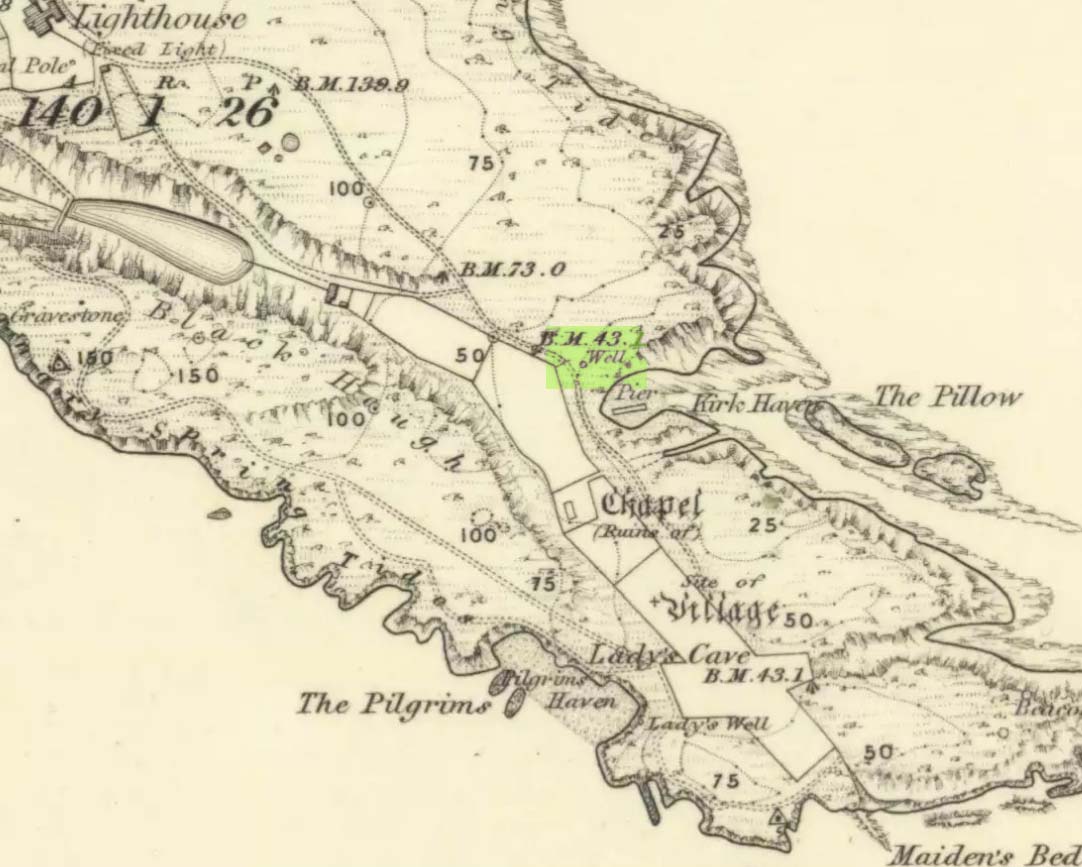
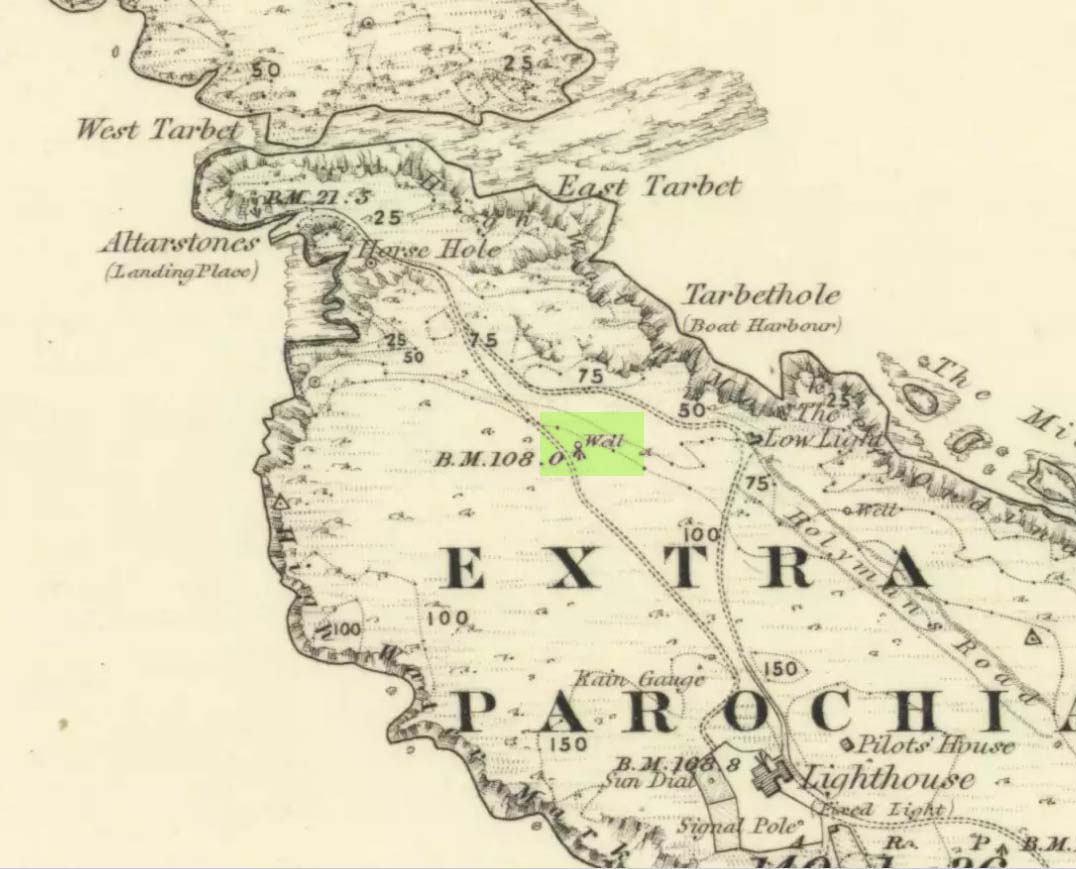
Sacred Well (lost): OS Grid Reference – NA 100 000
Also Known as:
- Well of Eternal Youth
Folklore
An old story told in previous centuries by the indigenous folk of Hirta (St. Kilda) described a long-lost well that was thought to be an abode of the little people, known as the Well of Eternal Youth. Not to be confused with the Well of Virtues near the Amazon’s House less than a mile west, the rough whereabouts of this site is cited by J. Sands (1878) in the folklore section of his otherwise historical account on these faraway Atlantic islands. He wrote:
“Once on a time an old fellow, in going up Connagher with a sheep on his back, observed a Well which he had never seen or heard of before. The water looked like cream, and was so tempting, that he knelt down and took a hearty drink. To his surprise all the infirmities of age immediately left him, and all the vigour and activity of youth returned. He laid down the sheep to mark the spot, and ran down the hill to tell his neighbours. But when he came up again neither sheep nor well were to be found, nor has any one been able to find the Tobair na h-oige to this day. Some say that if he had left a small bit of iron at the well—a brog with a tacket in it would have done quite well—the fairies would have been unable to take back their gift.”
Explorations of old maps and texts has failed to show with certainty where this legendary well may have been (the grid-ref is an approximation), but it was reported in Mrs Banks’ Scottish Calendar Customs (1937) to have been “issuing out of the face of a rock on the north-side of the east bay…only accesible by the inhabitants, no stranger daring to climb the steep rock.” Some of us would try!
References:
- Banks, M. MacLeod, British Calendar Customs: Scotland – volume 2, Folklore Society: London 1937.
- Sands, J., Out of the World; or Life in St. Kilda, Maclachlan & Stewart: Edinburgh 1878.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian