Legendary Rock: OS Grid Reference – NX 6694 7336
Also Known as:
- Cowcloot Stone
Getting here

OK—I’m cheating here, as I’ve not visited this site (bad of me!). The directions given here are from Harper’s 1876 Rambles in this area. He told that the stone “stands about 100 yards to the north of the march dyke betwixt Upper Ervie, now Ken-Ervie and Nether Ervie. There is little to indicate its whereabouts, but the visitor coming from Kenmure Bridge, and leaving the road on the left, opposite Ringour and Bennan farms, on the opposite side of Loch Ken, would come upon it without much trouble by following the march dyke half a mile up.” Basically, along the A713 just over 2 miles north of the bridge at Parton (½ mile before reaching the Galloway Activity Centre), 60 yards from the “Farm Access No Parking” spot, in the trees a long straight line of walling runs uphill. That’d be my route—straight up!
Archaeology & History
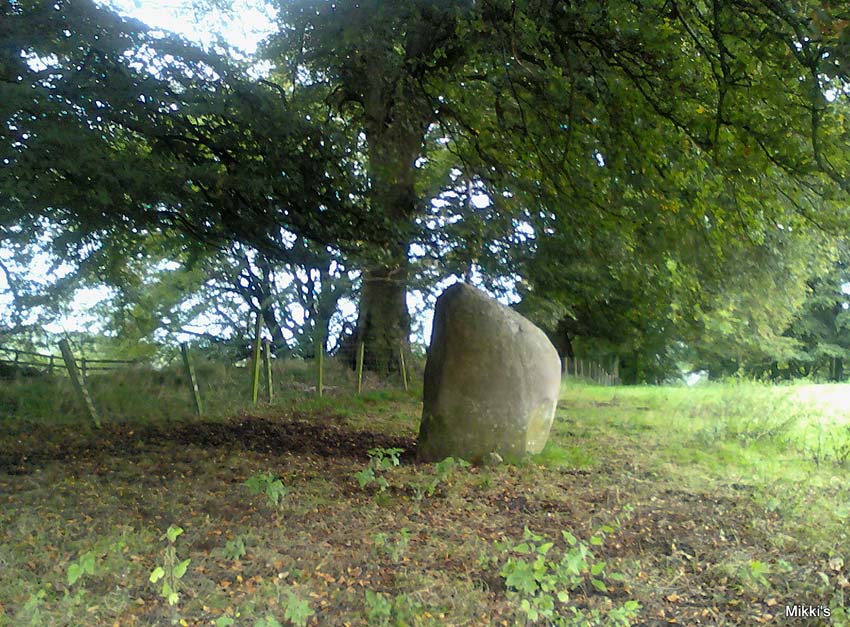
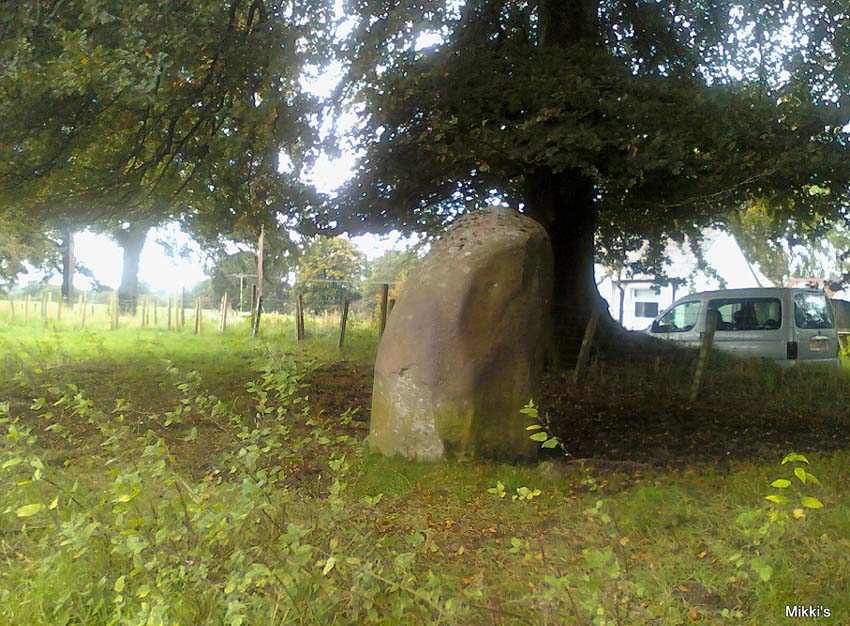
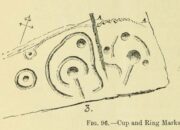
This is a curious entry that I’ve added without visiting the site; but as I might never get to see it I thought it should be displayed in the hope that others might check it out. The earliest literary reference to it is from Crosbie’s (1845) entry in the New Statistical Account, where he implies that the markings on the stone are not of Nature’s handiwork. In Malcolm Harper’s (1876) fine work exploring the history and folklore of this region, he gave us the first illustration of the stone, which looks suspiciously like elements that we find on cup-and-ring stones. Many years later when the Royal Commission (1914) lads followed up on Crosbie’s entry, they thought the markings were probably Nature’s handiwork. They told that:
“It is an irregular mass of outcropping rock about 3 feet in diameter, and bears on its surface certain depressed markings supposed to represent a cow’s foot, a horse-shoe, and impressions which might be made by a man’s foot and knee in the act of kneeling. The markings appear to be natural.”
But it’s the animistic elements and traditions here which are important and which gave the stone its very name…
Folklore
When Rev. W.G. Crosbie (1845) first wrote about this stone, he was narrating the tale told of it by local people, whose traditions were greatly neglected by the majority of writers at that time. Such stories should be preserved at all times, as they tell us more about the psychocosms of pre-industrial cultures. Here,
“On the farm of Arvie, there is a flat stone about three feet in diameter, on which are the marks of what might be supposed a cow’s foot, a horse shoe, the four nails on each side being very distinct, and the impression which might be made by a man’s foot and knee while he was in the act of kneeling, the knot of the garter being quite evident. The tradition connected with this remarkable stone, commonly called the ‘Cow Clout,’ is, that the proprietor, in order to get up arrears of rent, “drave the pun,” or in other words, carried off the hypothecated stock, while a fierce resistance was made by the people, and that over this stone, on which a man had just been praying for relief against his enemies, the cattle passed followed by an officer on horseback, and that it remains as a memorial to posterity of the cruel deed.”
If someone in that neck o’ the woods can find out if the stone’s still there and perhaps send us a photo, or stick it on our Facebook group, that’d be great! 🙂
References:
- Coles, Fred, “The Recent Cup and Ring Mark Discoveries in Kirkcudbrightshire”, in Proceedings Dumfriesshire & Galloway Natural History and Antiquarian Society, volume 5, 1888.
- Crosbie, W.G., “Parish of Parton,” in New Statistical Account of Scotland – volume 4, William Blackwood: Edinburgh 1845.
- Harper, Malcolm M., Rambles in Galloway, Edmonston & Douglas: Edinburgh 1876.
- Royal Commission Ancient & Historical Monuments & Constructions of Scotland, Inventory of Monuments and Constructions in Galloway – volume 2: County of the Stewatry of Kirkcudbrightshire , HMSO: Edinburgh 1914.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian