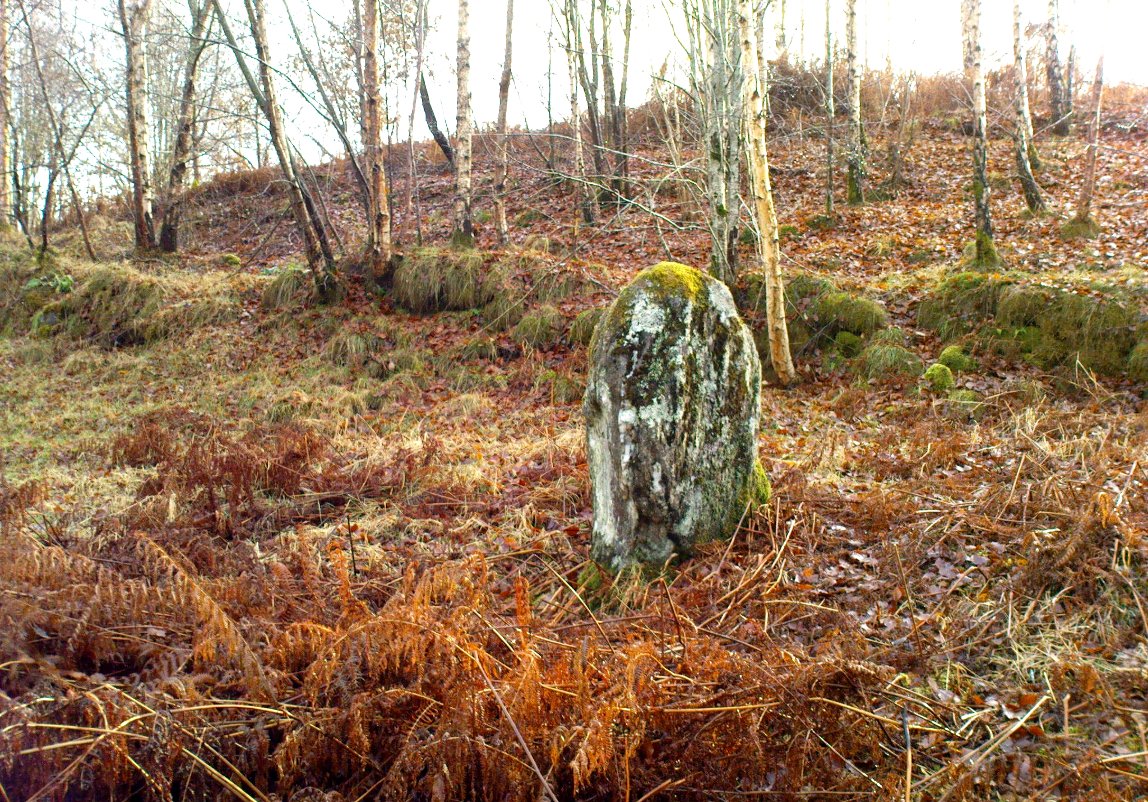
Stone Circle (remains of): OS Grid Reference – NN 9292 1246
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 26104
- East Hill
Getting Here
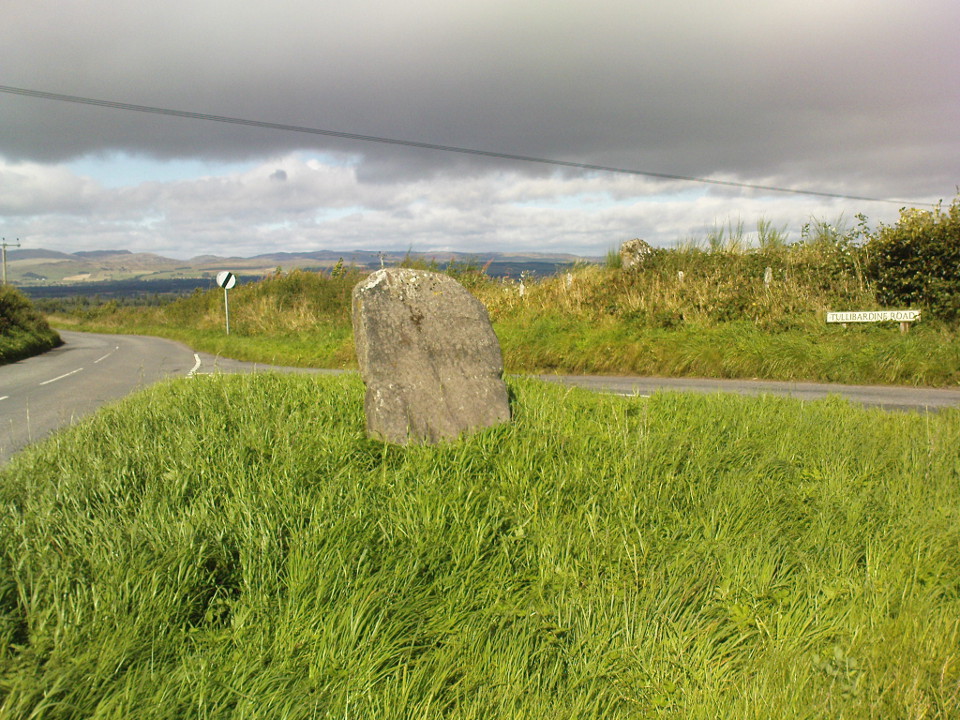

From Auchterarder’s A824 main street, going out towards the golf course take the Orchil Road on your right and then about fifty yards along, turn right again up Tullibardine Road. Park up somewhere about a hundred yards along, then just walk further down the road until you’ll see the standing stone right at the road junction. Look into the field on your right, above you, and another two are hiding in the brambles and grasses.
Archaeology & History
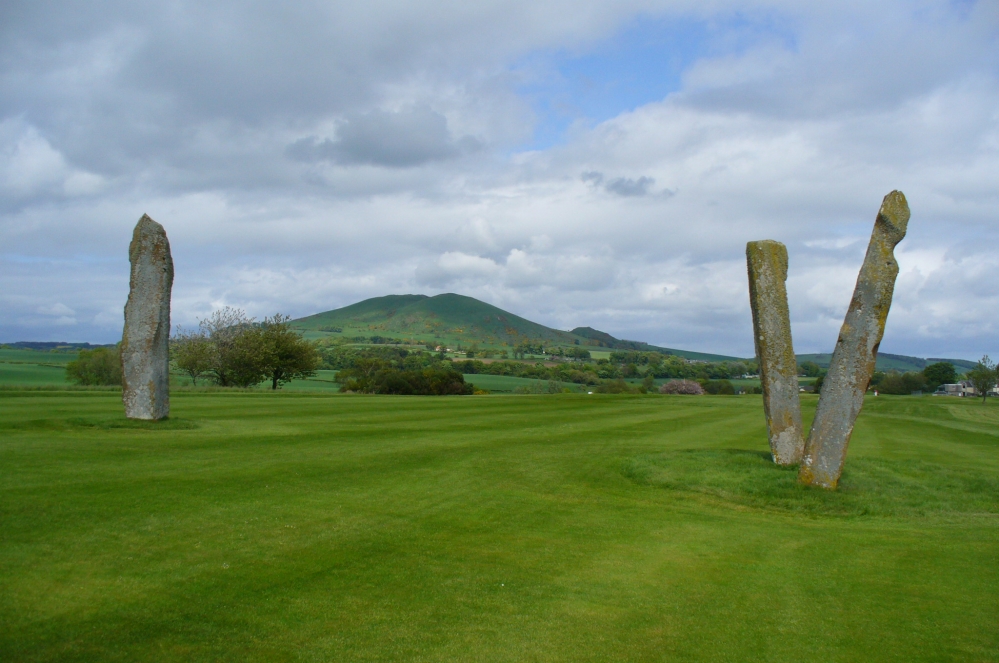
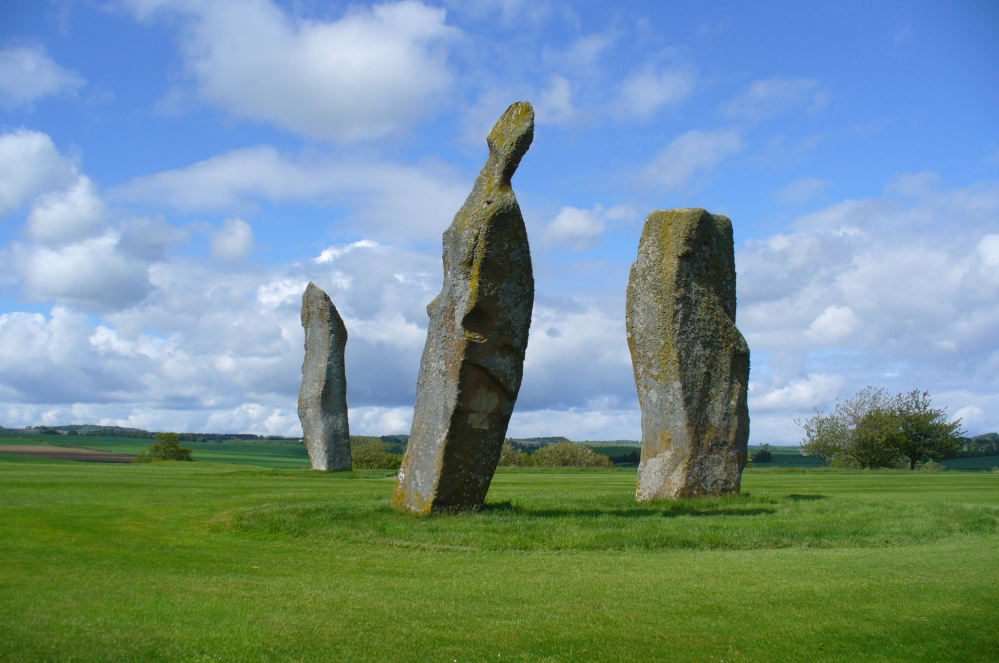
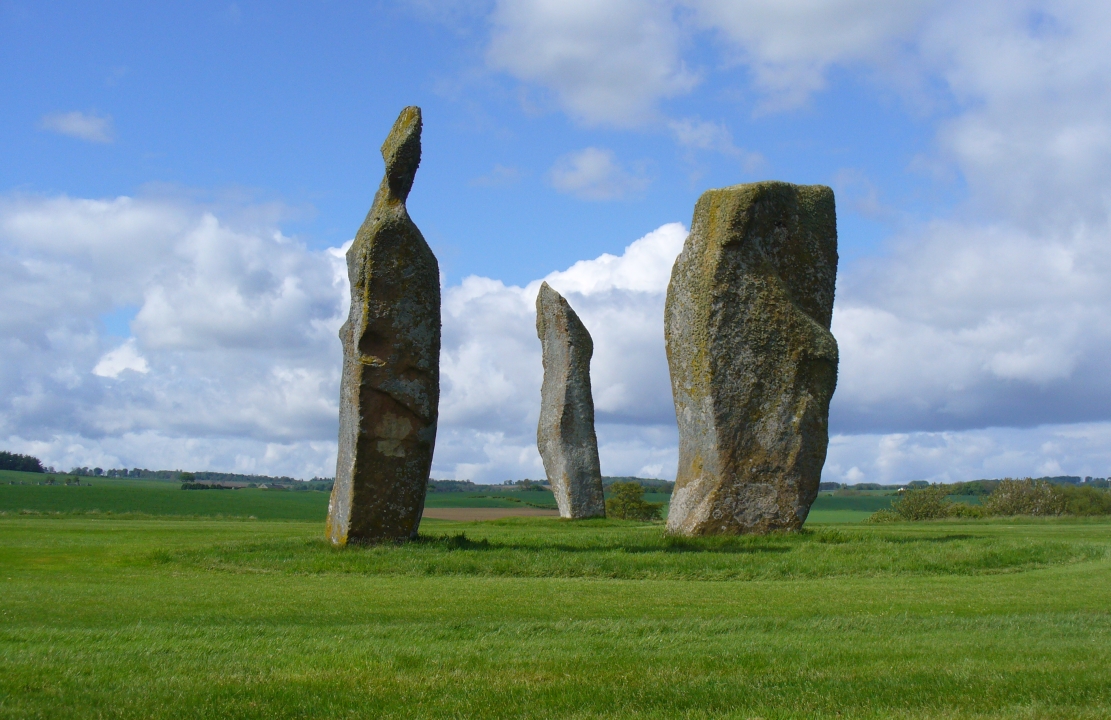
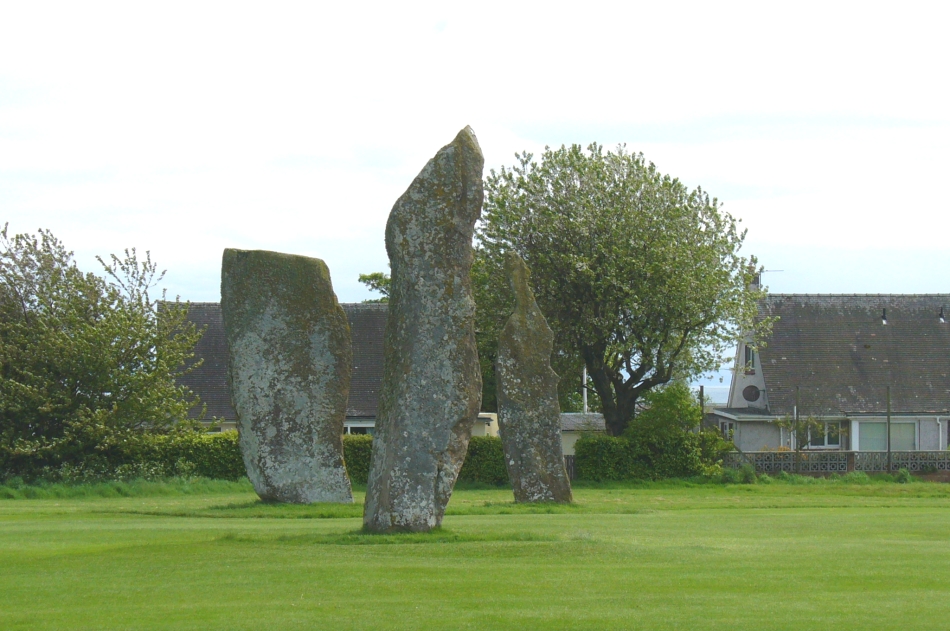
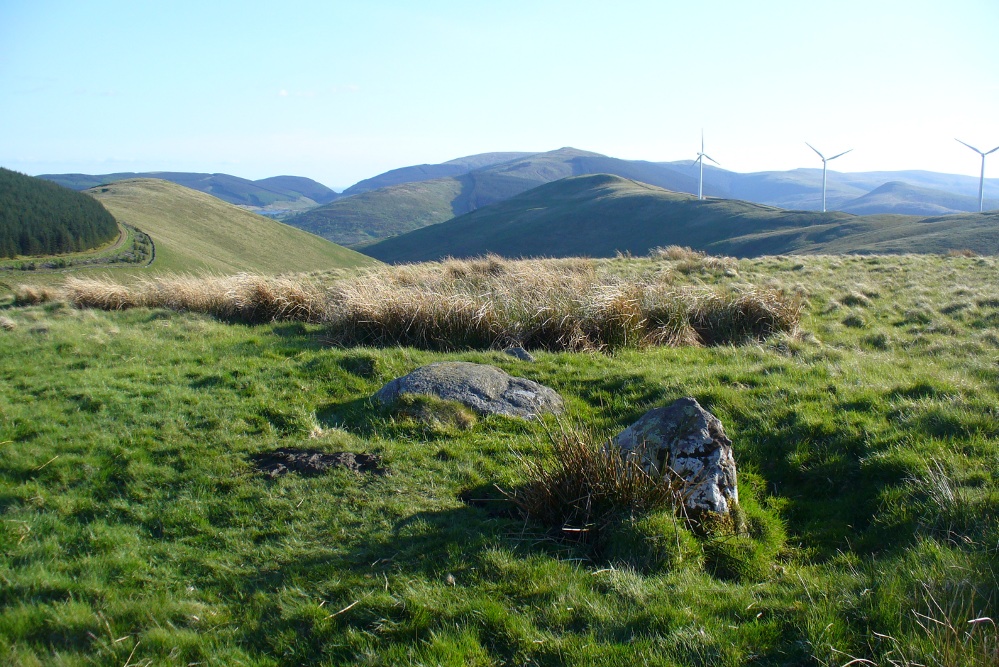
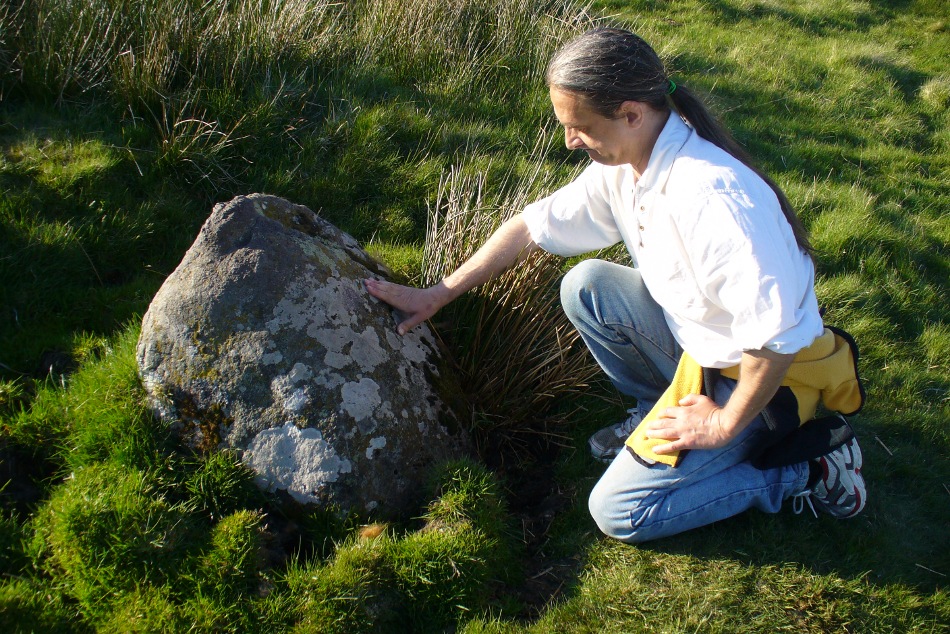
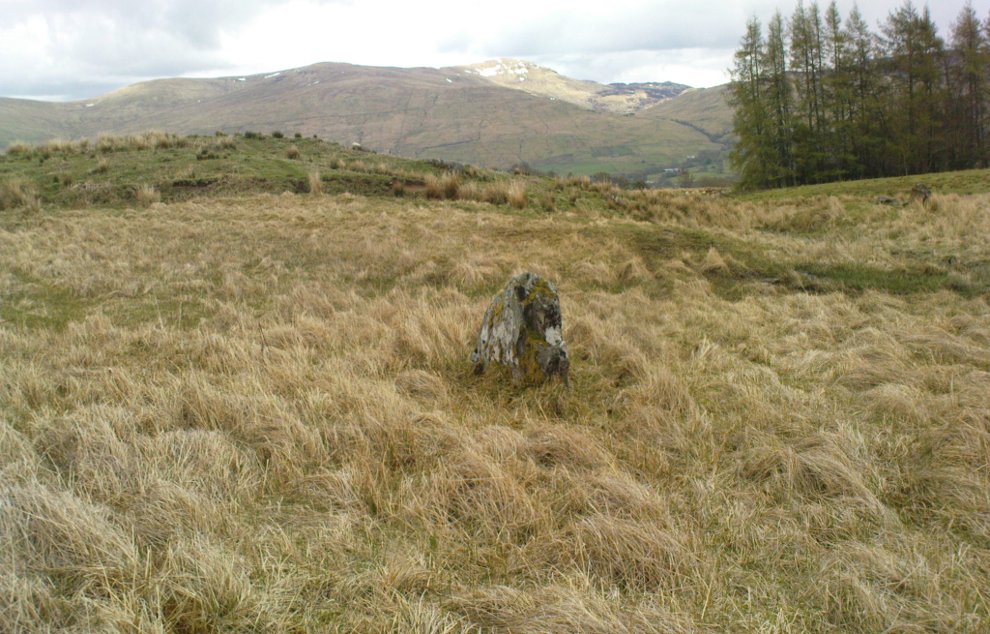
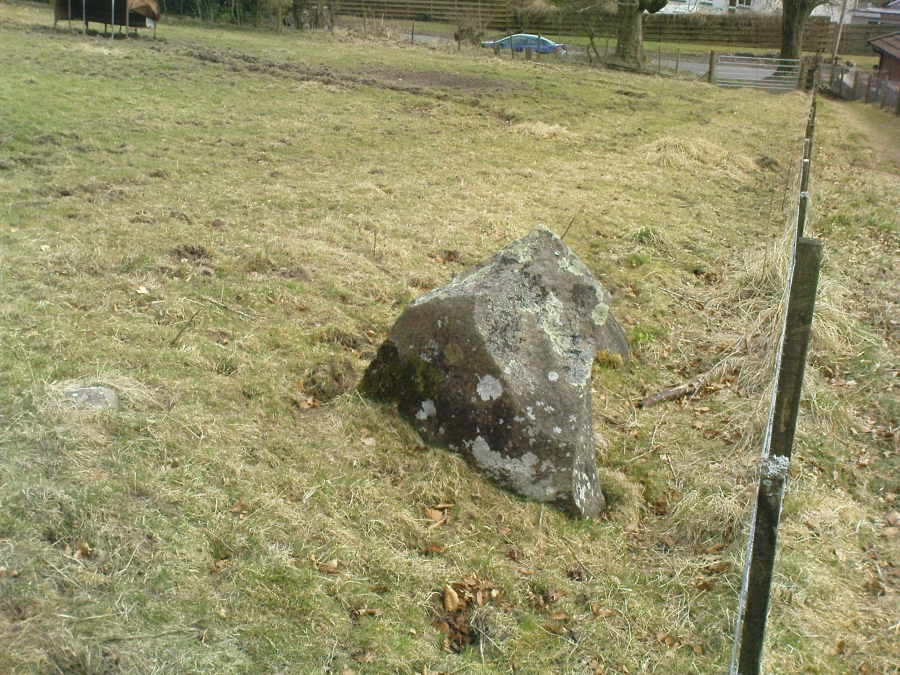
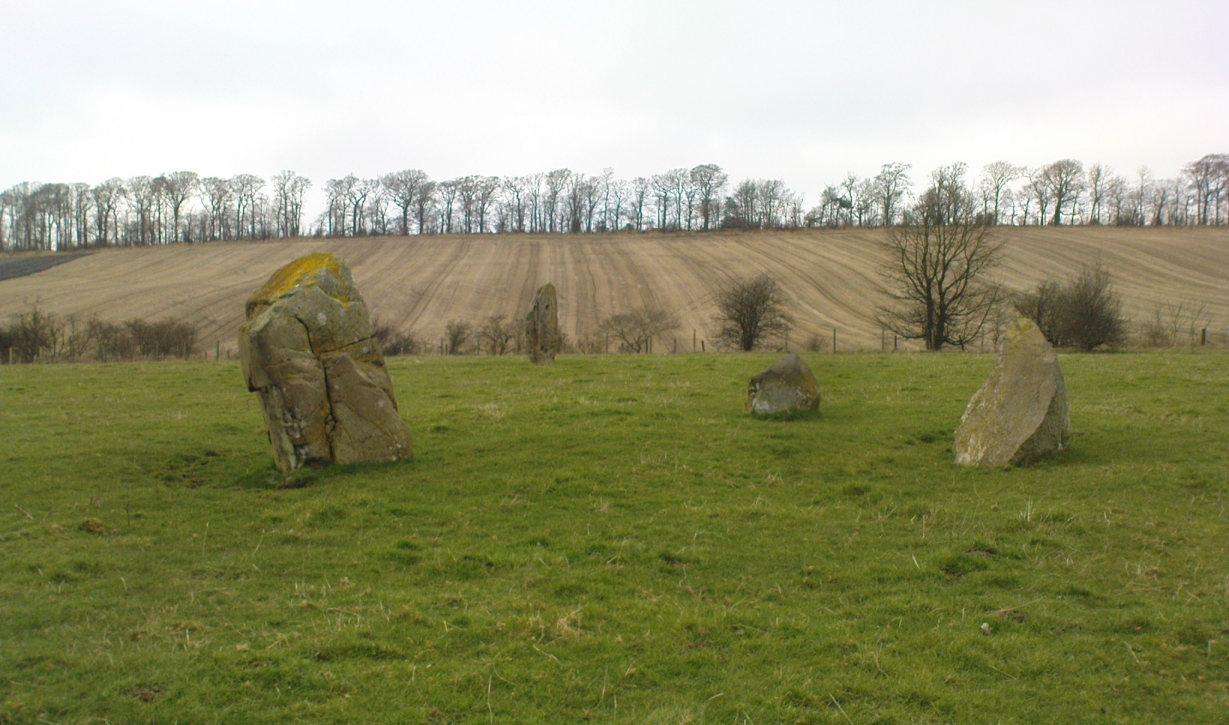
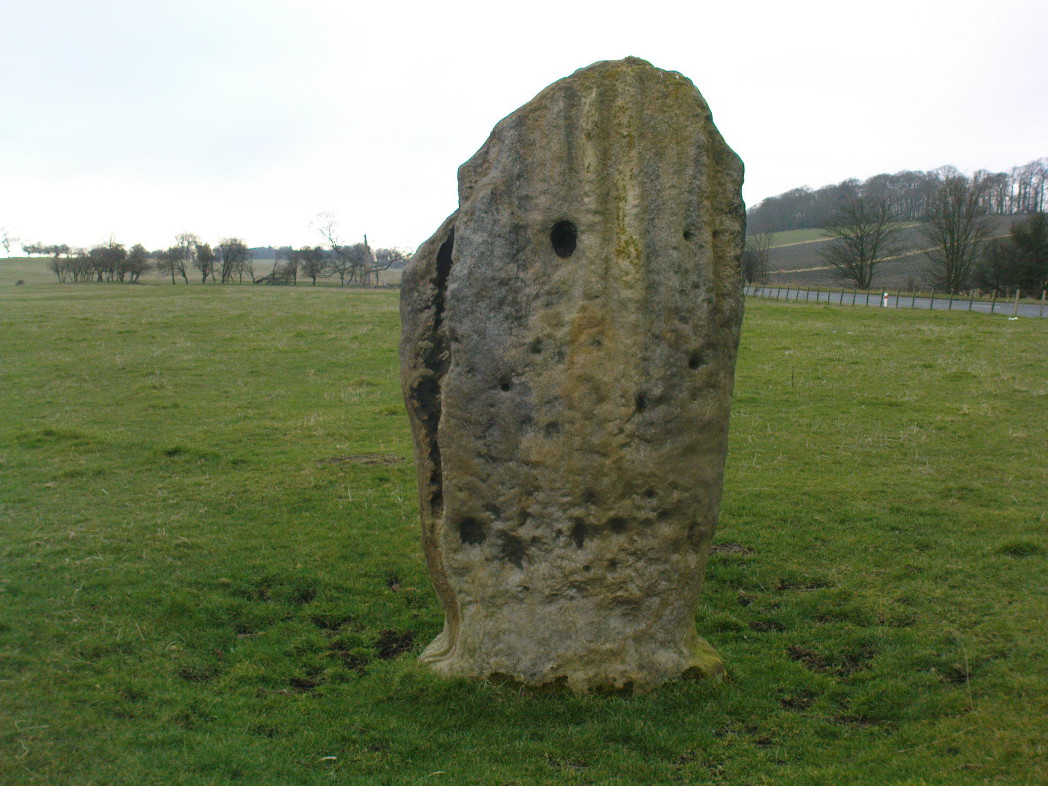
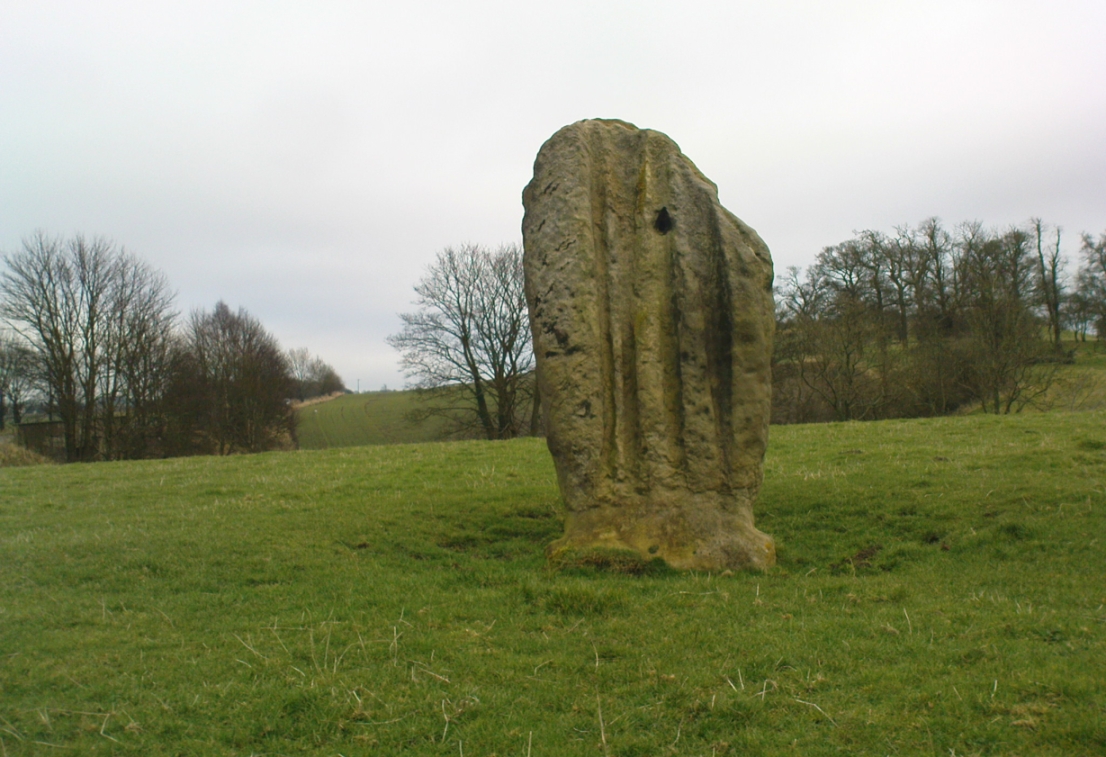
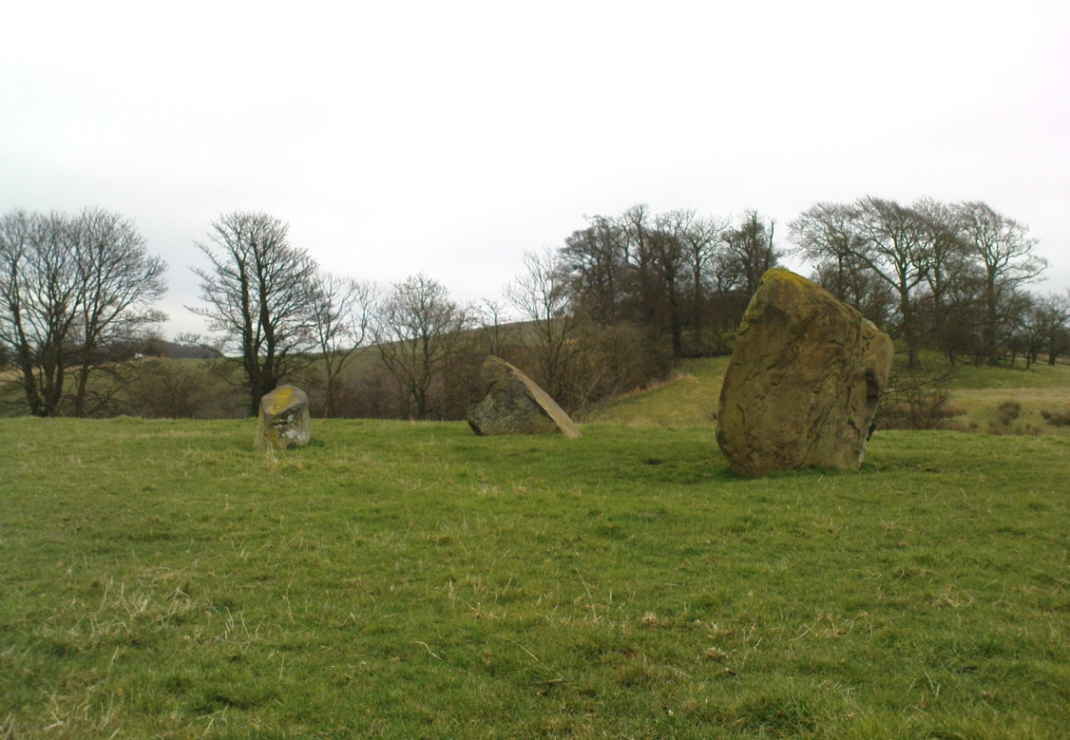
Included in Andy Finlayson’s (2010) fine local survey, this is an intriguing little group of three standing stones (and a fourth buried beneath the turf), all very close to each other. They are shown on the modern Ordnance Survey maps as “standing stones”, but have been catalogued by archaeologists as the denuded remains of a ‘Four Poster’ stone circle. Despite this, the circle wasn’t included in Aubrey Burl’s (1988) definitive work on the subject, nor his megalithic magnum opus. (Burl 2000)
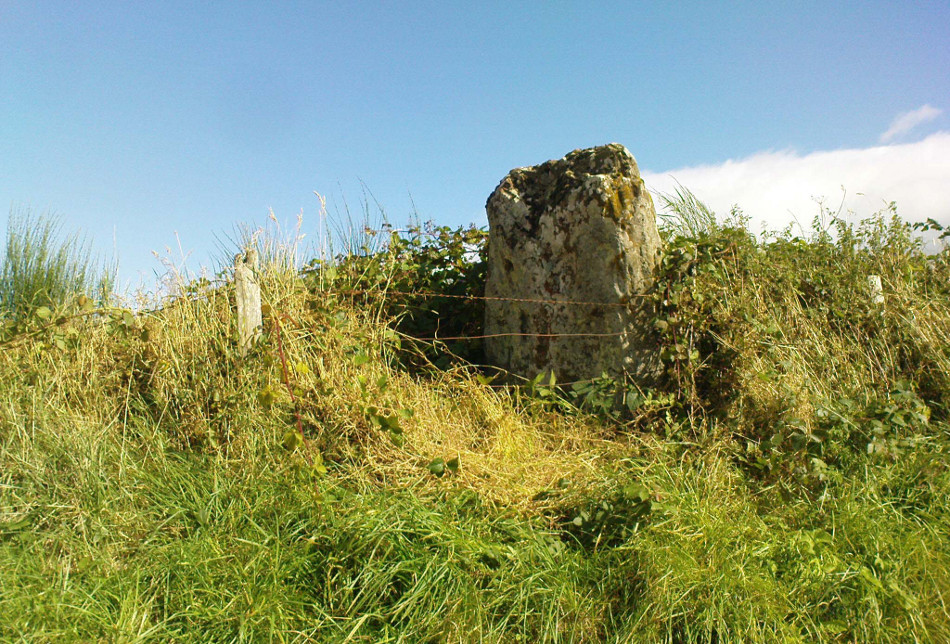


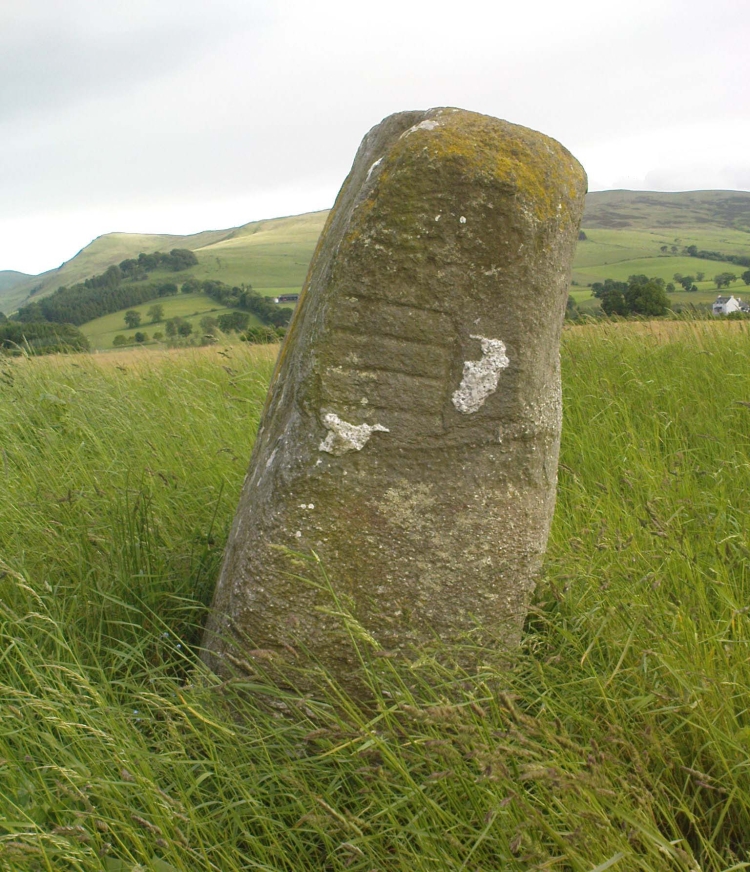
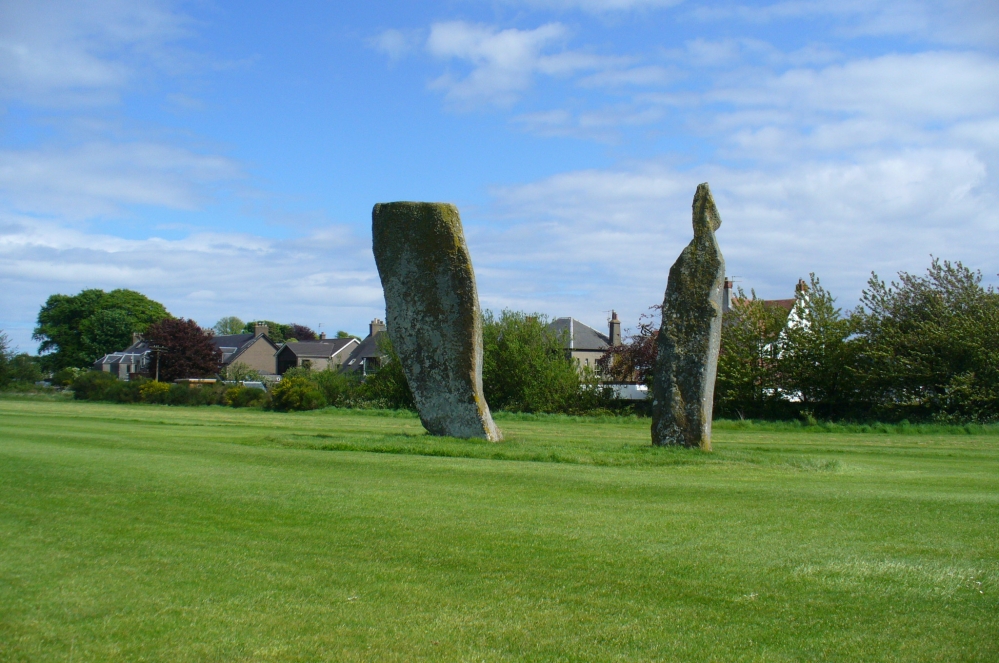
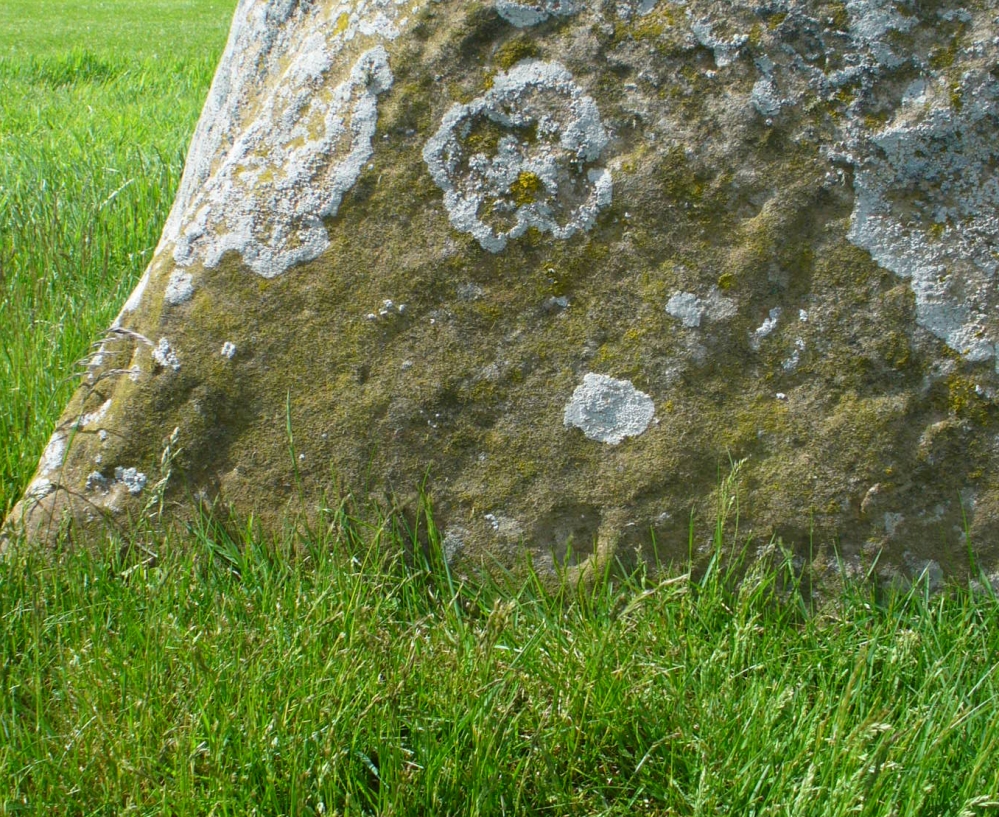
Of the two uprights above the roadside at the field edge, a faint carved hand can be found on the upright west-facing side of the southernmost of the two standing stones. Although faint, this doesn’t appear to be ancient. Written accounts of these stones are few and far between it seems. The earliest seems to be in the lengthy essay written by Mr Hutchison (1893), in which he gave an excellent account:
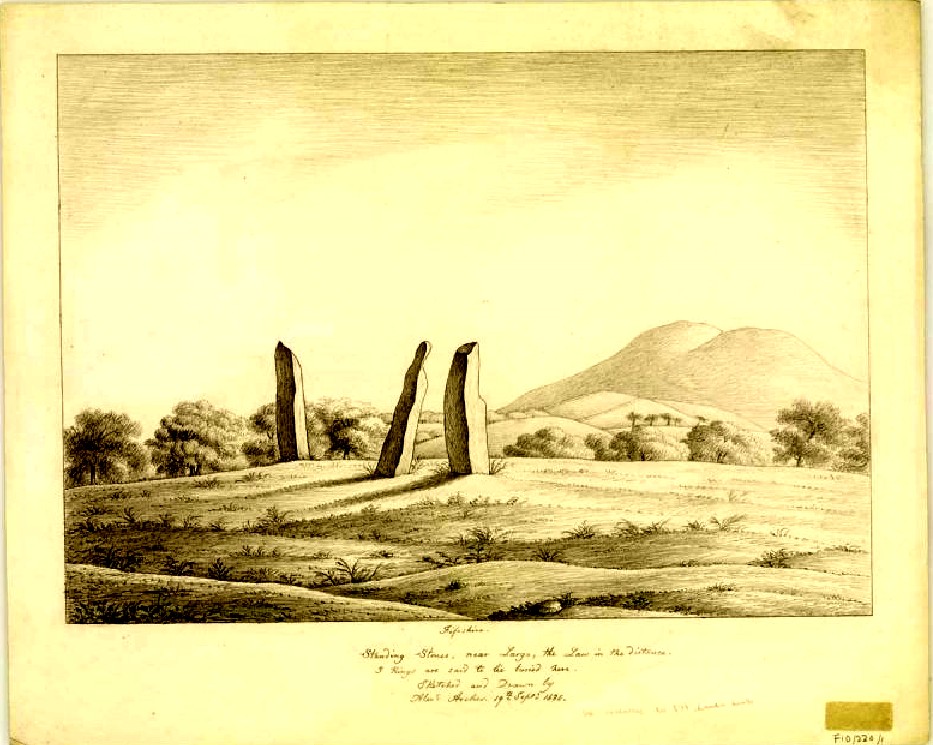
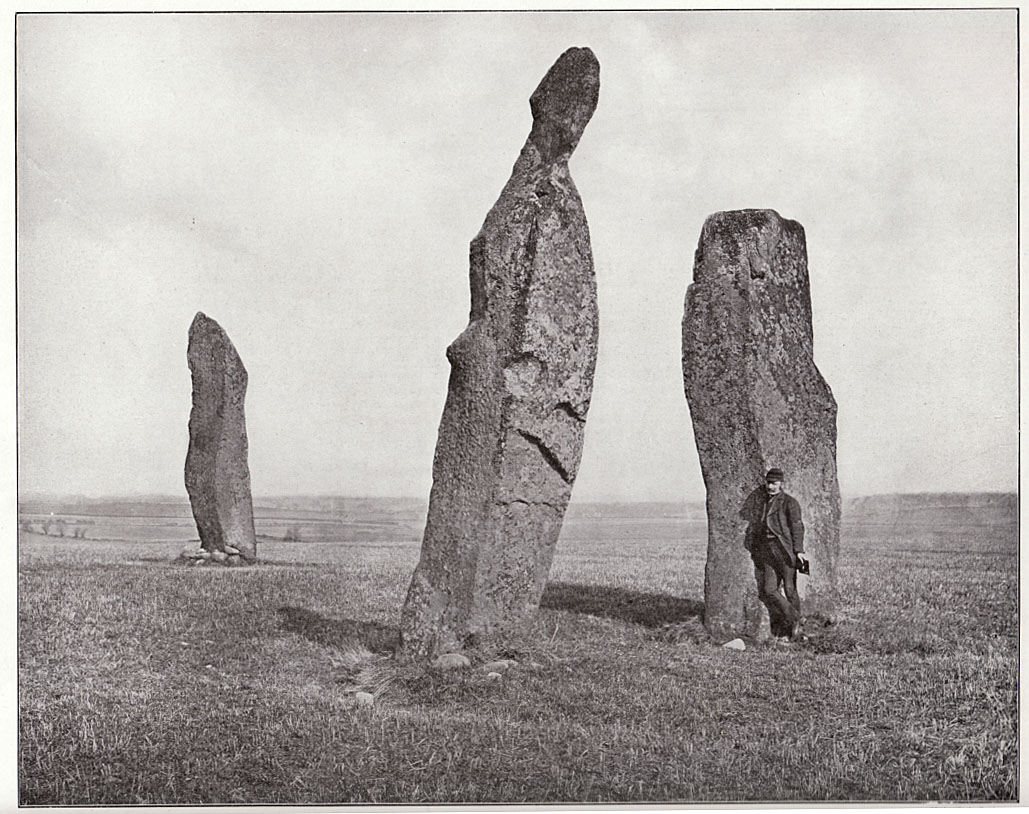
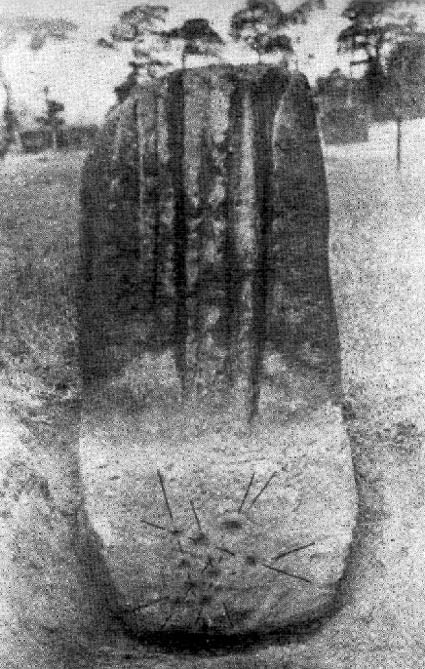
“Less than a mile to the west of (Auchterarder)…is a fine group of stones, two only of which are now standing. These stand on the summit of what has been a well-defined mound, and the stones now lying where the roads unite seem to have stood originally at the same height. The road has been driven through the group at a lower level than the summit of the mound, and the stones have been thrown down and laid in the waste space at the point of junction. The small mercy to be thankful for is that they have not been broken up altogether and used for road metaL This has probably been due to the circumstances that one of these stones has a curious encircling groove running round it, which perhaps impressed even the vandal roadmakers with the idea that it might be worthy of preservation. It would be interesting to know whether, when the circle or group of stones was cut through, any cist or interment was found. One would expect such to be the case, but I have not yet got any information on the point. There are several stones lying on the spot which may or may not be pieces of the original standing stones. Two considerable bits of old red sandstone, at least, look as if they were fragments of an original whole. Two great stones, however, are unmistakably prostrate standing-stones; and from the positions in which they lie, it seems to me as if the persons who had uprooted them had laid them down as nearly as possible on the sites they had occupied (at the original higher level, of course) when standing.
“The direction in which both of the standing stones point is 236º, and a line taken from each of the prostrate stones to the opposite standing one gives very nearly the same angle (240º). The prostrate stones are of metamorphic schist. The northerly one measures 7 feet in length by 3 feet in width, and is from 12 to 18 inches thick. A grove or furrow, 2 inches deep at its greatest depth, and from 2 to 4 inches wide, appears to run right round it, at a distance of 2 feet 10 inches from the end, which may have been about the middle height of the stone when erect. The lower side of the stone cannot be seen, but the appearance at the edges indicates that the furrow is carried all the way round. It looks just such a hollow as might be worn in stone by the long continued attrition of an iron chain. The more southerly prostrate stone is 6 feet in length, 4 feet wide, and has an average thickness of 18 inches. The two stones still standing are on the high bank above the road, just inside the hedge. These are both of old red sandstone, thinnish slabs, facing in the direction already mentioned. That to the south is 4 feet 10 inches in height, 2 feet 8 inch broad at the base, and 10 inches thick. The other is 5 ft. 3 in. at its greatest height, 3 feet 10 inches wide, and from 13 to 15 indies thick. On its northern face it shows a number of depressions or indentations curiously resembling prints of human feet. These Mr Kidston considers to be due to natural weathering.”
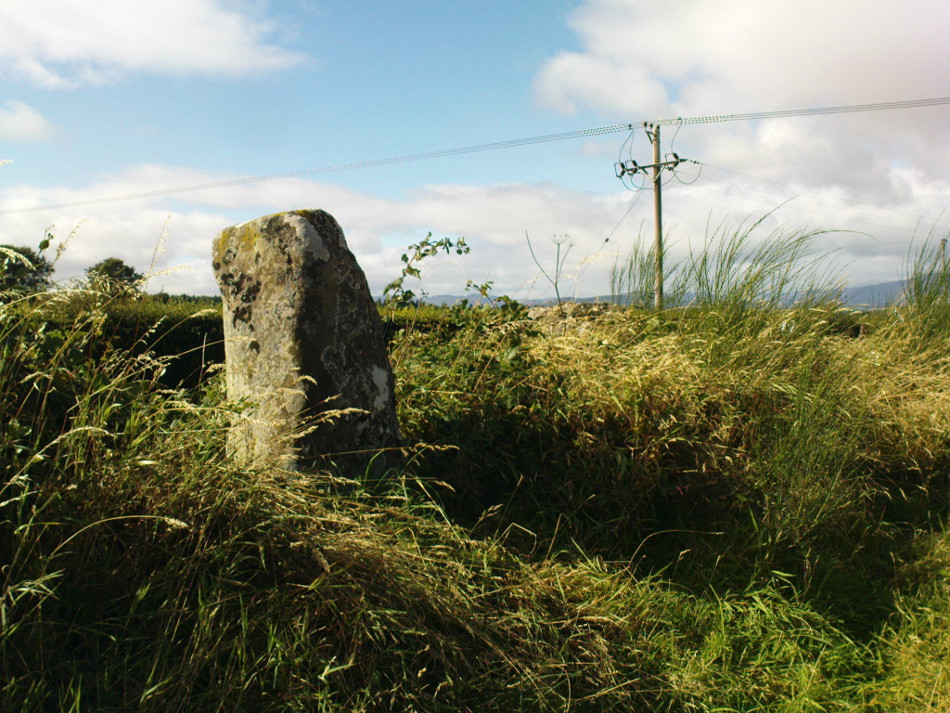

Yet the “prints of human feet” are very much man-made. A closer examination of these carvings is obviously needed.
Whether these stones originally played a part in an old tumulus, a cairn circle, or a typical stone circle, is hard to say with any certainty now. We are in a landscape where megalithic remains were once in great excess: with the standing stones of Blackford to the south; the lost circle of Gleneagles nearby; the megaliths near Muthill and many many more…
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, Four Posters: Bronze Age Stone Circles of Western Europe, BAR 195: Oxford 1988.
- Finlayson, Andrew, The Stones of Strathearn, One Tree Island: Comrie 2010.
- Hutchison, A.F., “The Standing Stones of Stirling District,” in The Stirling Antiquary, volume 1, 1893.
- Strachan, Favid (ed.), A History of Blackford, Blackford Historical Society 2010.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian