Holy Well (lost): OS Grid reference – SW 3550 2626
Archaeology & History
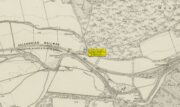
Highlighted on the 1888 Ordnance Survey map of Sennen Cove are the remains of Chapel Idne, just above the coast. Across the road from the chapel on its south-side, and also next to an old inn to its immediate west, springs of water are shown and it would seem more than likely that one of these two would have been the forgotten holy well of Sennen that was described, albeit briefly, in the great Mr Blight’s (1861) literary tour of the area. He told us that:
“At Sennen Cove was an ancient chapel, called by the people Chapel Idne, the “narrow chapel” being forty-five feet long and fifteen feet wide. It is now converted into a dwelling. Tradition says it was founded by one Lord of Goonhilly, who possessed dome portion of the land of Lyonesse. There was a holy well of some repute here also.”
The waters of St. Sennen’s Well were used in an act of ceremonial magick in the Arthurian tale known as the Battle of Vellan-druchar, as told in Robert Hunt’s (1865) great Romances. An attempted invasion by the Danes was met with by Arthur and nine other kings and the foreigners were slaughtered.
“A few had been left in charge of the ships, and as soon as they learned the fate of their brethren, they hastened to escape, hoping to return to their own northern land. A holy woman, whose name has not been preserved to us, “brought home a west wind” by emptying the Holy Well against the hill, and sweeping the church from the door to the altar. Thus they were prevented from escaping, and were all thrown by the force of a storm and the currents either on the rocky shore, or on the sands, where they were left high and dry. It happened on the occasion of an extraordinary spring-tide, which was yet increased by the wind, so that the ships lay high up on the rocks, or on the sands; and for years the birds built their nests in the masts and rigging.
Thus perished the last army of Danes who dared to land upon our western shores.
King Arthur and the nine kings pledged each other in the holy water from St Sennen’s Well, they returned thanks for their victory in St Sennen’s Chapel, and dined that day on the Table-men.
Merlin, the prophet, was amongst the host, and the feast being ended, he was seized with the prophetic afflatus, and in the hearing of all the host proclaimed–
“The northmen wild once more shall land,
And leave their bones on Escol’s sand.
The soil of Vellan-Druchar’s plain
Again shall take a sanguine stain;
And o’er the mill-wheel roll a flood
Of Danish mix’d with Cornish blood.
When thus the vanquish’d find no tomb,
Expect the dreadful day of doom.”
References:
- Blight, J.T., A Week at the Land’s End, Longmans Green: London 1861.
- Hunt, Robert, Popular Romances of the West of England, 1865.
- Straffon, Cheryl, “Chapel Idne and the Holy Well,” in Meym Mamvro no.34, 1997.
- Weatherhill, Craig, “A Guide to Holy Wells and Celebrated Springs in West Penwith,” in Meym Mamvro no.4, 1997.
Acknowledgements: Big thanks for use of the early edition OS-map in this site profile, Reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian