Standing Stone: OS Grid Reference – NS 72346 99409
Also Known as:
- Blair Drummond Stone
- Canmore ID 46064
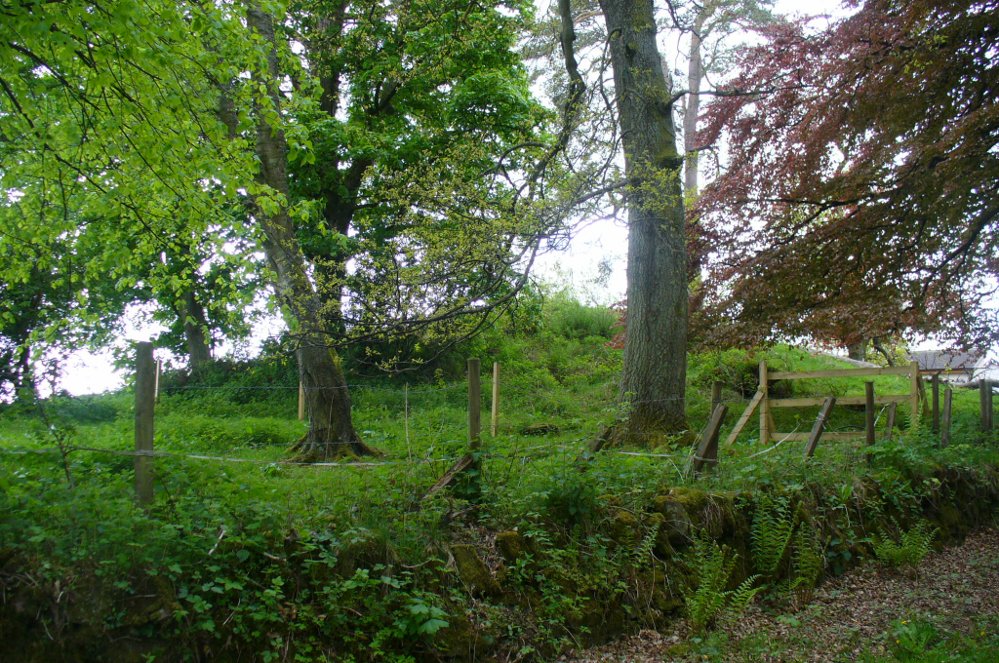
Along the A84 Stirling-Doune road, watch out for the minor Cuthill Brae road to the caravan park. A couple of hundred yards before reaching the entrance to the caravan park, note the copse of trees more than 200 yards north, on the left, across the field. Walk into the trees and, near the centre, you’ll see the upright stone.
Archaeology & History
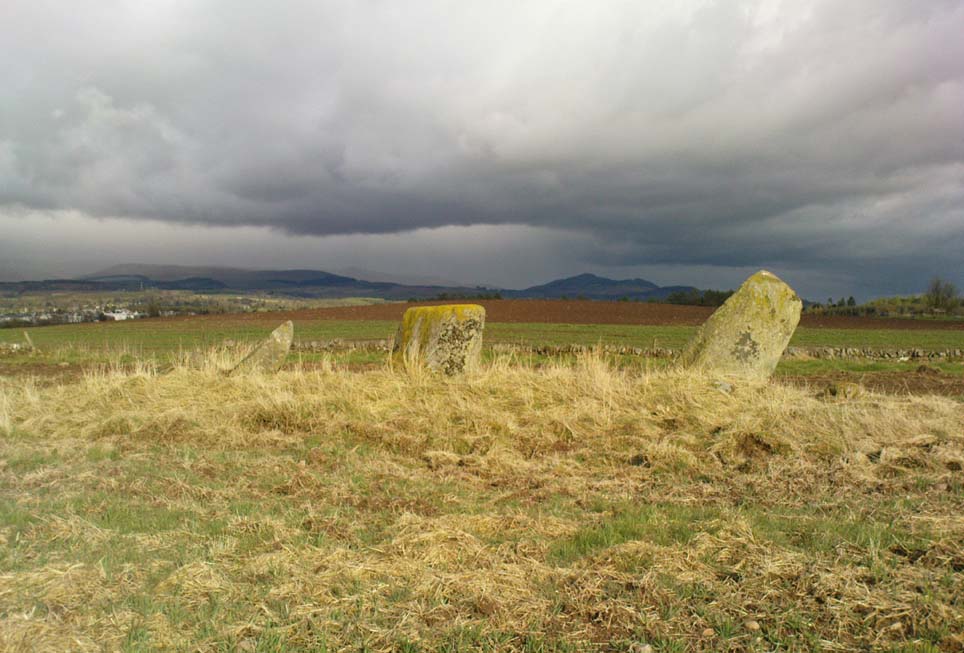
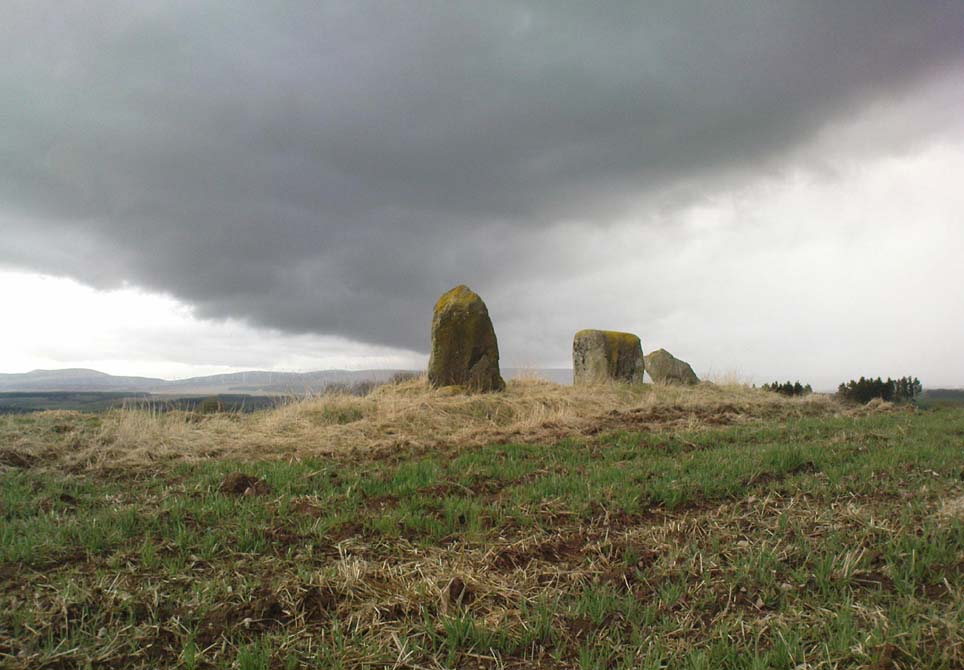
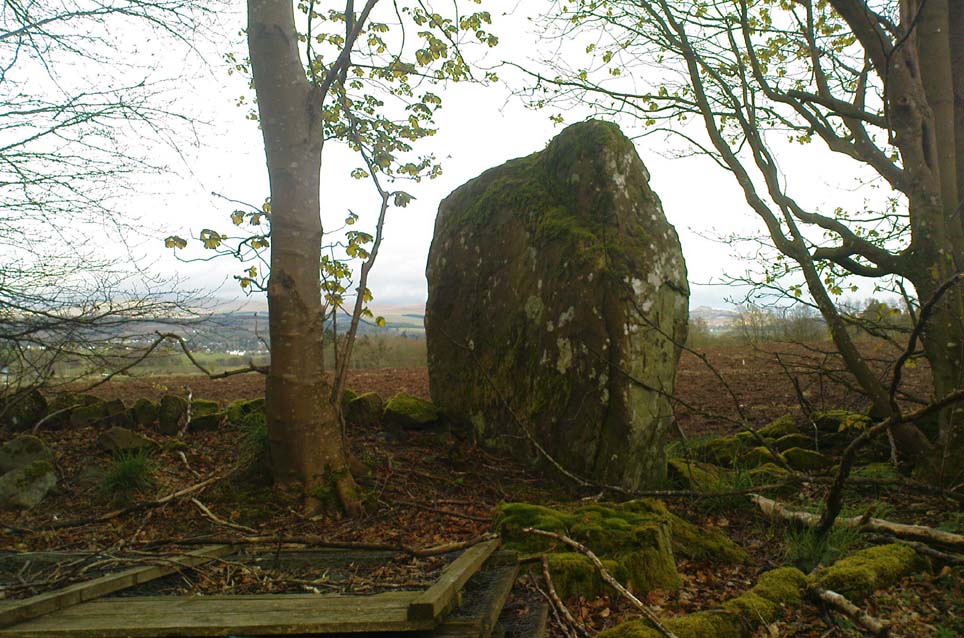
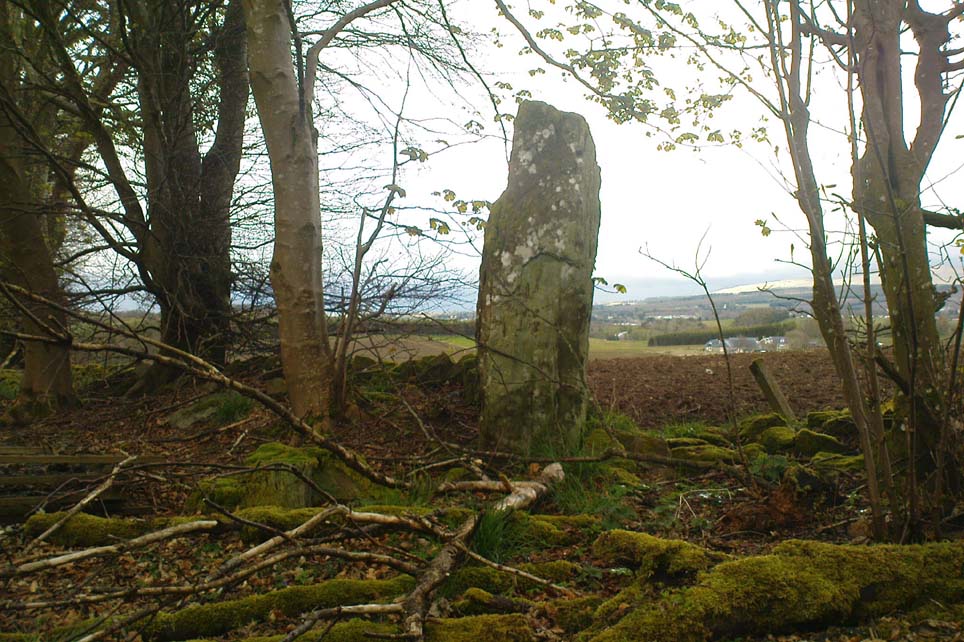
On the very top of this flattened tree-covered hill between Doune and Stirling, a single upright monolith more than 5½ feet tall quietly rests, seemingly forgotten by just about everyone. The stone was marked on the earliest OS-maps in the 1860s, though in non-antiquated lettering, as if to question its archaic veracity—and this has continued to the present day, with the likes of Hutchison (1893) and Canmore upholding it as little more than a geological erratic. Yet as our photos here show, this stone has much greater credibility as an authentic standing stone than Nature’s handiwork.
In Mr Hutchison’s (1893) article on the megalithic remains of the area he said of this stone:
“This is a very fine boulder of Highland grit, stranded on a gravel mound near the official residences on the Blair Drummond estate. The knoll is wooded, leaving a clear space in the centre for the stone. It would thus appear to have been thought worthy of preservation for some reason or other. It has no appearance however, of having been erected as a standing stone. It measures about 6 feet in height, and 12 feet at its widest circumference.”
The position of the stone is intriguing, giving a 360° view through the trees to a much greater vista all round, and this does seems to be quite deliberate. In all honesty, this does look like an authentic standing stone, contrary to the earlier views cited. A large prehistoric tumulus occurs only 400 yards to the south (recently damaged and built onto by the present land-owner) and other standing stones are in the area.
There are a number of scratch marks on the upright faces of the stone, no doubt caused by the forestry actions here over the last century. No modern excavations have occurred here.
Folklore
A couple of centuries ago, the New Statistical Account told that,
“a very vague tradition represents it as having been a place of religious worship in superstitious times. There are no other remains near to confirm this opinion; but whether it be correct or not, it is evident that its site is a very important one, and may have been useful as a signal station, as it commands a view not only of the road across the Moss of Kincardine, but also of the line of Roman stations along the Forth and Teith in the direction of the camp at Ardoch.”
References:
- Bennett, Paul, The Standing Stones of Stirling and District, TNA: Stirling 2020.
- Hutchison, A.F., “The Standing Stones of Stirling District,” in The Stirling Antiquary, volume 1, 1893.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian