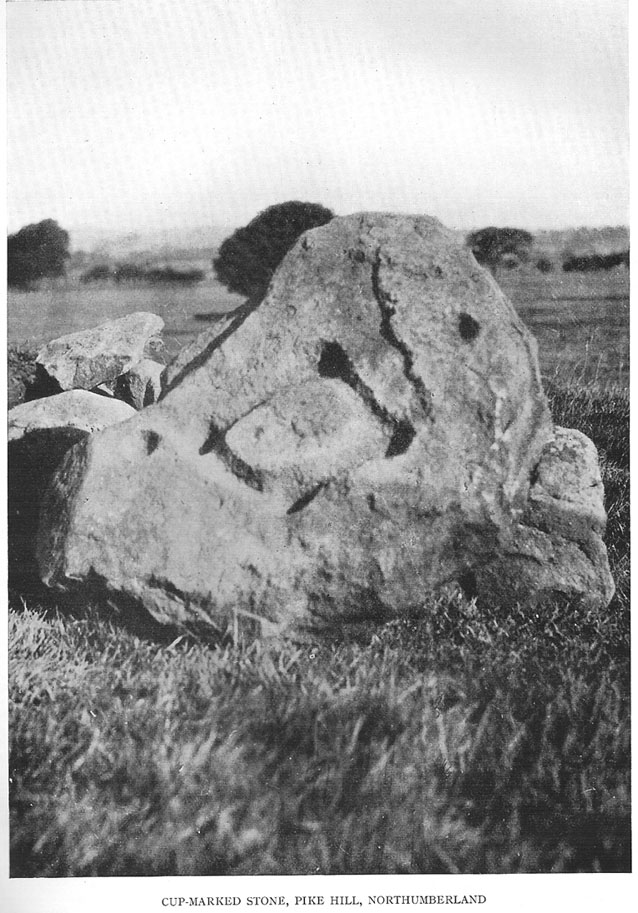
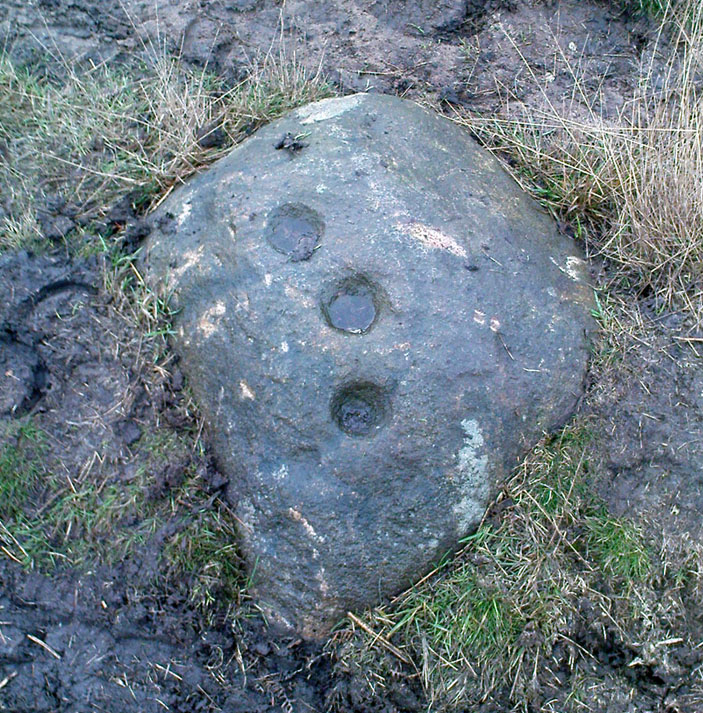
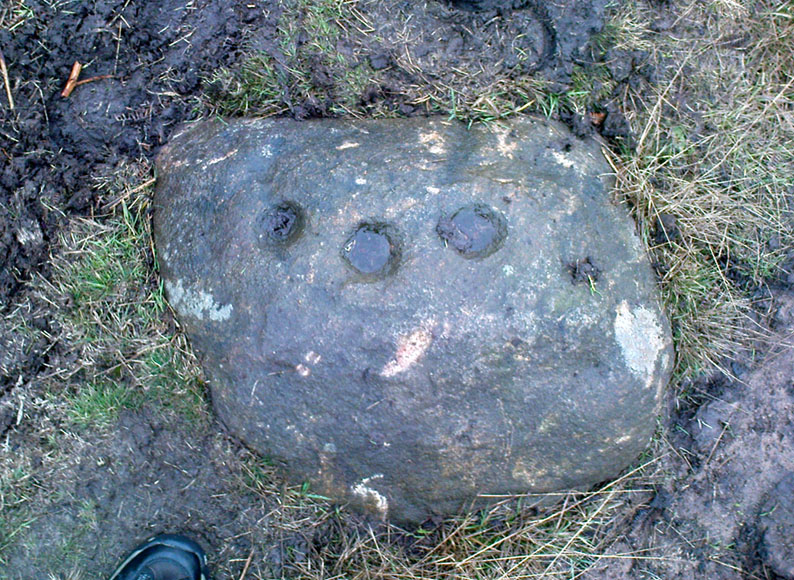
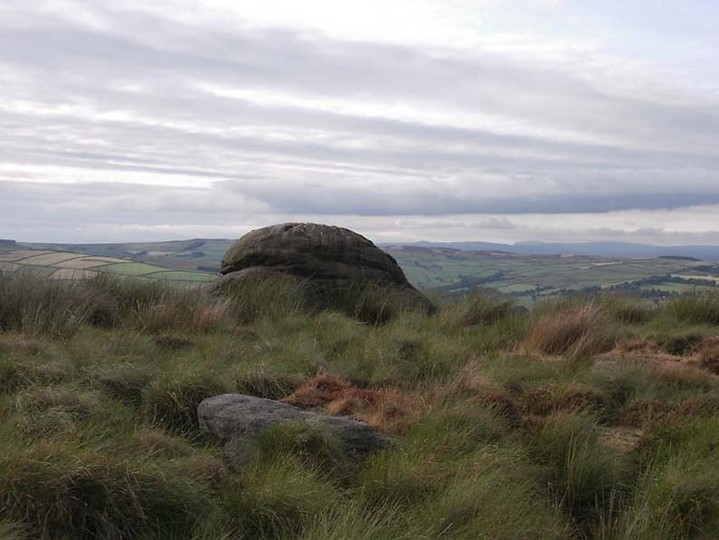
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – SE 18120 51201
Also Known as:
- Naked Jogger Carving
Getting Here
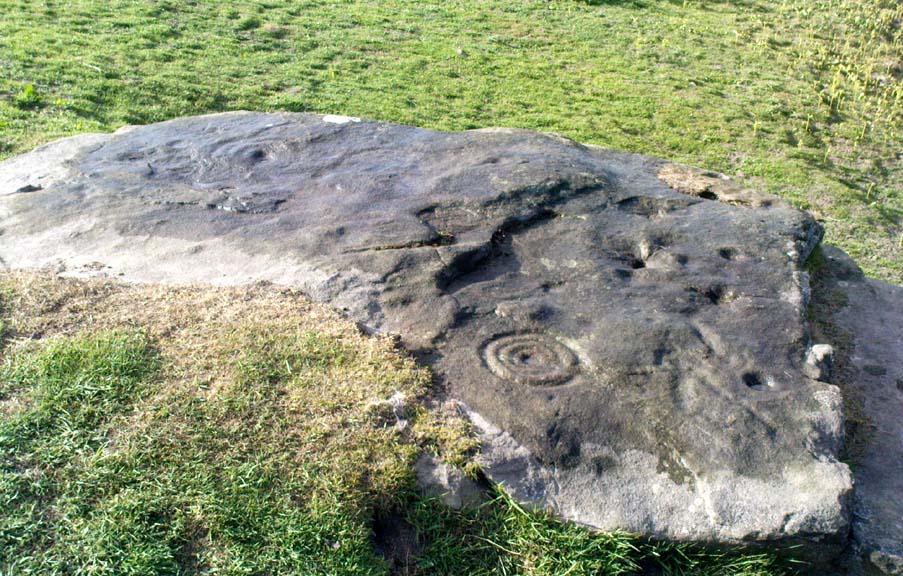

From Askwith village go up the Moor Lane and at the crossroads go straight across, down and along Snowden Carr Road until the road levels out and, watch carefully, for a small crag of rocks in the fields above on your left. Keep a keen eye out for the gate into the field immediately below these rock, right by the roadside (it’s easily missed). This carving is the large rock sticking out on the slope in front of you thru the gate (carving 613 is lower down to the right).
Archaeology & History
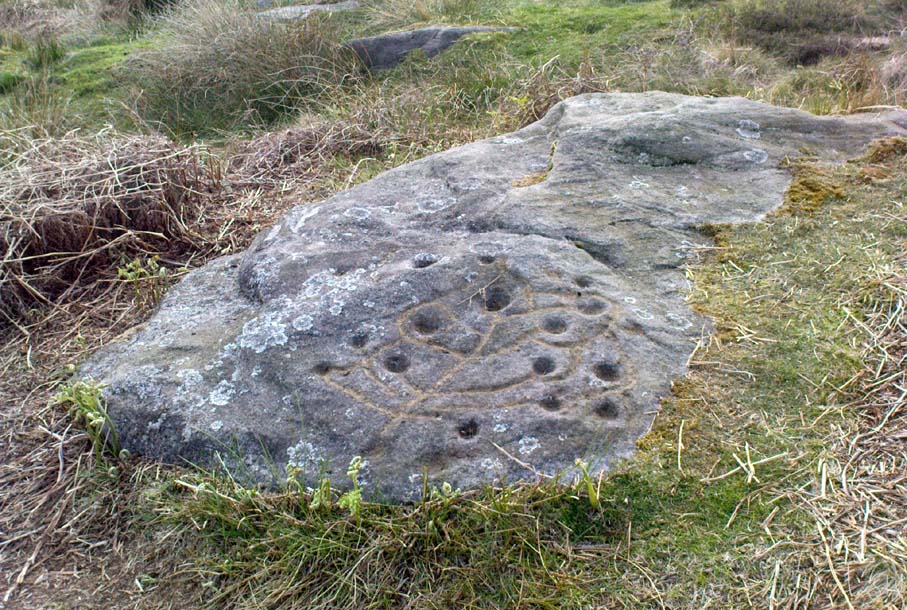
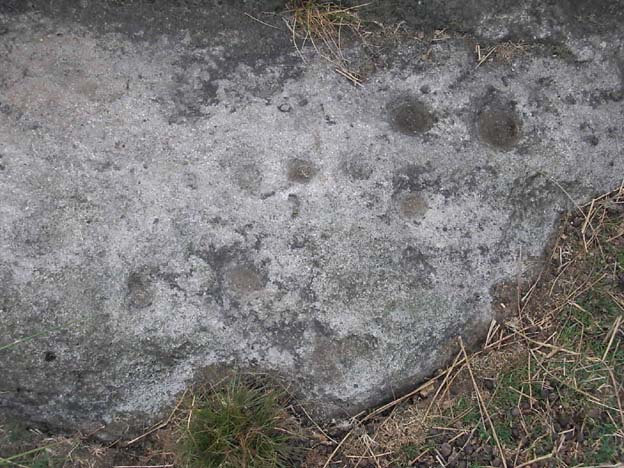
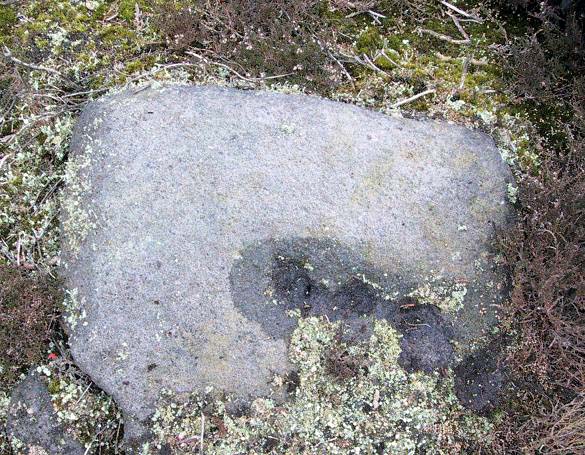
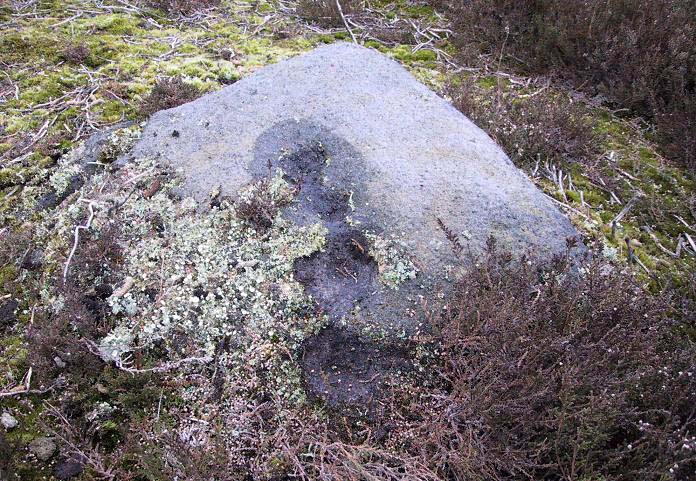
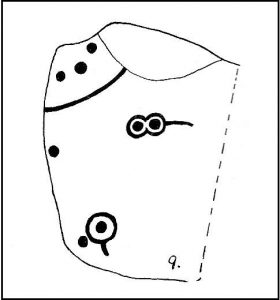
When seen in the right light, this carving’s a beauty! What you could call, an archetypal cup-and-ring stone. But the toll of time has played its part — on the uppermost section of the rock in particular. It seems as if the top, higher section of the boulder has always been exposed to the elements, whereas the slightly lower part of the rock has only been unearthed and exposed to the elements in more recent decades — perhaps by Stuart Feather, who made notes of some carvings in this region in 1973. This assumption is especially apparent when we look at the excellent, well-preserved multiple ringed design near the southern edge of the stone…and from where the carving gets its title, the Naked Jogger Stone.
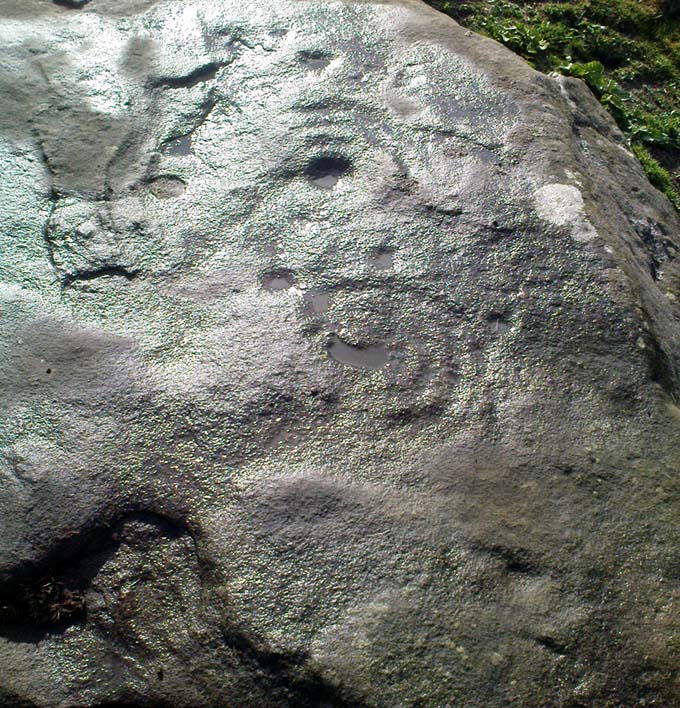
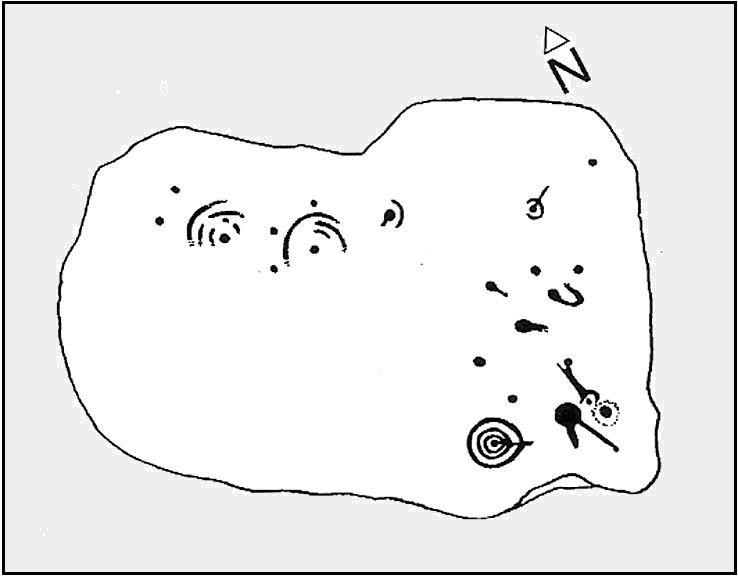
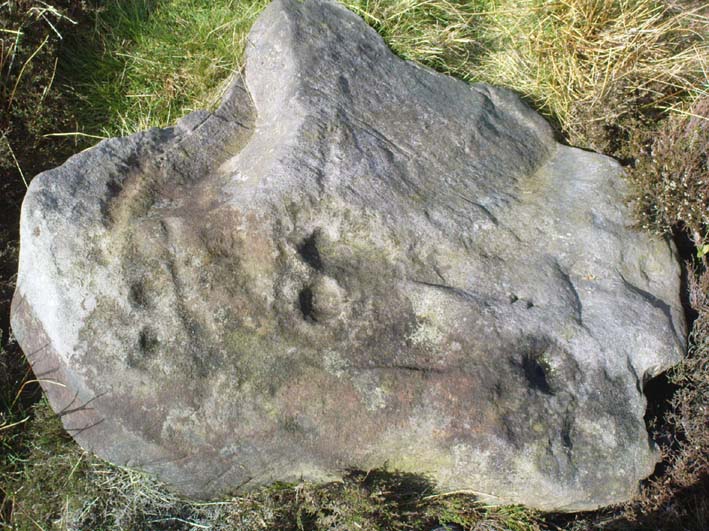
But let’s deal with the uppermost section of the stone first. There are various natural undulations and cracks over its surface and, at first sight, they can interfere or confuse some of the man-made carved aspects to this stone. But the main feature here — which becomes more and more noticeable the more you gaze and look — are at least two very faded multiple-rings surrounding faded central cups. It’s unknown whether or not these rings ever completely surrounded the cups, or whether they were actually left deliberately unfinished. The more faded of these two multiple-rings has between three or four cups around the outer ring at selected intervals (visible in the photo here). A few feet away from this we can also make out the faded remains of another cup-and-half-ring design. Several other cups have also been carved along this upper portion of the stone. When you sit above and look across this from the grass to the side, one may be forgiven for adding a solar interpretation to this section of the carving!
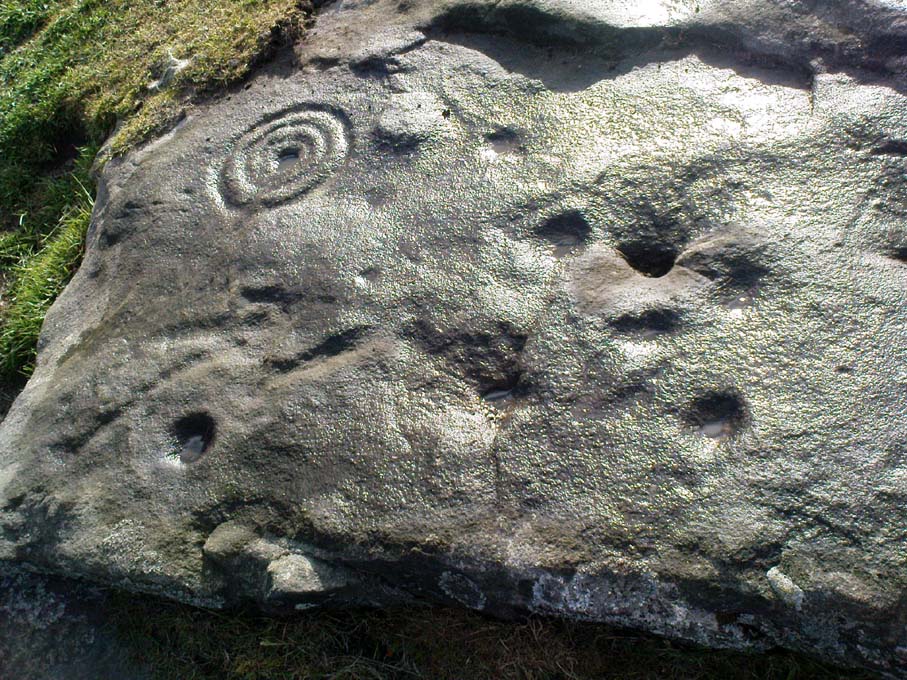


But another, more extrovert interpretation can be forgiven for the most notable aspect of this cup-and-ring stone. Near the southern edge of this large rock is the well-preserved multiple-ring design, surrounding a single cup. It’s impressive! And when you first see this you get the impression that it was uncovered in the very recent past (turf dug away obviously) as it is in such an excellent state of preservation. But there are other, odd-looking aspects below this primary feature: of cracks and lines and deep cups along this same level of the rock. The majority of the cups and lines on this part of the stone are in a much better state of play than the artistic elements on the upper layer of the stone. And one section of the carving in particular here gave me at least (pervert that I am!) the impression of a man running, with a distinctive hard-on sticking out in front as he’s jogging away! Keep looking at it in the photo here and see if that’s what you see as well. Note that the torso section of the ‘body’ (between his cock and the multiple-ringed head) is made-up primarily of a natural crack in the rock, but this should not be seen as unusual; for in rock art across the world, many of the natural cracks and markings on stones are regularly utilized. We know that such ‘cracks’ in rocks have been used by shamans as entrance points for their spirit to enter the rock itself.
Early carvings of humans in other parts of the world show bloke’s with hard-ons, either dancing or hunting — so why not here aswell, in deepest Yorkshire!? (check Dennis Slifer’s Serpent and the Sacred Fire for many North American examples) It could, of course, be little other than my very simple minds response to non-linear etchings in the old Rorscharch ink-blot style. Either way, it doesn’t really matter — unless of course you’re some academic or witchy character who’s after isolating early prehistoric fertility carvings for your thesis or religion. Oh – and there’s the more renowned Tree of Life carving a bit further up this hill, about 150 yards away: alleged in folklore to have been a place for Beltane rites—wholehearted fertility no less!
In the important archaeo-academia files, little has ever been written of this fine, ornate petroglyph. It was described by Boughey & Vickerman (2003) thus:
“About twenty cups, two very large, one cup having three rings and two more also having traces of three rings, with at least four others having parts of single rings, all very worn.”
Simple and to-the-point I suppose. But this old carving has much more grace and mythic history embedded within its scarred surface. It clearly speaks to other aspects of the landscape (as do some of the other carvings further up the hill, where oracular aspects predominate), but much more work is needed here before any archaeoholistic framework can be moulded. Nonetheless, this is an excellent meditation site!

References:
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock Art of the West Riding, WYAS 2003.
- Slifer, Dennis, The Serpent and the Sacred Fire: Fertility Images in Southwest Rock Art, Museum of New Mexico Press: Santa Fe 2000.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian