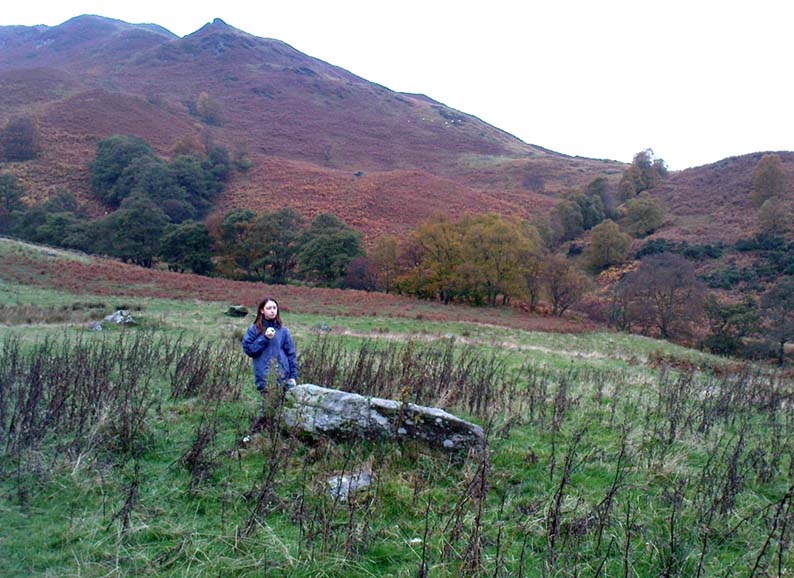
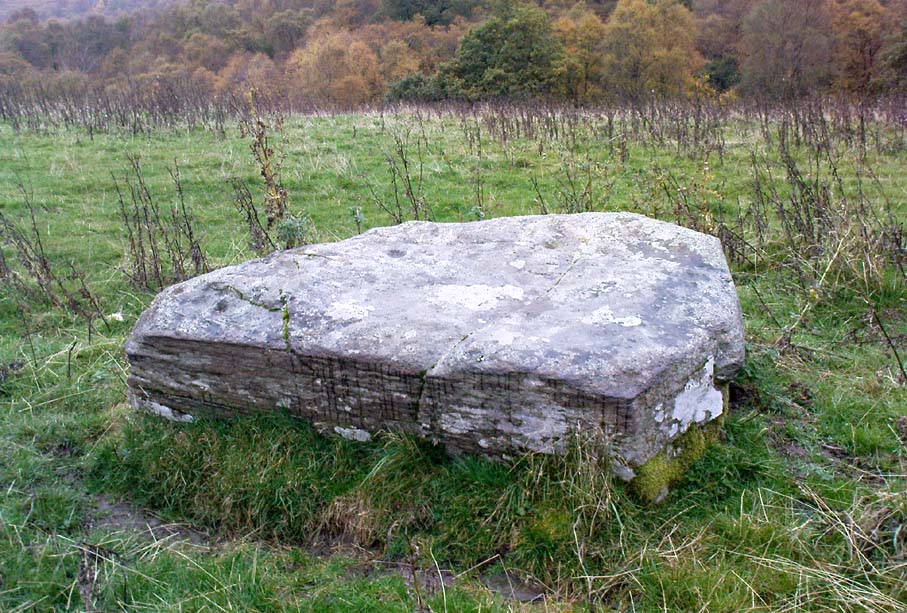
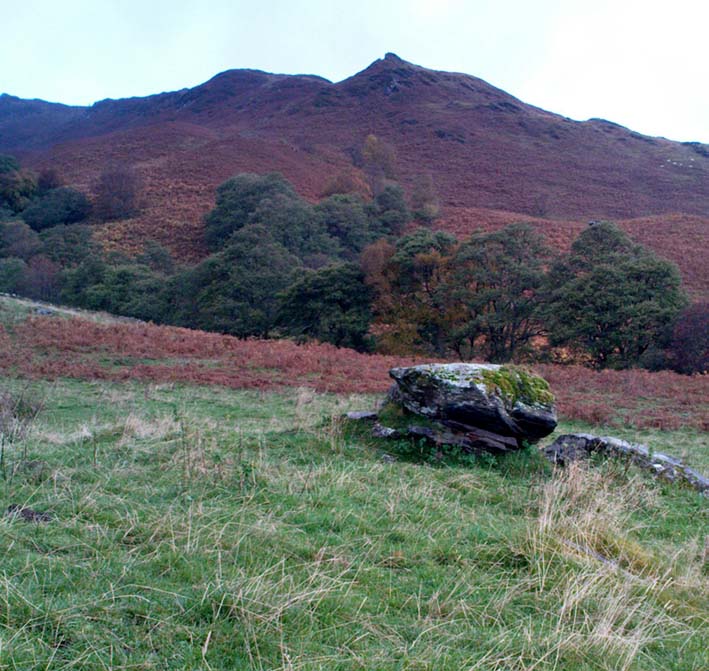
Enclosure: OS Grid Reference – TL 7357 0818
Archaeology & History
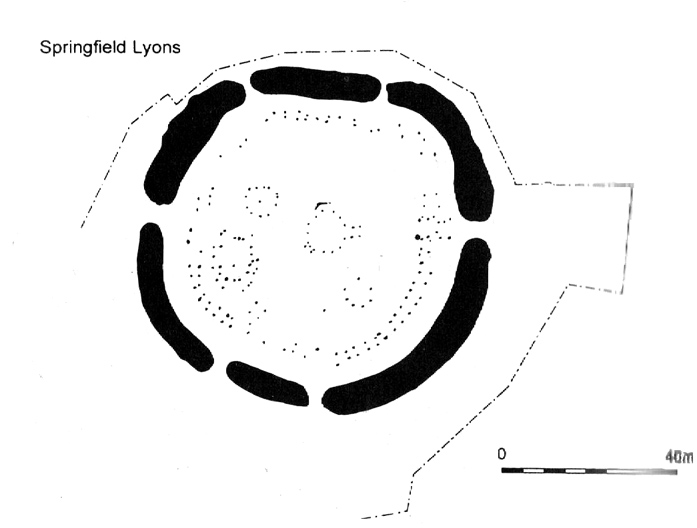
We’ve known that there was an excessive number of prehistoric archaeological sites in and around the Chelmsford region for quite a long time now, but defining precisely the age and nature of the finds takes some doing! (as you’d expect) It hasn’t helped, of course, with the housing estates and other ecologically destructive building operations in and around the area, screwing up a more accurate and patient assessment of the material there. And this predicament was exemplified with the Springfield Lyons neolithic causewayed enclosure just as much as at the Springfield Cursus and other sites nearby.
Although excavations here found a large, deep ditch with impressive ramparts and entrance, in Oswald, Dyer & Barber’s (2001) survey of these giant monuments, they defined the remains here as “probable,” pending further investigations. But the site was primarily defined by the large deep ditch, broken in several places round its edges with the ’causeways’ built leading onto the site. The enclosure gave good views over the small valley from here and had streams running either side of it.
Adjacent to the site were the remains of a “small circular enclosure with multiple entrances,” saying that excavation here,
“has proved that it is of late Bronze Age date and might be interepreted variously as a defended settlement, or a ritual monument.”
This external small enclosure site was then conjectured, quite spuriously it’s gotta be said, to be a mini-version of the great causewayed enclosure monument, saying:
“Its siting and form both hint that it could have been a conscious imitation of, or re-invention of, the perceived form of the earthworks of the neolithic enclosure.”
I like the idea, it’s gotta be said — but without direct evidence we’ve gotta take this idea with a large pinch of salt!
…to be continued…
References:
- Brown, N., ‘The Archaeology of Essex 1500 – 500 BC,’ in Bedwin, O. (ed.), The Archaeology of Essex, ECC: Chelmsford 1996.
- Brown, N., “The Late Bronze Age Enclosure at Springfield Lyons in its Landscape Context,” in Essex Archaeology & History, volume 32, 2001.
- Oswald, Alastair, Dyer, Caroline & Barber, Martyn, The Creation of Monuments: Neolithic Causewayed Enclosures in the British Isles, EH: Swindon 2001.
- Priddy, D., ‘Excavations in Essex, 1987,’ in Essex Archaeology & History, 19, 1988.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian