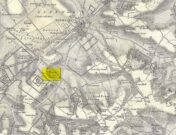
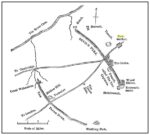
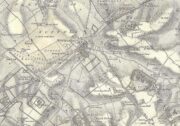
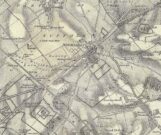
Cairn (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NO 1886 0890
Also Known as:
The easiest way is to turn south off the A91 at Gateside onto Station Road, and the site of the cairn is in the third field to the left over the railway bridge. I accessed the site walking along the old railway line and climbing up the embankment.
Archaeology & History
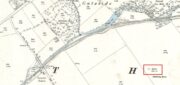
In the shadow of the Lomond Hills of Fife, what was once a very large pre-historic cairn, officially described as of ‘unassigned’ period, was quarried to destruction around two hundred and twenty years ago, presumably to provide stones for dykes (stone walls), at that time of enclosures of common land and what the landowners liked to call ‘agricultural improvements’.
In the early nineteenth century, this part of the Eden Valley between Gateside and the Lomond Hills was what would now be called a ritual landscape. There were, according to Miller:
‘nearly in a line between the two Laws ( Lomond Hills) no less than eight “druidical temples” (Stone circles) close together‘
and a number of impressive burial cairns, of which Easter Nether Urquhart seems to have been the largest. There were in addition large numbers of graves containing masses of cremated of human bones. Nearly all this archaeology has been subsequently destroyed by the farmers.
Two local antiquarian writers proposed that all these human remains had been buried there following the battle of Mons Graupius between the Roman Invaders under Agricola, and the Caledonians, and went on to argue that the Eden Valley was the site of this historic defeat for the ancient Caledonians defending their homeland. Whatever and whenever the origins of the cairns and human remains, subsequent researchers disagree with these nineteenth century arguments in favour of the Eden Valley, and tend to favour a more northerly location for Mons Graupius. Nevertheless we have these two historians to thank for leaving us descriptions of the cairn.
One of the antiquarians, Rev. Andrew Small wrote in 1823:
‘The Slaughter here seems to have been so dreadful, that even after the lapse of 17 Centuries the Common tradition of the Country bears, and seems to be as fresh in the Mouths of both old and young as though the battle had been fought only a hundred years ago, – that after this battle the River Eden ran red with blood for two days…’
It seems more likely that the event remembered was part of the campaign by Roman Emperor Septimus Severus and his son Caracalla to subdue the Caledonians around 209-210 CE. Modern writer, Simon Elliott:
‘Archaeological data is now emerging to show ….. a major depopulation event, indicating something close to a genocide was committed by the Romans in the central and upper Midland Valley.’
Andrew Small describing the cairn and some of the cremation remains in 1823:
‘There was also a very large cairn laid upon these ; and the proprietor lately told me that when removing the stones, besides the ashes already mentioned, there was also a pit of pure fine sand by itself, about as fine as is usually put into sand-glasses, which he thinks had been used for regulating the fire in burning of the dead. This cairn stood a little north of an ancient Druids temple, only one stone now remaining, out of ten of which it formerly consisted ‘.
Lieutenant – Colonel, Miller writing in 1829:
‘Farther west ….a very large cairn stood, containing upwards of two thousand cart-loads of stones. Upon removing it about thirty years ago, a pit six feet long, two broad, and of the same depth, was found, quite full of burnt bones; and near it another, two feet square and two deep, full of the finest sand. An urn was also found, near the surface of the cairn, full of bones. A very fine Druid’s temple stood on the south side of it, consisting of seven very large stones…’
As the builders of the cairn didn’t have access to carts, and that the stones all had to be moved by hand, it gives an indication of the manpower needed to build the cairn, and the status of the individuals whose remains were buried there. And we have to question why a special chamber been built into the base of the cairn to hold fine sand, and what was the purpose of this sand?

Centre – View looking south. Right – The cairn recycled? Walling on the south side of A91 at
Gateside
Folklore
While not writing specifically of the cairn, Revd. Small recounts these tales of the surrounding land, relating it to his belief that it was the site of Mons Graupius:
‘I cannot forbear to mention here, also, a singular circumstance I had from the landlord and landlady, both yet alive, — viz. that before parking or inclosing took place, they were accustomed to have folds built of feal or turf for the cattle lying in at night ; but that, when the folds happened to be in this place where the dead had been burnt, the cattle would never lie in them, but always broke through or leaped over the dyke ; that they were obliged to give a man a boll of barley extra to watch them, when they lay in this spot, which was obliged to be repeated every four or five years in rotation ; but that sometimes the man was not able to keep them in by all his endeavours, the cattle looking wild and terrified in appearance ; and sometimes it required the united efforts of all the hands that could be had to keep them in, oftentimes springing over the fold dykes close beside them, and frequently crouching and trembling as if they would have fallen down with terror, although nothing appeared visible to the visual organs either of the man or those that occasionally assisted him. However, after the discovery of so many ashes and fragments of human bones, the man declared that, had he known of these being so near, he would not have been so fond of watching.’
‘The late farmer of Upper Orquart, a most respectable man, with whom I was well acquainted, and upon whose farm the principal part of the battle was fought, told me also that always when the folds happened to be both at where the Caledonians were burnt as well as the Romans — but particularly he specified the spot where the Romans had been burnt, or the Witch Know or Knoll — the cattle would never lie in the fold, but were always breaking ” the fauld,” as he called it, except when they were particularly watched ; and even that was not always effectual for keeping them from doing it either. This would insinuate as if the spirits of these departed heroes of antiquity sometimes visited and hovered about the places where their ashes had been deposited ; though invisible to the more refined visual organs of the human eye, yet obviously visible in some shape or other to the more gross visual organs of the irrational or bestial tribe, else how can these forementioned occurrences be accounted for? This hypothesis seems to be borne out by Balaam’s Ass perceiving the Angel twice, when he himself could not do so till his eyes were supernaturally opened.’
Afterword
Although the cairn no longer exists, its stones were probably reused for local walling, and it’s likely, but not provable, that the wall on the south side of the A91 past the Station Road turning is built from stones removed from the cairn.
References:
- Elliott, Simon, Septimus Severus in Scotland, Greenhill Books, 2018.
- Miller, Lt. Col., “An Inquiry Respecting the Site of theBattle of Mons Grampius“, 1829, published in Archaeologica Scotica vol. IV, 1857.
- Small, Andrew, Interesting Roman Antiquities Recently Discovered in Fife, John Anderson, Edinburgh, 1823
Links:
© Paul T Hornby 2020