Holy Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 15942 34208
Also Known as:
- Ash Well
- Holy Well Ash Well
- Pin Well
Archaeology & History
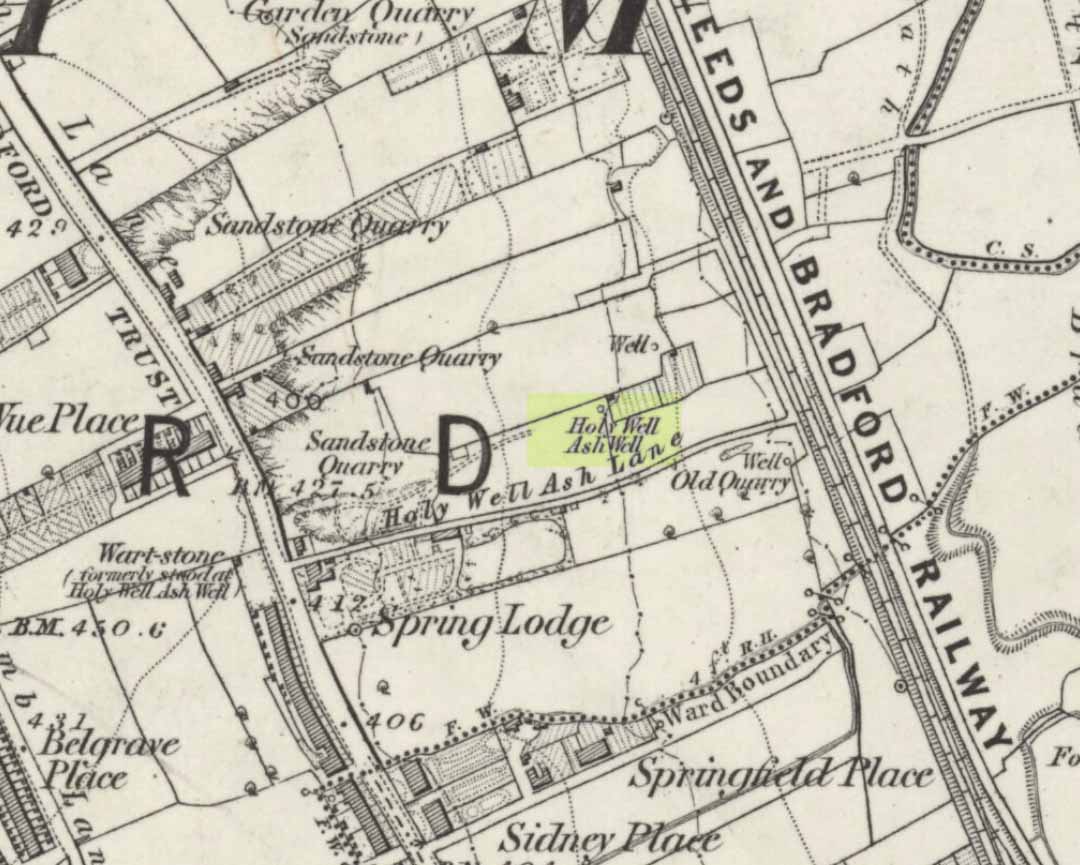
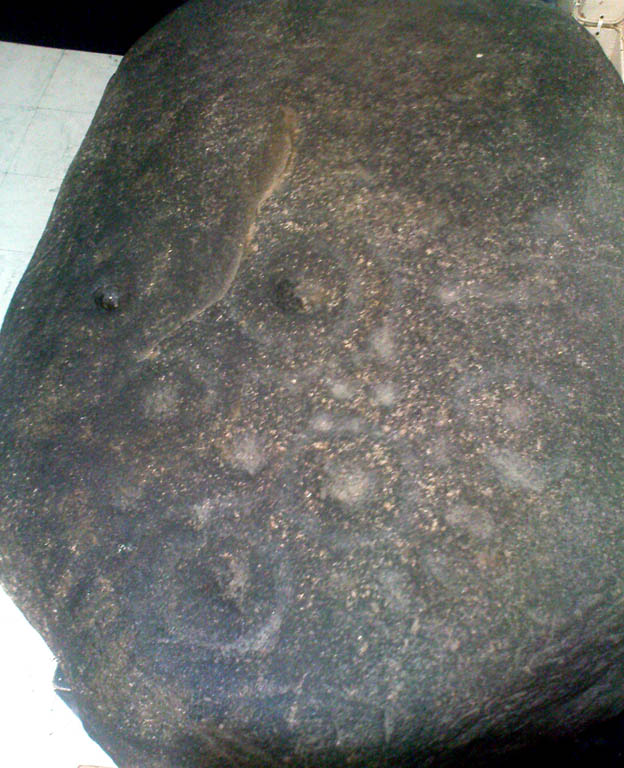
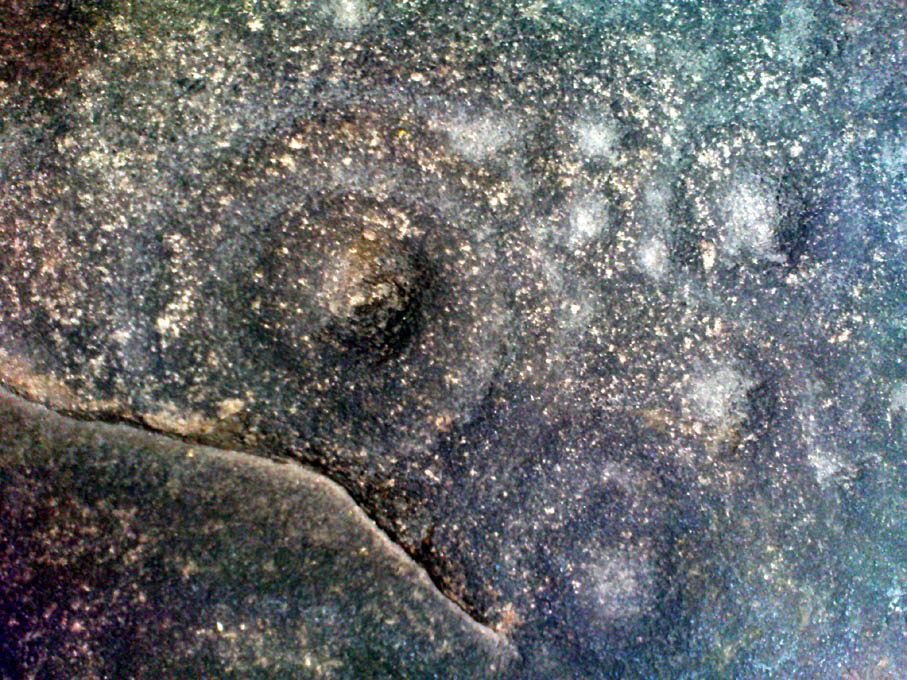
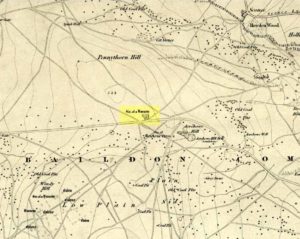
Either right next to, or perhaps now beneath Bradford City’s Valley Parade football ground, was once a very important sacred well site. Known as the Holy Ash Well and variants thereof, this healing spring was of considerable renown to people all around Bradford district in bygone days. The site was illustrated on the 1852 OS map, and there was also a sacred stone adjacent to the well known as the Wart or Pin Stone, which had some animistic healing properties related the waters.
The old well was described by local historian Abraham Holroyd (1873) who said that:
“In Manningham Lane there is a fine well, in old deeds called Hellywell, i.e., holy well, in a field now called Halliwell Ash, now a stone quarry… Near this is the ancient Pin Stone.”
A few years later, in Robert Charles Hope’s (1893) monumental study, he described how,
“This holy well, not far from Manningham Lane, probably derived its name from having at some time been dedicated to some saint. The inhabitants of Bradford were wont in ancient times to resort on Sundays to these wells as a common place of meeting, to drink of the waters and partake of their preternatural virtues.”
Which was another was of saying that he didn’t really know too much about the place!
The Bradford historian William Preston (1933) described this site in one of his early essays, where he informed us that local people knew the accompanying rock hereby as the Ash Stone, due to its proximity and ritual relationship to a great old ash tree (Fraxinus excelsior) that grew next to the well. The mythic history of this particular tree should not be understated: it was a Creation deity par excellence in northern and Viking myths, but whatever old tales and power might once have been had here, in Bradford, they’ve long since been forgotten. But it was the industrial historian William Cudworth (1896) who told the most of this all-but forgotten site, saying:
“On the sloping ground between Belle Vue and the Midland Railway there once existed a spring of water, supposed to have preternatural virtues. The name it bore within present recollection is probably a corruption of Holy-well. The holy wells of England as elsewhere had not all the same virtues attached to them. Some were blessed if used for baptisms, to others were attributed curative properties, especially for sore or weak eyes, while others were supposed to possess mystical powers, insomuch as any article dipped in them became charms or safeguards against witchery. Any traditions associated with the spring at Halliwell (or Holywell) Ash are lost, but certainly in the early part of the present century the place was a favourite resort of the townspeople on Sundays.
“The derivation of the name is doubtful. In the survey of 1638 a close called ” Helliwell Ash” is mentioned as containing 2a. 3r. 26p., but without any indication as to its locality. The spelling of the name is of little moment. Mr. James, in his “History of Bradford,” states that he had seen the place referred to in old deeds as “Helly-well.” By his will, dated May, 1685, Thomas Lister, of Manningham, devised to his two daughters, Juliana Lambrecht and Elizabeth Stapleton, equal shares in two closes of land called “Holywell Ash” and ” Delf Close,” besides other lands in Manningham. In the will disposing of the possessions of Juliana Lambrecht, her moiety of “Holywell Esh” was bequeathed to Francis Stapleton, her nephew. In due course the lands in question were inherited by Francis Sharp Bridges, and have latterly belonged to Sir Francis Sharp Powell, M.P., in whose writings the form of spelling is given as ” Halliwell Ash.”
“Upon the ground in question there used to be a fine well of water issuing out of the higher ground, to which tradition assigned healing virtues. Might not the name of “holy” come from this circumstance? Sufficient importance attaches to the tradition, however, to have led the farmers of the recent ordnance plan of Manningham to preserve the name, although the widening of the Midland Railway below Thorncliffe Terrace has almost obliterated the site.”
A more recent updated overview of the site was written by one of my old school-mates, Dave Pendleton (1997), who said of the place:
“Prior to 1886 the only feature of any real note in the Valley Parade environs was a holy well that emerged near the corner of the football grounds Midland Road and Bradford End stands; hence the road Holywell Ash Lane. Today the site of the well is covered by the football pitch.
Only the road name survives as a reminder of what was apparently one of the district’s foremost attractions. On Sundays and holidays people would gather to take the waters and leave pins, coins, rags and food as offerings to the spirit that resided in the waters.
Accounts suggest that the well was covered and had a great ash tree standing over it (hence ‘holy ash’). There was also a standing stone called the wart stone of unknown antiquity. The stone had a carved depression that collected water. It was believed that the water was a miraculous cure for warts. Indeed, as early as 1638 the Holy Well had been credited with healing powers.
The well suffered a decline in popularity during the late nineteenth century and its keepers resorted to importing sulphur water from Harrogate, which they sold for a half penny per cup. The well disappeared under the Valley Parade pitch during the summer of 1886 and the wart stone was moved to the top of Holywell Ash Lane – which then ran straight up to Manningham Lane. The stone was still there as late as 1911 but thereafter it seems to have disappeared into the mists of time.”
A night-club adjacent to the Valley Parade football ground—called Bibby’s—was said to have had an old well in its cellar, which the owner of the place, Mr Pearl Gladstone Minott, said was ‘haunted’.
Unfortunately I’ve not been able to find any old photos or drawings of this lost holy well – though I imagine that some local, somewhere must be able to help us out with this one. Surely there’s more of this site hidden away somewhere….?
References:
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Milverton 2001.
- Cudworth, William, Manningham, Heaton and Allerton, W. Cudworth: Bradford 1896.
- Holroyd, Abraham, Collecteana Bradfordiana, Saltaire 1873.
- Hope, R.C., The Legendary Lore of the Holy Wells of England, Elliot Stock: London 1893.
- Pendleton, David & Dewhirst, John, Along the Midland Road, Bradford City AFC 1997.
- Preston, W.E., ‘Some Bradford Holy Wells’, in Bradford Antiquary, volume 7, 1933.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian