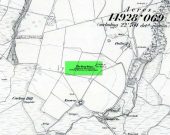
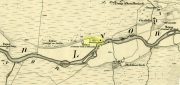
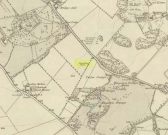
Standing Stone: OS Grid Reference – NN 80102 22666
Also Known as:
Take the A85 road between Comrie and Crieff. Nearly 1.7 miles (2.7km) east out of Comrie—or 4 miles (6.44km) west out of Crieff—keep your eyes peeled on the fields to the south-side of the road, below and across the mansion of Lawers House. Alongside a long but small plantation of trees you’ll see a large upright stone. You can walk along the track adjacent to the field and through the gate.
Archaeology & History
Shown on the early Ordnance Survey maps of the area, this probably neolithic monolith was suggested by Fred Coles (1911) to have once been part of a larger megalithic circle—although Aubrey Burl (2000) didn’t consider it as a good enough contender to be listed as such in his gazetteer; and unless we can have some positive affirmation, either through folklore or excavation, we should maintain its status as a singular monolith. There is the possibility that it stood as an outlier or had some relationship with a nearby prehistoric tomb—but even this is contentious. Nevertheless, the stone itself is an impressive one!
Mr Coles curiously got the size of the old stone wrong too (although, we have to give him credit, as he did all of his work without electricity or any of our modern ‘stuff’). He wrote that:
“This massive boulder of whinstone is rounded at the base, where it girths 10 feet 3 inches, but tapers upwards to its apex of 5 feet 10 inches, with the eastern edge somewhat jagged and broken. Near its base on the west is a small slab-like fragment of stone, quite earthfast. The north and south surfaces are smooth and nearly vertical, and the longer axis is ESE 75º by WNW 75º.”
The stone is actually larger than Coles described, being more than 6 feet 6 inches tall. His sketch (right) “shows the stone from the east”, and is pretty much as we find it today. A notable crack in the stone along the southern face, about a third of the way up, suggests that the stone was broken at some time in the past.
Local architect Andrew Finlayson (2010) included the stone in his local megalith guide and noted how the axes of the stone, east-west, lines it up with Ben Halton to the west and The Knock to the east.
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
- Coles, F.R., “Report on stone circles in Perthshire principally Strathearn,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 45, 1911.
- Finlayson, Andrew, The Stones of Strathearn, One Tree Island: Comrie 2010.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian