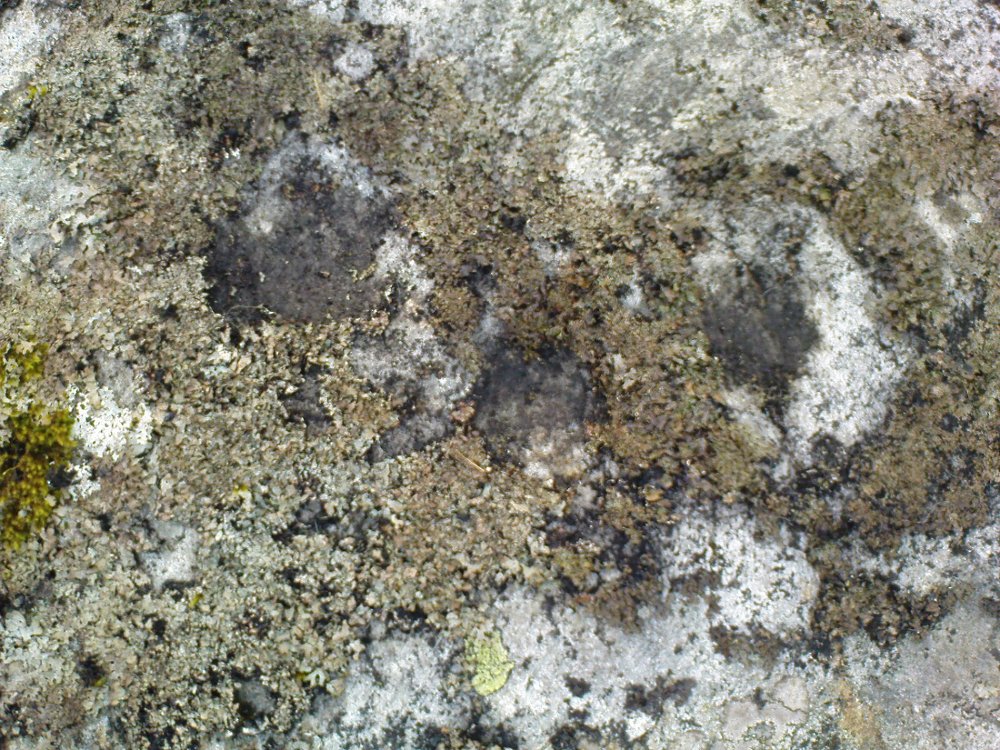
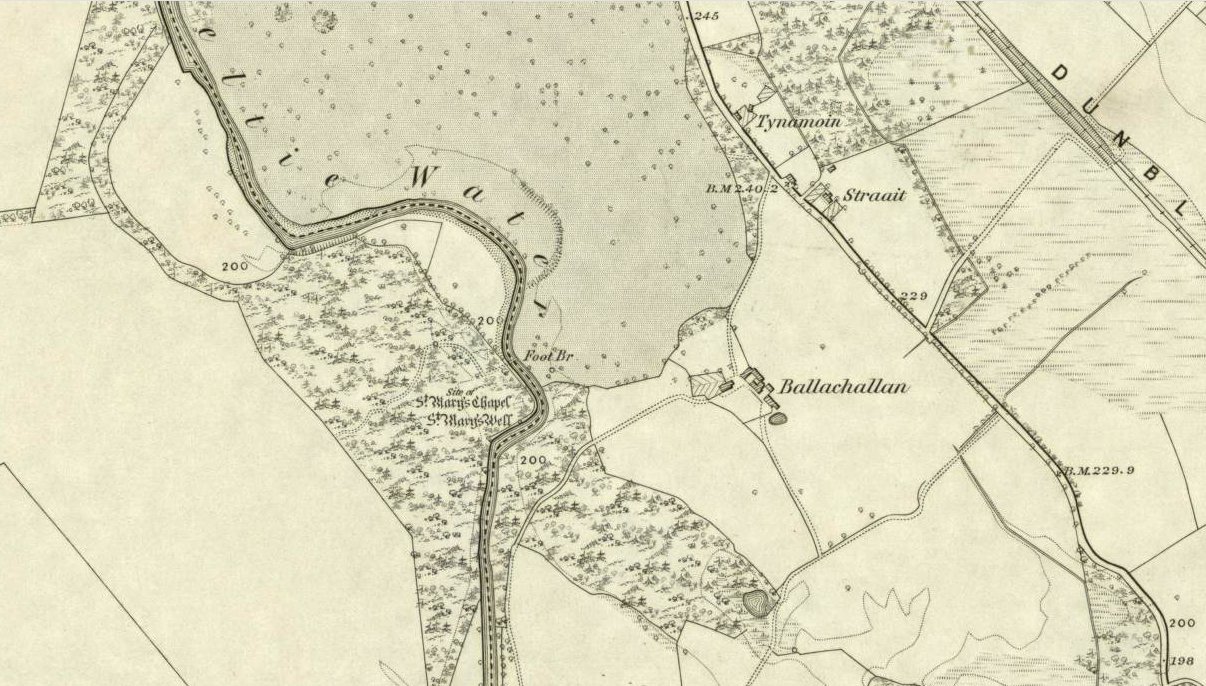
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – NS 6926 9399

Take the A811 road between Stirling and Kippen and go up into Gargunnock, From the village centre, go along the Leckie Road (not the Main Street!) for half-a-mile, then turn left up the tiny road. ¾-mile (1.15km) along, a small bridge crosses the Leckie Burn (a.k.a. St Colm’s Burn). From here, walk up the footpath into the woods for 100 yards or so and cross the waters. When you see the large overgrown rocky rise of the Leckie Broch covered in pesky rhododendrons, walk up its left-side where (presently) a clearing has been made and the carved rocks stand out.
Archaeology & History
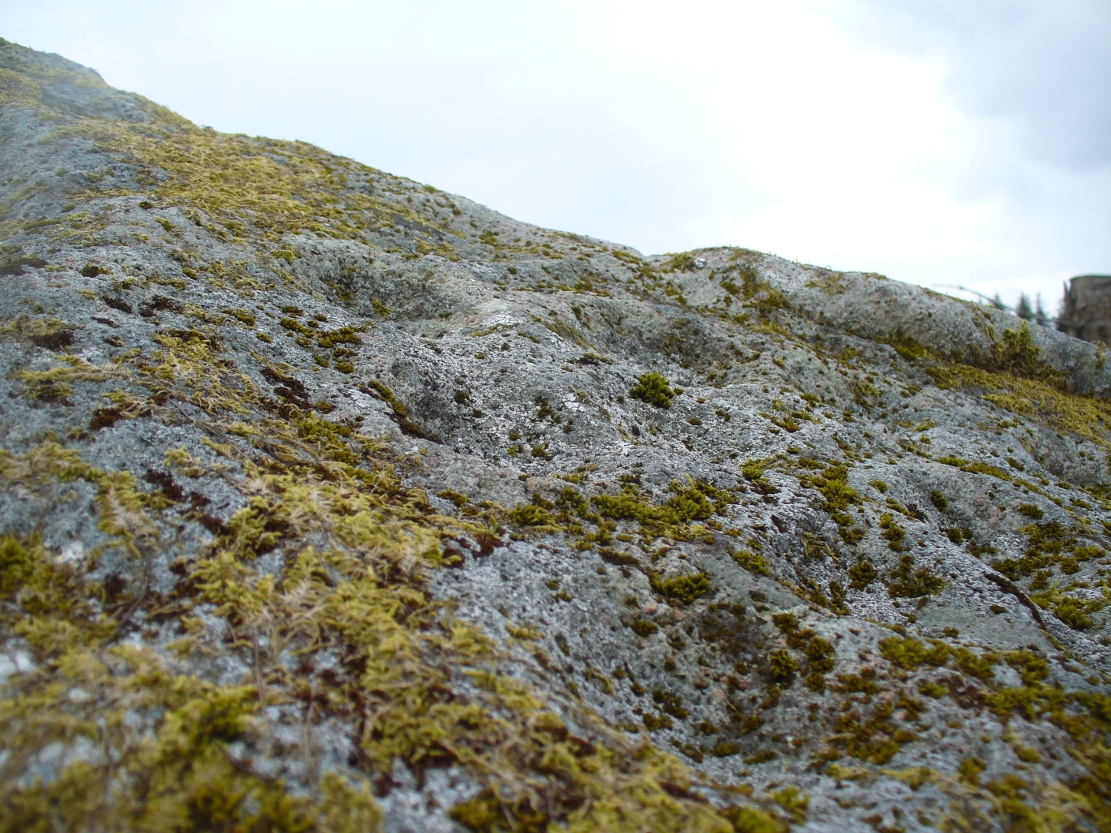
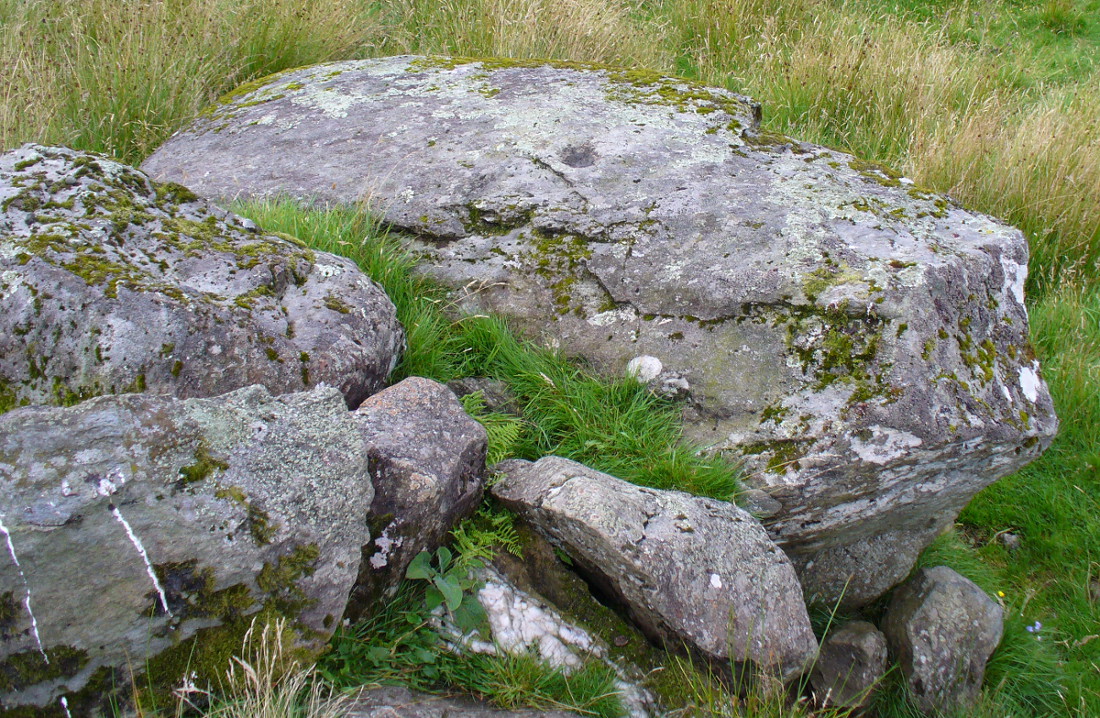
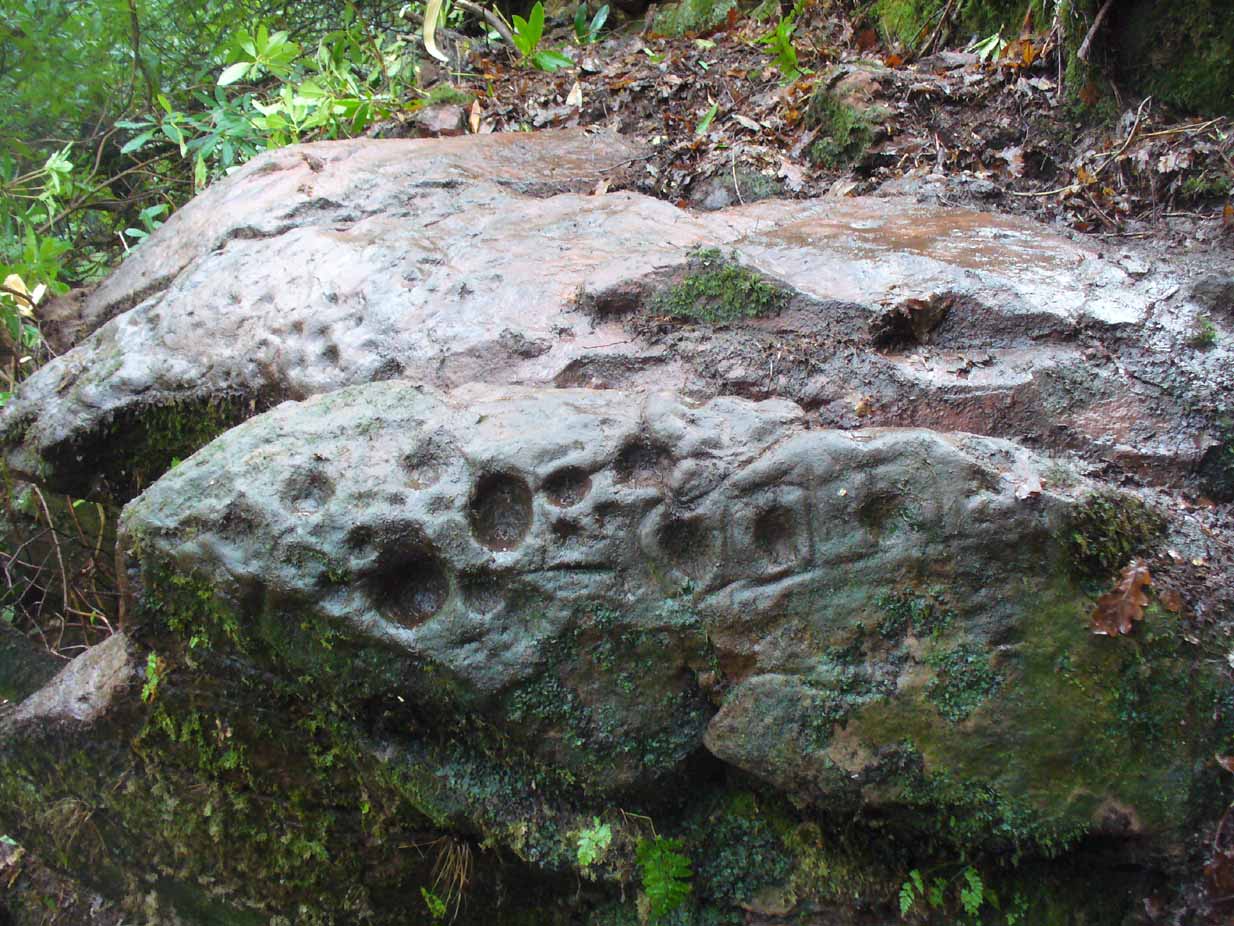
A very curious design here! Possibly carved at the same time as the Leckie broch to which it is attached—possibly not—we have here a curious amalgam of Nature’s incisions and human design, culminating in cup-and-rings and cups-and-squares no less! When we came to visit it a few days ago, Lisa Samsonowicz found the stone hiding away, buried beneath a thin layer of natural cover. The rest of the team thereafter enabled a much clearer pictures of the carving.
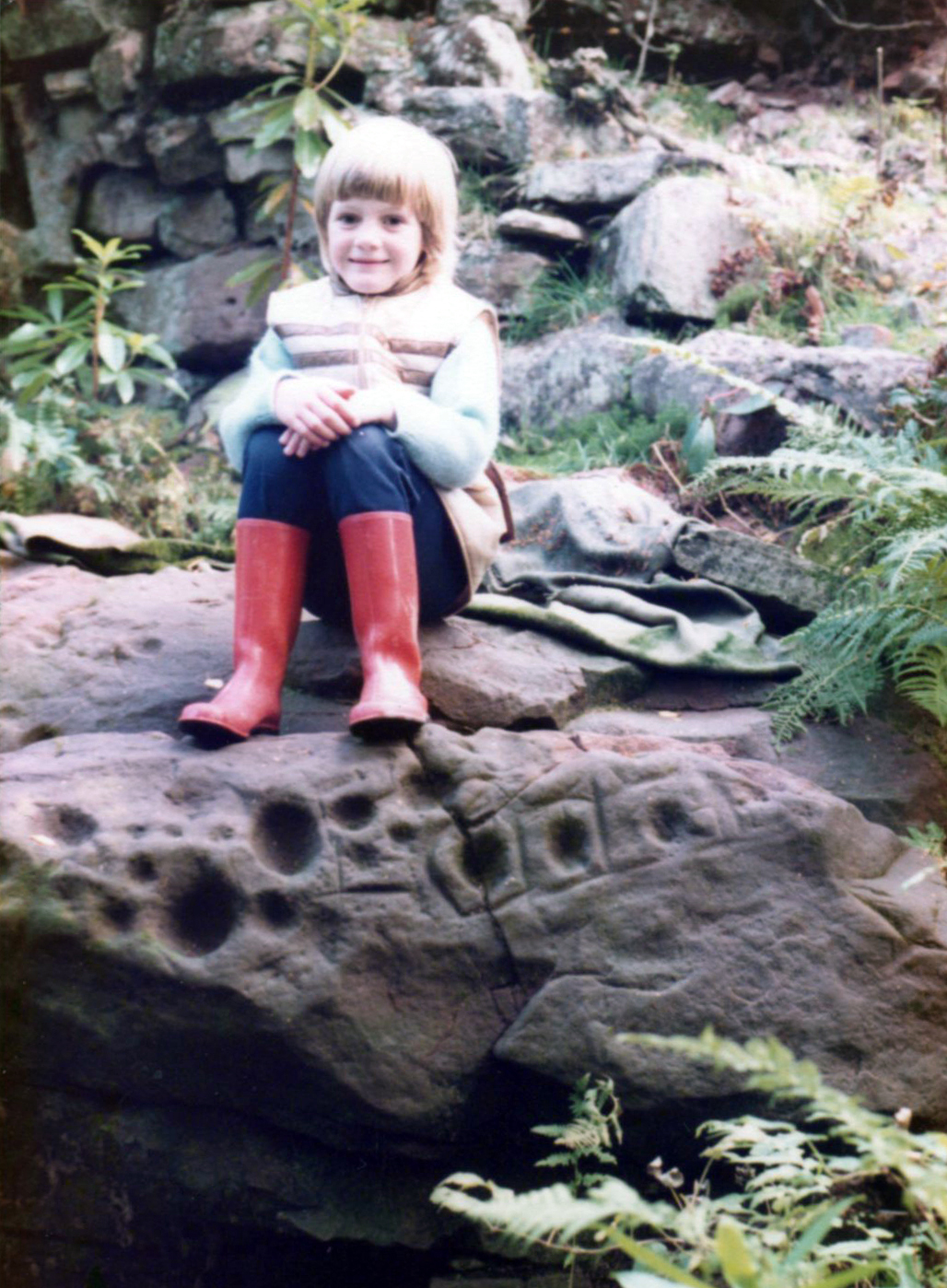


We’re not quite sure who first rediscovered the carving. In an early photo of the site taken in the late ’70s or early ’80s, a young Allison McLaren sits highlighting the design. But she wasn’t the fortunate lass who discovered it! One account describes a local woman, Lady Younger of Leckie House, who was out walking her dog, accidentally dislodging some of the rocky debris of the Iron Age broch and unearthing the petroglyphs, thereafter taking Allison along to see it. The other account tells of it being noticed for the first time during an excavation of the broch by Euan MacKie and his team. Whichever it was, Prof Mackie (1970) was certainly the first person to write about it. He told:
“Part of the sandstone face of the northern end of the promontory on which stands the Leckie dun is covered with well preserved cup-marks, presumably much older than the dun. They were discovered when rubble and soil fallen from the dun was removed. Some of the cup-marks stand alone and some are surrounded by what appear to be incised rectangles in a ladder pattern. There are other, less clear markings.”
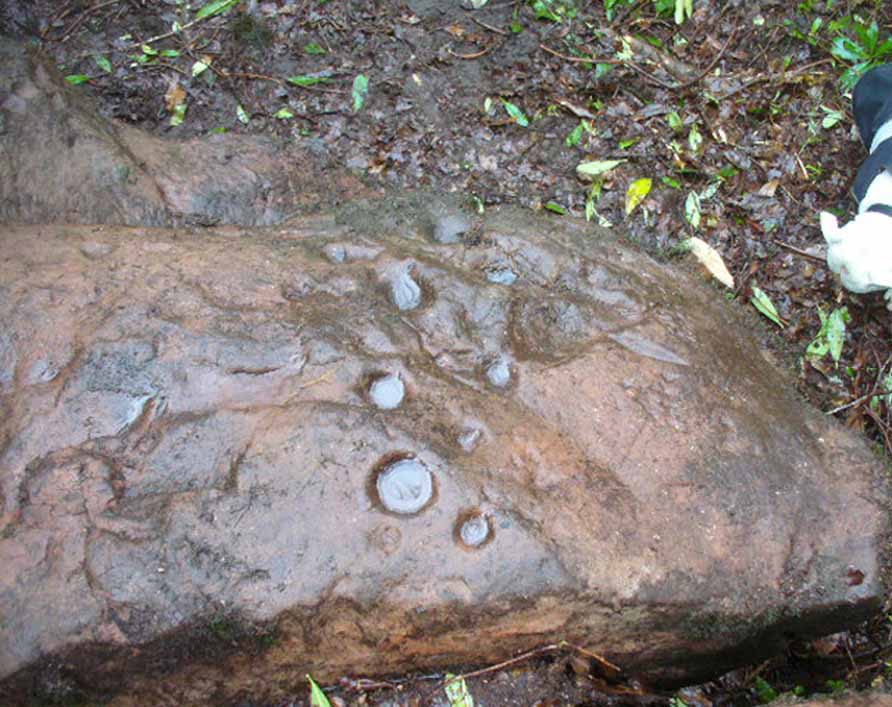
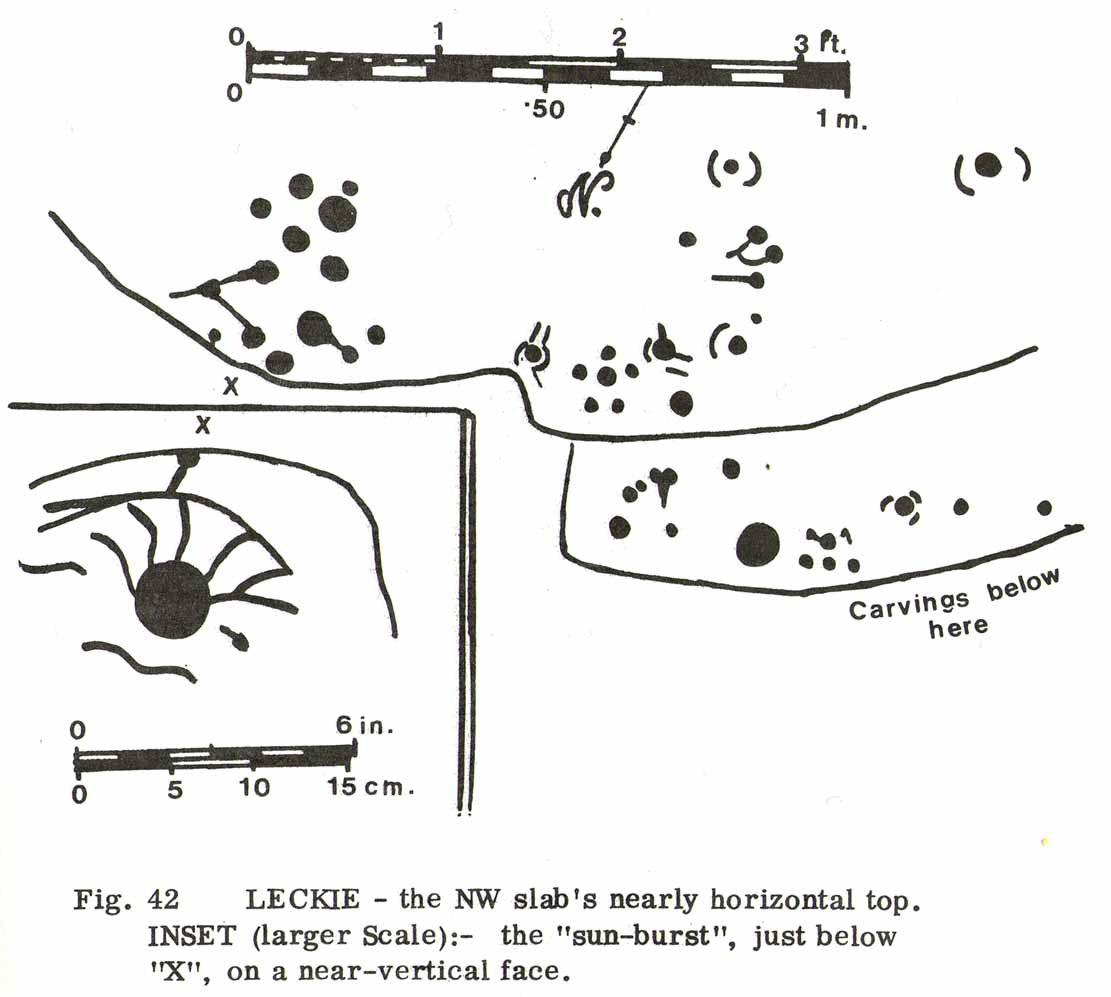

There then followed a series of written accounts, small and large, about the Leckie broch—but little else was said of the carvings. It wasn’t until Ronald Morris (1981) came to see them a few years later that they gained a slightly lengthier description. He described how the petroglyph was,
“carved over about 3m (yds) at heights of 1-2m (yds) on faces now sloping mostly 0-90º NW, with 3 cups-and-one-near-hexagonal-ring up to 12cm (4½in) diameter, a ‘sun-burst’ and other grooves, and at least 40 cups up to 12cm (4½in) diameter and up to 8cm (3in) deep. On a vertical E-facing slab there are also many grooves, some of which connect lines of cups. Some grooves resemble a ‘sea-horse’, an ‘axe’, etc. All except the cups are probably incised, but some may be natural.”
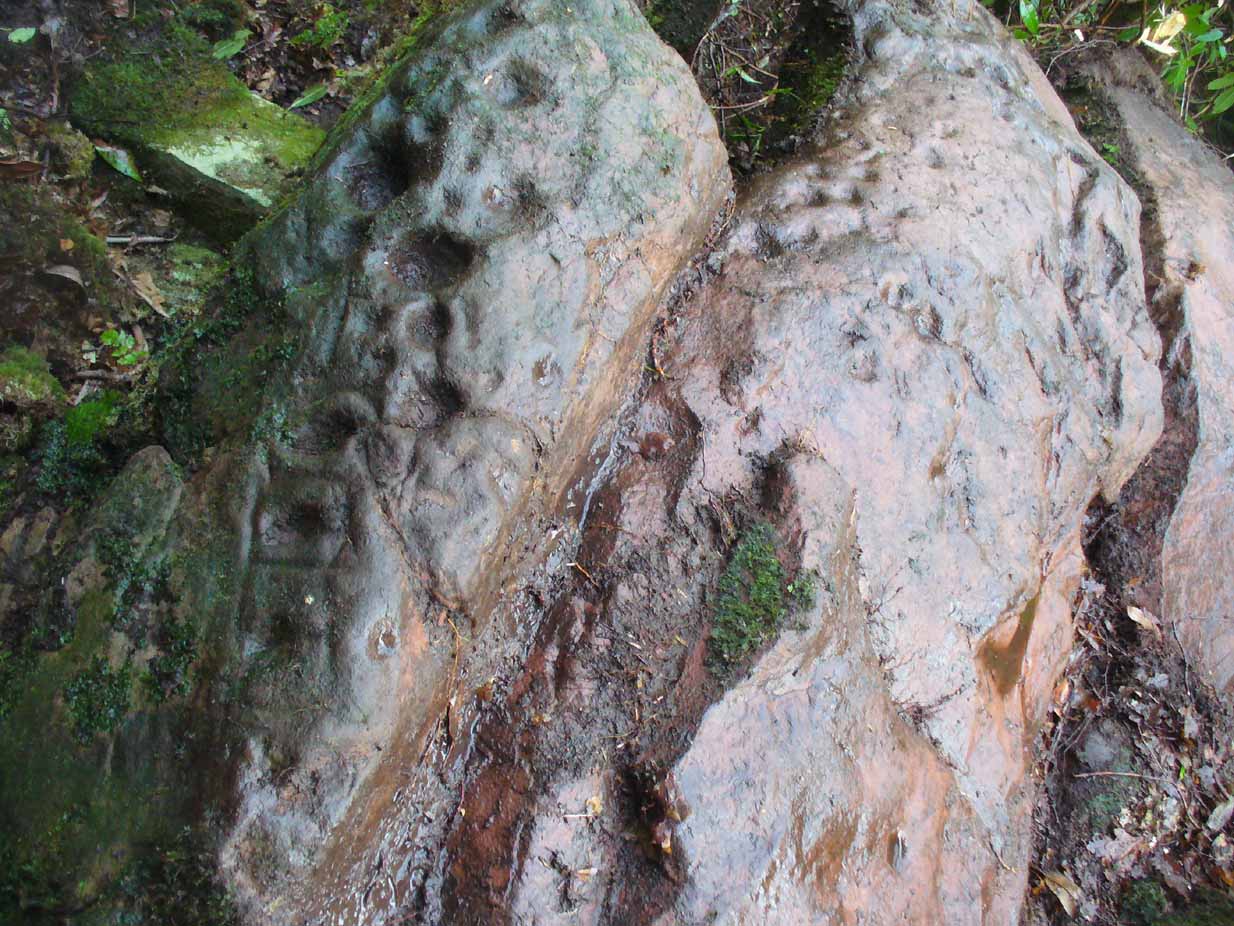


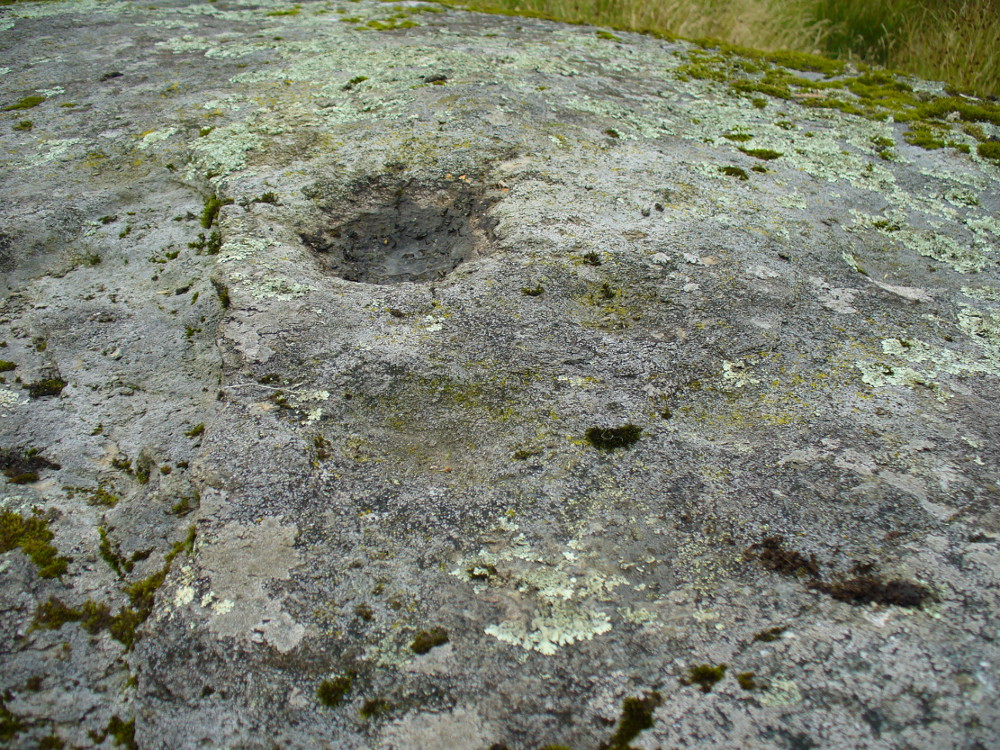
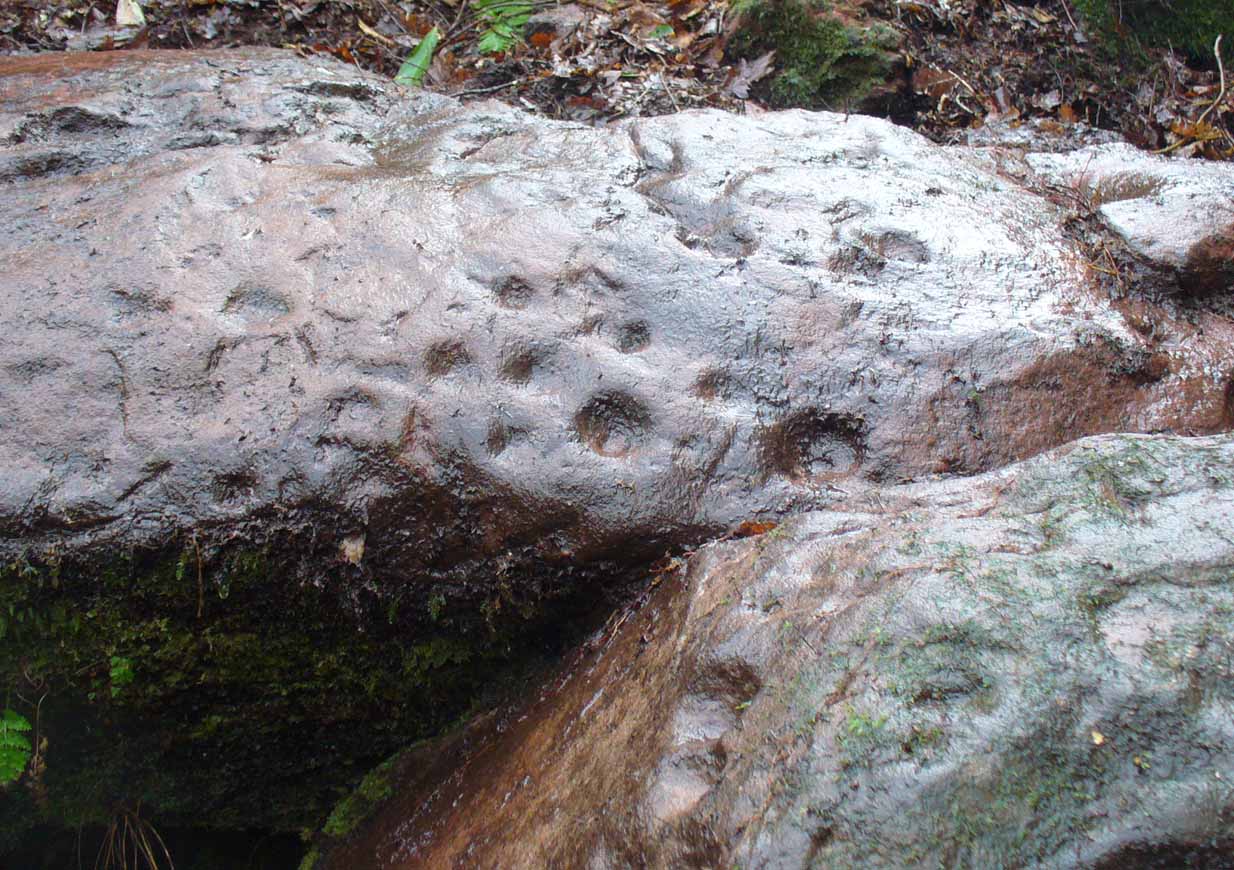
The entire design in fact covers two separate sections of rock. On the vertical face of one stone is a curious conjoined cup-and-rectangle, attached to a cup-and-square, attached to a traditional cup-and-ring. A cluster of other cups, large and small, are immediately left of this odd geometric pattern. The ‘cups’ within this section of the petroglyph are quite deep and, it would seem, were geological in nature but have been touched-up by human hands. Immediately below this rectangle-square-circle sequence, faint carved lines run a little further down the face of the rock. They were difficult to see clearly and require subsequent visits to enable a more complete picture. Along the top of this section of rock are several cups, one or two of them seeming to have faint rings around them. (at the very bottom of this vertical carved face, at ground level, a small section of man-made walling is visible, which was no doubt a section of the huge broch)
Above the top of this vertical carved face is a gap between this and a second, larger earthfast stone. This has a series of cups, some with faint rings around them, but most of them are just cups, both shallow and deep, running down the slope of the rock. A notable ‘star’ of five cups surrounding a single-cup stands out on this section. Some of them seem to have been geophysical in nature, but again have been touched-up and added to.
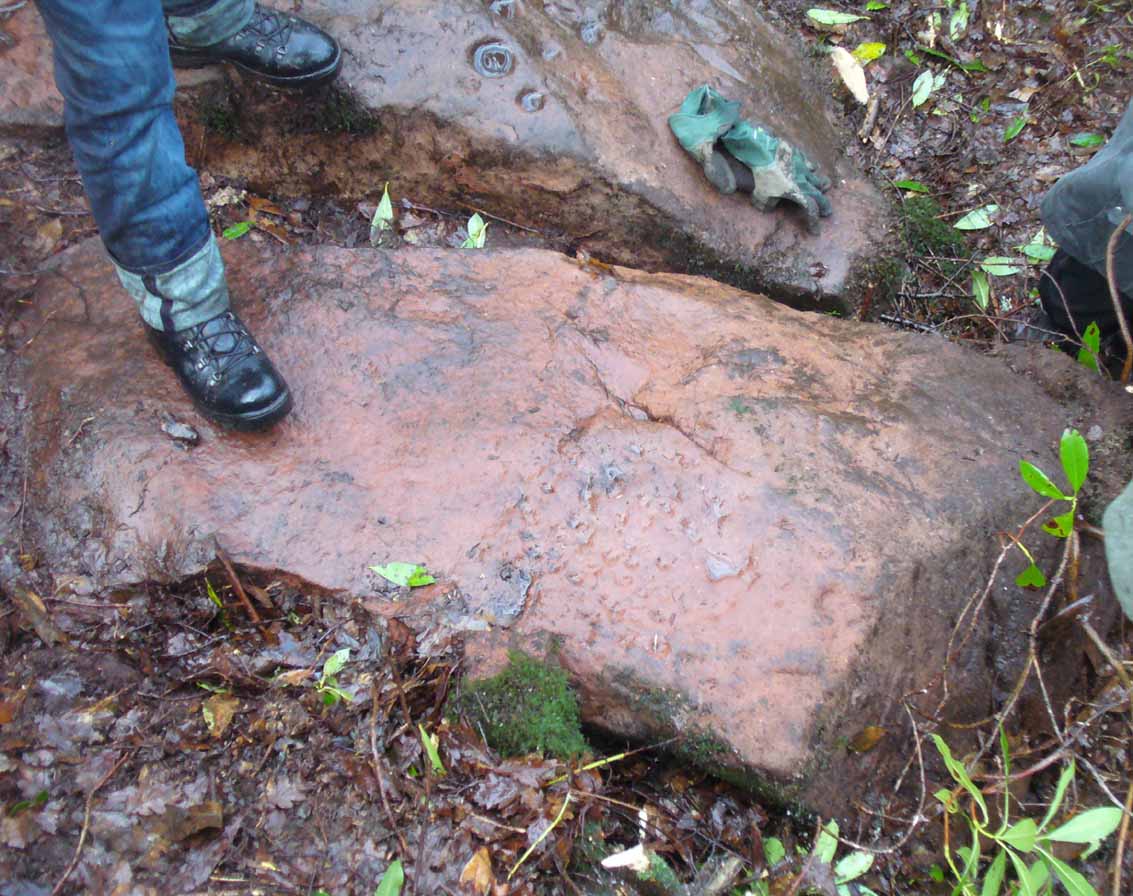

Slightly higher still, on another third section of rock, a curious cluster of weird ‘pecks’, almost in a square pattern, with a possible cup-mark close to the edge of the stone is clearly visible. The edge of this rock seems to have been quarried and the markings here may just be mason marks preceding the breaking of the stone in the Iron Age.
Walk around to the south-side of the broch and there, in the walling, on a vertical stone face, is the small cup-marked Leckie 1 carving.
One final note of concern: the carving (and the broch) have become overrun with rhododendrons, to the point where they are severely damaging the monuments here. They need to be curtailed before further archaeological destruction occurs. Help!
References:
- MacKie, Euan, “Leckie, Cup-Marked Rock,” in Discovery & Excavation Scotland, 1980.
- MacKie, Euan, “The Leckie Broch, Stirlingshire,”, in Glasgow Archaeological Journal, volume 9, 1982.
- McLaren, John, Personal Communications, 7.2.17 & 16.2.17.
- Morris, Ronald W.B., The Prehistoric Rock Art of Southern Scotland, BAR: Oxford 1981.
Links:
Acknowledgements: Immense thanks to Lisa Samsonowicz, Fraser Harrick, Nina Harris, Frank Mercer and Paul Hornby for all their work, enabling a clear picture of the site. And a huge thanks to John McLaren of the Gargunnock Village History site for allowing us to include the early photo of the carving here – thanks John! 🙂
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian