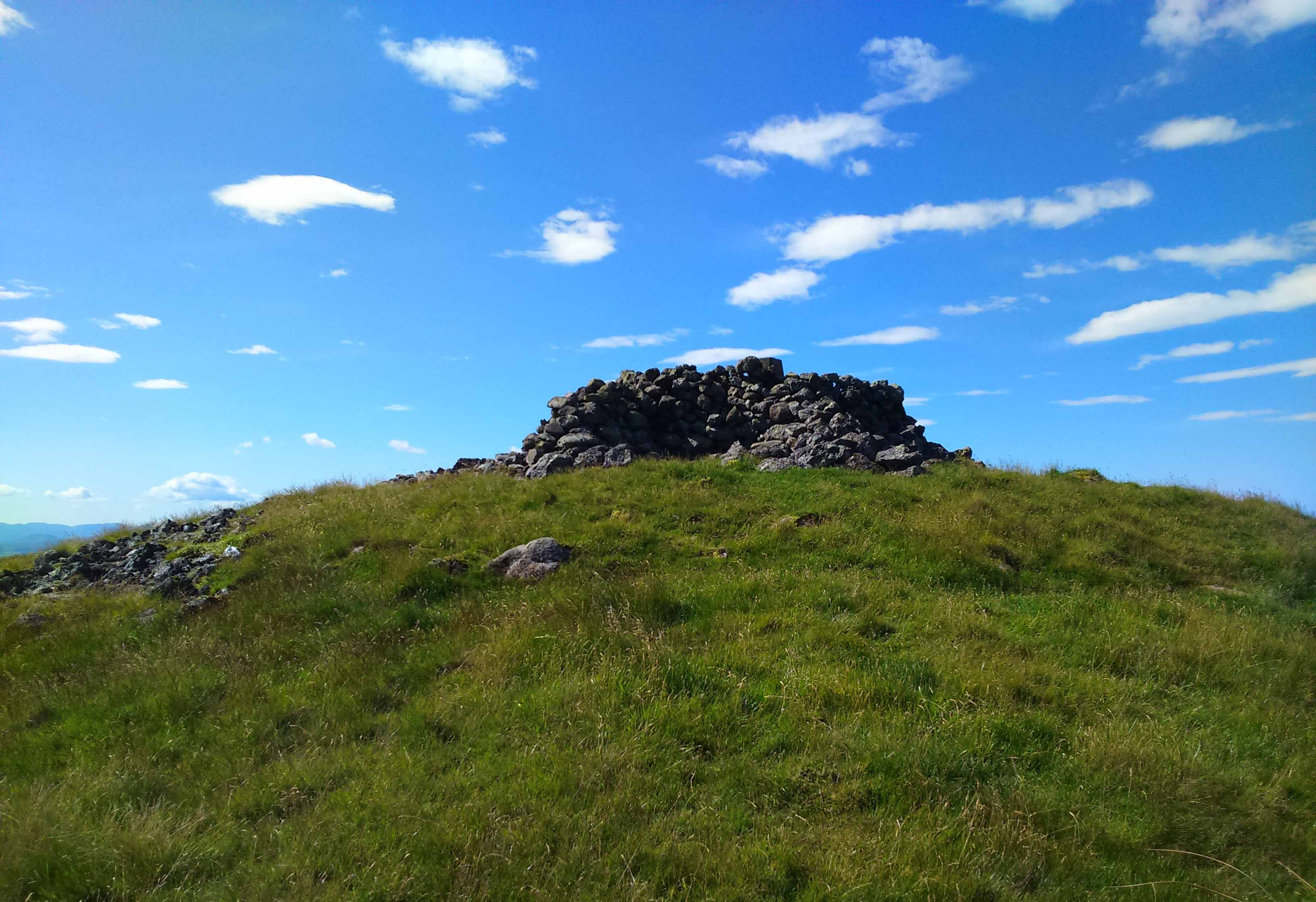
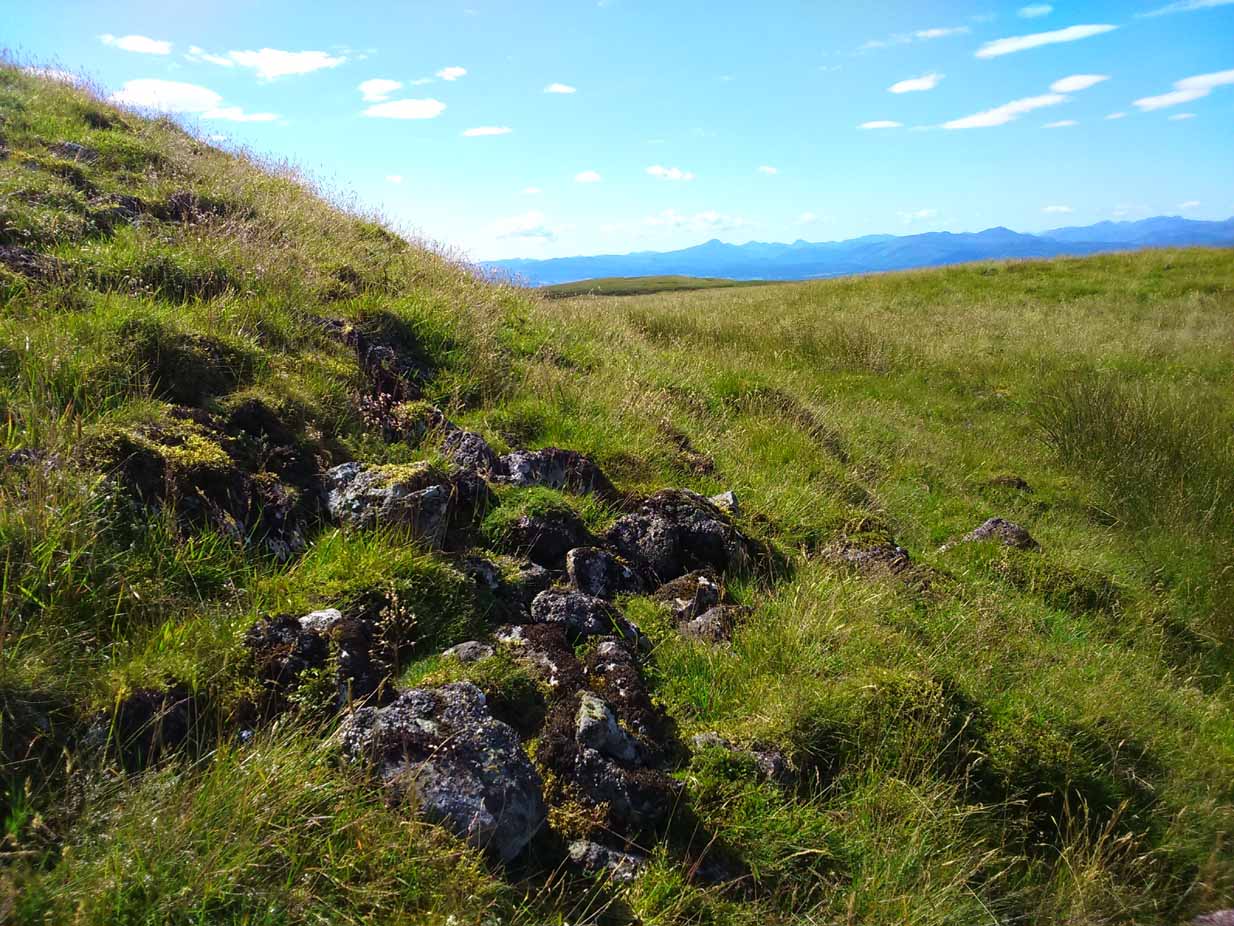
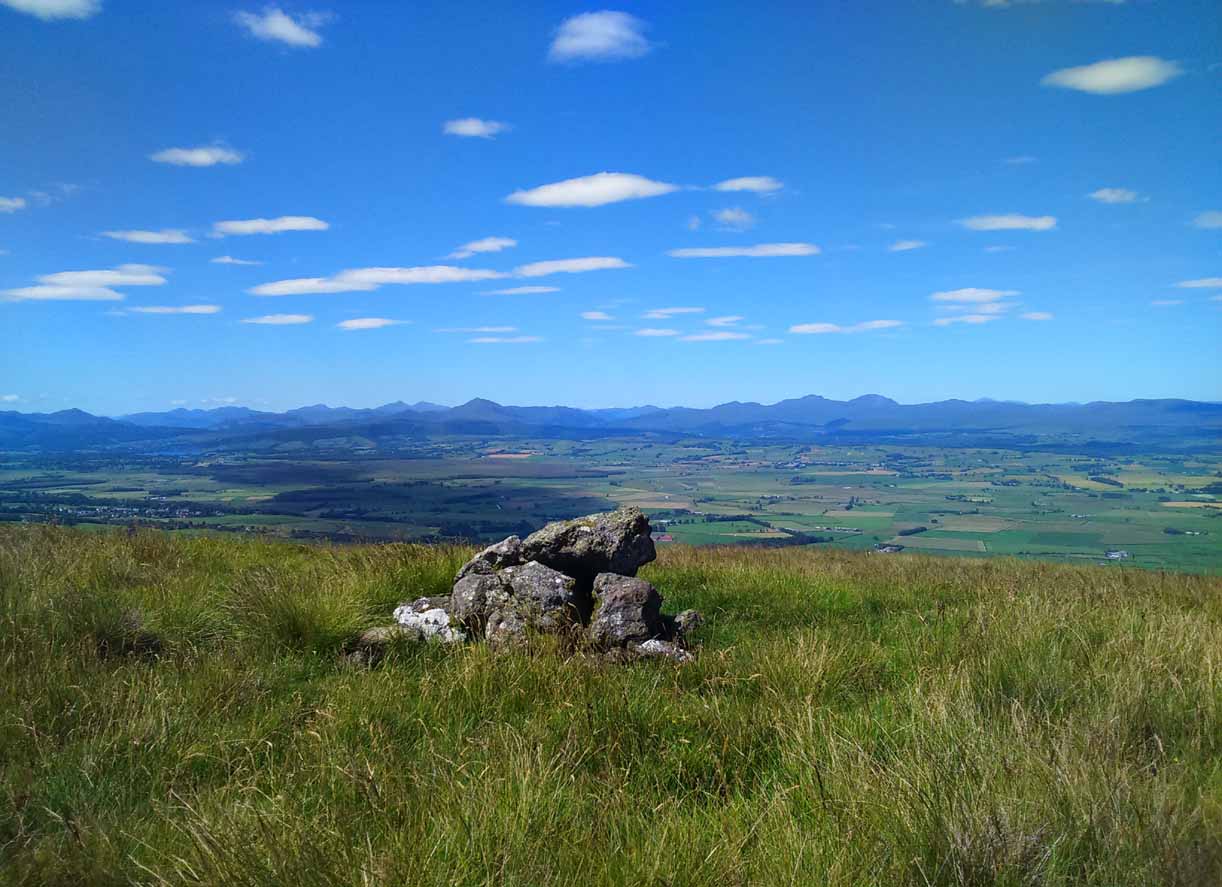
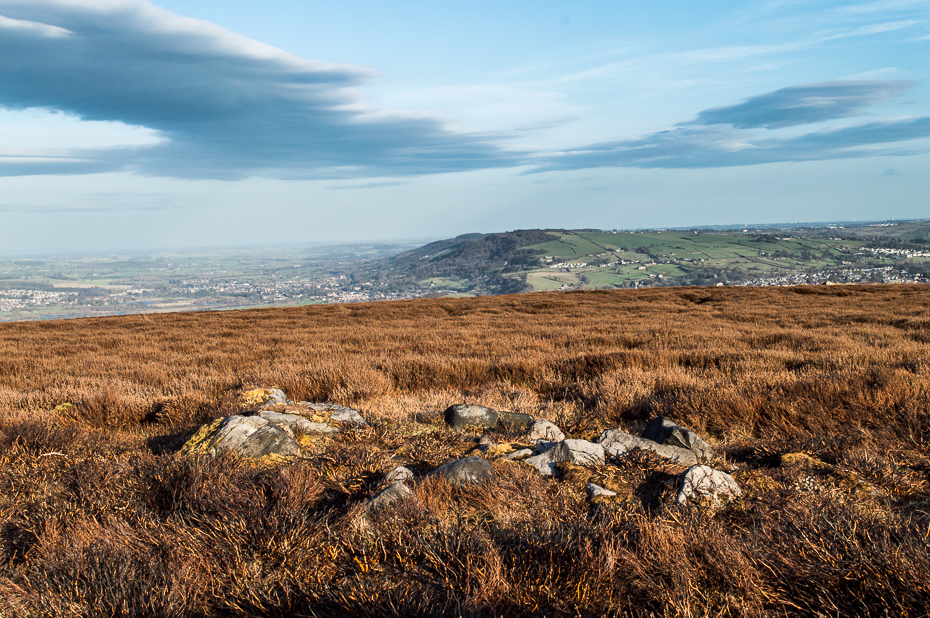
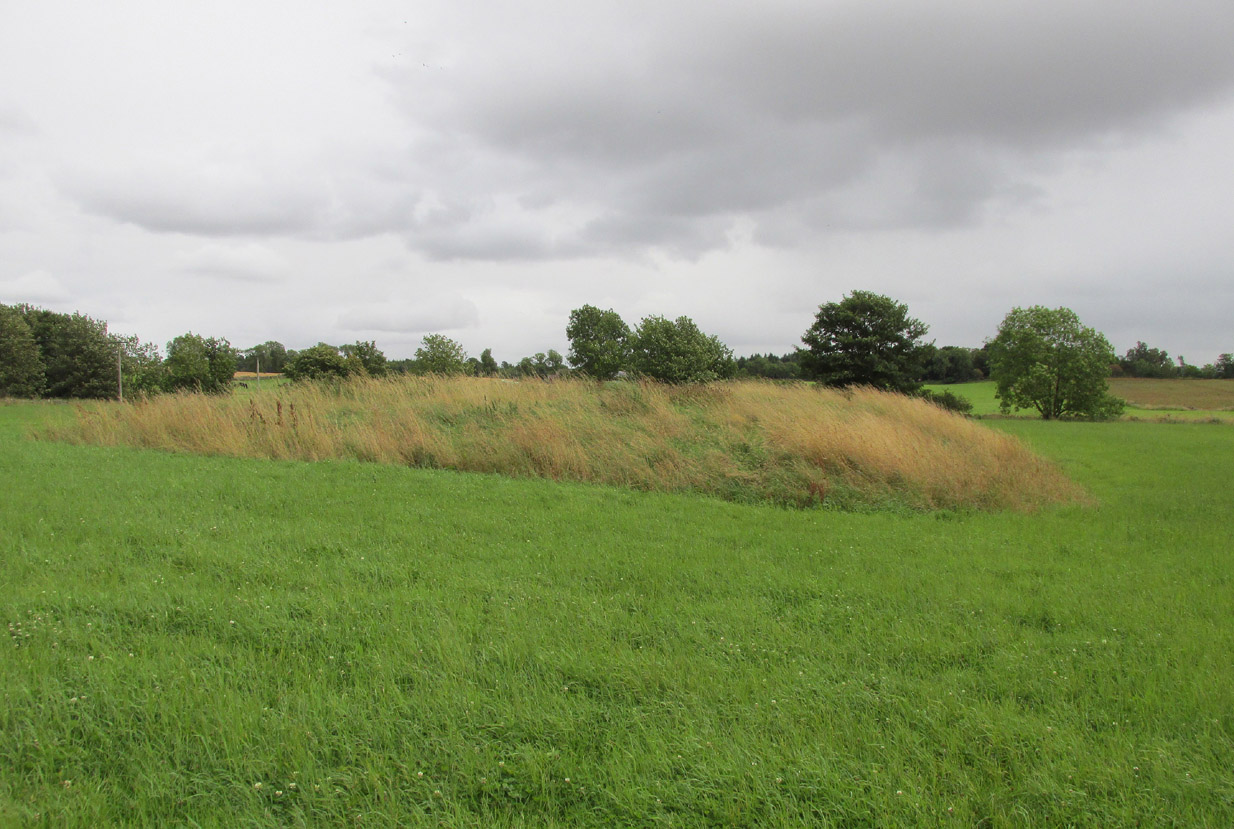
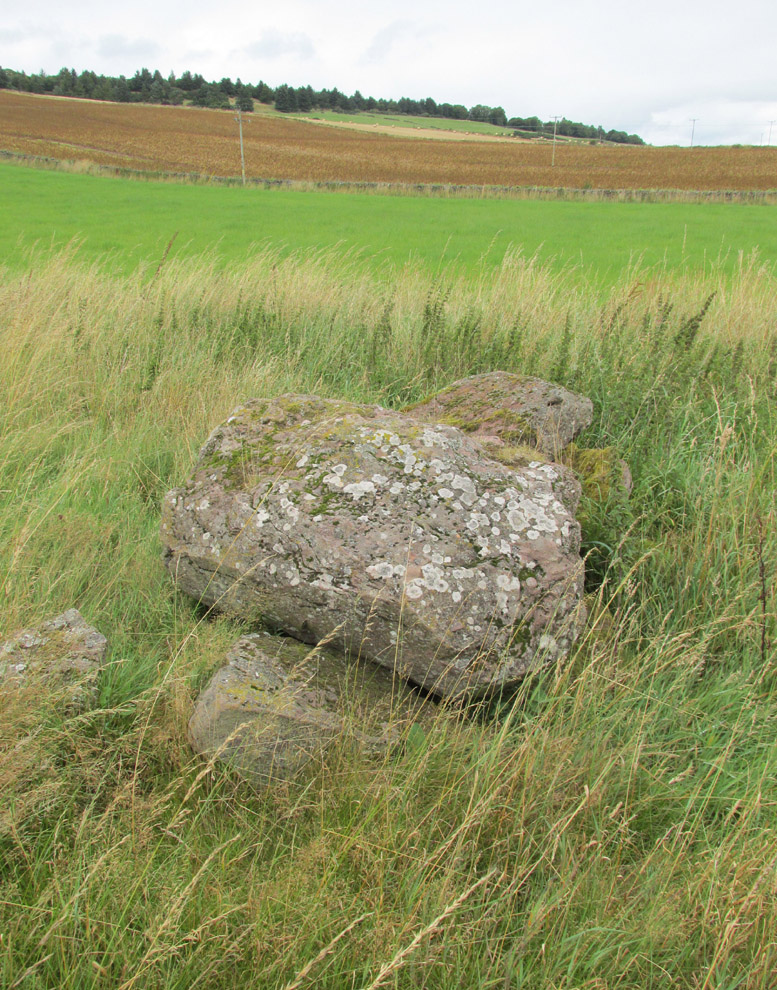
The site has been damaged and elements of it have been stripped for walling that are visible all around here. The cairn is more than 55 yards in length, running from its southeastern stone ‘entrance’ to the gradually diminishing northwestern edges. At its widest it is 14.6 yards (13.5m) across, near its southeastern end. The main three standing stones at its entrance are four-feet tall at the highest, with one of them leaning upon another; an adjacent fourth stone, smaller than the main three, is more embedded into the cairn mass a couple of yards away. Cup-marks on one of the three larger uprights here are recent gunshot marks; whilst the possible cup-marks on the largest upright are natural.
In standing on top of the long cairn, just above the large stones, you can see how sections of it have been stripped away. Just beneath the surface is a line of internal walling, with what seems to be another one running parallel. These run for a few yards until we reach a large circular depression within the overall cairn mass, a yard deep and 6-7 yards across; on the northern edge of which we can clearly see a section of walling beneath the surface. When we look at the aerial view of this on Google Earth, we can clearly see how this walling actually begins way outside of the cairn mass itself, as a much denuded line of it (probably medieval in origin, though possibly Iron Age) curves across the grasslands from the west, crosses the long cairn and re-emerges on the other side of the adjacent boggy ground at its southeastern edges and continues on its way: indicating that the cairn mass beneath the wall is much older than the walls running across it.
Audrey Henshall (1972) described the existence of another prehistoric chambered tomb like this one at Cairnhowit 1.95 miles (3.14km) southwest, and we find the Stockie Muir long cairn 3.12 miles (5.02km) to the northwest, clearly showing that the incidence of this monument is not an isolated one. Others can be found not much further away. The existence of the raised geological plate known as Carneddans Wood just over a mile south may have once been home to another chambered cairn.
Please note that the grid reference for this site fixes on the southeastern section of the cairn, where the upright stones are.
References:
- Henshall, Audrey S., The Chambered Tombs of Scotland – volume 2, Edinburgh University Press 1972.
Acknowledgements: First and foremost to Nina Harris, for unknowingly finding the place; also to Paul Hornby and Marion Woolley for visits to the site.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian