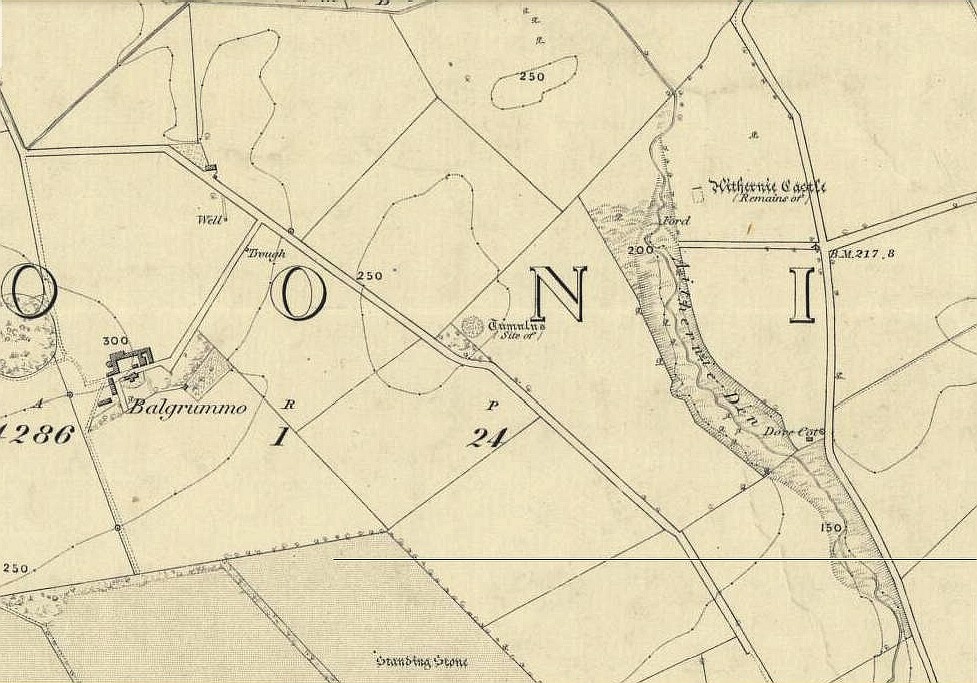
Tumulus (destroyed): OS Grid Reference — NT 237 861
Archaeology & History
Very little is known about a prehistoric tomb that once existed near the coast at Craigkennockie. Its existence was briefly described in Andrew Young’s (1913) fine history of the township where he told that it had been highlighted on an old Estate Map of the area and marked as, “an artificial cairn, probably a place of sepulture.” On old maps just below the cited place we find the place-name of ‘Lammerlaws’, which may indicate a name once given to the site, as the element -law is commonly found relating to prehistoric cairns.
Although the modern place-name researchers in central Scotland have opted that the word ‘law’ is primarily “a rounded hill”, they have curiously forgotten or omitted its other derivation. Throughout northern England and beyond, the English Place-Name Society finds that many ‘law’ place-names derive from the old English and Saxon word, hlaw, which is originally told to be “a mound, a hill.” This has been the reference cited throughout in Taylor & Markus’ (2006-2012) otherwise fine multi-volume analysis of Fife county. But there’s much more to it than that. I hope that readers will forgive me reciting A.H. Smith’s (1956) full entry about this simple term, as it can (and many times does) show our history is much richer than initially thought. Prof Smith told that law, hlaw, hlæw, has the following etymological origin:
“(1) In OE (old English) the common meaning in literary contexts is ‘an artificial mound, a burial mound, a mound in which treasure is hidden’, as in Boethius Metr. 10.43, ‘in what hlæwa do the bones of Weland cover the ground?; Beowulf 2802, ‘Bid them make a hlæaw…on Hronesnæsse’; Guthlac 4 ‘there on the island was made a great hlæw, which through the lust for treasure had been dug up and broken into’; or Gnomic Verses 26, ‘a dragon shall be on hlæw’, an allusion (as in Beowulf 2773) to the Germanic tradition that mounds containing valuable grave-goods were guarded by dragons. The word glosses Latin, agger, ‘something heaped up, a mound, a rampart’ (Wright’s Anglo-Saxon & Old English Vocabularies 355.4). This meaning ‘tumulus, artificial mound, burial mound’ is well attested in place-names. According to Grundy, it always denotes a tumulus in the OE charters and doubtless those place-names in which it is combined with personal names are the burial places of the men so named; at Taplow at least a remarkable burial treasure was discovered and Cuckhamsley, Berkshire, is named from Cwichelm, the West Saxon king who died in 593. The majority of such places-names belong to the heathen period when this method of disposing of the dead was practised. Particular compounds also suggest that it could be an artificial mound which formed the centre of a place of assembly; Oswaldslow Hundred (Place-names of Worcestershire, 87), for example, was created in 964 and it was to meet at a place to be henceforth called Oswaldeslaw in honour of Bishop Oswald (Cartularium Saxonica 1135).
“(2) The meaning ‘hill, a conical hill resembling a tumulus’ is also found in OE, as in Leechdoms Vol.3, 52, ‘they rode over the hlæw’, and local topography establishes this meaning as a common one in place-names and dialects in certain parts of the country; it survives as law in Durham and Northumberland and as low in northwest Midlands…
“(3) The two forms hlaw and hlæw are on record, the latter being better evidenced in literary use, especially in West Saxon texts, and the former in place-names; hlæw normally becomes low, north country law, whilst the i-mutated hlæw (found in place-names only in the south and south Midlands) later becomes lew, as in Lew, Oxfordshire, Lewes, Sussex and is more frequent in middle-english spellings; it is often later replaced by –low as in Dragley, Lancs, Cuckhamsley, Berkshire…”
Smith continues with many topographical evidences regarding a ‘burial-mound’ derivation for the place-name ‘law’, finally adding notes on relative linguistic similarities, like the “Gothic hlaiw, ‘grave’; old High German hleo, ‘grave mound, hill’; old Saxon hleo, ‘grave mound’…” It seems pretty convincing, and so we need to take this into account in our walks over the hills if we are exploring ancient history.
As if to emphasize this derivation—’law’ as prehistoric tombs—we find it is cited in the massive Scottish National Dictionary (6,1:16) where—alongside the ’rounded hill’ aspect—Mr Grant (1962) tells it to be,
“An artificial mound or hillock, specif.: (1) a tumlus or barrow, grave-mound….”
thereafter giving a number of Scottish examples. The same meaning is echoed again in the modern version of Concise Scots Dictionary (2005), along with the rounded-hill. Jamieson’s (1885) Scottish Dictionary cites similarly, ‘law’ as both hill, aswell as “a tomb, grave or mound.”
This association of ‘law’ with ancient burial mounds in Scotland should not be that surprising. Despite it having an Anglo-Saxon origin, we must remember that the Saxon kingdom is known to have stretched all the way up to the Firth of Forth (Edinburgh) and across to Glasgow. So if the linguistic roots have any credibility at all, it doesn’t take much stretch of the imagination to have this simple word travel further north amongst the people. Perhaps this is why, more recently, Margaret Gelling (2000) has said that the association of hlaw with burial mounds up here lessens in Scotland. Nonetheless, let us not presuppose one meaningful definition of the word above another, as it can, consciously or otherwise, be seen as more symptomatic of the all too common English attitude of papering over another country’s rich and ancient heritage by depleting its language—again…
(Law has another element attached which has all but fallen out of historical analysis. Prof Smith touched briefly upon it, mentioning ‘law’ as being a meeting place—otherwise known ‘moots’. Moots occurred everywhere in early times: in England, in Europe and in Scotland too. They were originally where local tribal gatherings took place, for the purpose of what we might call council or political decisions, amongst other things. Some of these moots occurred on burial mounds of great age, aswell as stone circles—and evidence indicates that some of them originated way back in prehistoric times. Although written accounts of many such moot spots have fallen from historical texts, the term law or low (and their variants) is again found in Scottish etymological and topographical lore. Mr Grant again cites it to mean:
“Law cairns, or court cairns…the judicial sites of baronial court of justice…”
Thereafter giving numerous citations of its use in both the common tongue and sites where it is known. As far north as the Shetland Isles, where such law-courts aer known from the Scandinavian ting of thing, the 18th century Statistical Account of Tingwall states there being “the Law Stone” at the cite of the parish court.)
Folklore
Also in Mr Young’s (1913) work, he told how this old tomb was a place that seemed cursed or should not be disturbed, saying,
“About 50 years ago, any illness in the neighbourhood of Craigholm was ascribed to the influence of this burial place…”
adding that an adjacent spring of water, of high esteem, was close by.
References:
- Grant, William (ed.), Scottish National Dictionary – volume 6, SNDA: Edinburgh 1962.
- Jamieson, John, Etymological Dictionary of the Scottish Language, W.P. Nimmo: Edinburgh 1885.
- Robinson, Mairi (ed.), Concise Scots Dictionary, Aberdeen University Press 2005.
- Smith, A.H., English Place-Name Elements – volume 1, Cambridge University Press 1956
- Young, Andrew, History of Burntisland, Fifeshire Advertiser: Kirkcaldy 1913.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian