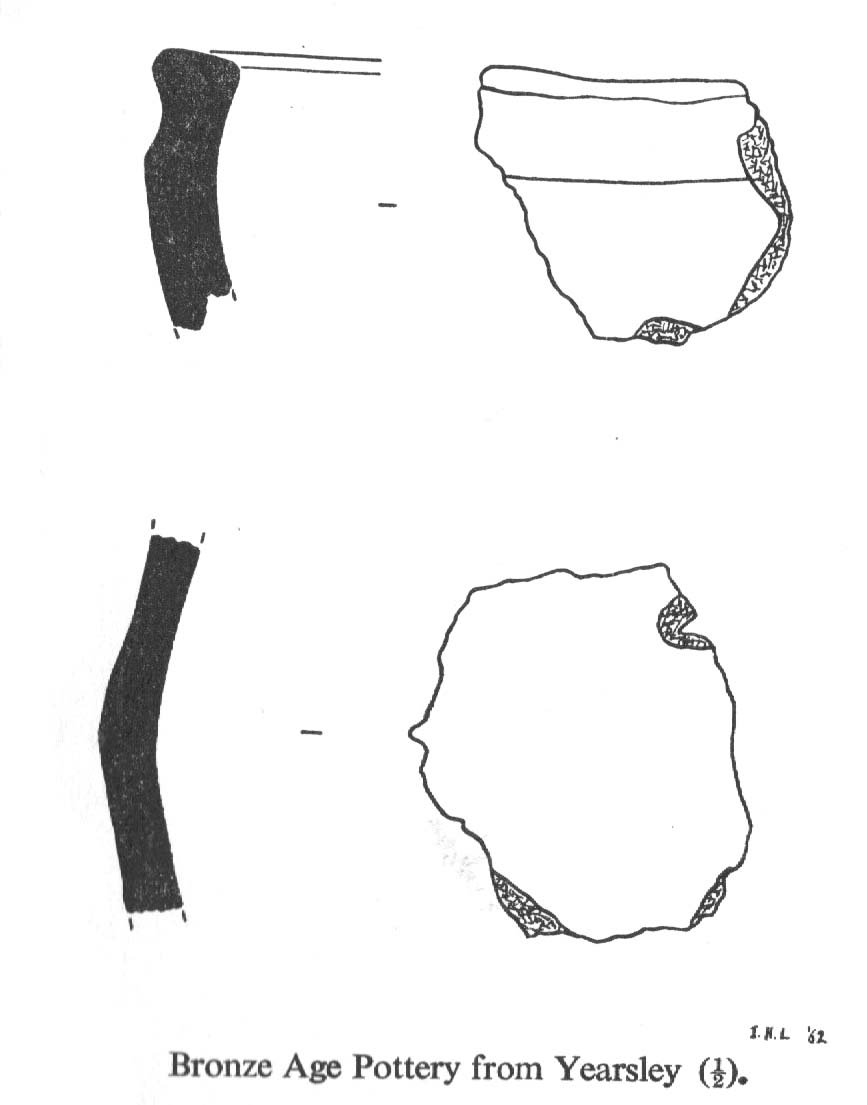
Tumulus (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 4733 2444
Also Known as:
- Mound 2 (Pacitto)
- Roundhill Field
Archaeology & History
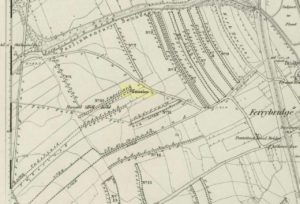
Close to the important ceremonial monument of Ferrybridge Henge could once be seen be this singular grave and ring-ditch, 53 yards north of the curiously-named Angel Moon tumulus. But, thanks to that regular ingredient of self-righteous industrialism, neither of the sites exists anymore. It had initially been damaged by some agricultural ignorance (they like to the PR-term ‘agricultural improvement’), but was thankfully rediscovered following excavation work on the Angel Moon site by A.L. Pacitto in April 1962, in advance of the construction of the Ferrybridge C power station. (in truth, the exact position of this Round Hill tumulus was in an area that has not been built onto, at the southeastern edge of the modern car-park on the grassy area next to the trees; showing that it could have easily been preserved).
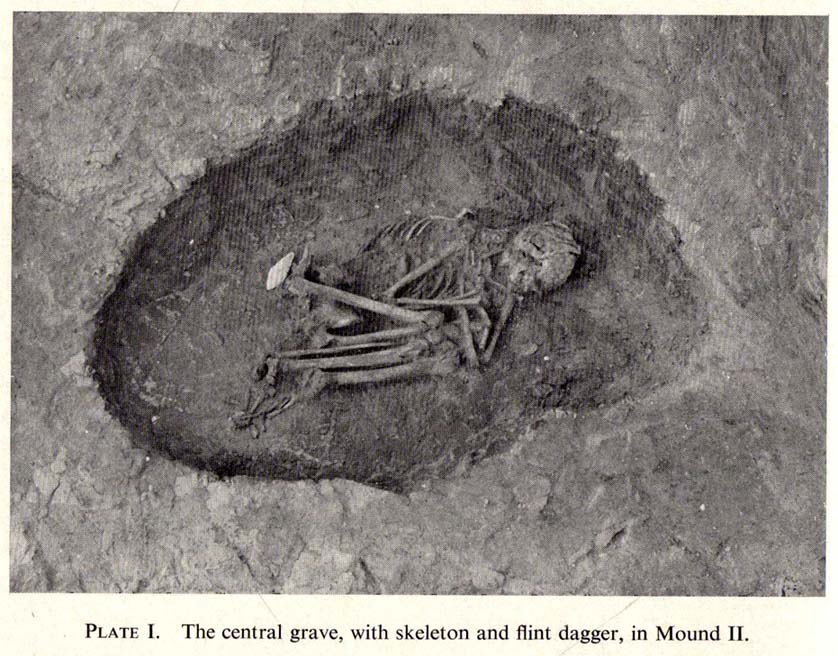
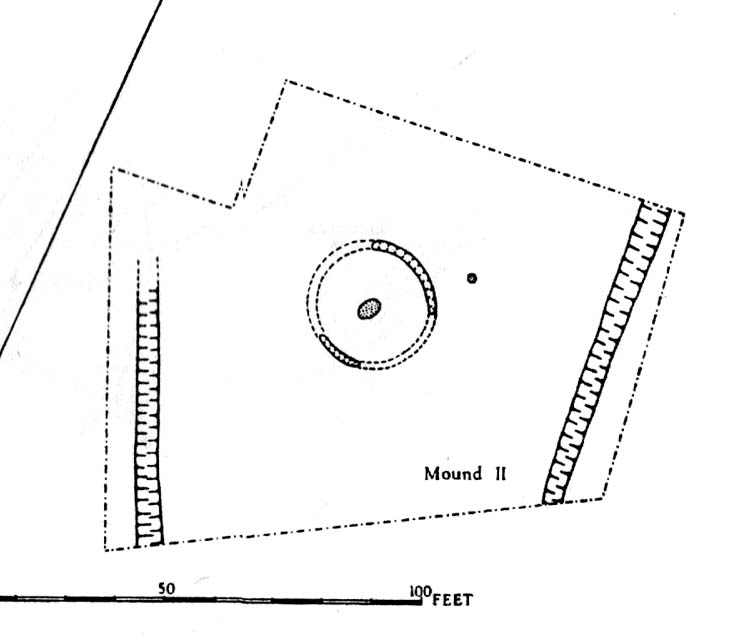
The site was certainly an important one amidst what Ian Roberts (2006) called “the ritual landscape” in this part of prehistoric Airedale. When the archaeological team came to do their work here, very little of the monument could be seen on the surface—Mr Pacitto described it as “barely perceptible”—but they were both pleased and surprised at what they found. Detailing their excavation work, Pacitto (1969) wrote:
“Natural rock was found immediately below the ploughsoil, and it had been scored by ploughing. In view of the complete lack of stratification the first traverse of the (Drott) machine was arranged so that it cut across the mound from side to side, with one edge coinciding with a line drawn through the centre. This first traverse exposed half an oval grave pit, measuring 3ft 9in by 5ft. On excavation it proved to be only 5in deep, but in spite of this it contained an undisturbed crouched inhumation. The body was on its left side, facing south, and a notched flint dagger behind the pelvis was perhaps attached to a belt at the time of burial. The dagger…is very neatly flaked from a fine flint with a pale blue patina. It has three notches on each side of the haft and is very similar to one found in Doncaster in 1935. The filling of the grave also included several fragments of human bone, one of which had been calcined.
“The grave was surrounded at a distance of 11ft to 12ft by the remains of a circular ditch. Only two segments of this had survived, representing less than half of the total circumference. Doubtless ploughing had destroyed much of the original rock surface.
“Outside the ditch and 20ft to the southeast of the grave was a small circular pit. With a flt bottom and vertical sides, it measured 2ft 3in in diameter and was 1ft 2in deep. The filling was mainly of broken and crushed limestone fragments, and there was no clue to its date or purpose. This pit was sited on the line of an east-west fault or joint in the rock.”
References:
- Forrest, C., The History and Antiquities of Knottingley, W.S. Hepworth: Knottingley 1871.
- Pacitto, A.L., “The Excavation of Two Bronze Age Burial Mounds at Ferry Fryston in the West Riding of Yorkshire,” in Yorkshire Archaeological Journal, volume 42, part 167, 1969.
- Roberts, I. (ed), Ferrybridge Henge: The Ritual Landscape, WYAS 2006.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS: Huge thanks to the Yorkshire Archaeological Society for use of images in this site profile.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian