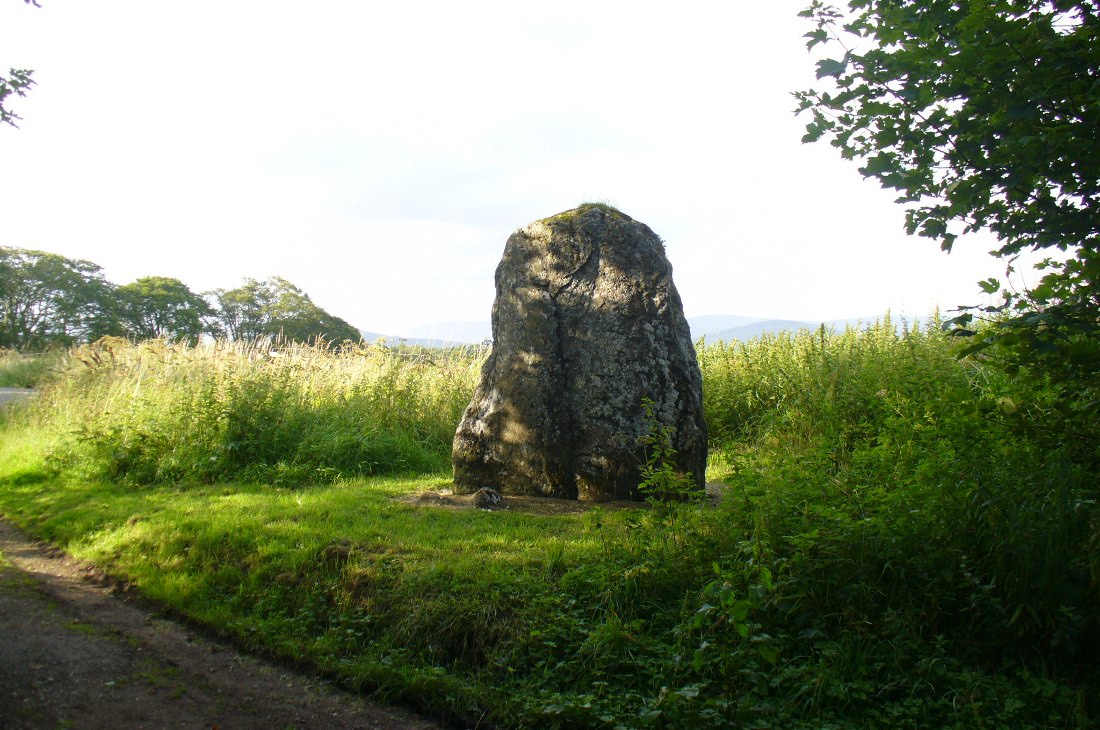
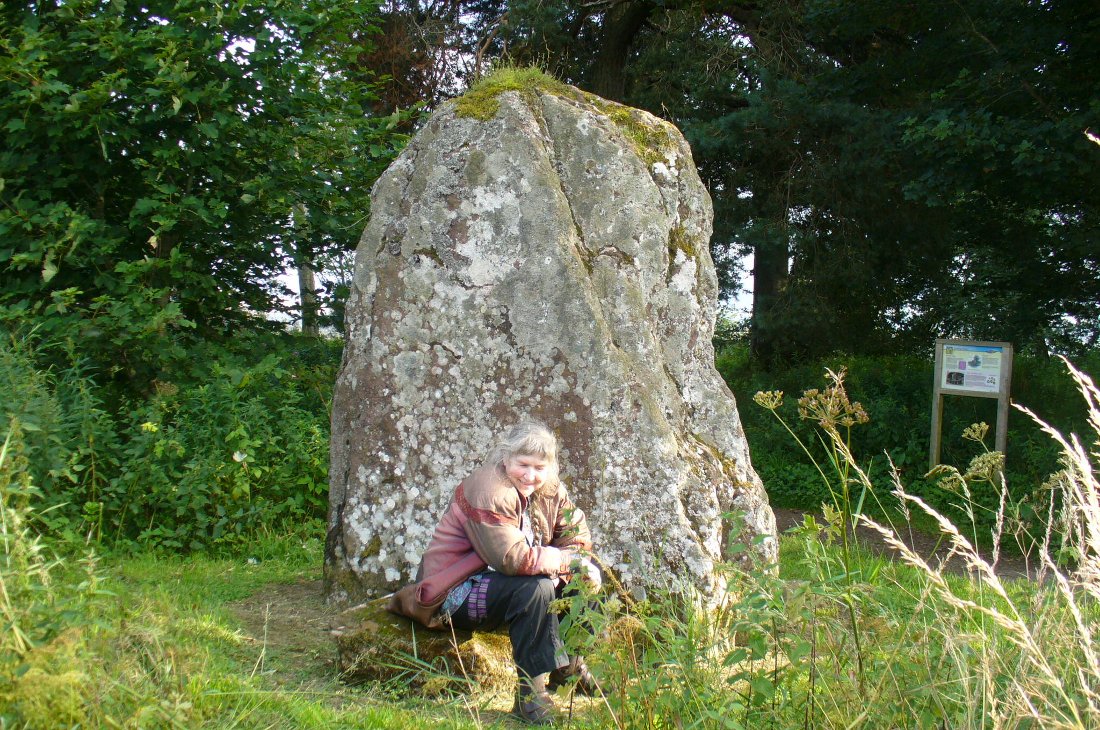
Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – NY 25706 96638
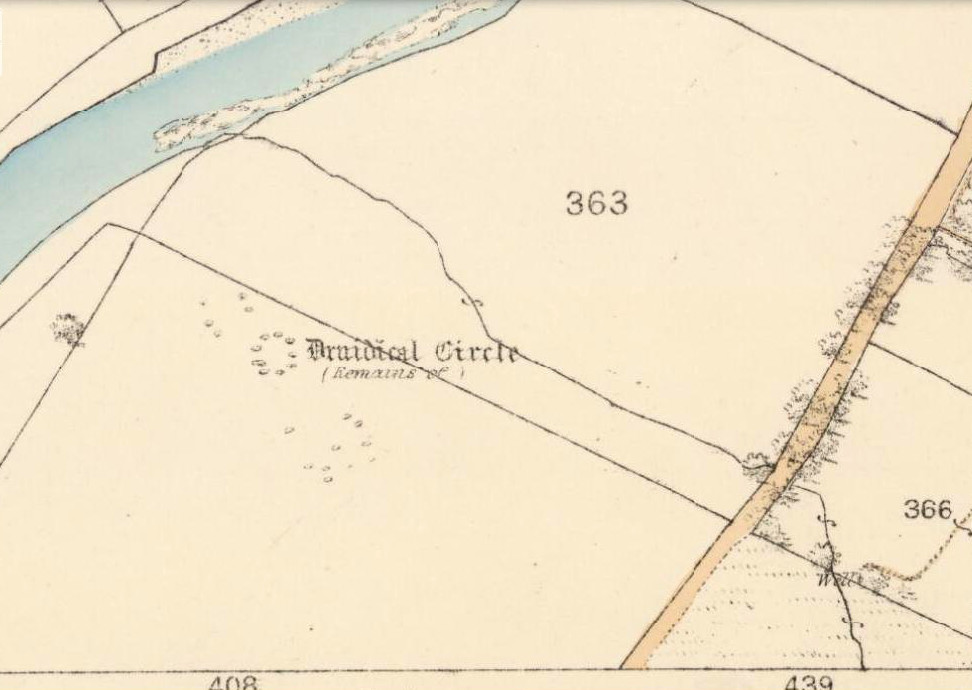
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 67232
- The Cote
- Hartmanor
- Loupin Stones
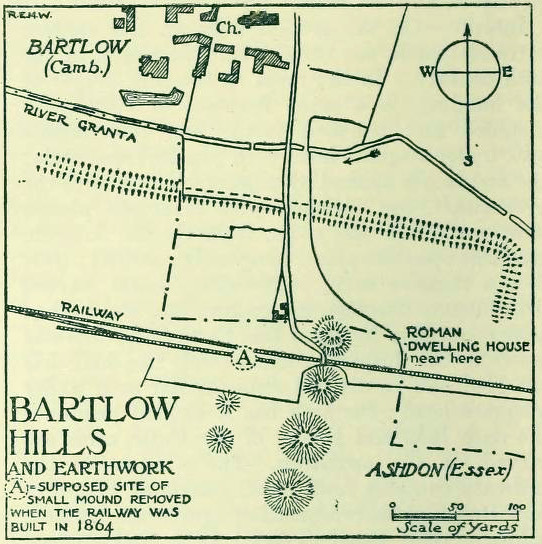
From the hamlet of Eskdalemuir, take the B709 road over the river bridge and keep going for about a mile, past the Hartmanor Hotel. Keep your eyes peeled for the small parking spot on the left-hand side of the road soon after the hotel. Once here, cross the road and walk down the footpath towards the river, following the line of the fence, pass the superb apple trees. You’ll walk straight to it!
Archaeology & History
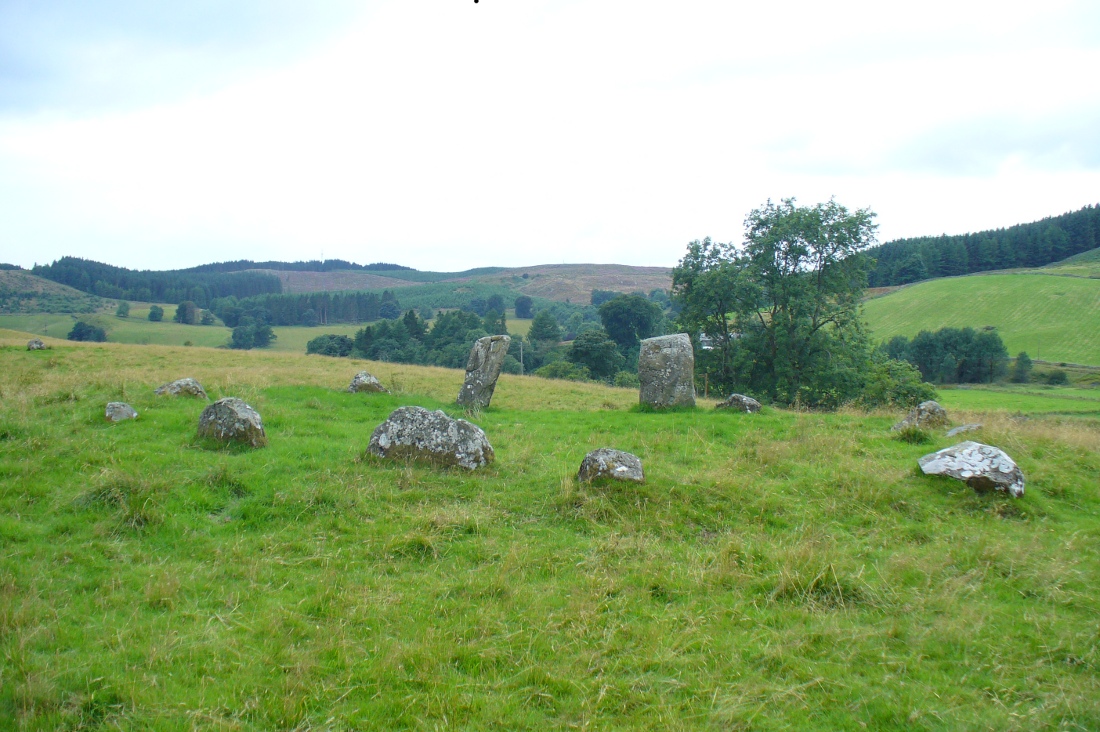

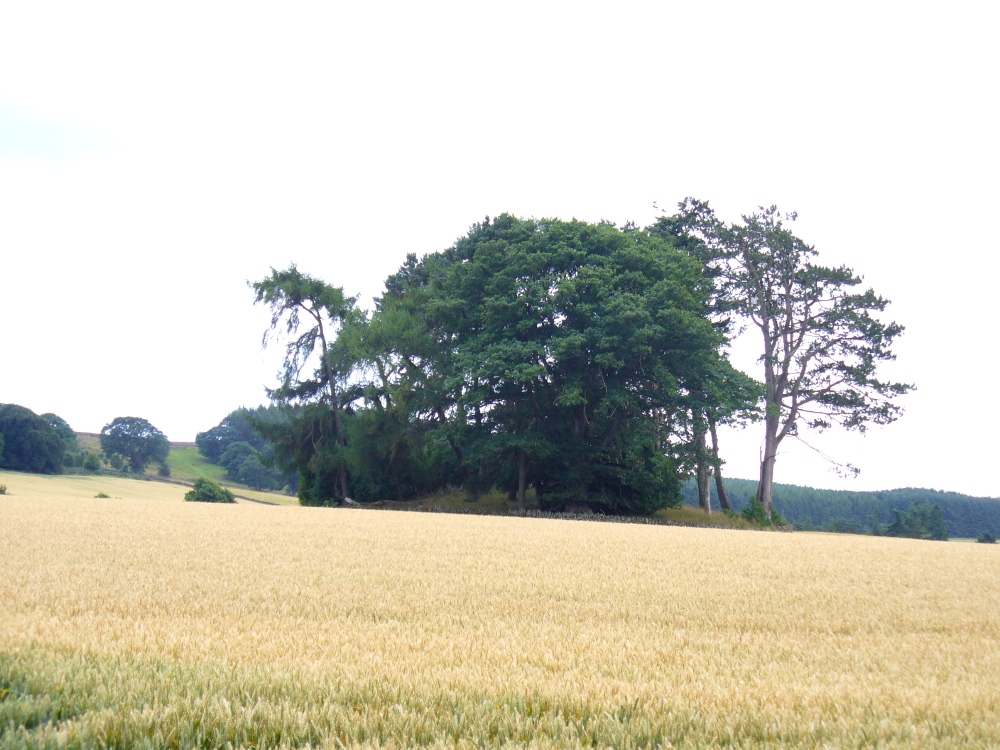
A long distance from anywhere out here in the hills, my short foray here with fellow antiquarian Paul Hornby told that there was once much more here than presently meets the eye. Aubrey Burl (1979) hinted at the same, as did our mathematical megalithic magus Alexander Thom. (1980) There are curious stones near and not-so-near the circle you’re about to meet, many of them speaking of relationships just hiding beneath their historical surface. Sadly we only spent a short time here at the Loupin Stanes. A full day or two would have been much better!
Despite this circle (and its nearby companion the Girdle Stanes) hiding miles away from anywhere out here, the legendary compilers of the 18th century Statistical Account of Scotland still managed to find it, telling us simply,
“On the farm of Coatt there are two circles of erect stones, the one entire measuring about 90 feet (i.e., in girth), and the other, having a part of it worn away by the Esk, measuring about 340 feet.”
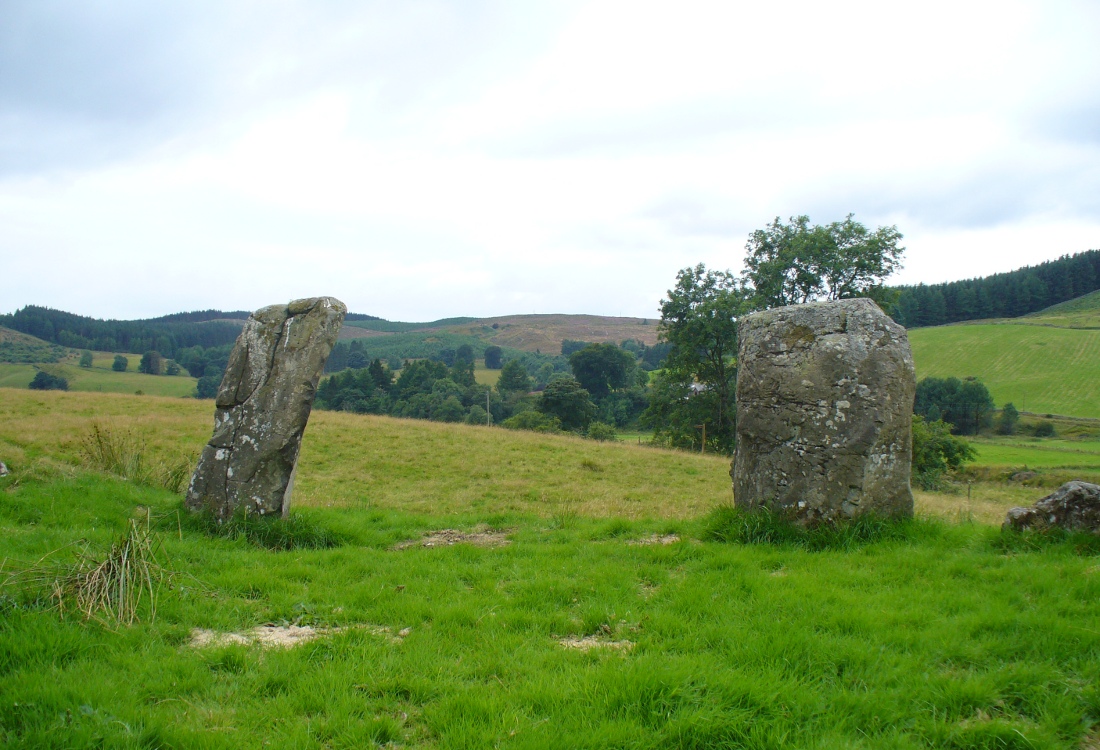


Another century was to pass by before anyone else came and wrote about these hidden stones, sitting upon a level man-made platform built by neolithic or Bronze Age ancestors. In Dave Christison’s (1897) lengthy article for the Scottish Society of Antiquaries, he gave a pretty lengthy description of the Loupin Stanes, which is still as accurate today as when he wrote it 120 years ago. He told:
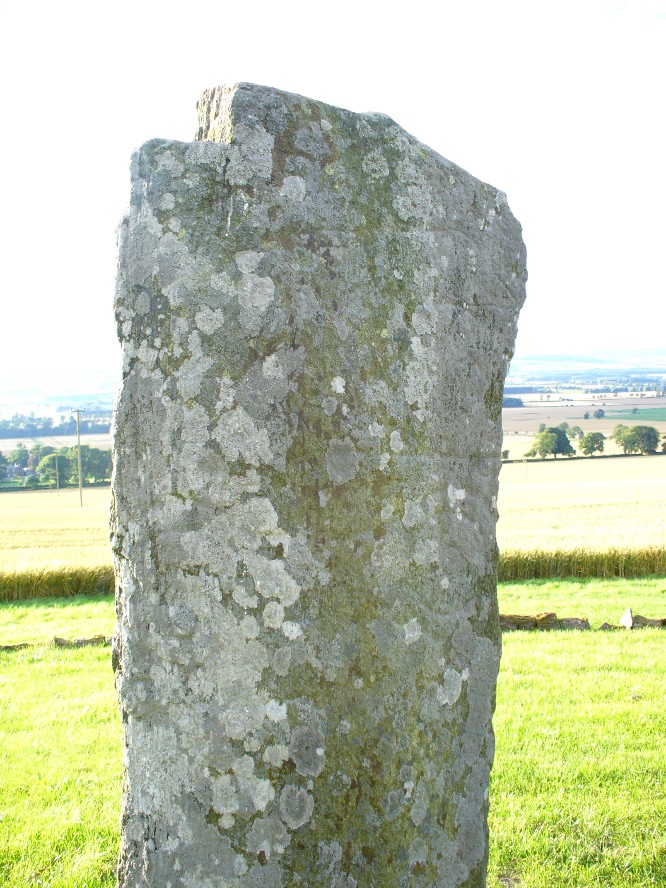
“The site of the smaller circle is at Hartmanor, retired about 80 yards from the river, in a gently undulating field, and it has been banked up nearly all round from a foot to 18 inches, perhaps with the object of making the interior level. The circle consists of thirteen stones…not reckoning one which seems too small to be included, but from the inequality of the intervals it is likely that a number have been carried off, and this seems proved by one hollow…left in all probability by the removal of a stone, and – by another within the circle opposite a blank in it, probably caused by digging to uproot a second stone. The developed view…shows this irregularity of the spacing. But it also shows that two neighbouring stones greatly exceed the others in size, and alone can be considered truly standing, as they are pillar-like and set on end, whereas the smaller ones are so shaped that it does not much matter on which end they are placed. The two large stones are about 5 feet 4 inches high, and are flat-topped. One is a massive rectangular block, about twice the bulk of the other. Few of the smaller stones stand a foot above ground, and the two highest do not exceed a couple of feet. The large stones (in this ring) are known as ‘the loupin’ stanes…
“…In its present state the ‘circle’ is slightly oval, the cross diameters, measured from the inner faces of the stones, being about 35 and 31 feet. The entrance, if we may call it so, between the two pillar-stones, looks out about E.S.E.”
Of course, Christison meant WSW, not ESE. Probably the best description of the Loupin Stanes (and the nearby Girdle Stanes) was done, not surprisingly, by a local historian. In the superb work on the Langholm district, the brothers Hyslop (1912) gave commendable descriptions—including ingredients which, I’m pleased to say, the likes of Mr Hornby and myself wondered over in our short visit here. Burl and Thom thankfully noted the very same elements.
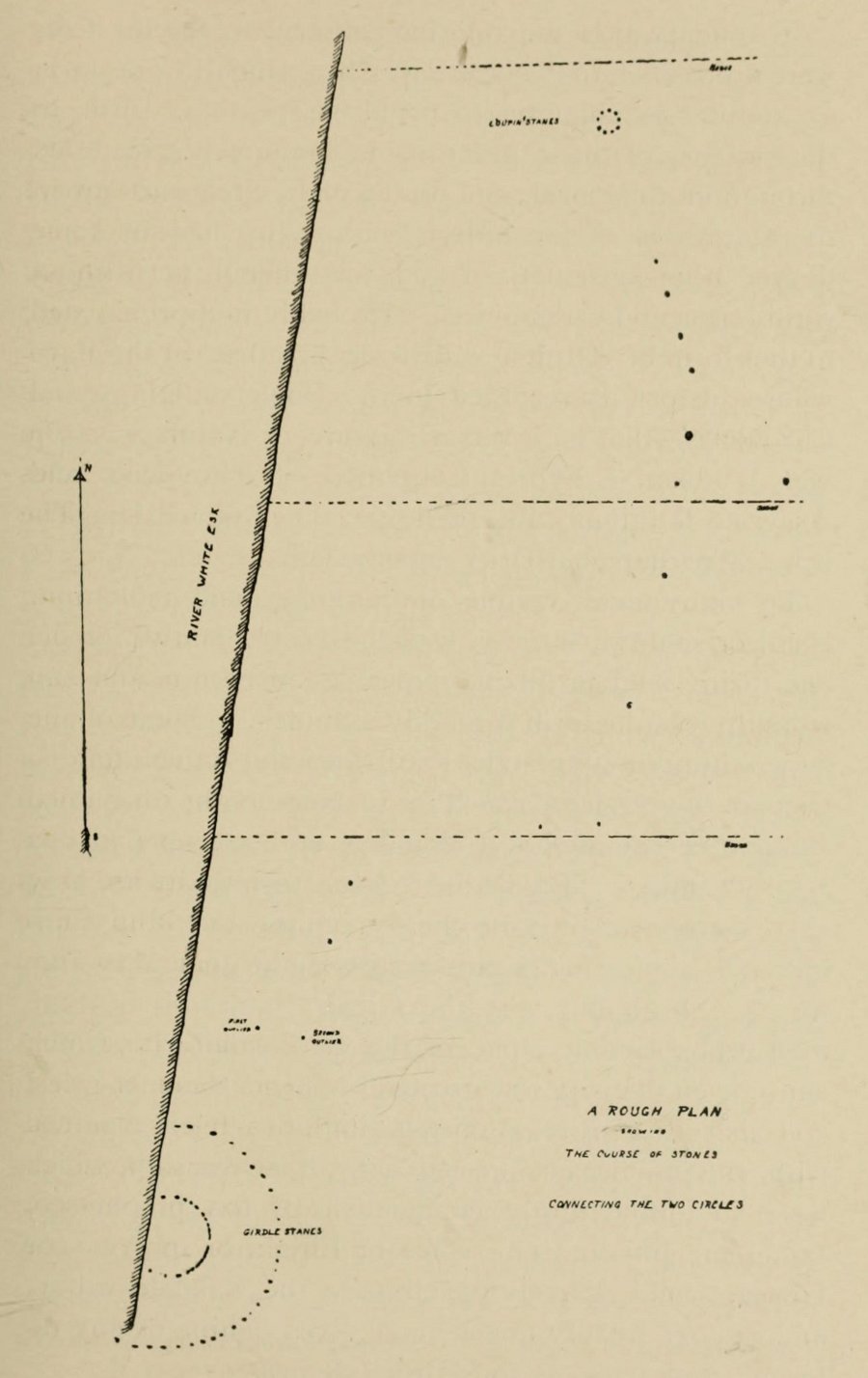
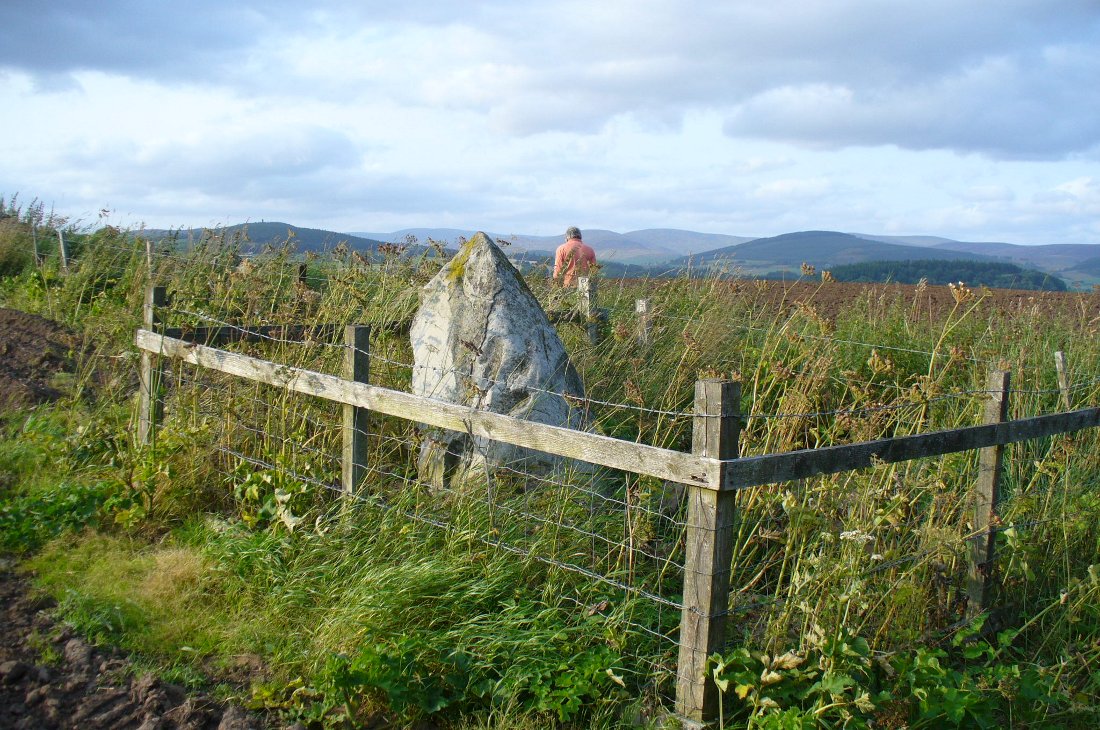
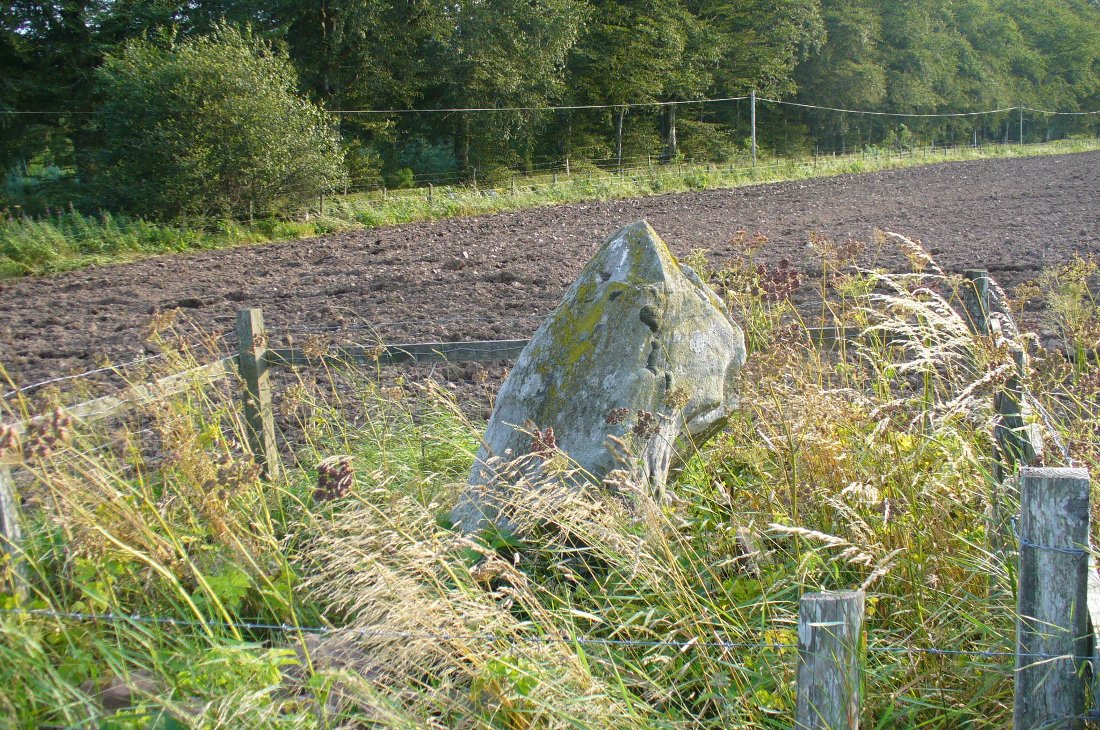
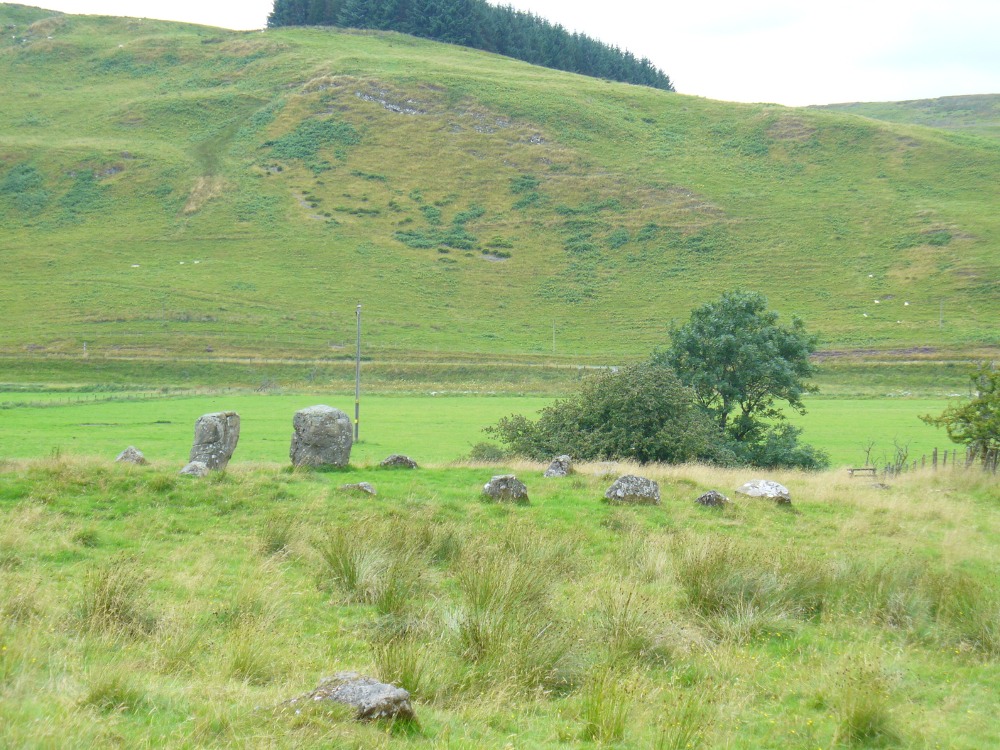
The casual visitor here cannot fail to note the curious scatter of other stones close to this megalithic ring. Before you actually reach the circle there is a scatter of small stones which have more of a ‘feel’ to them being related to the actual circle than proof has yet afforded. Both Thom and Burl postulate this scatter of stones as the remains of another damaged stone circle. One of these stones has three cup-marks upon it. But there are other stones reaching away up the slope of the field to the south. Our impression here was that these had some relevance to the circle when it was first built, probably 4000 years ago. Paul suggested the idea of an ‘avenue’ perhaps linking it with the Girdle Stanes circle about 600 yards away. He wasn’t the first to do so. John and Robert Hyslop (1912) talk of the likely relationship these two stone circles had with each, and much more:
“Though now forming separate circles 600 yards apart, that they were at one time, though possibly not originally, parts of one scheme is clearly indicated by their relative positions and especially by the irregular line of large stones stretching from one to the other. Only two of the stones of the first Circle are now standing. One stands 4 feet 9 inches above ground and measures 19 feet 5 inches in girth. The other is also 4 feet 9 inches high but is only 7 feet 8 inches in girth. It is quite possible that some of the other stones composing the Circle are in their original positions, though they are now greatly weathered and broken… This…Circle when built appears to have consisted of nine* large stones, and was nearly 36 feet in diameter, or some 113 feet in circumference by inside measurement.
“A little to the south-east of the Loupin’ Stanes there is what, to the casual observer, appears to have been, and probably was, another Circle also of nine stones, with a centre stone. Some of these stones have been displaced, and the contour of the Circle is consequently broken. Nearer the Esk, and almost touching the Loupin’ Stanes, are four single stones whose relation to the other members of the group it is very difficult even to guess. Fancy or guesswork might weave a simple theory which could neither be proved nor absolutely refuted — but it is wiser not to guess in questions like this! Reference has already been made to the “avenue,” or line of single stones stretching from the Loupin’ Stanes to the Girdle Stanes. Though the line is not a straight one, and is broken, it seems to afford fairly conclusive proof that all these stones at the Cote are parts of what must once have been a prehistoric monument of considerable importance, and, needless to add, of great antiquity.”
The ‘avenue’ between the two circles was later described with a bit more detail and the suggestion of an astronomical function arose. Again, the Hyslop’s (1912) told that the avenue was,
“a course of 11 stones placed at intervals between the two Circles, rudely joining them, but not in a straight line. The last four of these (nearest the Loupin’ Stanes) form very nearly a straight line in a direction S. 16 34′ E., but no satisfactory significance has been found for this line.
“…Whether there was a single or double line of stones in the “avenue” between these two Circles cannot be said until a careful survey has been made. The theodolite and the link-chain have a curious habit of settling these disputed points and spoiling many a charming theory — without regrets or apologies! But this much may safely be said: if an “avenue” existed between the Loupin’ Stanes and the Girdle Stanes, as appearances suggest, it was probably for ceremonial rather than for astronomical purposes.”
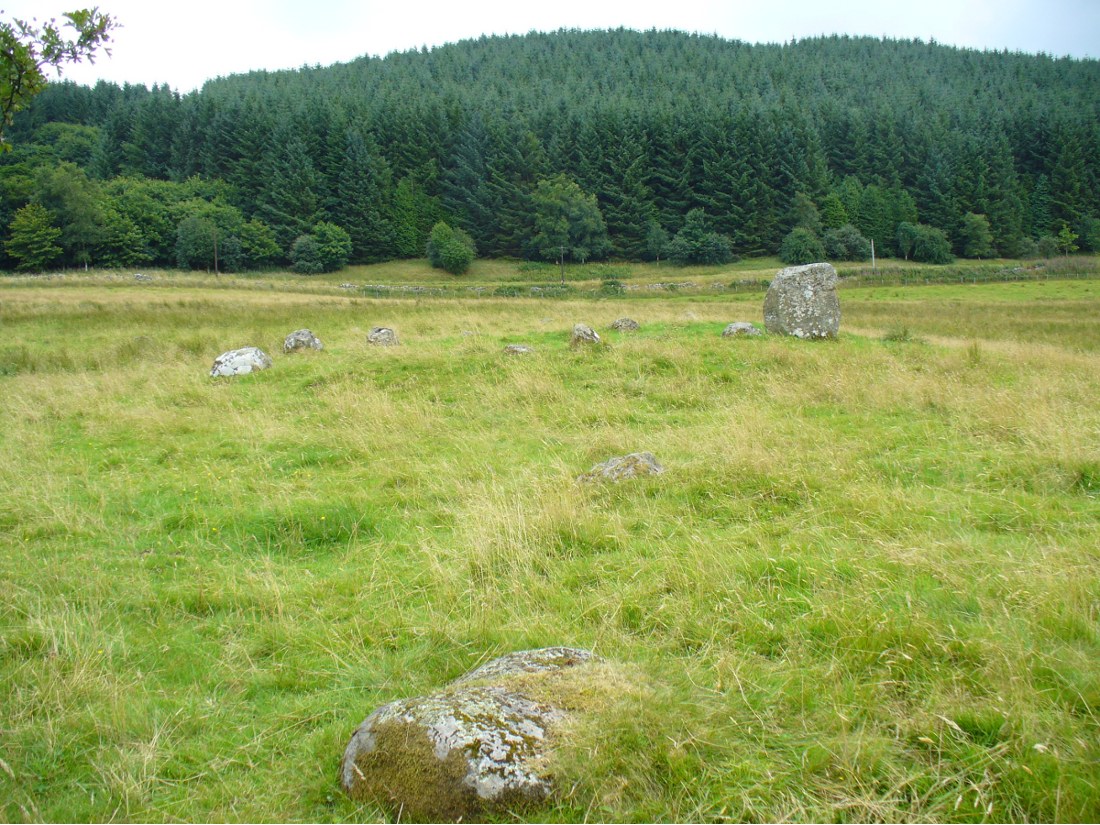

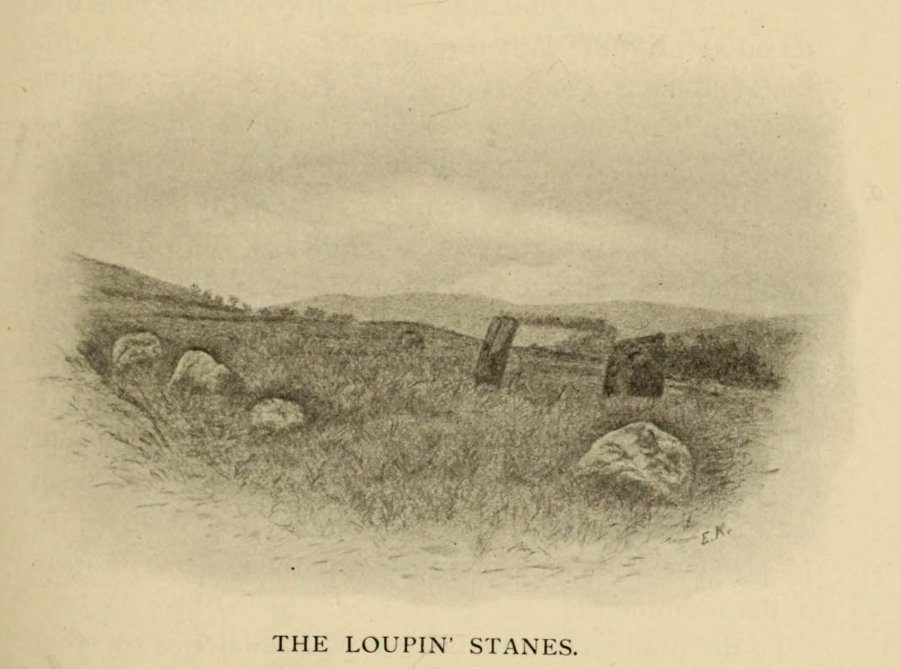
Very true indeed. But whether this alignment of weaving stones has actual relevance to the megalithic arena, only detailed excavations will tell for sure. Yet on the western side of the Loupin Stanes, we see at least four stones (possibly six) which run down to the River Esk. This also may be remains of an old avenue, taking us to an important water source.
No ‘avenues’ were mentioned in the survey by the Royal Commission (1920) lads, written several years after their visit here in July 1912. They described the site as follows:
“The stone circle known as the Loupin Stanes…is situated at an elevation of 600 feet above sea-level, on an undulating meadow some 80 yards from the left bank of the White Esk and 600 yards north-east “of the Girdle Stanes circle…. It consists of twelve stones placed at irregular intervals, of which, on the west side, only two, standing 8 feet apart (A and B on plan, fig. 64), are true pillars, all the others being simply boulders.
“The setting does not form a true circle but is flattened on the western arc; it measures some 38 feet in diameter from north to south and 31 feet from east to west. The pillar stones, which are flat-topped, measure about 5 feet 4 inches in height, and the two highest of the smaller stones do not exceed 2 feet, while few of them reach 1 foot. The site has been banked up nearly all round from 1 foot to 1 foot 6 inches, perhaps with the object of making the interior level. There are numerous large stones adjacent, some of which may be the remains of other circles, but others are probably merely boulders naturally deposited or outcrop of rock. The field was in a hay crop at the date of visit, and the fallen stones were not easily seen.”
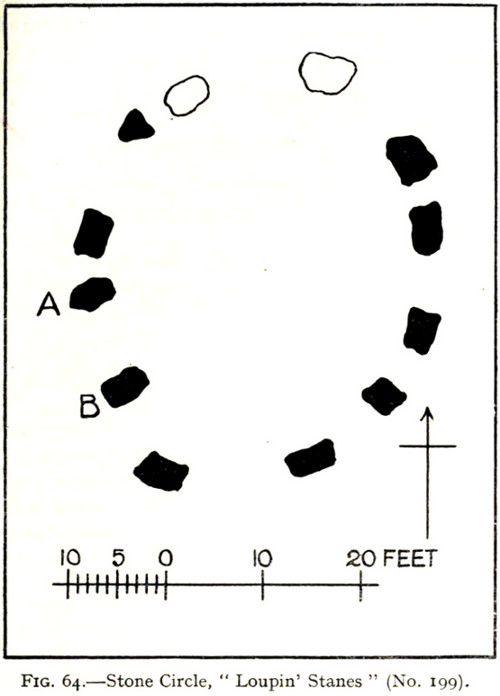
When Alexander Thom (1980) came here and measured the site, he thought there was a ‘possible’ midsummer sunrise from the stones—but even he didn’t seem convinced. Described as a Type A Flattened Circle, he did find units of his ‘megalithic yard’ in the construction of the site.
Folklore
In David Christison’s essay (1897) on this and its companion site—the Girdle Stanes—he told:
“The large stones are known as ‘the loupin’ stanes,’ because it is said that lads, and even a lass, were in the habit of jumping from the top of one to the other; but as the distance is 8 feet, the people of the district must be uncommonly good ‘loupers’ to accomplish the feat without breaking their legs. However it may be with their limbs, so little are the powers of observation of the natives cultivated that, although all know ‘the loupin’ stanes,’ they generally deny the existence of a circle.”
This narrative was repeated in the Hyslop’s (1912) work. Though it should be noted here that Mr Christison’s final remark about the local people denying the existence of any such circle is something I’ve encountered a few times, despite them knowing otherwise. But for good reason, it has to be said.
…to be continued…
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, Rings of Stone, Frances Lincoln: London 1979.
- Burl, Aubrey, A Guide to the Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, New Haven & London 1995.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
- Christison, David, “‘The Girdlestanes’ and a neighbouring stone circle, in the parish of Eskdalemuir, Dumfriesshire”, in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 31, 1897.
- Hyslop, John & Robert, Langholm As it Was, Hills & Company: Sunderland 1912.
- Macauley, Anne, Megalithic Measures and Rhythms, Floris: Edinburgh 2006.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments, Scotland, Inventory of Monuments and Constructions in the County of Dumfries, HMSO: Edinburgh 1920.
- Thom, Alexander, Megalithic Sites in Britain, Oxford University Press 1967.
- Thom, A., Thom, A.S. & Burl, H.A.W., Megalithic Rings, BAR: Oxford 1980.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian